Assessment, diagnostic and manifestations
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
health history and risk factors
Smoking, environmental/occupational exposures
Chronic illnesses (asthma, COPD, CF, heart disease)
Allergies, prior lung infections, family history
Medications (steroids, inhalers, diuretics)
respiratory effort
(work of breathing, accessory muscle use, tripod position)
breathing rate/pattern
(tachypnea, bradypnea, apnea, orthopnea)
breath sounds
(wheezing, crackles, stridor, diminished/absent)
color
(pallor, cyanosis, clubbing in chronic hypoxia)
mental status
(restlessness → confusion → LOC changes)
assessment
Pulse ox and vital signs
ABG (Arterial blood gas)
Checks oxygenation (PaO₂), ventilation (PaCO₂), acid-base balance (pH, HCO₃).
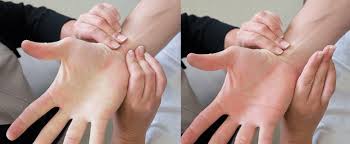
allen test
Performed before radial artery puncture to confirm adequate collateral circulation.
capnography
Noninvasive, continuous monitoring of CO₂ in exhaled breath.
Normal ETCO₂: 35–45 mmHg.
Early warning of hypoventilation/respiratory compromise.
bronchoscopy
Scope inserted into bronchi; used for diagnosis, biopsy, secretion removal.
Pre: NPO, consent, sedation.
Post: Check gag reflex before food/water, monitor for bleeding, hypoxia, pneumothorax.
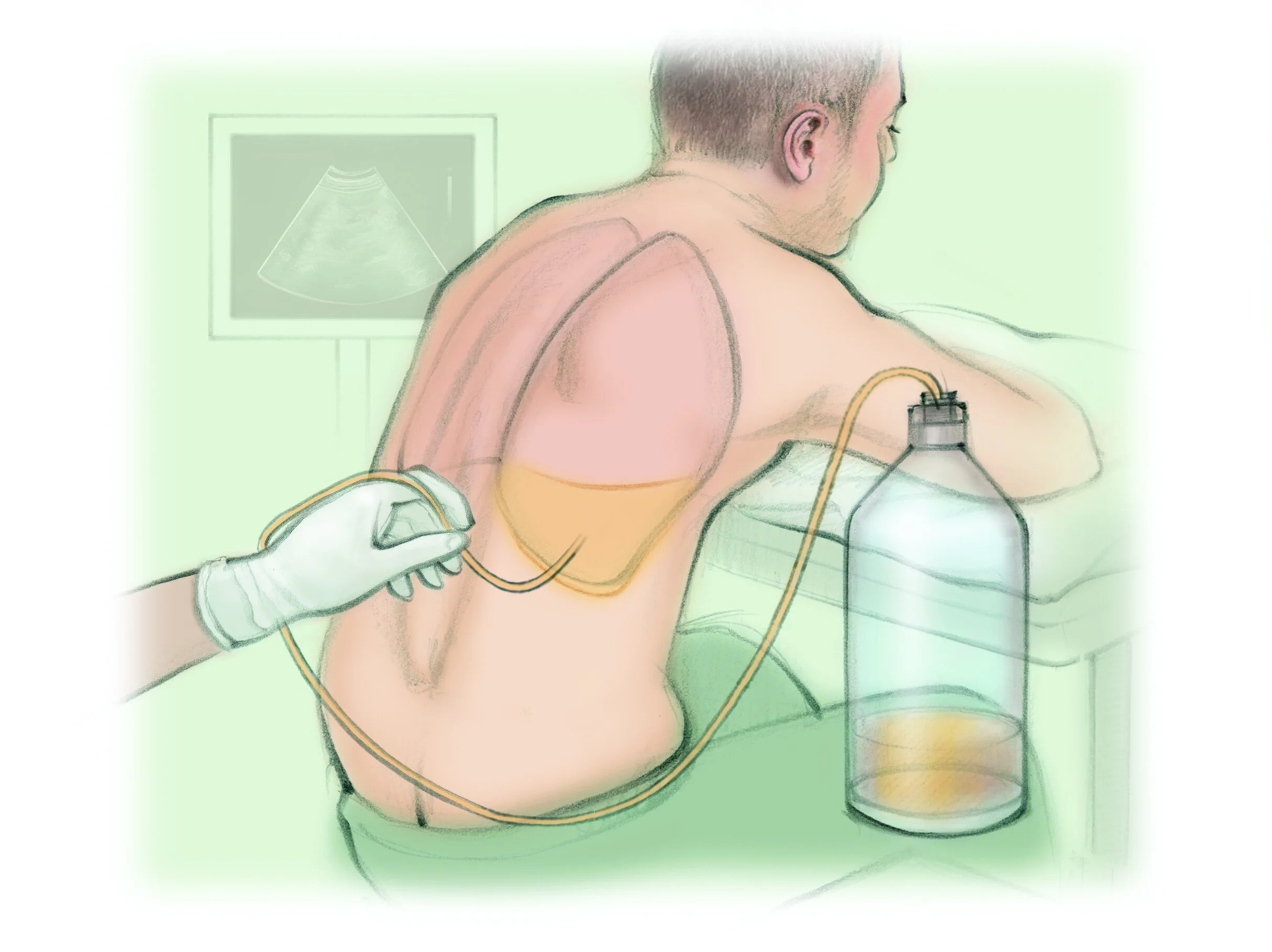
thoracentesis
Needle inserted into pleural space to remove fluid/air.
Position: Upright, leaning forward.
Risks: Pneumothorax, bleeding, infection.
Post: Monitor breath sounds, O₂ sat, chest X-ray to rule out pneumothorax.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Recurrent upper airway obstruction during sleep.
Signs: Loud snoring, witnessed apneas, daytime sleepiness, morning headache.
Risk: HTN, arrhythmias, heart failure.
Tx: CPAP, weight loss, avoid sedatives/alcohol.
laryngectomy
Surgical removal of larynx (partial/total).
Total → permanent tracheostomy, no natural speech.
Risks: Airway obstruction, altered communication, aspiration risk.
asthma
Reversible airway inflammation/bronchoconstriction.
Classic triad: SOB, wheezing, chest tightness.
Severe: Silent chest (ominous), status asthmaticus = life-threatening.
Tx: Rescue bronchodilators, steroids, trigger avoidance.
copd
Chronic airflow limitation (emphysema + chronic bronchitis).
Symptoms: Dyspnea, chronic cough, sputum, barrel chest, clubbing.
Risk: Cor pulmonale, chronic hypoxia, CO₂ retention.
Caution with O₂ (hypoxic drive).
tonsilitis
Inflamed tonsils (viral or strep).
Symptoms: Sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever.
Tx: Antibiotics (if bacterial), pain control; T&A surgery if recurrent/severe.
croup
Viral inflammation of larynx/trachea.
Symptoms: Barking cough, stridor, worse at night.
Tx: Cool mist, corticosteroids, racemic epinephrine if severe.
epiglottitis
Sudden airway obstruction from epiglottis swelling.
4 D’s: Drooling, Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Distressed breathing.
Tx: Keep calm, NPO, O₂, prepare for intubation. Never use tongue depressor.
Peds Emergency
bronchiolitis/RSV
Viral infection (infants, <1 yr).
Symptoms: Tachypnea, wheezing, retractions, copious mucus.
Tx: Supportive, hydration, O₂, suction. Palivizumab for prevention in high-risk infants.
cystic fibrosis
Genetic disorder → thick mucus in lungs & GI.
Respiratory: Chronic cough, infections, wheezing.
GI: Steatorrhea, poor weight gain, FTT.
Tx: Airway clearance therapy, bronchodilators, mucolytics, pancreatic enzymes, high-calorie/protein diet.