Unit 2- Geology
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
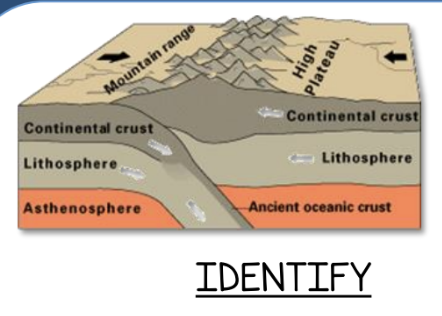
How do underwater mountain ranges form?
sea-floor spreading
List the three main layers of Earth.
crust, mantle, core
The _____ includes all of the crust and the upper part of the mantle.
lithosphere
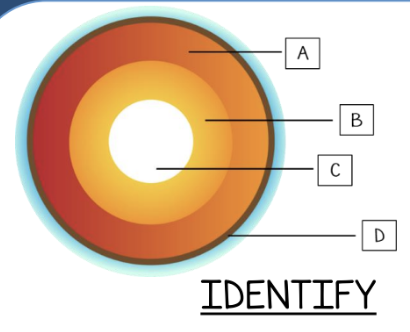
Identify the layer labeled C.
inner core
_____ first proposed the theory of
continental drift.
Alfred Wegener
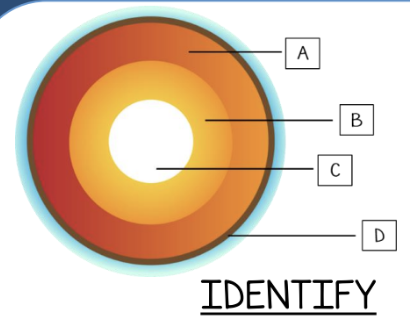
Identify the layer labeled D.
crust
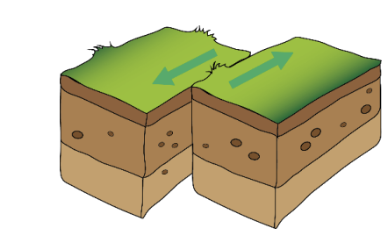
A _____ boundary is a boundary between two plates that move away from each other.
divergent
Determine the name of the process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor.
sea-floor spreading
Continental crust consists mainly of rock called _____.
granite
Identify the three layers the mantle is divided into.
lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle
The supercontinent that began to break apart about 225 million years ago is called _____.
Pangea
Explain what direct evidence is used to help geologists learn about Earth’s interior.
rock samples drilled from deep inside Earth
List the three types of heat transfer that occur in Earth’s processes.
radiation, conduction, convection
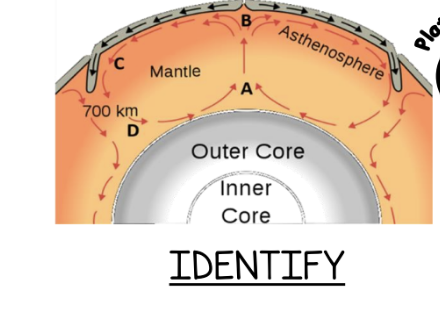
Identify the heat current illustrated above.
convection
_____ is the measure of how much mass there is in a volume of a substance.
Density
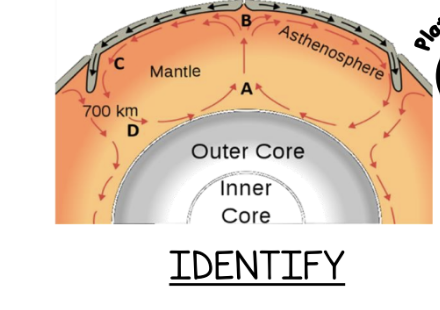
Explain what is occurring at point D.
core causes temperature to increase, therefore density decreases
Wegener had all of the following evidence EXCEPT _____.
sea-floor spreading
Explain the evidence Hess used in his theory of sea-floor spreading.
molten material, magnetic stripes, drilling samples
J. Tuzo Wilson proposed that the lithosphere is broken into separate sections called _____.
plates
List the three types of plate boundaries.
divergent, convergent, transform
Most divergent plates occur along _____.
mid-ocean ridges
Identify the type of plate boundary illustrated above.
transform
When two plates collide, what determines which plate comes out on top?
density of the plates
Explain at least two highlights of the Theory of Plate Tectonics.
plates float on top of asthenosphere; convection currents rise cause plates to move; changes in Earth’s surface (volcanoes, mountain ranges, deep ocean trenches
Oceanic crust consists mainly of rock called _____.
basalt
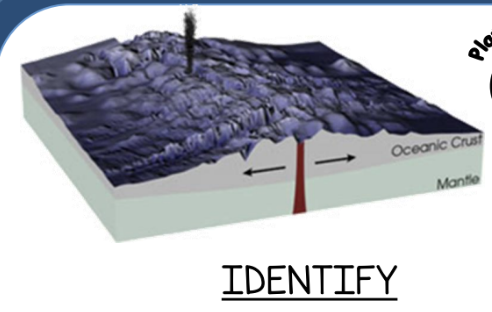
Identify the type of plate boundary
illustrated above.
convergent
A _____ occurs when a deep valley is formed along a divergent boundary that develops on land.
rift valley
Describe how plates move at a transform boundary.
two plates slip past each other in opposite directions
Explain how the magnetic stripes form on the ocean floor.
rocks lie in patter that shows record of reversals of Earth’s magnetic field
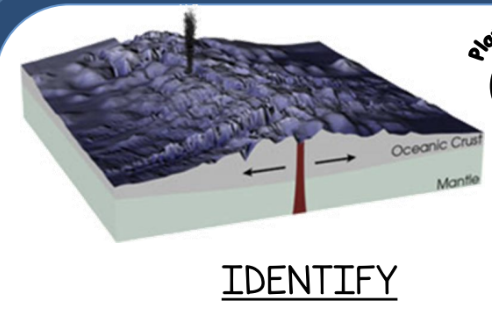
Identify the type of plate boundary illustrated above.
divergent
When two plates of oceanic crust collide, one plate is subducted beneath the other forming a _____.
trench
Determine what many geologists think is the major driving force of plate tectonics.
heat from Earth’s interior
The relatively soft layer of the upper mantle is the _____.
asthenosphere
Describe what happens when two continental plates collide.
the collision squeezes crust into mountain ranges
Breaks in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other are called _____.
faults
Explain the Theory of Plate Tectonics.
states that pieces of Earth’s crust are in constant, slow motion
The layer of rock the forms Earth’s outer “skin” is the _____.
crust
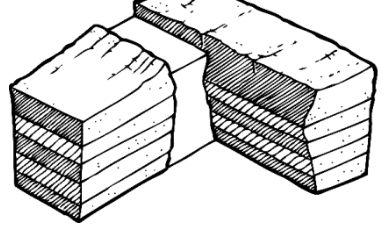
Determine if the rock is older or younger at the point marked with a than the rock at the boundary.
older
Compare the difference between the inner and outer core of Earth.
inner- dense ball of solid metal; outer – molten material that moves creating Earth’s magnetic field
Determine how temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth.
both increase
A change in rock that is caused by stress but is NOT permanent is called ____ strain.
elastic
List three different type of stress that can occur in Earth’s crust.
tension, compression, shearing
List three different type of stress that can occur in Earth’s crust.
compression
Explain what stress is in terms of rocks.
force that acts on rocks to change its shape or volume
A change in rock that is caused by stress and creates a permanent change is called ____ strain.
plastic
Identify the fault in the illustration above.
strike-slip fault
Mid-ocean ridges and continental rifts are landforms created by ____.
tension
Explain what a seismograph is used for.
an instrument used to measure and record ground movements during an earthquake
A measurement of an earthquake's strength is called it’s ____.
magnitude
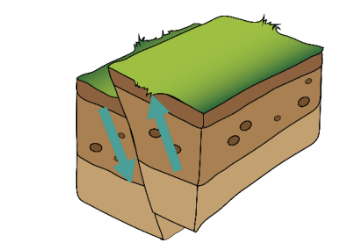
Identify the fault in the illustration above.
reverse fault
Transform faults and fault zones are created as a result of this type of stress: ____.
shearing
Determine the order in which the three types of seismic waves arrive at a seismograph.
p-waves, s-waves, surface waves
The ____ is the point below Earth’s surface which breaks and triggers an earthquake.
focus
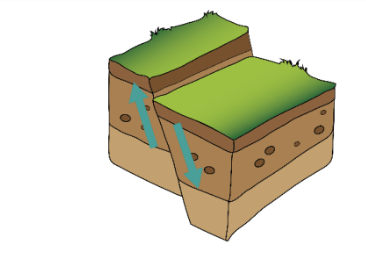
Identify the fault in the illustration above.
normal fault
The point on the surface directly above the focus is the ____.
epicenter
Determine which type of seismic wave produces the most severe ground movements.
surface waves
A block of rock that lies above a fault is called a ___ wall.
hanging
Explain how scientists locate the epicenter of an earthquake.
scientists triangulate data from at least 3 different seismographs
The ___ is the arrival time difference between the first P- wave and the S-wave.
lag time
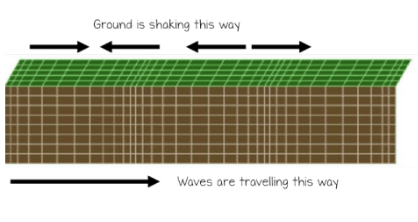
Identify the type of wave illustrated above.
p-wave
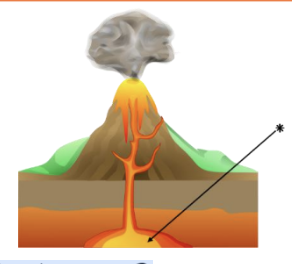
What is feature *?
magma chamber
Define a volcano.
weak spot in Earth’s crust where magma comes to surface
When magma reaches the Earth’s surface, it is called ___.
lava
Explain where most volcanoes form.
along plate boundaries where crust often fractures
A(n) ___ eruption has magma that slows easily with gases bubbling out gently.
quiet
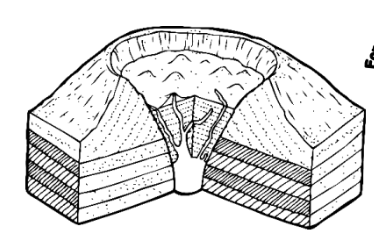
Identify the type of volcanic landform illustrated above.
caldera
A ___ is a volcano that is currently not active, but may become active in the future.
dormant
Describe a geyser.
fountain of water and steam that erupt from ground when pressure is released
A string of islands, called a(n) ____ is created by volcanos near boundaries where two oceanic plates collide.
island arc
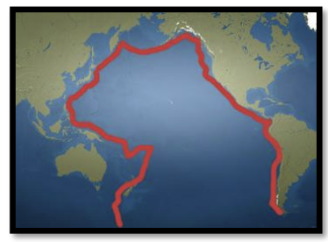
Identify the major volcanic belt in the picture above.
Ring of Fire
When lava has high viscosity, it produces ash and cinder bombs which build up around vent forming a steep mountain called a ___ volcano.
cinder cone
List the three stages of volcanic activity.
active, dormant, extinct
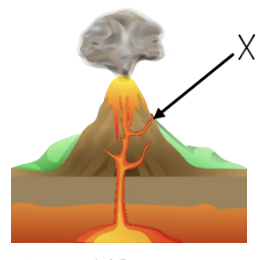
What is feature X
vein
Identify the volcanic landform illustrated here.
lava plateau
A ____ is formed when groundwater is heated by a nearby body of magma and eventually rises to surface to collect in a natural pool.
hot spring
List at least three landforms created from magma.
volcanic neck, batholith, dike, sill, dome mountain
Water heated by magma can provide an energy source called ____ energy which can heat homes and make electricity.
geothermal
Explain what occurs during a pyroclastic flow.
eruption that hurls out ash, cinders, and magma bombs
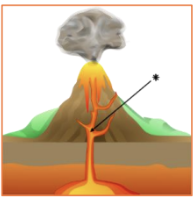
What is the feature *?
pipe
Compare the difference between
pahoehoe and aa.
pahoehoe – fast moving, hot lava; aa – slower moving, cooler lava
A ____ is a scientist who studies, collects and classifies fossils.
paleontologist
Describe a carbon film.
extremely thin coating of carbon on rock
The gradual change in living things over long periods of time is called ____.
evolution
Fossils are usually found in what type of rock?
sedimentary
When an organism no longer exists and never will again, they are considered ____.
extinct
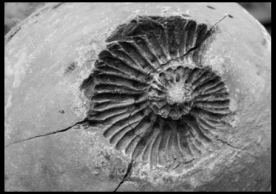
Identify the type of fossil pictured above.
mold
Fossils in which minerals replace all or part of an organism are called ____ fossils.
petrified
Describe at least two pieces of information that paleontologists can gather from the fossil record.
history of life, organisms changing over time, past climates, changes in Earth’s surface
Magma that forces its way into rocks and hardens is called a(n) ____
intrusion

Identify the type of fossil pictured above.
Index fossils are useful because they tell the ____ ages of the rock layers in which they occur.
relative
Explain the Law of Superposition.
oldest layer of rock is on bottom, each layer above is younger than the one below it
The time that is required for half of an element to decay is called it’s
half-life

Identify the type of fossil pictured above
trace
Geologists use ____ to determine the absolute ages of rocks by first determining the amount of radioactive element in a rock.
radioactive dating
Describe the difference between relative age and absolute age of a rock.
relative age is compared to another rock layer; absolute age is number of years since rock layer formed
The earliest life forms were ____.
single-celled organism
Identify the three periods the Mesozoic Era is divided into.
Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
Scientists hypothesize that Earth formed roughly ____ years ago.
4.6 billion
Determine the order of the following from oldest to youngest: Mesozoic Era, Precambrian Time, Cenozoic Era, Paleozoic Era
Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic