Neurology: Physiology-Unit 4
1/199
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
Nervous System Functions (3)
Sends & receives messages
Detects stimuli
Controls all bodily activities.
Nervous Systems Organs (4)
Brain
Spinal Cord
Nerves
Neurons
Nervous System Divisions (2)
Central Nervous System (CNS):
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
Nervous Tissue Group
N
Nervous Tissue Function
Receives neurotransmitters & sends impulses within body.
Nervous Tissue Specialized Cell
Neurons
Central Nervous System
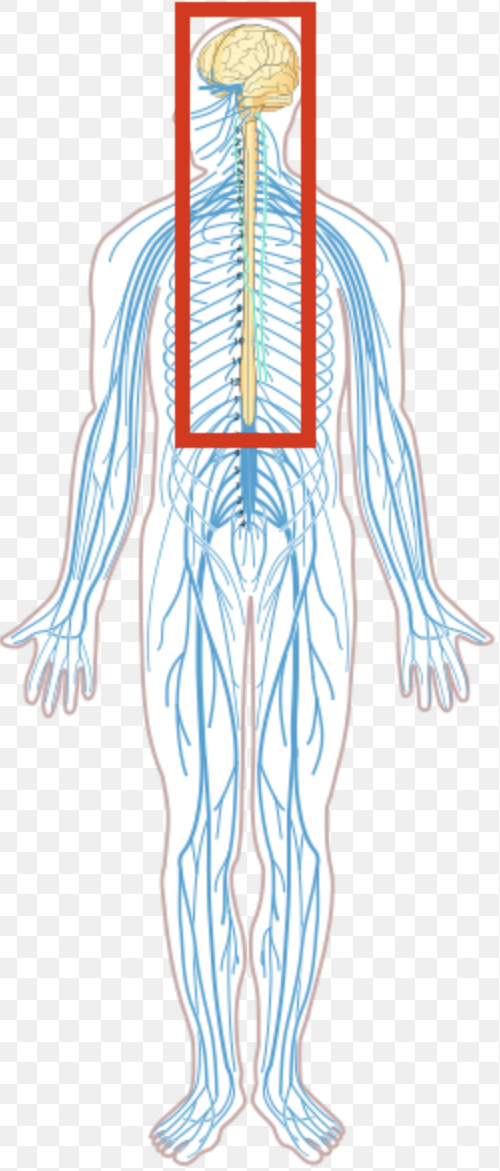
Central Nervous System includes (2)
Brain
Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System
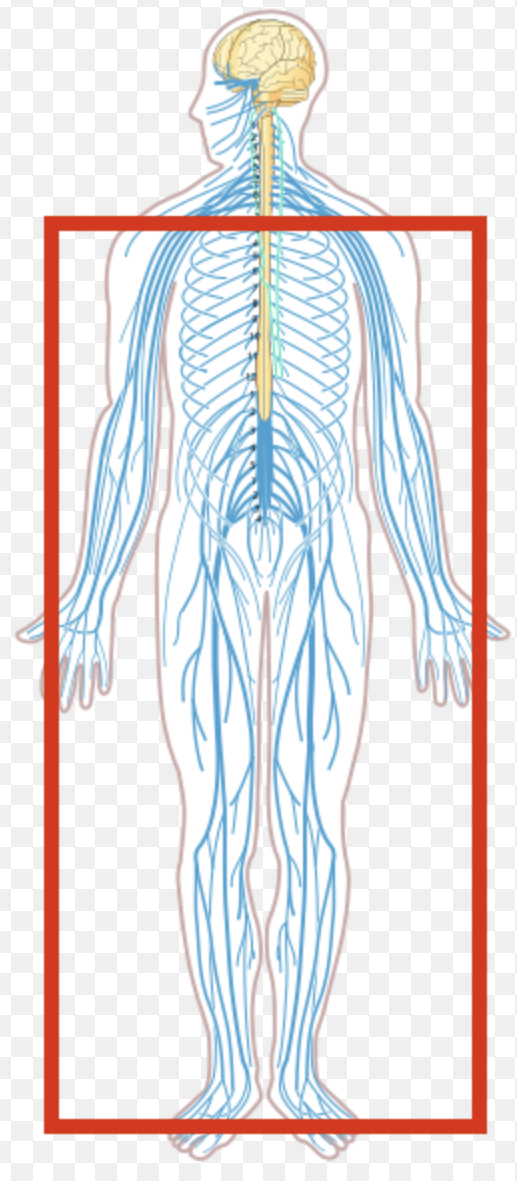
Peripheral Nervous System Includes (1)
Nerves
Central Nervous System (CNS) includes: (2)
Brain & Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) includes:
5 Senses (nerves that extend from CNS)
Stimulus
Something that causes a person to respond (can be internal or external)
Response
An action taken
Reflex (4)
Involuntary (autonomic)
Processed by spinal cord
Quick, defense mechanism
Ex: touching a hot stove or shivering (response to temp)
Reaction (4)
Voluntary (somatic)
Processed by brain
Complex response
Ex: swinging a bat
Reflex Arc (3)
Neurons send signal that skin made contact with fire.
SPINAL CORD processes info
Neurons tell muscles in hand/arm to move away
Reaction (3)
Neurons send signal that there is a ball to hit.
BRAIN processes info.
Neurons tell muscles to contract in hand to click & swing bat
Sensory Neuron Function
DETECTS change in stimulus & CARRIES INFO TOWARD interneuron.
Sensory Neuron Location
Along all 5 senses (within skin, tongue, nose & behind eyes, ears).
Interneuron Function
PROCESSES INFO received from sensory neurons.
Interneuron Location (2)
Brain
Spinal Cord
Motor Neuron Function (2)
Make muscles contract/ relax.
Performs job interneurons command
Motor Neuron Location
On/over muscles.
Cell Body
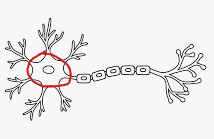
Dendrite
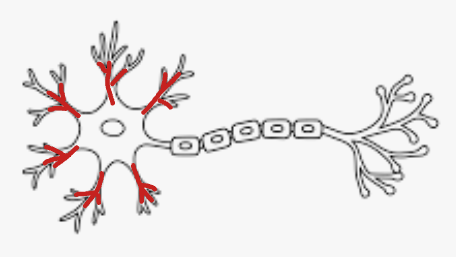
Receptor Protein
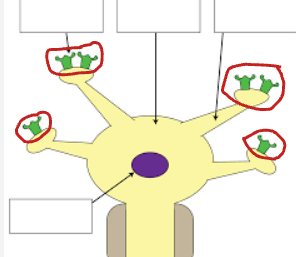
Nucleus
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Axon Terminal Branch
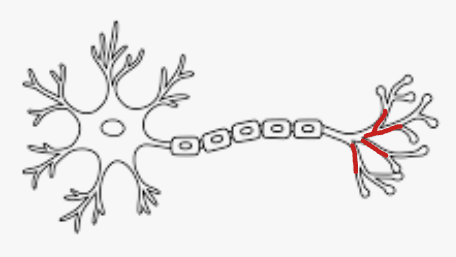
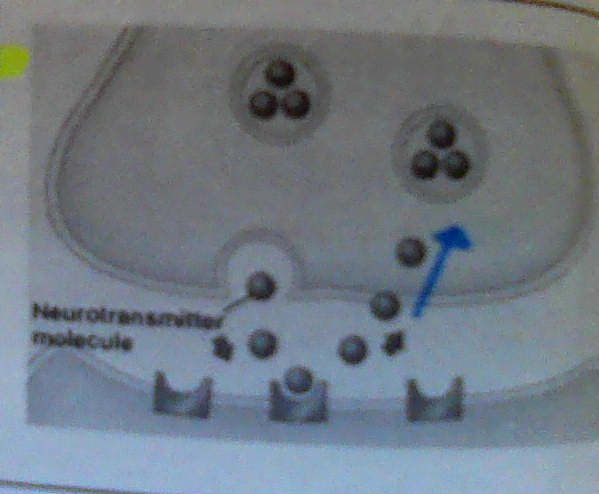
Neurotransmitter

Vesicle
Synapse
Cell Body Function
Carries out life activities
Dendrite Function
Receives chemical signals
Receptor Protein Function
Attaches to chemical signal molecules
Nucleus Function
Controls life activities
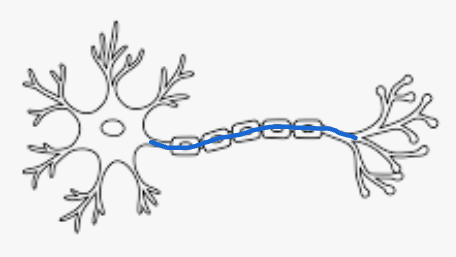
Axon Function
Conducts electrical signals called impulses, over long distances.
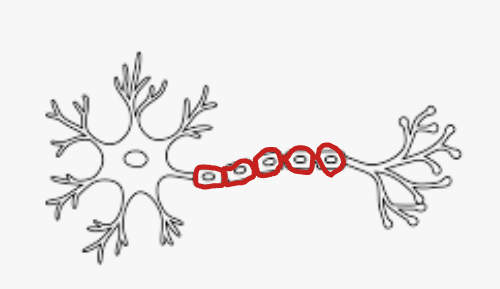
Myelin Sheath Function
Insulates Neuron & speeds up impulse conduction (surrounds axon)
Axon Terminal Branch Function
Sends message to next neuron
Neurotransmitter Function
Chemical message (dopamine, etc)
Vesicle Function
Stores & release neurotransmitters
Synapse Function
Gap between two neurons
Nervous System is divided into (2)
Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
Central Nervous System Uses (1)
Interneurons
Interneurons include
Include Brain & Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System Uses (2)
Sensory Neurons
Motor Neurons
Motor Neurons can be used in (2)
Involuntary: Autonomic N.S.
Voluntary: Somatic N.S.
Autonomic N.S. is ____&____ muscle
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Somatic N.S. is ___ muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Concussions aka
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
What happens to brain during concussion
Brain hits skull abruptly.
How one can get a concussion
Generally only event where your body stops abruptly (falling, accidents, sport).
Prevention method to concussion
Generally anything would prevent an accident & help cushion your brain on impact (helmets, etc).
Immediate symptoms of concussion (3)
Confusion
Vomiting
Nausea
There is ___ on brain after impact
Swelling
Treatment for concussion (4)
Rest
Limiting Screen time
Break from homework/ critical thinking
Eating healthy during recovery.
REST (2)
Minimizes swelling
Gives opportunity for stretching to heal
Limiting Screen Time & Break from homework/ critical thinking both
Limit “firing” of neurons
Eating healthy during recovery
Replenishes fuel that is missing from brain to make ATP.
Breaking axon (2)
Permanent damage
Axons cannot send info at all.
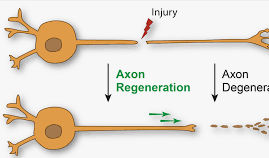
Stretching Axon (2)
Temporary damage
Axons cannot send info while swollen
Both stretching or breaking of axon can cause a ____________ &_______
Leakage of proteins in brain.
Destabilizes Neuron cells.
Action Potential
Electrical impulse that triggers a change in charge across the axon membrane.
Rested Axon
Negative inside membrane, positive outside.
Stimulated Axon
Positive inside membrane, negative outside.
Arrow of neuron represents
Direction of impulse / action potential.
Steps of Communication within a Neuron (4)
Neuron AT REST
A message is received from another neuron
The ACTION POTENTIAL
When the axon is DONE sending a signal.
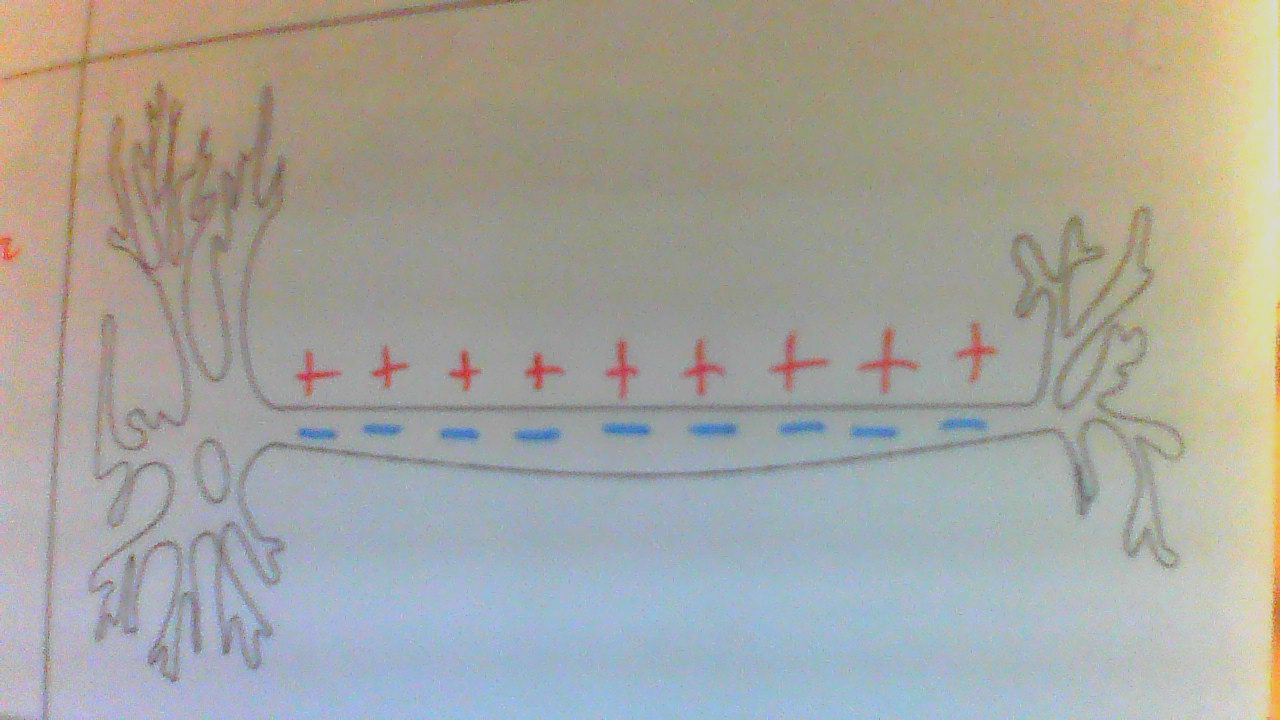
Neuron at Rest (2)
Not sending any messages
Has a negative charge inside and a positive charge outside the Neuron.
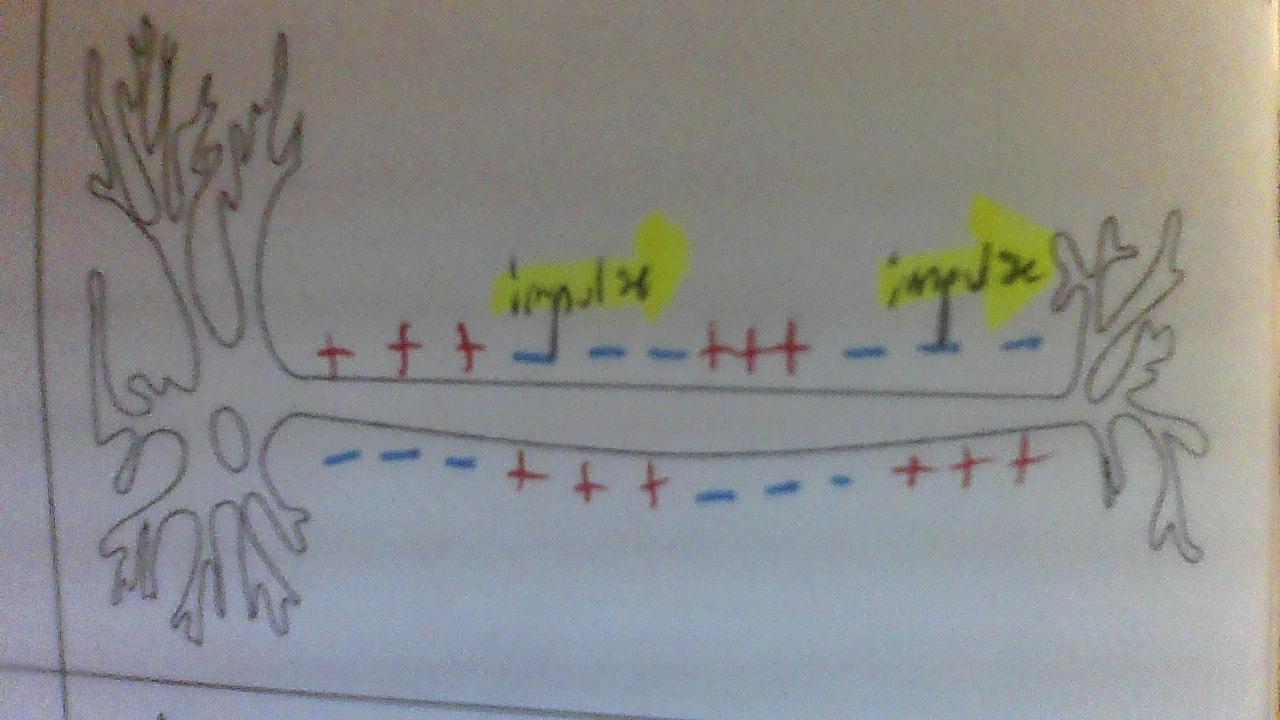
A message is received from another neuron
An electrical signal called an impulse or action potential travels along the axon of a neuron.
The ACTION POTENTIAL (2)
Temporarily causes the charges to change.
There is a positive charge inside & a negative charge outside the neuron.
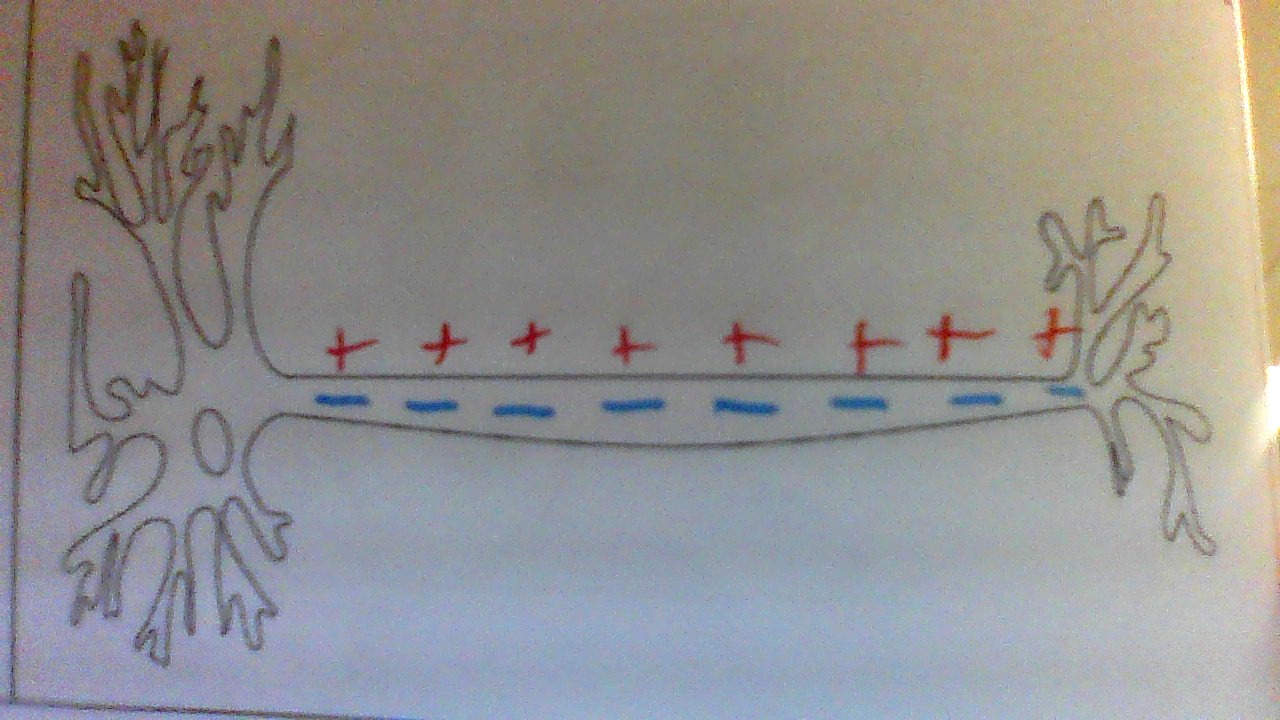
When the axon is DONE sending a signal (2)
Will return to its resting phase
Now ready to send another signal
Neuron at Rest visual
Message received from another neuron visual

Action potential visual
When axon is DONE sending signal visual
(last step)
Focal
One part of brain
Generalized
All over brain
Immediate symptoms of seizures (3)
Jerking movements of arms & legs.
Staring into space
Loss of consciousness
Common causes/triggers of seizures (4)
Fever/ infection
Having a stroke
Head injury
Epilepsy
Treatment: Medication
Sedative drugs can calm overactive neurons.
Seizure First Aid (3)
Keep person safe from falling
Shift on side to keep airways open.
Stay with them until help arrives.
Concussion causes (2)
Torn axon
OR
Axon bubbles up.
Seizure causes (2)
Sustained neuron firing
AND
Shortened rest periods.
Neuron Error 1: Misfiring Neurons (2)
Neurons fire out of sequencing.
Info not received so that it is understood.
Neuron Error 2: Excess Electrical Activity (3)
Neuron = continually firing.
Overstimulation of info
Neuron cannot relax between signals.
Diffusion
Surrounding cells absorb excess NT.
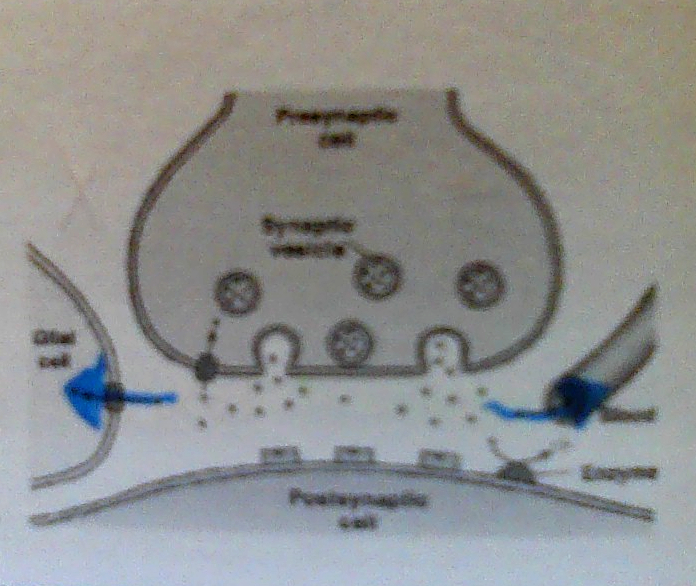
Reuptake
Transporter proteins in axon terminal remove NT.
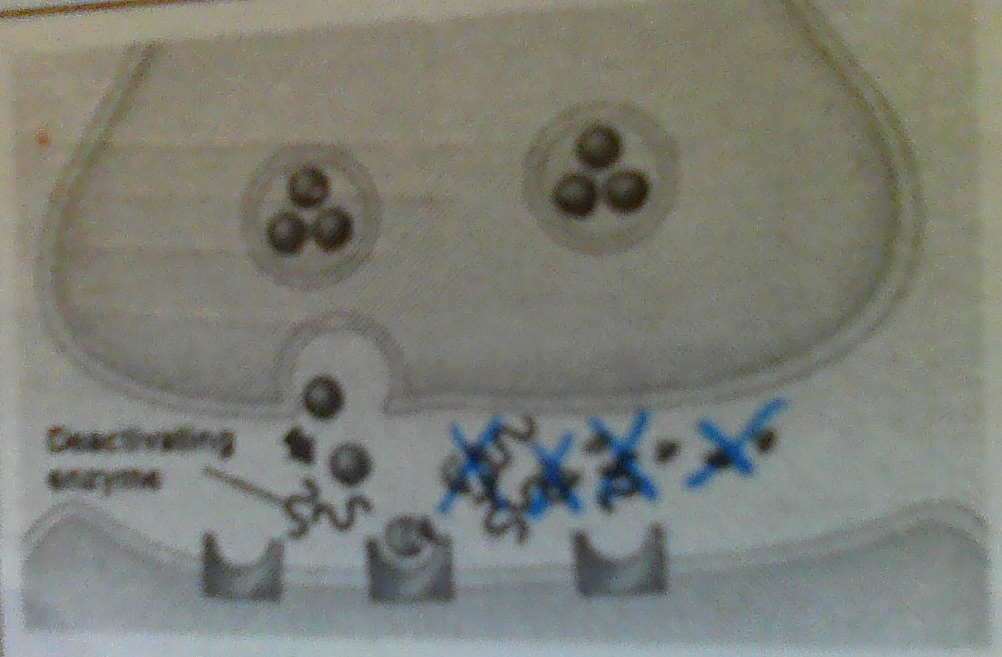
Degradation
Enzymes in synapse break down NT so they lose function
Substance (Drugs/Alcohol) Effects (3)
MIMIC
BLOCK
Increase Production (of neurotransmitter in synapse)
Dopamine Function & Drug that affects in (2)
Pleasure/ reward system
Cocaine
Serotonin Function & Drug that affects in (2)
Regulates mood (happiness)
Ecstasy
Endorphins Function & Drug that affects in (2)
Natural painkillers, sedation
Heroin
GABA Function & Drug that affects in (2)
Blocks impulses
Alcohol
Acetylcholine Function & Drug that affects in (2)
Muscle contraction, memory centers
Nicotine
Anandamide Function & Drug that affects in (2)
Regulates appetite, sense of time & short term memory.
Marijuana / THC
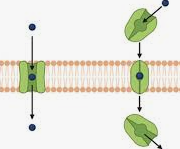
Transporter Proteins
Take up excess neurotransmitters from synapse
Inhibitory ____,____,____ impulses of neuron
Block
Stop
Slow down
Excitatory ____,____,____ impulses of neuron
Enhance
speed up
increase impulses of neuron