biopsychology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
what is the structure of the nervous system
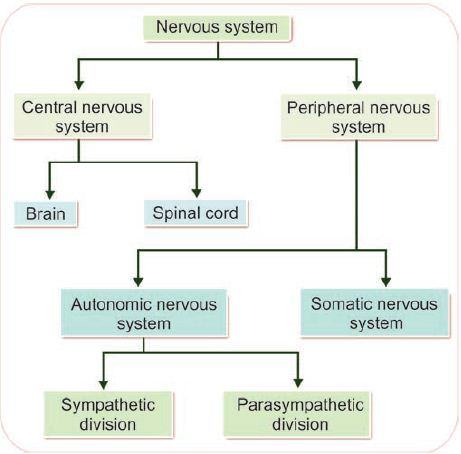
what is the function of the central nervous system
central coordinator for all bodyily functions
function of the brain
cerebral cortex is the decision maker
function of the spinal cord
reflex responses
relays messages between peripheral nervous system and brain
function of peripheral nervous system
neurons transmit messages to and from central NS
collects info from internal and external environment and sends to central NS
function of somatic NS
carries sensory and motor infor to and from spinal cord
-responsible for deliberate, voluntary and conscious actions
function of autonomic NS
responsible for unconscious, involuntary actions
eg digestion, heart rate
function of sympathetic NS
initiates fight or flight response before our conscious mind has recognised threat
shuts down unnessecary functions eg digestion, immune system
function of parasympathetic NS
shuts down fight or flight response
works antagonistically with sympathetic NS
restarts responses eg decreases heart rate, increase sailva production
what is the steps of the fight or flight response
hypothalamus identifies threat, instructs sympathetic NS to act
adrenaline released from adrenal glands into blood
adrenaline promts physical changes to prepare
parasympathetic activated to return body to its normal resting state. (occurs slower than sympathetic)
define hormone
chemicals secreted by the endocrine glands into the bloodstream which distributes it around the body
give 4 examples of endocrine glands
pituitary gland
thyroid gland
pineal gland
pancreas
what does the pituitary gland do
-controls growth, metabolism, blood pressure and reproduction
-secretes FSH
what does the thyroid gland do
controls growth, energy use and body temp
secretes thyroxine
what does the pineal gland do
controls sleep patterns and circadian rythm
secretes melatonin
what does the pancreas do
controls sugar levels within body
secretes insulin
what is a neuron
cells that conduct nerve impulses and make up the nervous system
function of the dendrite
receives the nerve impulse from other neurons
function of the axon
electrical impulse passes along
function of myelin sheath
insulates and protects the axon from external influences that might affect the transmission of the impulse
function of the nodes of ranvier
speed up the transmission by forcing it to jump
function of the axon terminals
send signals to adjacent cell
what are the three types of neurons
sensory
relay
motor
describe the sensory neuron
carries messages from peripheral NS to central NS
long dendrites and short axon
unipolar
describe the relay neuron
transfers messages from sensory neuron to motor neurons
short dendrites and short axon
multipolar
describe a motor neuron
transfers messages from central NS to effectors eg muscles
short dendrites and long axon
describe the process of the reflex arc
environmental stimuli detected by sensory neuron in peripheral NS
message reaches relay neuron
transfers message to motor neuron which carries message to an effector eg muscle
muscle contracts and pulls away from environmental stimuli
describe process of how neurons fire
neuron has a negative charge before receiving a signal
when a message is received, the charge of neuron changes to positive which creates an action potential
action potential allows electrical signal to travel down axon meaning neuron has fired
what is a neurotransmitter
chemicals that are released from a pre synaptic neuron into a synapse
describe process of synaptic transmission
electrical impulse travels along axon of the transmitting neuron called action potential
triggers nerve endings of pre synaptic neurons axon terminal to release from the vesicles
neurotransmitters diffuse across synapse and bind w specialised receptors on post synaptic neuron
receptors on post synaptic neuron bind to specific neurotransmitters which stimulates post synaptic neuron to transmit electrical impulses
remaining neurotransmitters left in synaptic cleft are reuptaken in vesicles of pre synaptic neuron and reused or broken down by enzymes
what is excitation
neurotransmitters can be excitatory meaning it is more likely the next neuron will fire
eg acetylcholine
what is inhibition
neurotransmitters can be inhibitory meaning it is less likely the next neuron will fire
eg serotonin
what is localisation of function in the brain
the theory that specific areas of the brain are associated w particular physical and physiological functions
what is lateralisation
dominance of one hemisphere of the brain for particular physical and physiological functions
what are the three layers of the brain
central core
limbic system
cerebrum
describe the central core layer of the brain
regulates our autonomous behaviours eg breathing
regulates eating and drinking
regulates endocrine system to maintain homeostasis
describe the limbic system layer of the brain
controls our emotions
key roles in memory as contains structures like hippocampus
describe the cerebrum layer of the brain
regulates our higher intellectual processes
outermost layer is cerebral cortex which appears grey because of location of cell bodies
made up of left and right hemisphere connected by corpus callosum which enables messages between left and right hemisphere
what are the 4 lobes
frontal
temporal
occipital
parietal
what is the frontal lobe responsible for
for our awareness of what we are doing within our environment
what is the temporal lobe responsible for
auditory info and memory acquisition
what is the parietal lobe responsible for
sensory info and coordination
what is the occipital lobe responsible for
visual info
what is the motor cortex
responsible for voluntary motor movements
located in the frontal lobe of both hemispheres
different parts of cortex control different parts of the body
describe the process of processing sound in the auditory centres
sound waves converted to nerve impulses in cochlea
impulses travel to auditory cortex via auditory nerve
basic decoding occurs at brain stem eg duration
thalamus acts as a relay station which carries out further processing
sound is recognised and finally reaches auditory cortex
describe the somatosensory cortex
detects sensory events from different regions of the body
located in the parietal lobe
processes sensory info related to touch
uses sensory info from skin to produce sensations which are localised to specific body regions
describe the process of processing visual info in the visual centres
light enters retina and strikes receptors
nerve impulses from retina travel to areas of the brain via optic nerve
some travel to areas involved in circadian rhythms
most terminate in the thalamus which acts as relay station passing info to visual cortex
function of broca’s area
responsible for production of speech
function of wernickes area
responsible for comprehension of speech
describe broca’s research
he treated patient who could only say 1 word
treated 8 others with lesions on left frontal hemispheres who had similar language deficits
patients with damage to right frontal lobe had no similar issues
led to development of broca’s area
describe wernicke’s research
patients w lesions on wernickes area could speak but couldnt understand language
proposed that language has 2 regions - language and cognitive tasks
AO3 of localisation
supporting case studies. phineas gage injured in an accident where a tamping pole went through his pre frontal cortex. his personality switch from normal and kind to crude, vulgar and mean. this change supports the theory of localisation as it suggest injured area is responsible for personality.
brain scan evidence to support theory. study used brain scans to demonstrate how wernicke’s area was active during a listening track and broca’s area was active during a reading task suggesting different areas had different functions. highlt scientific and objective method for measuring brain activity
supporting neurological evidence. practices of surgically removing areas of the brain to control behaviour developed in the 1950s eg lobotomy. study had 44 OCD patients undergo neurosurgery. at post surgery check up 1/3 had met criteria for successful response. the success of these procedures suggest that behaviours associated w mental disorders are localised
lashley’s research. he suggested that higher cognitive functions eg learning, are not localised but distributed in a more holistic way. he removed 10-50% of cortex in rats that were learning a maze. he found no area proved to be more important than any other area. shows the learning process requires every part of cortex rather than localised areas. learning is too complex to be localised and requires brain as a whole.