Meiosis, Mitosis, and Genetic Mutations Overview
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Somatic Cells
Diploid cells located in various parts of the body including nerve cells, blood cells, and adipose cells.
Gametic Cells
Haploid cells usually referred to as reproductive cells, located in the ovaries and testes.
Chromosome pairs 1-22
Autosomes that relate back to somatic cells.
Chromosome pair 23
Gametic chromosome pair that ties into sex chromosomes, X and Y, determining gender in mammals.
Mitosis
A process that produces genetically identical cells, results in diploid cells, takes place throughout an organism's lifetime, and is involved in asexual reproduction.
Meiosis
A process that produces genetically unique cells and results in haploid cells.
Crossing Over
The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes that occurs during prophase 1 of meiosis 1.
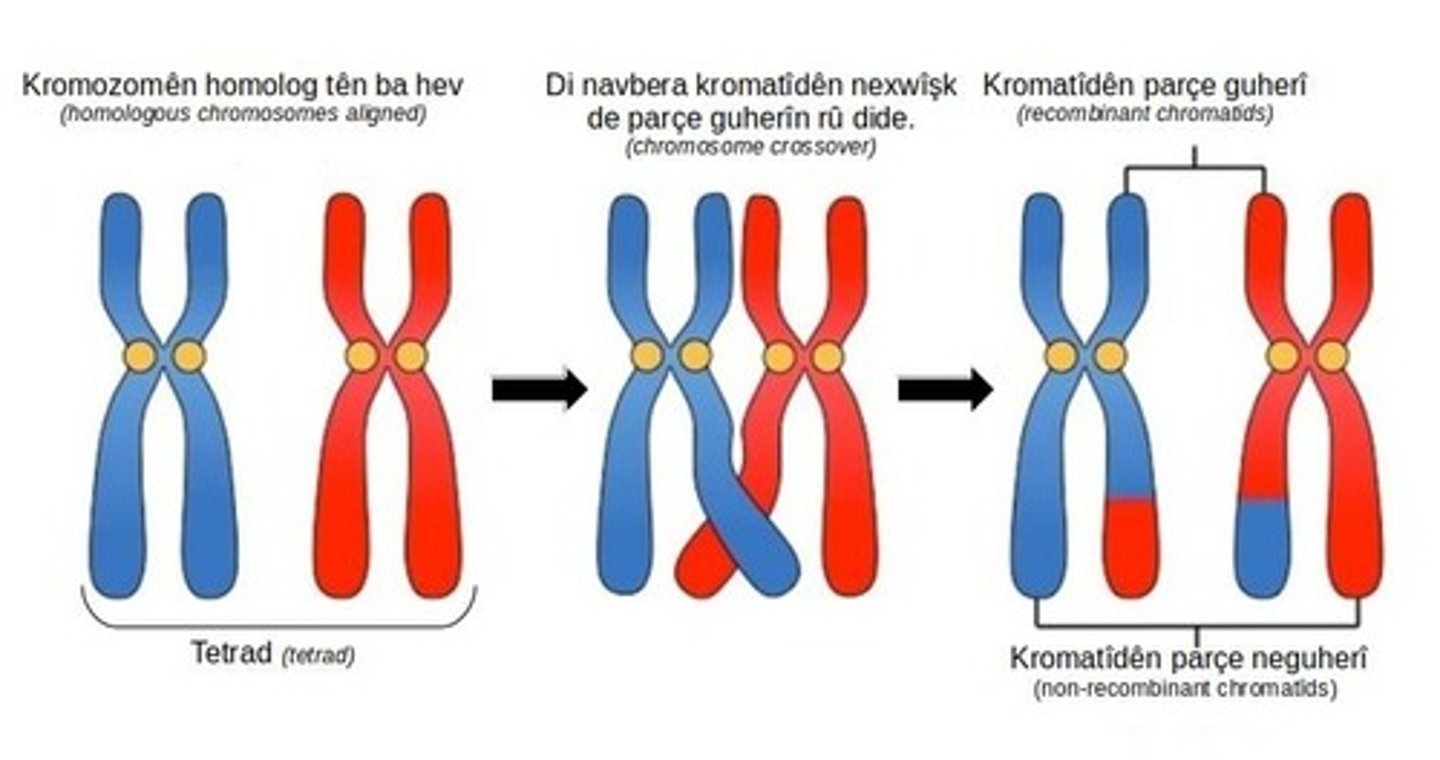
Genetic Linkage
The tendency of genes located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together.
Mutations
Changes or damages to a DNA gene that alter the genetic message, occurring in somatic cells or gametes.
Effects of Mutations
Some mutations have little or no effect, some produce beneficial variations, and some negatively disrupt gene function.
Source of Genetic Variability
Mutations are the source of genetic variability in a species, allowing for evolution.
Causes of Mutations
Mutations can be caused by chemicals and UV radicals.
Repair of Mutations
Many mutations can be repaired by enzymes.
46 chromosomes
The total number of chromosomes in each diploid cell.
Haploid Cells
Cells that contain half the number of chromosomes, specifically one set of chromosomes.
Diploid Cells
Cells that contain two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Asexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction that involves only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring.
Sexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction that creates unique combinations of genes through the process of meiosis.
Prophase 1 of Meiosis 1
The stage in meiosis where crossing over occurs.
Chromosomes
Structures that contain many genes, which can be separated during crossing over.
Genetic Linkage Maps
Maps that show the likelihood of genes being separated by crossing over based on their distance on a chromosome.
Chromosome Segments
Parts of chromosomes that can be exchanged during crossing over.
Neutral mutations
No effect on organism's survival; increase genetic diversity in a species (Example: eye color)
Harmful mutations
Decrease organism's survival; produce genetic disorders or unfavorable traits (Example: cancers)
Helpful mutations
Increase organism's survival; produce favorable traits (Example: antibiotic resistance in bacteria)
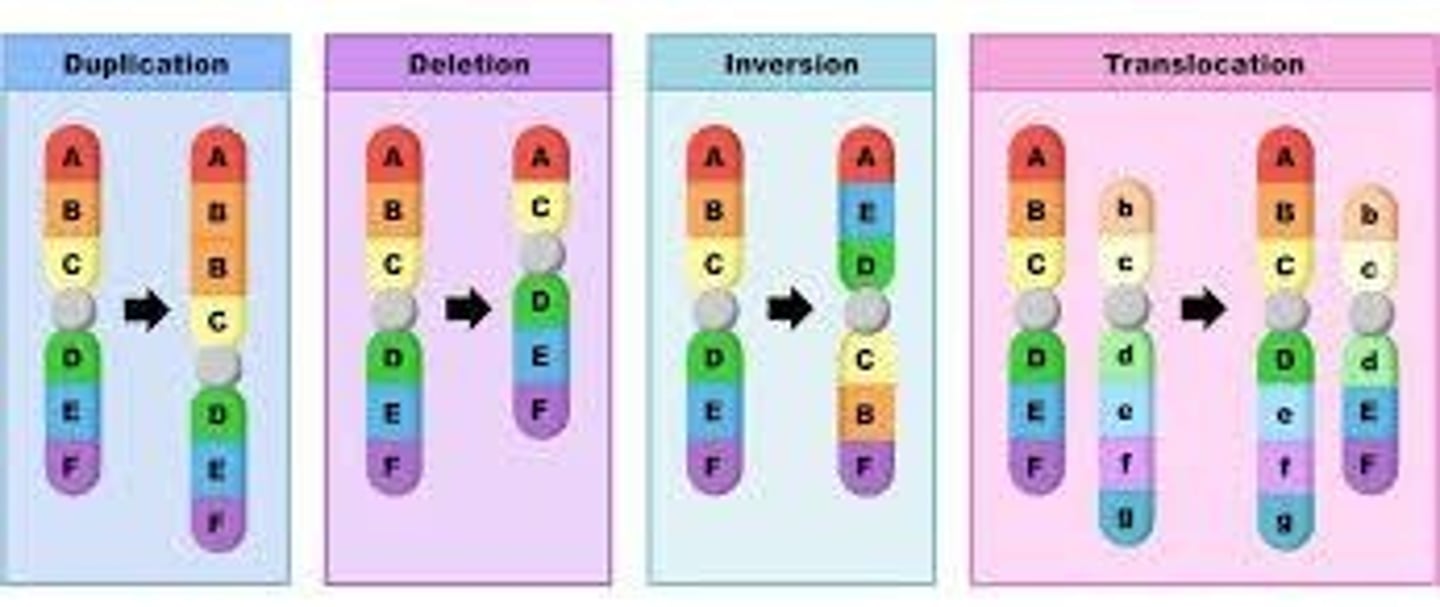
Chromosome mutations
Changing the structure of a chromosome or the loss or gain of part of a chromosome
Deletion
Involves the loss of all or part of a chromosome
Inversion
Reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome
Translocation
Occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division
Duplication
Produces an extra copy of all or part of a chromosome
Gene mutations
Change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene
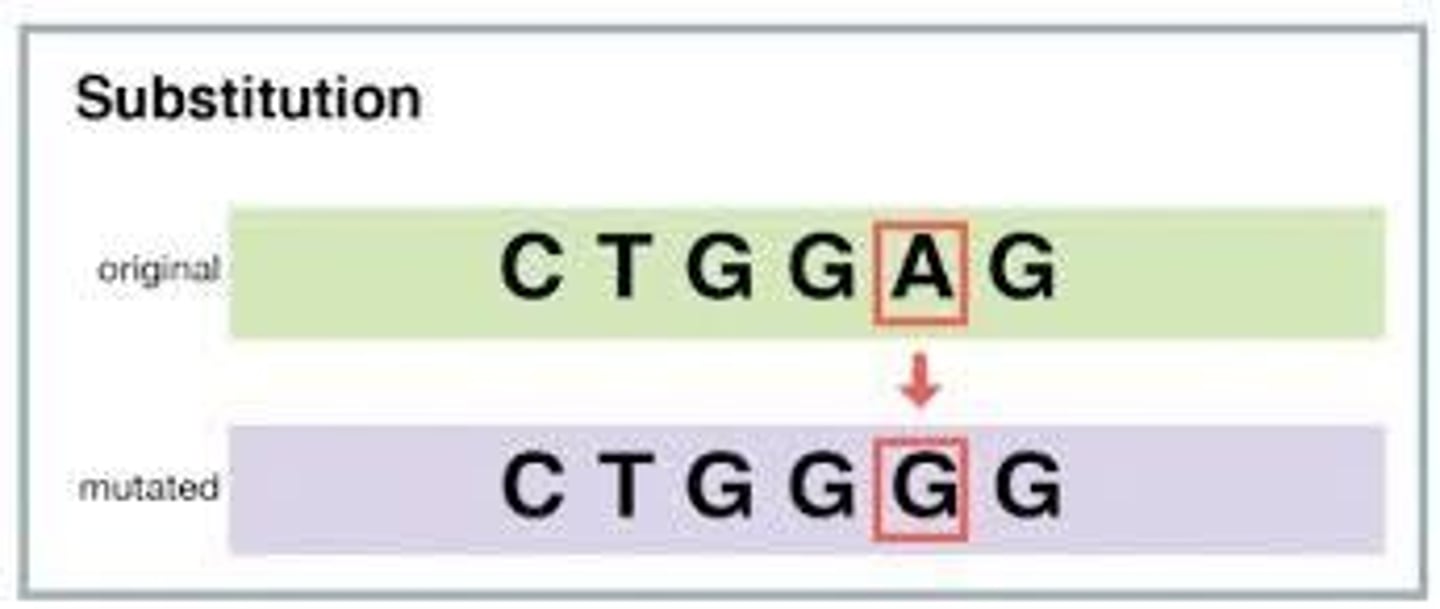
Point mutations
Mutations that involve a change in a single nucleotide
Substitutions
In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base (Example: adenine replaced by guanine)
Insertions
Point mutations where one base is inserted into the DNA sequence
Deletions
Point mutations where one base is removed from the DNA sequence
Frameshift mutations
Mutations that shift the reading frame of the genetic message, potentially altering every amino acid that follows
Gregor Mendel
Commonly referred to as the 'Father of Genetics' and laid the groundwork for most of our knowledge on genetics today
Mendel's experiments
Involved using only purebred plants, controlled breeding, and observing either/or traits
Dominant
In genetics, describes an allele that is fully expressed whenever this allele is present in an individual
Recessive
In genetics, describes an allele that is expressed only when no dominant allele is present in an individual
Segregation
When meiosis makes sex cells, each cell has one allele from mom and one from dad; no allele is favored or has an advantage over another
Independent assortment
Each trait is passed on independently of other traits
Heterozygous
Describes an individual that carries two different alleles of a gene
Genome
The complete genetic material contained in an individual or species
Genotype
The entire genetic makeup of an organism; also the combination of genes for one or more specific traits
Phenotype
An organism's appearance or other detectable characteristic that results from the organism's genotype and the environment
Punnet Square
A graphic used to predict the results of a genetic cross
Monohybrid Cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
Testcross
A cross between an organism with an unknown genotype and an organism with a recessive phenotype
Dihybrid Cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene