Brain Anatomy -- Midterm 1
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
bilateral symmetry
When cut down the sagittal plane, the outcome will (pretty much) be mirror images
radial symmetry
When cutting down multiple planes, the outcome will (pretty much) be the same.
cephalization
Specialized head & brain area
Concentrated sense organs at anterior end of body
Dorsal
toward the back
ventral
toward the stomach
anterior
toward the front end
posterior
toward the rear end
superior
above another part
inferior
below another part
lateral
toward the side, away from the midline
medial
toward the midline, away from the side
proximal
located close to the point of origin or attachment
distal
located more distant from the point of origin or attachment
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
rostral
toward the front of the head, towards the nose
caudal
toward the back end, toward the tail end
coronal plane
plane that shows brain structures as seen from the front
sagittal plane
plane that shows brain structures as seen from the side
horizontal plane (transverse plane)
plane that shows brain structures as seen from above
central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nerves and ganglia located outside of the brain and spinal cord
somatic nervous system
controls voluntary muscles and conveys sensory information to the CNS
autonomic nervous system
regulates many involuntary processes such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, etc.
sympathetic nervous system
response to stressful situations; raises heart beat, slows digestions, dilates pupils, etc. (flight-or-fight system)
parasympathetic nervous system
restores body to original state after stress
ventricles
4 interconnected cerebrospinal fluid-filled cavities within the brain that connect with the central canal of the spinal cord
meninges
membranes the surround the brain and spinal cord (from the outside to inside): dura mater —> subarachnoid mater —> subarachnoid space (with css) —> pic mater —> cerebral cortex
major structures in the hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum
where is the hindbrain located?
just rostral to the spinal cord
what is the hindbrain responsible for?
regulation of many involuntary processes such as breathing and heart rate
nucleus (nucelei)
cluster of cell bodies
ganglion (ganglia)
group of somas (cluster of neuron cell bodies)
major function of ganglia
motor control, motor learning, behaviour and emotions
nerves
grouping of axons that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body. impulses help feel sensations and control autonomic nervous system
tract (fibre tract)
neural pathways that connect the brain and the spinal cord; responsible for carrying sensory and motor messages to and from the periphery
afferent nerves
conduct sensory signals from sensory structures to the CNS
efferent nerves
conduct signals from the CNS to target tissues
mixed nerves
contain some afferent axons and some efferent axons
cranial nerve I.
olfactory — smell
cranial nerve II.
optic — vision
cranial nerve III.
oculomotor — control of eye movements, pupil constriction
cranial nerve IV.
trochlear — control or eye movements
cranial nerve V.
trigeminal — skin tensions from most of face; control of jaw muscles for chewing and swallowing
cranial nerve VI.
abducens — control of eye movements
cranial nerve VII.
facial — taste from the anterior two thirds of the tongue; control of facial expressions, crying, salivations, and dilation of the head’s blood vessels
cranial nerve VIII.
statoacoustic — hearing, equilibrium
cranial nerve IX.
glossopharyngeal — taste and other sensations from throat and posterior third of the tongue; control of swallowing, salivation, throat movements during speech
cranial nerve X.
vagus — sensations from neck and thorax; control of throat, esophagus, and larynx parasympathetic nerves to stomach, intestines, and other organs
cranial nerve XI.
accessory — control of neck and shoulder movements
cranial nerve XII. hypoglossal
control of the muscles of the tongue
the pons
contains the locus coeruleus which produces norepinephrine and plays and important role in arousal, attention, and the stress response
Contains the nuclei for several cranial nerves
Contains a portion of the reticular formation
many fibre tracts pass through the pons — axons from each half of the brain cross to the opposite side of the spinal cord such that the left hemisphere controls the muscles of the right side of the body
the cerebellum
Extensively folded – an outer cerebellar cortex of grey matter surrounding the white matter
Helps regulate motor movement, balance, and coordination
Important for shifting attention between auditory and visual stimuli
Critical for certain types of learning such as forming procedural memories
what structures make up the brainstem?
Medulla, pons, and midbrain
the divisions of the midbrain
the tectum (dorsal region) and tegmentum (ventral region)
structures in the tectum
Superior colliculus: processes and integrates sensory information to allow for a rapid response to sensory input from different locations
Inferior colliculus: processes and integrates sensory information to determine the locations of sound
structures in the tegmentum
The rostral region of the reticular formation
Substantia nigra: gives rise to the dopamine containing pathway facilitating readiness for movement
Ventral tegmental area (VTA): controls certain behaviours such as reward processing, drug addictions, learning and memory, and stress modulation
Cerebral peduncle (crus cerebri): fibre tracts
The nuclei for two cranial nerves
two major regions of the forebrain
diencephalon and telencephalon
structures in the diencephalon
thalamus, pineal gland, hypothalamus, and posterior pituitary gland
thalamus
relay station from the sensory organs; receives sensory input from almost all body region; it filters and integrates sensory information (except olfactory/smell) before relaying it to the cerebral cortex. It contains many nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) – visual processing
hypothalamus
Involved in maintaining homeostasis, so regulates many processes, including those affecting water balance, blood pressure, appetite, metabolism, and body temperature
Associated with behaviours such as eating, drinking, sexual behaviour, and other motivated behaviours
Regulates the endocrine system by controlling release of hormones from the pituitary gland
nuclei in the hypothalamus
Mammillary nuclei: spatial and episodic memory function – spatial: places/where an event occurred (where did I put my keys?), positions of things or events in space – episodic: things that have happened (wedding, graduation, etc.)
Lateral hypothalamus (LH):
Stimulates appetite (hunger center), feeding behaviour and arousal – reward pathway
Paraventricular nucleus (PVN/PVH):
One of the most important autonomic control centers in the brain
Neurons play essential roles in controlling stress, metabolism, growth, reproduction, immune, and more.
Supraoptic nucleus:
Collection of magnocellular neurosecretory cells located within the anterior hypothalamus
Main function of these cells is to produce and secrete the peptide hormone vasopressin (aka antidiuretic hormone ADH and oxytocin)
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN):
Bilateral structure and the central pacemaker of the circadian timing system and regulates most circadian rhythms in the body
Medial preoptic area (MPOA):
Essential brain region to coordinate sleep and body temperature, and male sexual behaviour
2 regions of pituitary gland
anterior and posterior pituitary gland
anterior pituitary gland
composed of axons of neurons of the hypothalamus (from the paraventricular nucleus and supraoptic nucleus) that release hormones directly into the blood
Produces oxytocin and vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) for kidneys and water absorption, and dilating/constricting blood vessels
anterior pituitary gland
composed of endocrine cells that produce hormones, including hormones that regulate hormone production by other glands e.g.,
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH): target thyroid to secrete thyroid hormone to increase metabolic rate
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): tells adrenal glands in your kidneys to secrete cortisol
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH): testes and ovaries for testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone
pineal gland
Produces melatonin
Light inhibits melatonin production
In many vertebrates, the pineal gland is photosensitive
In mammals, information about photoperiod is sent from the retina of the eye into the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus then via several other regions of the nervous system to the pineal body
the limbic system of forebrain
Consists of several interlinked structures of the diencephalon and telencephalon that form a border around the brainstem
Includes the olfactory bulb, hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, and cingulate gyrus of the cerebral cortex
Associated with motivation, emotions, anxiety, aggression, and behaviours such as eating, drinking, and sexual activity
structures in the telencephalon
cerebral cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulbs
olfactory bulb function
olfactory sensory information (smell) is processed here
basal ganglia function
Associated with planning of motor movement, and with aspects of memory, motivational behaviour, and emotional expression
Also important for attention, language planning, and other cognitive functions
Includes the caudate nucleus, the putamen, nucleus accumbens, and blobus pallidus
caudate nucleus function
helps process visual information and control movement
putamen function
learning motor control, including speech articulation, language functions, reward, cognitive functioning, and addiction
nucleus accumbens function
neural interface between motivation and action, plays a key role on feeding, sexual, reward, stress-related, drug self-administration behaviours, etc.
globus pallidus function
primary function is to control conscious and proprioceptive movements
hypothalamus
A large structure located between the thalamus and cerebral cortex
Critical for certain types of memory, especially memories for individual events, but also spatial memory and navigation
2 hemispheres of the cerebral cortex
right cerebral hemisphere and left cerebral hemisphere
what divides the cerebral cortex into two halves?
longitudinal fissure
the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex consists of the cellular layers on the outer surface of the two cerebral hemispheres
Each side receives sensory information from the opposite (contralateral) side of the body and controls motor movement on the opposite side of the body
There are differences in folding of the cerebral cortex in different species of mammals
The number of neurons per unit of volume also varies from species to species
Cells of the cortex are also divided into columns that lie perpendicular to the laminae
what is the outer surface of the cerebral cortex called?
pial surface
4 lobes of the cerebral cortex
occipital, parietal, temporal, frontal
occipital lobe
Processing of visual sensory information including:
Colour
Distance and depth perception
Space and location
Motion
Receiving visual information from the retina of the eyes via the thalamus (and other structures) and sending processed visual information to the other lobes of the cerebral cortex for further processing
parietal lobe
Processing sensory information from the somatosensory system to allow for perception of bodily sensations
Integrating sensory information from most body regions
Spatial navigation and reasoning, visual mapping
Coordinating movement, particularly the fine motor movement of the hands required to manipulate objects
temporal lobe
Processing auditory sensory information (hearing)
Processing visual information to allow recognition of objects and faces
Processing emotions
Comprehension of language
Formation of memories, particularly long-term memories, including visual memories, episodic memories, factual memories, verbal memories
frontal lobe
Cognitive functions including reasoning, planning, making decisions, judgement, problem solving, working memory
Planning and controlling voluntary movement
Processing emotions, including understanding and reacting to other people’s feelings
Producing language
Formation of long-term memories
Motivation and control of reward-seeking behaviours
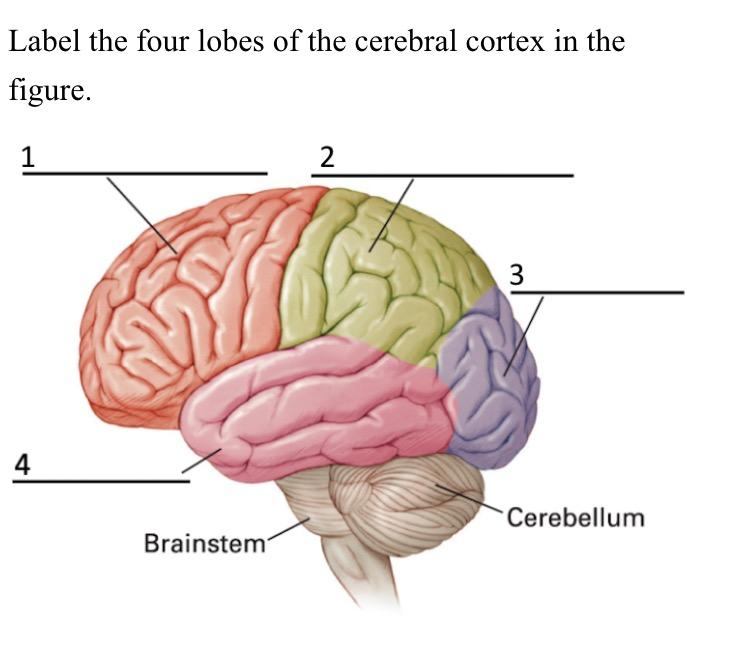
what is 1 called
frontal lobe
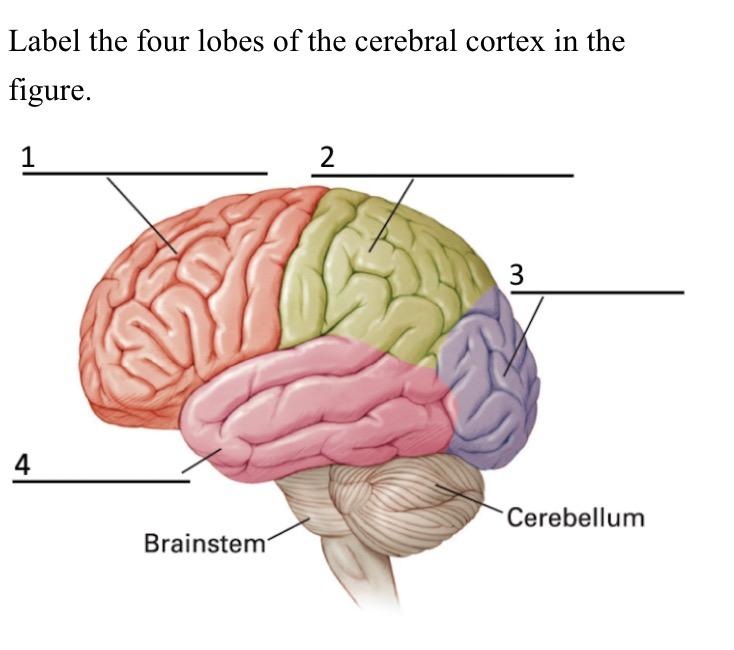
what is 2 called
parietal lobe
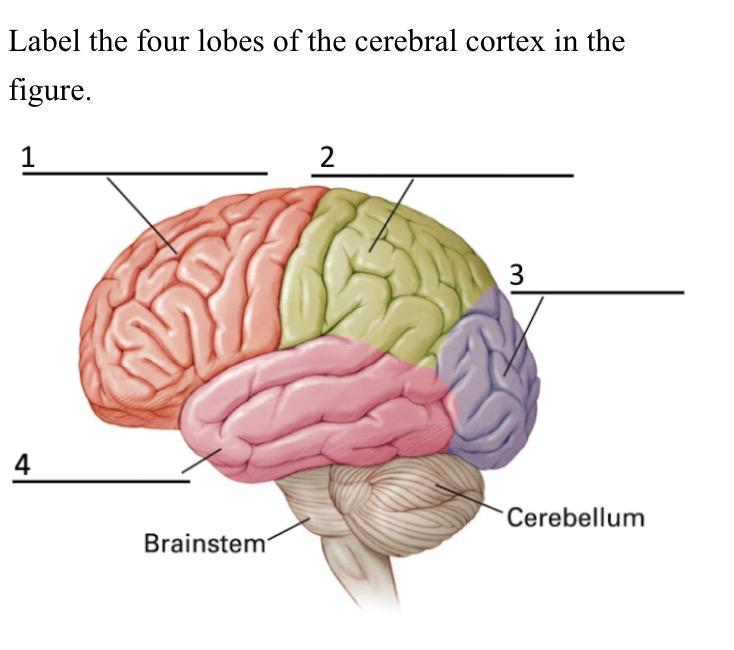
what is 3 called
occipital lobe
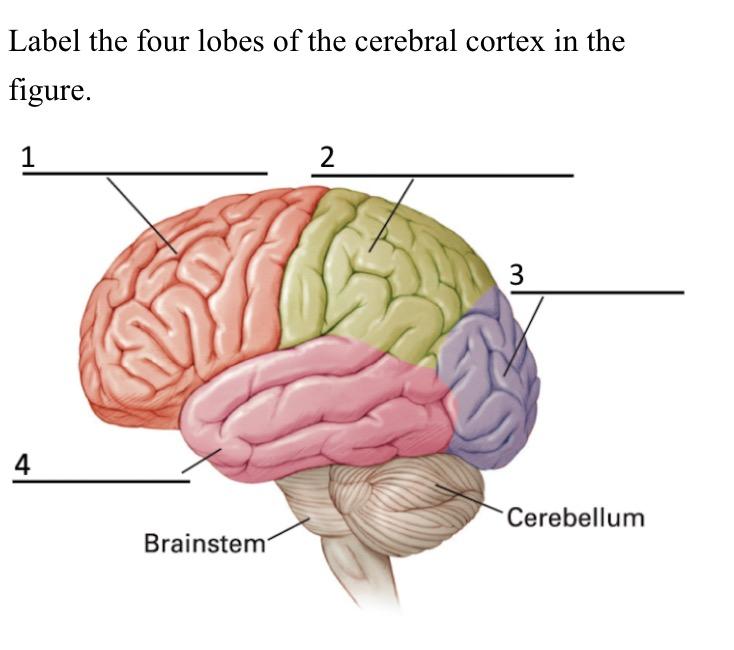
what is 4 called
temporal lobe
what are the bulges of brain tissue in the cerebral cortex
gyri
what are the deep fissures in the cerebral cortex called
sulci
grey matter function & location
processing, outer layer of brain
white matter function
communicating, inner part of brain