GEL Week 4- Rock cycle and Igneous Rocks (1)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
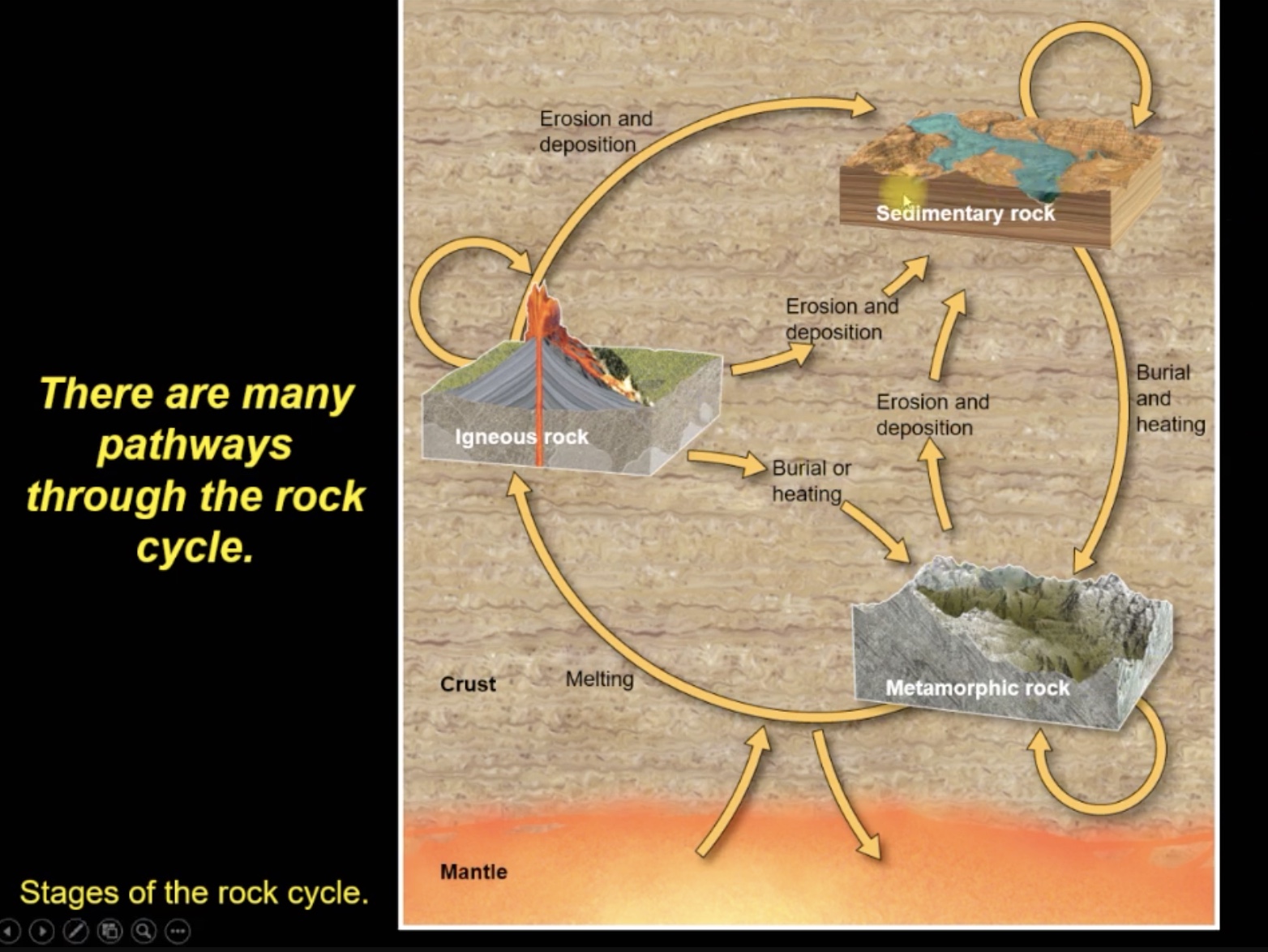
What is the purpose of the rock cycle?
The rock cycle describes the pathways that can create each of the 3 rock types
Igneous process
Internal heat melts rocks to create magma; cools and becomes igneous
Sedimentary process
Erosion creates sediments, can become sedimentary
Metamorphic process
Rocks can be squeezed and heated, changing their characteristics. This change produces metamorphic rocks
Igneous rocks
Solidified molten rock that freezes as it cools (1,000 C to 650 C)
T/F: Earth is not made up of igneous rock
False: Earth is mostly igneous rock
What is magma?
Magma- subsurface melt (molten rock beneath surface)
What is lava?
Lava- melt at the surface (magma leaving Earth’s interior and rises towards surface
Difference between lava and magma
The difference between magma and lava is significant as their varying characteristics lead to the formation of distinct rocks
How is Earth’s internal temperature described?
Geothermal gradient- temperature increases with depth (varies by location)
How does magma form?
Magma forms as existing rocks melt. It occurs in the crust and upper mantle.
Does magma move?
Yes, magma doesn’t stay put; it tends to rise upward. It is less dense-buoyant (so it rises to surface)
What are the 3 components of magma?
Solid, liquid, and gas
Solid
Mineral crystals in the melt (molten rock)
Liquid
comprised of mobile elements (mostly Si and O)
Gas
Magmas contain abundant amounts of dissolved volatile (vaporus) gas.
Name the percentage of volatiles in magma
Up to 15% volatiles- gas (Water vapor- H2O)
What is the role of element composition in magma?
Different mixes of elements yield different magmas, which lead to different rocks