BIO 305: Biology of Microorganisms Exam II
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
How does population size of microbes influence efficacy of microbial control agents?
The larger the population, the longer it will take to kill.

How does temperature influence efficacy of microbial control agents?
The reaction rate of microbial control agents increases as temperature increases (to a point). This means the agents will generally more effective at higher temperatures. Lower temperatures will, however, cause slower growth in the population.
Are all microbes equally as easy to control?
No. Depending on the species, especially if endospores can be formed, certain microbial agents will be more or less effective.
Will a bacteria in the log phase be more or less susceptible to control agents?
More
When looking at a microbial death graph, what does the loss of one log (base 10) represent?
The loss of 90% of the population over that time.
Thermal Death Point (TDP)
the lowest temperature required to kill all microbes in a sample in 10 minutes
Thermal Death Time (TDT)
shortest length of time required to kill all test microbes at a specified temperature
Decimal Reduction Time (DRT)
Minutes to kill 90% of a population at a specified temperature
Sepsis
bacterial contamination
Asepsis
the absence of significant contamination
Disinfection
destruction of harmful microbes on inanimate objects; NOT STERILE
Antiseptic
literally means "against infection;" chemical disinfection of living tissues
Sterilization
ALL forms of microbial life are destroyed including bacterial endospores and viruses
Germicide
chemical agent that kills microbes, but not necessarily endospores
Bacteriostasis
growth of bacteria is stopped, but bacteria are not killed (flat curve)
Bactericidal
kills bacteria (negative curve)
Sanitization
removal of most microbes; think of doing dishes or laundry
How does filtration suppress microbial growth?
A sample is passed through a membrane or screen with a tiny pore size. The resulting filtrate will have had all microbes >0.22 µm removed.
What microbes are relatively unaffected by lower temperatures?
pshychrotrophs and psychrophiles
What is lyophilization?
freeze drying; process involves freezing the sample and subjecting to a vacuum; will affect microbes accordingly
What can higher pressures do to control microbes?
Denature proteins
What is desiccation and how does it affect microbial growth?
drying out of sample; absence of water will prevent microbial metabolism
How does osmotic pressure affect microbial growth?
high concentrations of salt or sugar create a hypertonic environment and eventual plasmolysis
Which is generally more effective at microbial control? Moist or dry heat methods?
Moist
What are examples of moist heat?
boiling, autoclaving, pasteurization
What are examples of dry heat?
incineration, hot air oven
You know you want to subject a sample to high temperatures to eliminate contamination, however the material is susceptible to corrosion. What type of method might you use?
dry heat
How does ionizing radiation kill cells?
it ionizes water causing formation of hydroxyl radicals damage DNA causing lethal mutations
How does nonionizing radiation kill cells?
ultraviolet radiation damages DNA specifically causing thymine dimers
How do microwaves kill cells?
by creating heat; not especially antimicrobial
How are disinfectants and antiseptics different?
Disinfectants destroy microbes on inanimate objects while antiseptics chemically disinfect living tissues.
How do phenols control microbes?
By damaging lipids in the plasma membrane.
What chemicals found in essential oils make them effective antimicrobials?
phenolics and terpenes
How does iodine control microbes?
By impairing protein synthesis and altering memranes
How does chlorine control microbes?
is an oxidizing agent; shuts down cellular enzyme systems
How do alcohols affect microbes? Are they more effective pure or in solution? Do they affect endospores and nonenveloped viruses?
denature proteins and dissolve lipids; in solution, specifically between 60 and 95% alcohol; they do not
What side group do heavy metals react with to denature proteins?
-SH
How do chemical food preservatives work to control microbes?
by inhibiting metabolism
How do aldehydes work to control microbes?
cross link functional groups to denature proteins and inactivate nucleic acids
What aspect of antibiotics is not found in physical and chemical control agents?
specificity
What is the Central Dogma?
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
Genetics
the study of heredity (genes)
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
Chromosome
DNA containing structures that carry hereditary information
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Genetic Code
the ordering of nucleotides in DNA and RNA molecules that carries the genetic information in living cells
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
how genes are expressed
Genomics
the branch of molecular biology concerned with structure, function, evolution, and mapping of genomes
What type of chromosome do bacteria have?
single circular chromosome
What enzymes initially relax the DNA strands in replication?
Topoisomerase and gyrase
What enzyme separates the DNA strands during replication resulting in a Replication fork?
helicase
How many replication forks are created during prokaryotic replication?
Two. They begin at the same point of origin and move in opposite directions around the circular chromosome until meeting at the terminal point.
Three Steps of Transcription
initiation, elongation, termination
RNA polymerase
enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
mRNA
A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA, that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein.
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up ribosomal subunits
Start Codon
AUG
Stop Codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
What does the size of the zone of inhibition suggest in reference to the disk diffusion method?
A larger zone of inhibition suggests are more effective microbial control agent.
What qualities are specific to prokaryotic protein synthesis?
Lack of introns, simultaneous transcription and translation in cytoplasm, a single mRNA can carry code for multiple proteins at once (polycistronic)
Operon
a set of operator, promotor sites and the structural genes they control
Promotor
the segment of DNA where RNA polymerase initiates transcription
Operator
the segment of DNA which controls transcription of genes
Photolyases
use visible light energy to separate UV-induced thymine dimers
Excision Repair Enzymes
distortion/lesion or damaged base is identified; one strand is cut out and replaced
Mismatch Repair Enzymes
recognize the mismatched pair, remove a section of the newly synthesized strand that contains the incorrect base, and fill in the correct bases; specific to errors in replication
Base Substitution
a point mutation in which one base is substituted for another
Missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
Silent Mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
Nonsense Mutation
A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of the three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein.
Base deletions/insertions
a base is skipped or added to sequence
Frame Shift Mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
Horizontal Gene Transfer
transfer of genes between cells of the same generation; parent cell to recombinant cell; includes transduction, transformation, and conjugation
Vertical Gene Transfer
flow of genetic information from one generation to the next; parent cell to daughter cell; cellular division
Transformation
DNA from naked cell floating in solution is captured and integrated into DNA of competent cell
Conjugation
cell to cell contact via pili; donor cell transfers DNA to recipient cell
Transduction
occurs by viral transfer; bacteriophage carries DNA from one cell to another
Plasmid
A small segment of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome; involved in horizontal gene transfer
Transposons
(jumping genes) short strands of DNA capable of moving from one location to another within a cell's genetic material
Constitutive Genes
genes that are expressed at all times
Repressible Genes
genes that are expressed by default; can be turned off when not needed
Inducible Genes
genes that are NOT expressed by default; can be turned on when needed
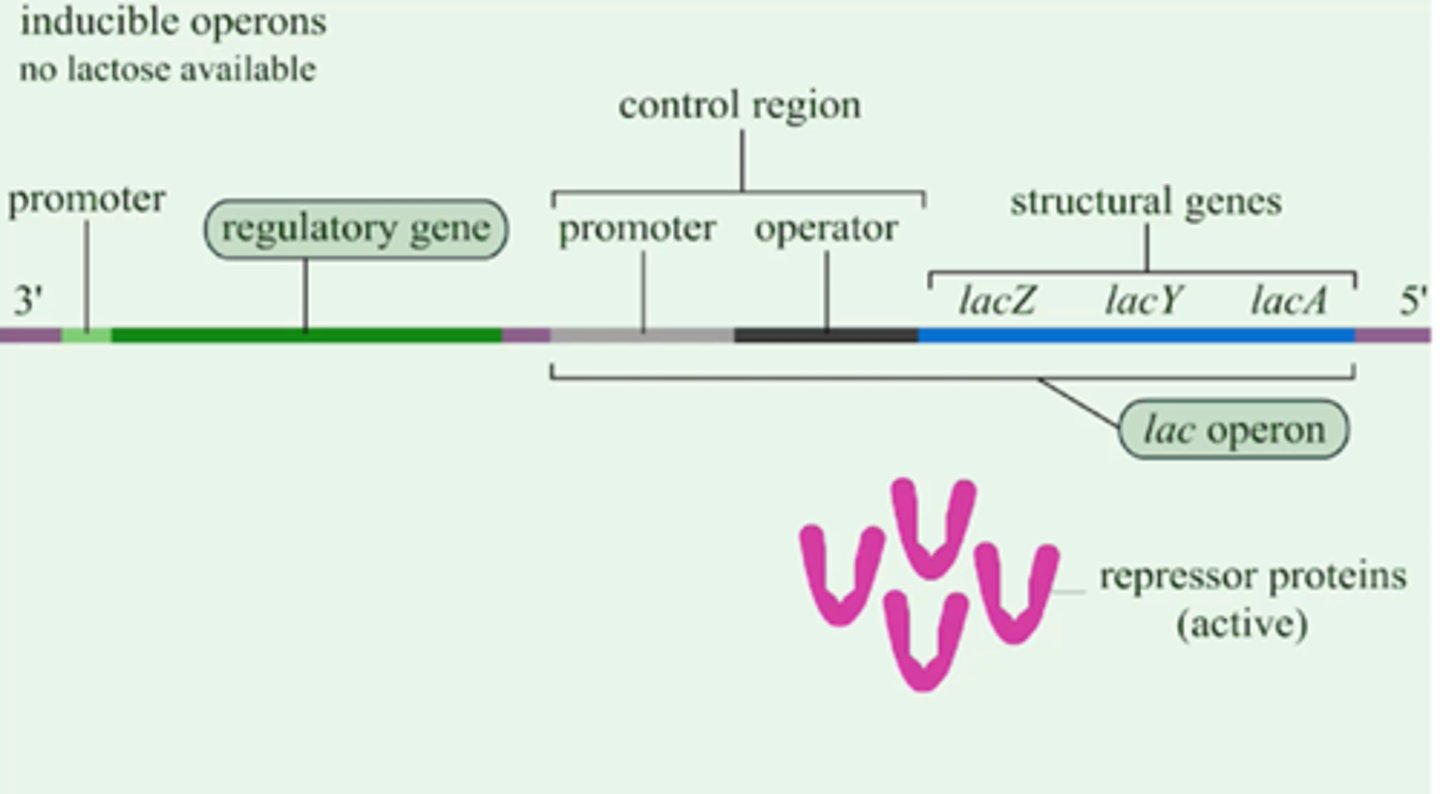
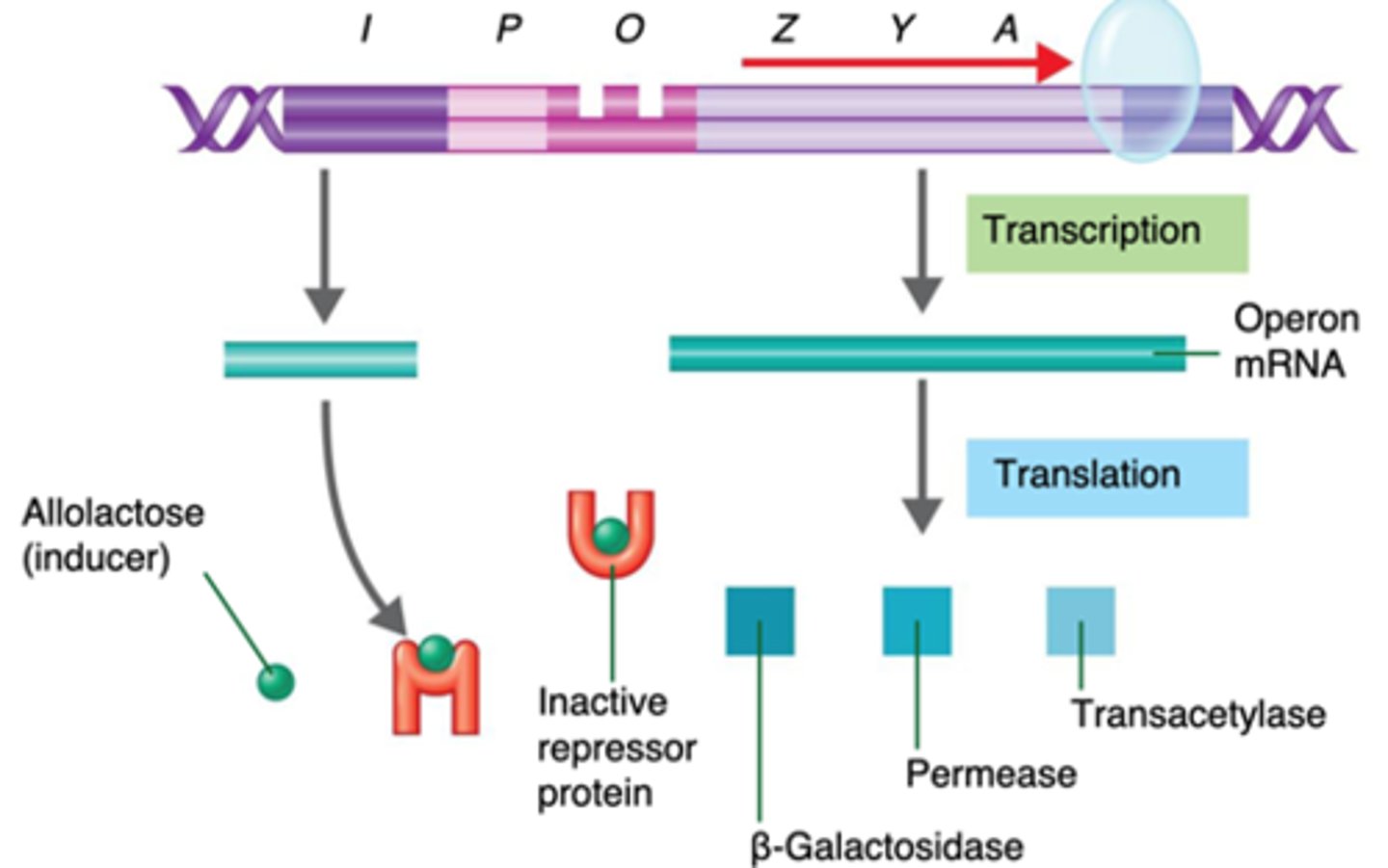
Lac Operon
an inducible operon which contains genes that code for enzymes used in the hydrolysis and metabolism of lactose; allolactose, an inducer, inactivates repressor proteins which switches on the transcription of structural genes
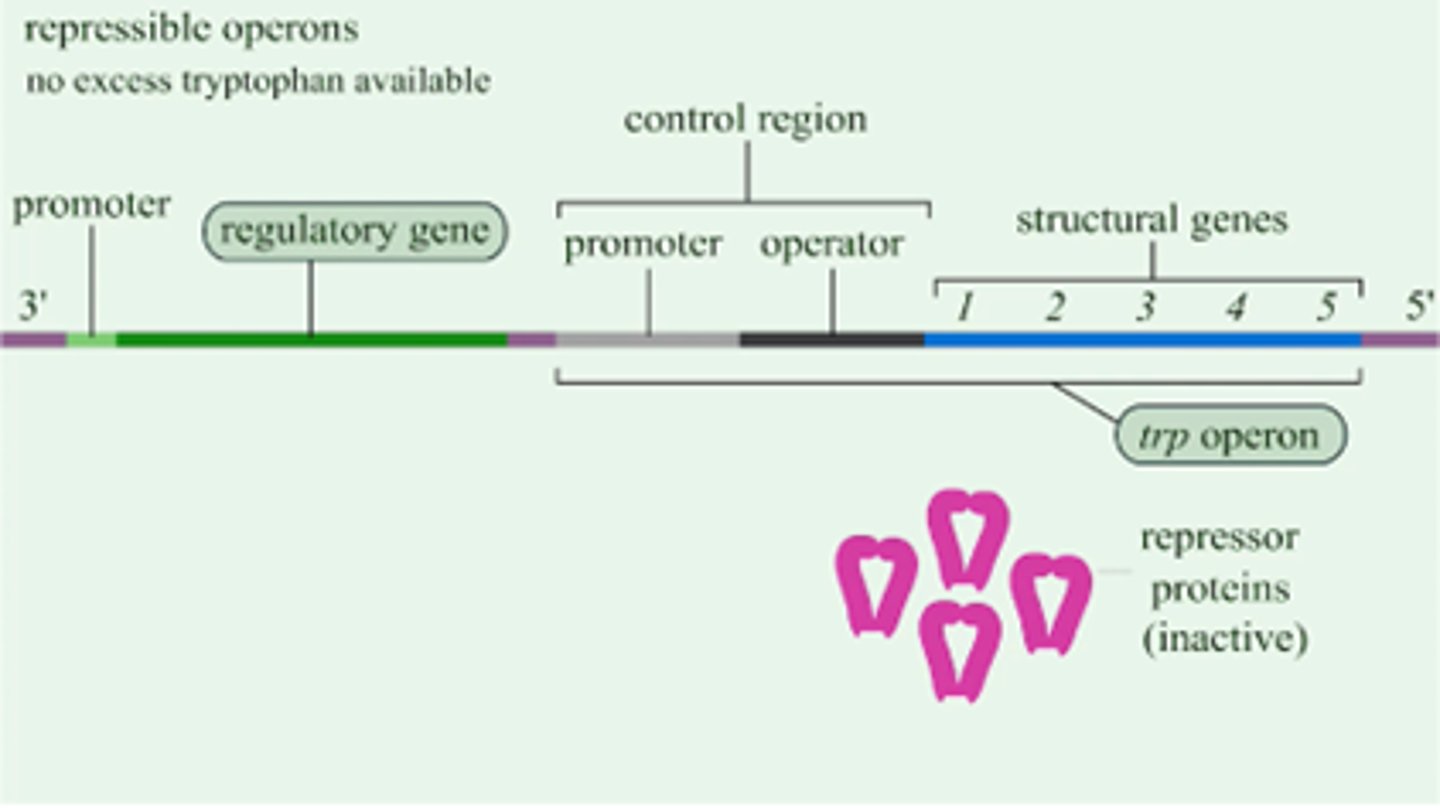
Trp Operon
a repressible operon which contains genes that code for tryptophan; excess tryptophan acts as a corepressor meaning it binds to the repressor protein and enables it to repress gene transcription
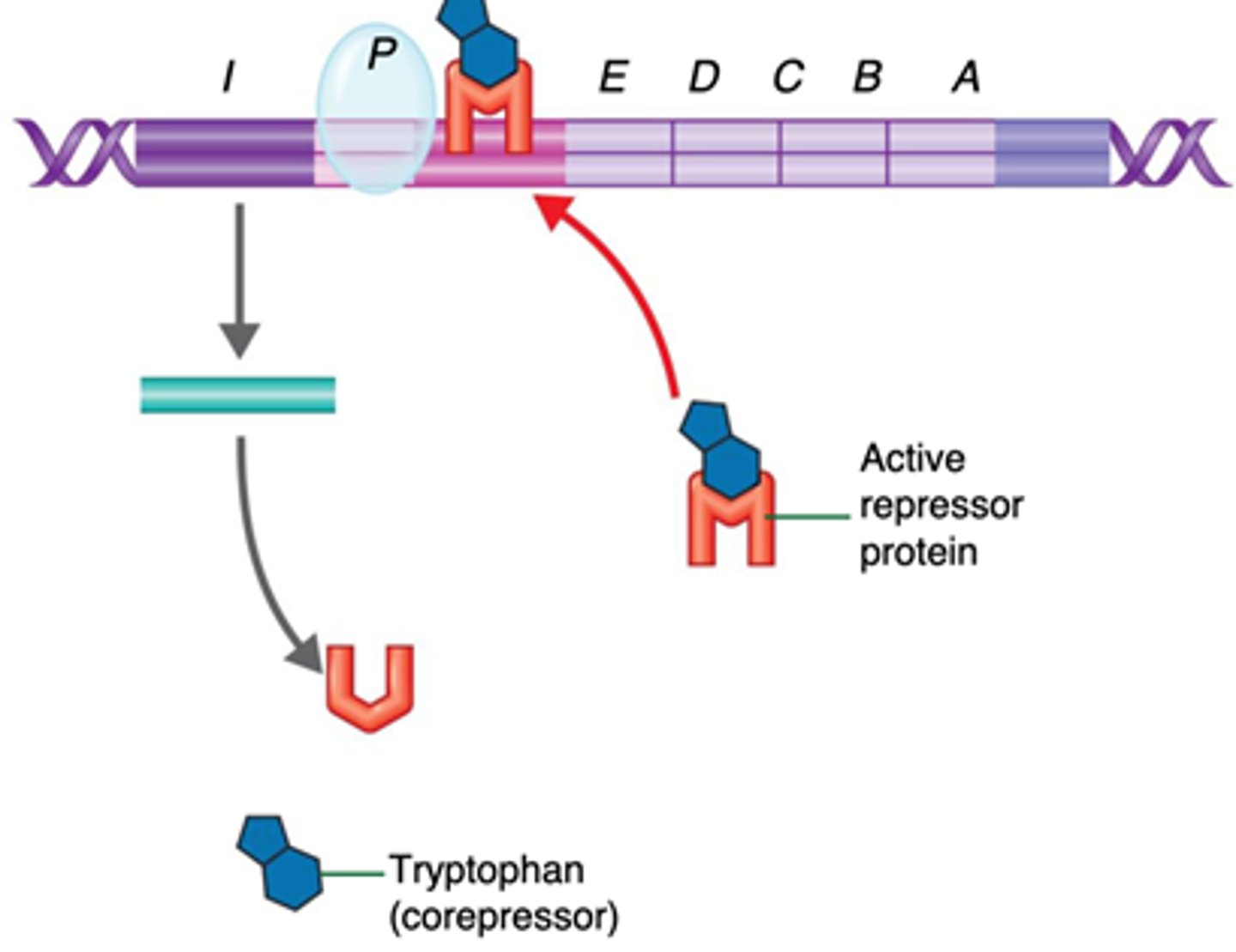
Repressor Protein
a regulatory protein that binds to an operator and blocks transcription of the genes of an operon
Catabolite Repression
The ability to regulate metabolism of specific energy sources.
Describe how glucose availability affects the lac operon.
If glucose levels are low, cAMP is produced. cAMP binds to the cAMP Receptor (aka Catabolite Activation Protein) which encourages RNA polymerase binding to lac operon promotor. This enables lactose processing. If glucose levels are high, no cAMP is produced and lac operon is effectively inactivated.
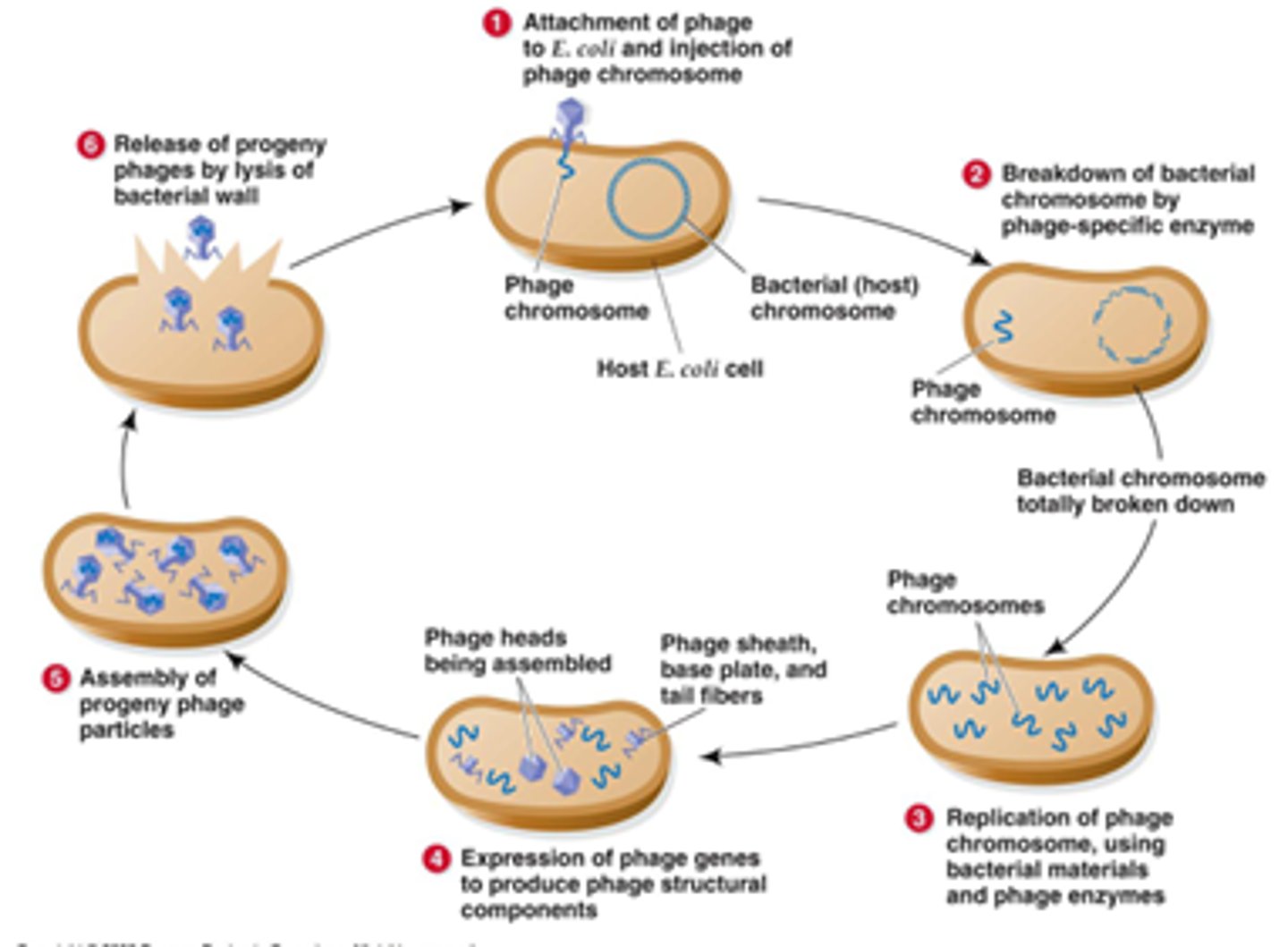
Lytic cycle
A type of viral (phage) replication cycle resulting in the release of new phages by lysis (and death) of the host cell.
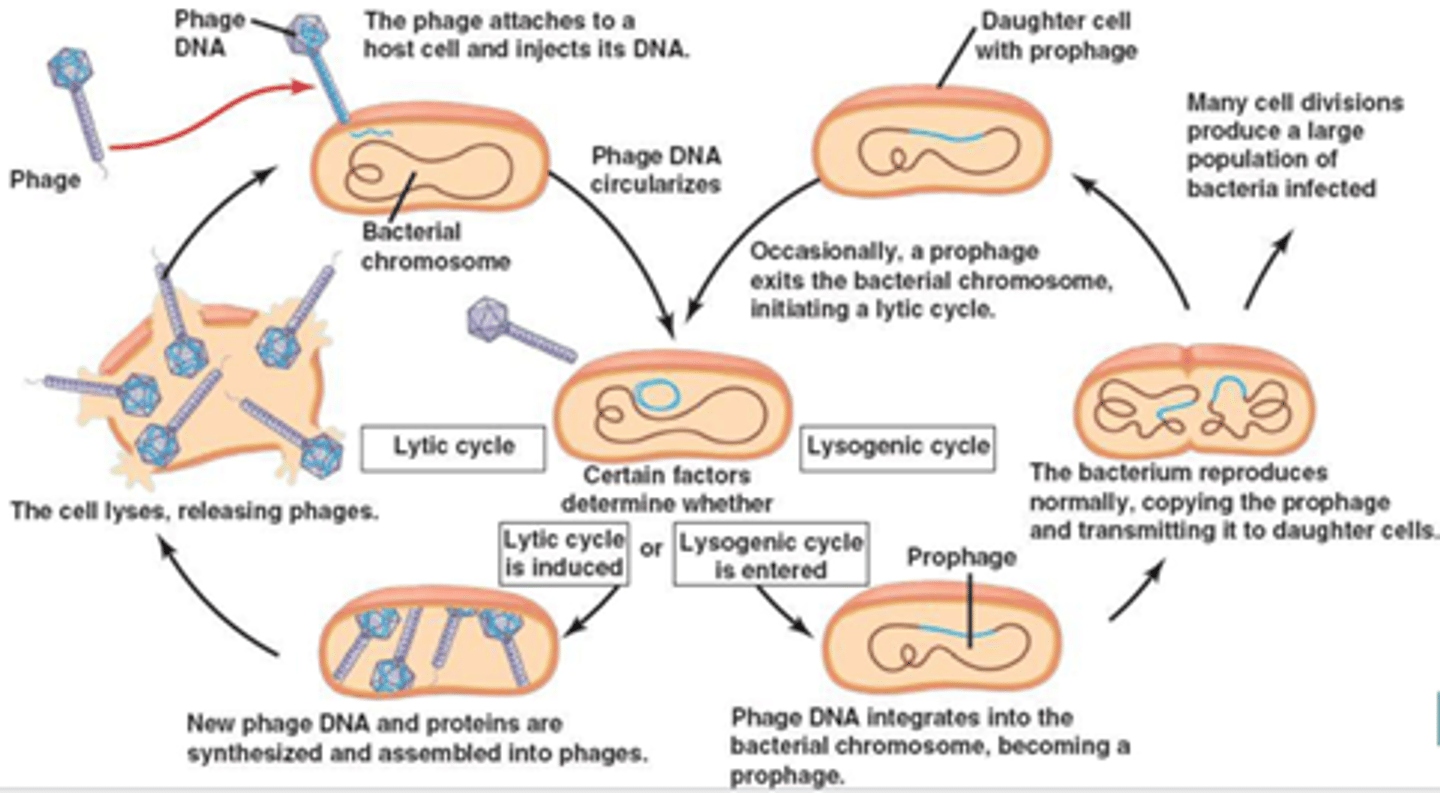
Lysogenic Cycle
A phage replication cycle in which the viral genome becomes incorporated into the bacterial host chromosome as a prophage and does not kill the host until a stressor activates the Lytic Cycle.
Generalized Transduction
lytic cycle accidently places host DNA into a phage, which is brought to another cell
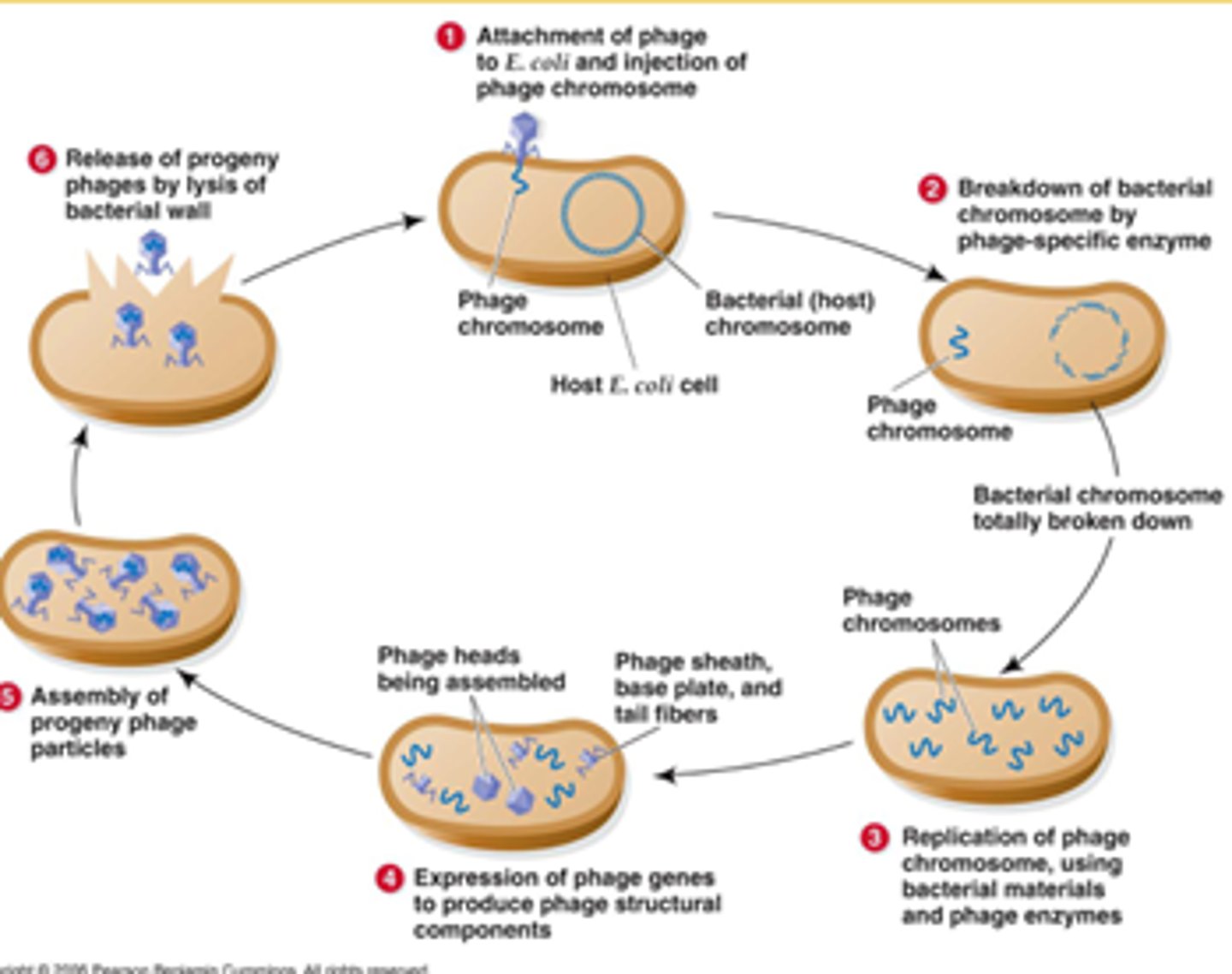
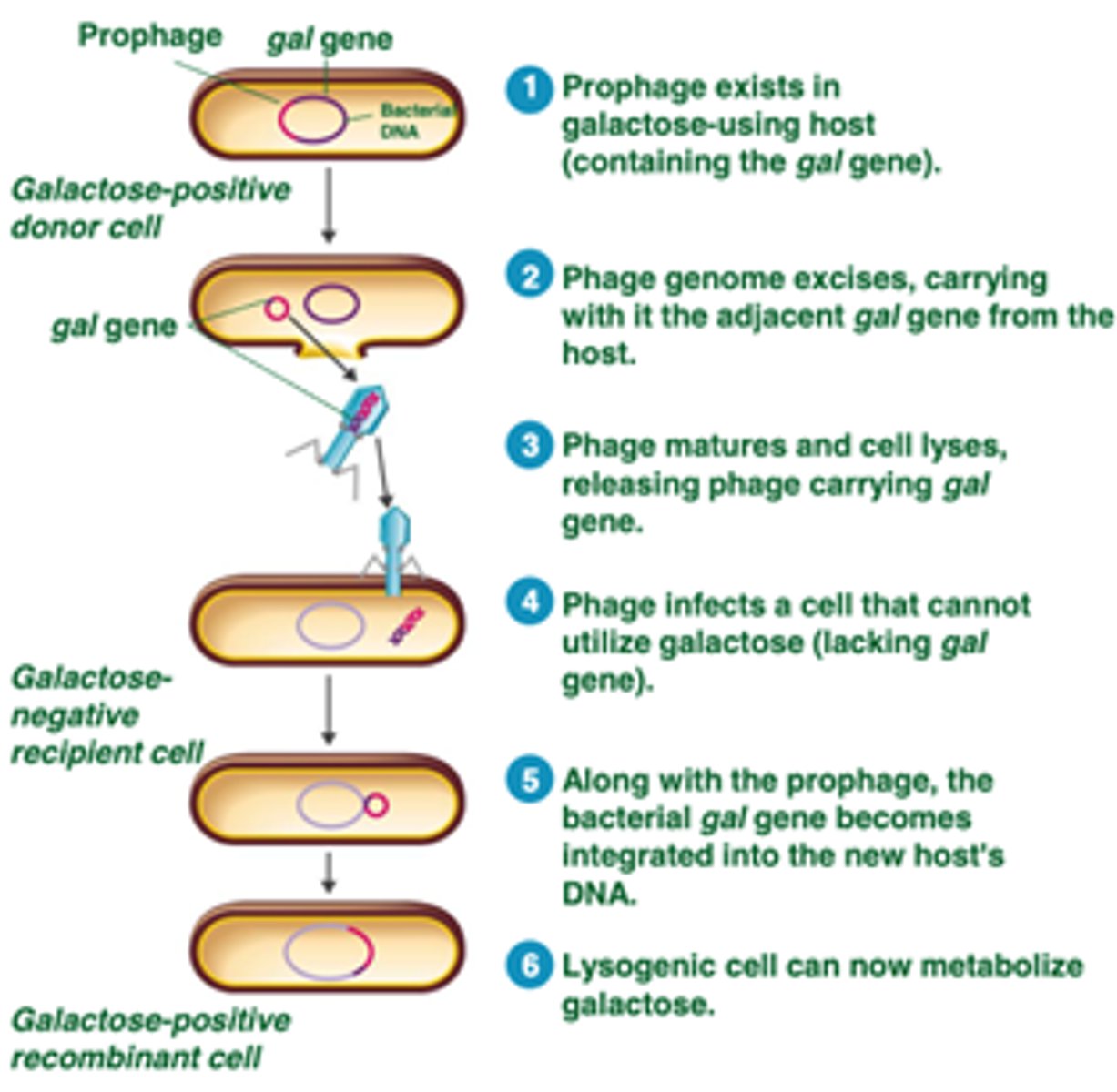
Specialized Transduction
a prophage excises from host cell and carries bacterial DNA from host to new cell which is then incorporated into new host's DNA