Abdominal Vascular System: Aorta/IVC
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
aortic root
section of AO that emerges from the heart (attached to heart)
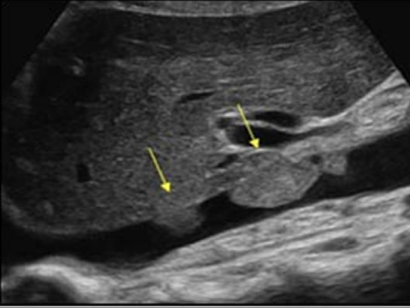
ascending aorta and aortic arch
upward curve shortly after aorta leaves the heart + curve—”candy cane”
descending aorta
thoracic aorta (in chest)
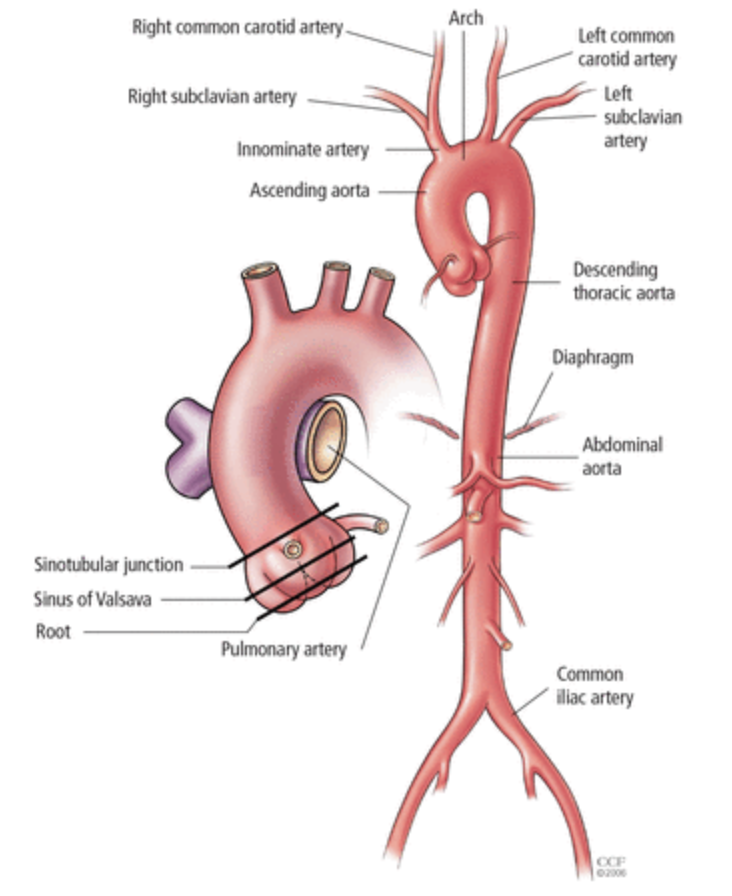
aortic bifurcation
aorta branches into iliac arteries
function of circulatory system
transport gases, nutrients, other essential substances to tissues
transport waste products for excretion
anatomy of vascular structures
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
tunica intima (inner layer)
contains layer of endothelial cells (in lumen) and connective tissue
elastic layer made up of network of elastic fibers
SONO: echogenic
tunica media (middle layer)
contains layer of smooth muscle, elastic fibers, and collagenous tissue
thickest layer for greater elasticity to maintain steady blood flow
SONO: anechoic
tunica adventitia (outer layer)
contains layer of loose connective tissue with bundles of smooth muscle fibers and elastic tissue
has "vaso vasorum” (tiny arteries and veins that supply the walls of blood vessels)
SONO: echogenic
veins vs. arteries
veins carry blood back to heart
veins have thinner walls than arteries because they handle lower blood pressure
only veins are collapsible due to lack of elastic tissue and contain valves
arteries carry blood away from heart
where does the AO originate from?
left ventricle
location of AO
retroperitoneal
travels superior to inferior; to left of spine
posterior to LLL, body of pancreas, SPL A, SPL V, LRV, and pylorus
anterior to psoas muscle
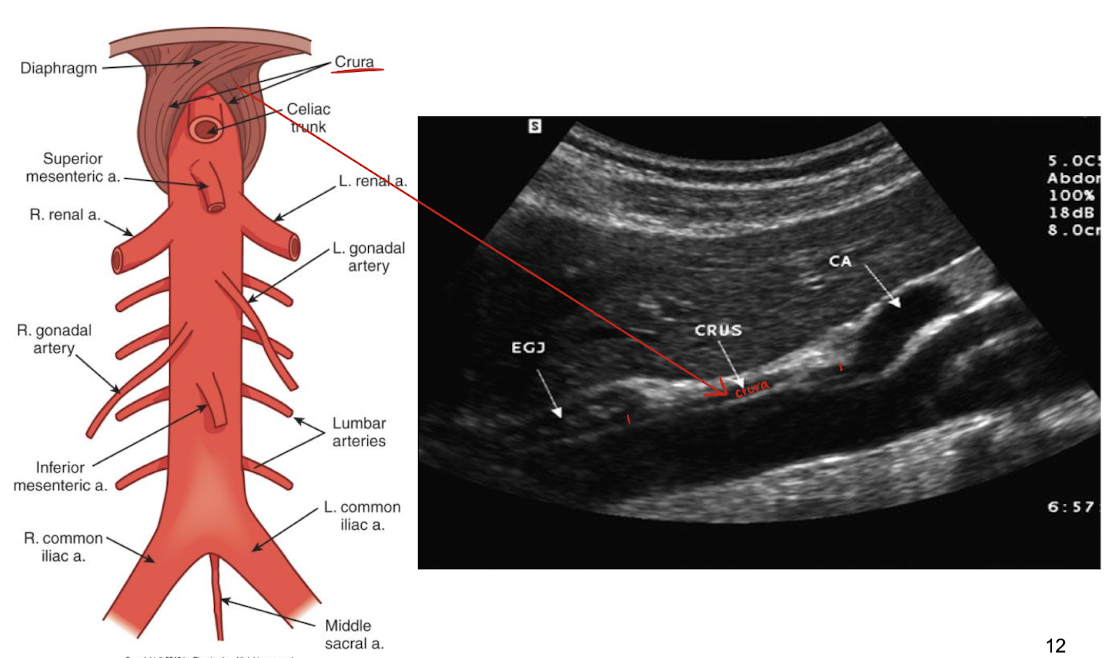
aorta and crus (crura) of diaphragm
crura=extensions from the lumbar vertebrae that anchor the diaphragm
crura is anterior to AO
AO info
largest artery in body
tortuous
pulsatile with no changes in respiration
function of AO
provide oxygenated blood to organs and tissues
ensure metabolism
maintain blood pressure and homeostasis
control bleeding
renin is released in the event of bleeding —> vasoconstriction to maintain BP
indications for imaging AO
screening/evaluate for AAA; bruit or palpable mass
lower back pain, flank pain, or abdominal pain
hemodynamic compromise in legs
assess diameter, arterial grafts, presence of calcification, thrombus, stenosis, or dissection
AO above how many cm is considered an aneurysm?
3 cm
exceeding 7 cm requires immediate medical intervention
aortic dissection
blood splits the tunica walls, causing them to separate —> blood leakage between walls
SONO: echogenic line running down the center of AO
type I dissecting aortic aneurysm
begins at root of AO and may extend entire length of arch, ascending, and descending AO
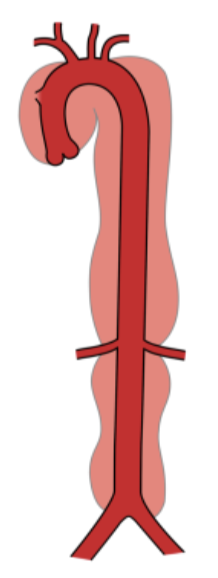
type II dissecting aortic aneurysm
involves ascending AO only
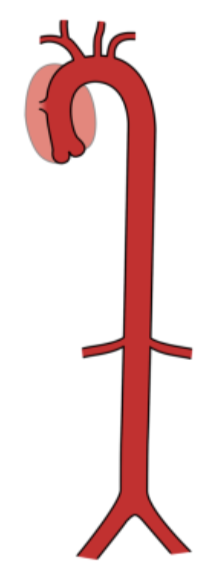
type III dissecting aortic aneurysm
begins at lower end of descending AO and extends into abdominal AO
patients must be NPO for how long with AO exams?
6 hours
scanning techniques for imaging AO
pt. supine or slightly decubitus
anterior or coronal approach
curvilinear probe
measure outer-to-outer wall; low to medium gain (to show walls but no lumen artifact)
use breathing technique or “push belly out”
high resistance waveform
sharp brisk systolic peak
low diastole
organs with intermittent flow (does not require constant blood flow)
low resistance waveform
slow systolic upstroke
high diastole
organ needs constant blood flow
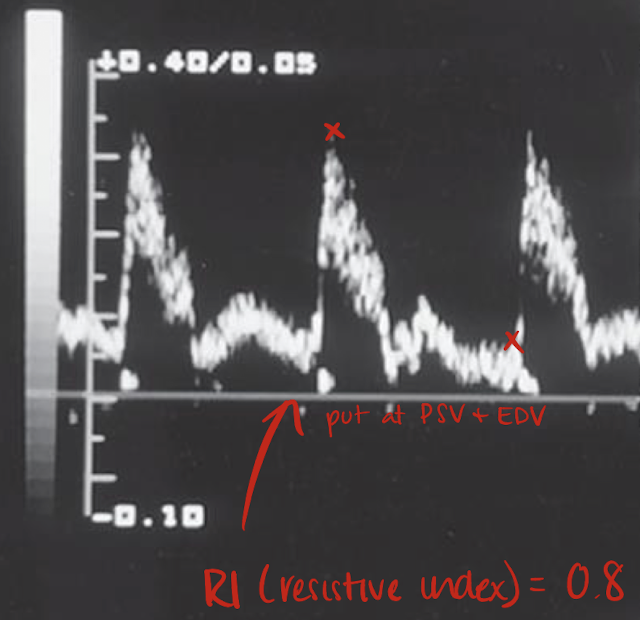
AO Doppler waveform
high and low resistant waveform; sharp brisk upstroke; significant reduced diastolic flow; no spectral broadening
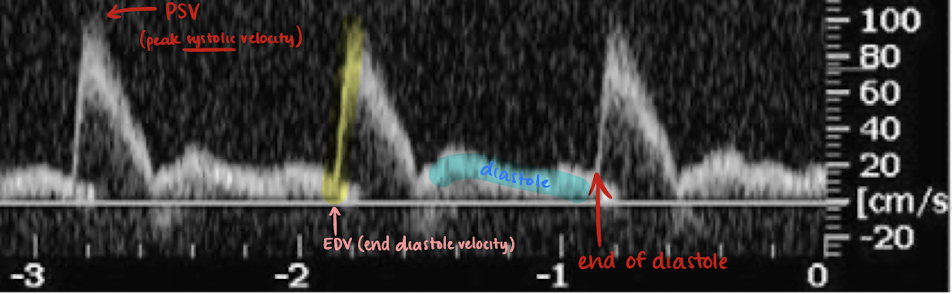
PSV and EDV
PSV=peak systolic velocity
EDV=end diastole velocity
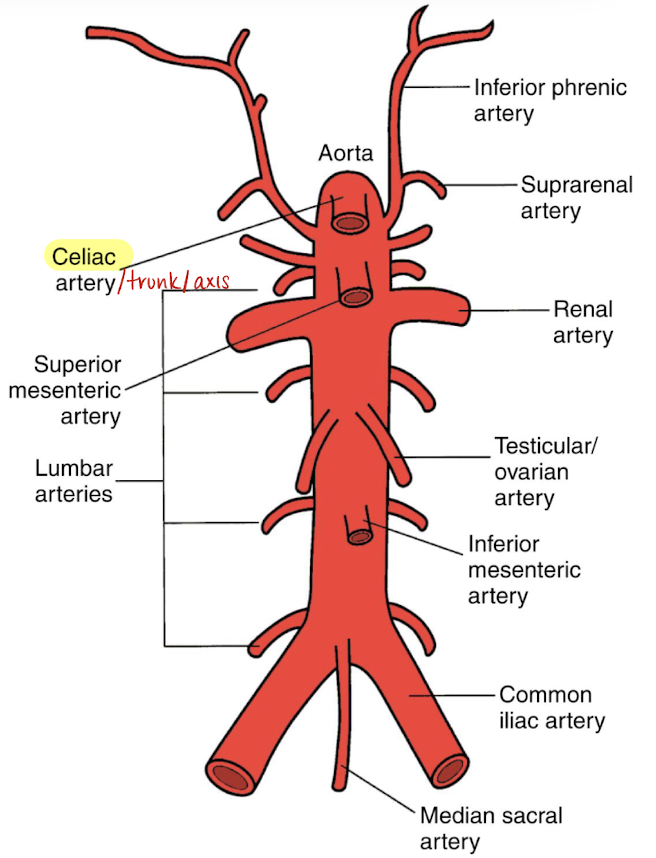
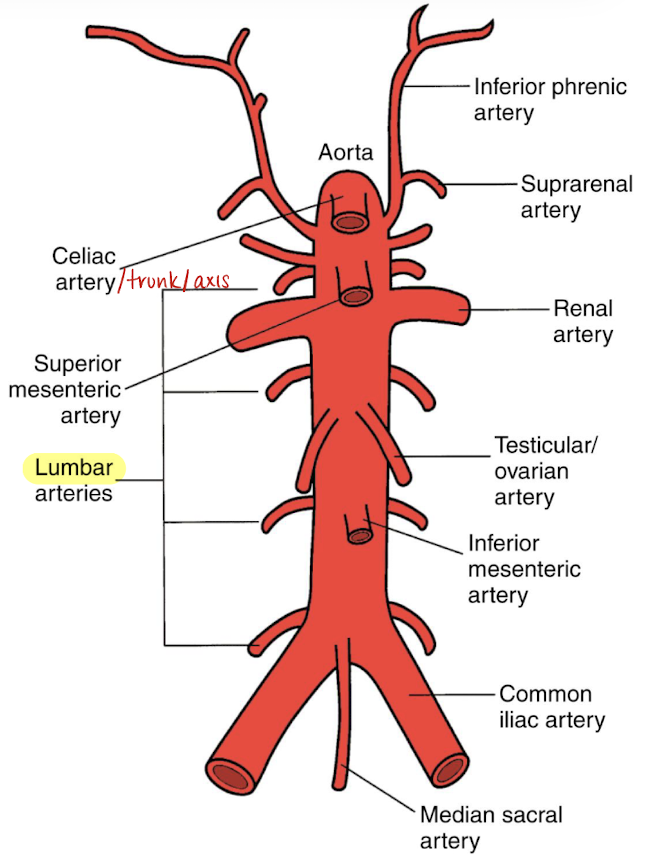
anterior branches of AO (in order)
celiac artery (CA)
superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
gonadal arteries (testicular or ovarian)
inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
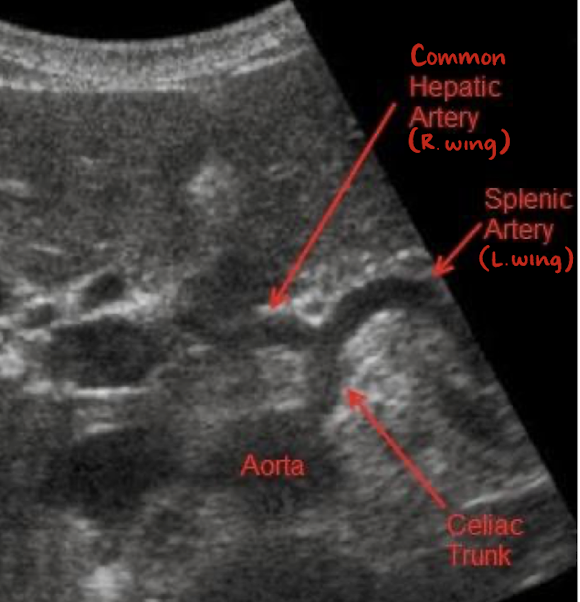
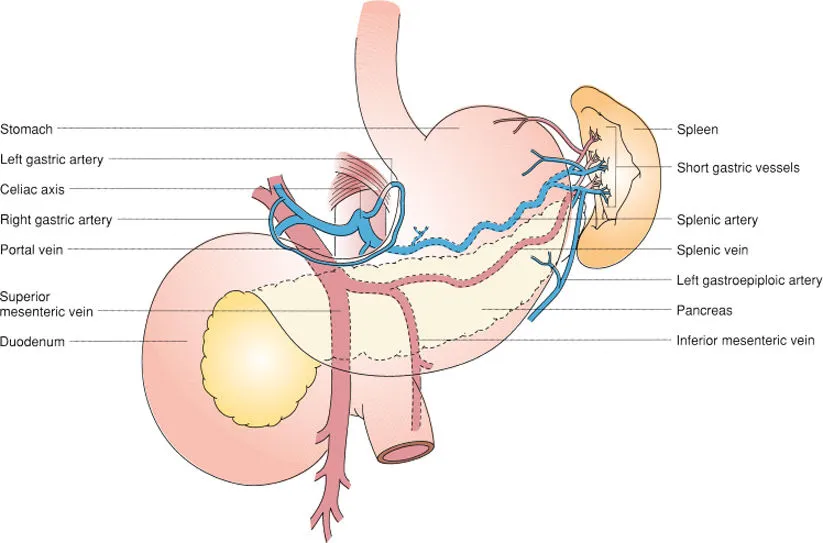
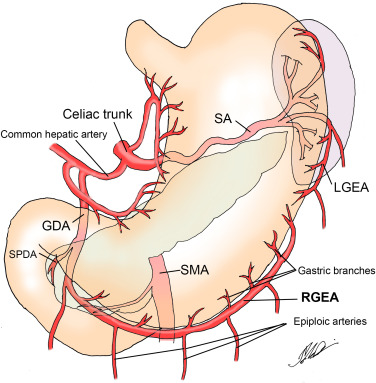
celiac trunk/artery/axis
1st branch off AO
measures less than 1 cm
“seagull sign”
consists celiac trunk, common hepatic artery (right wing), and splenic artery (left wing)
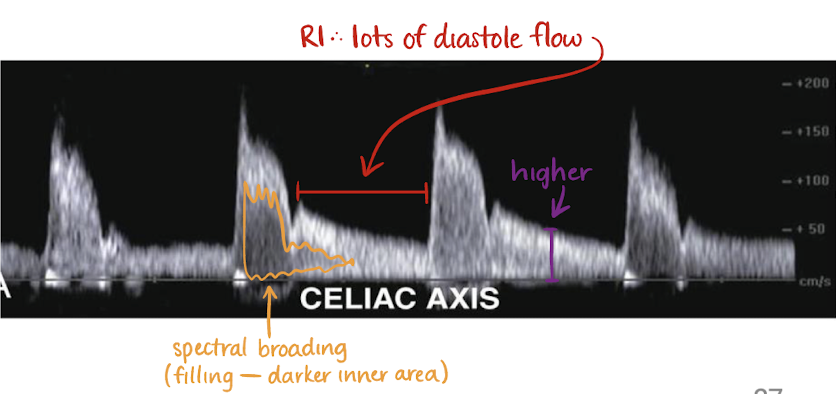
CA Doppler waveform
low resistant waveform (sharp brisk upstroke; significant diastolic flow)
has spectral broadening
no change in flow after meals
branches of CA
common hepatic artery
splenic artery
left gastric artery
left gastric artery (LGA)
branch of CA
courses superiorly (up esophagus) and to the left (descending along lesser curvature of stomach)
supplies lower 3rd of esophagus and lesser curvature of upper right stomach
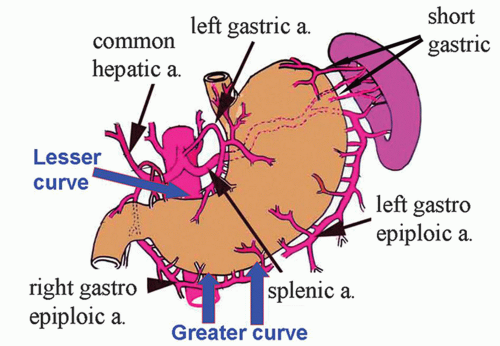
splenic artery (SPL A)
branch of CA
courses horizontally to the left along superior pancreas border
supplies spleen, pancreas, and left side of greater curvature of stomach
common hepatic artery (CHA)
branch of CA
courses horizontally to the right
branches into GDA and PHA
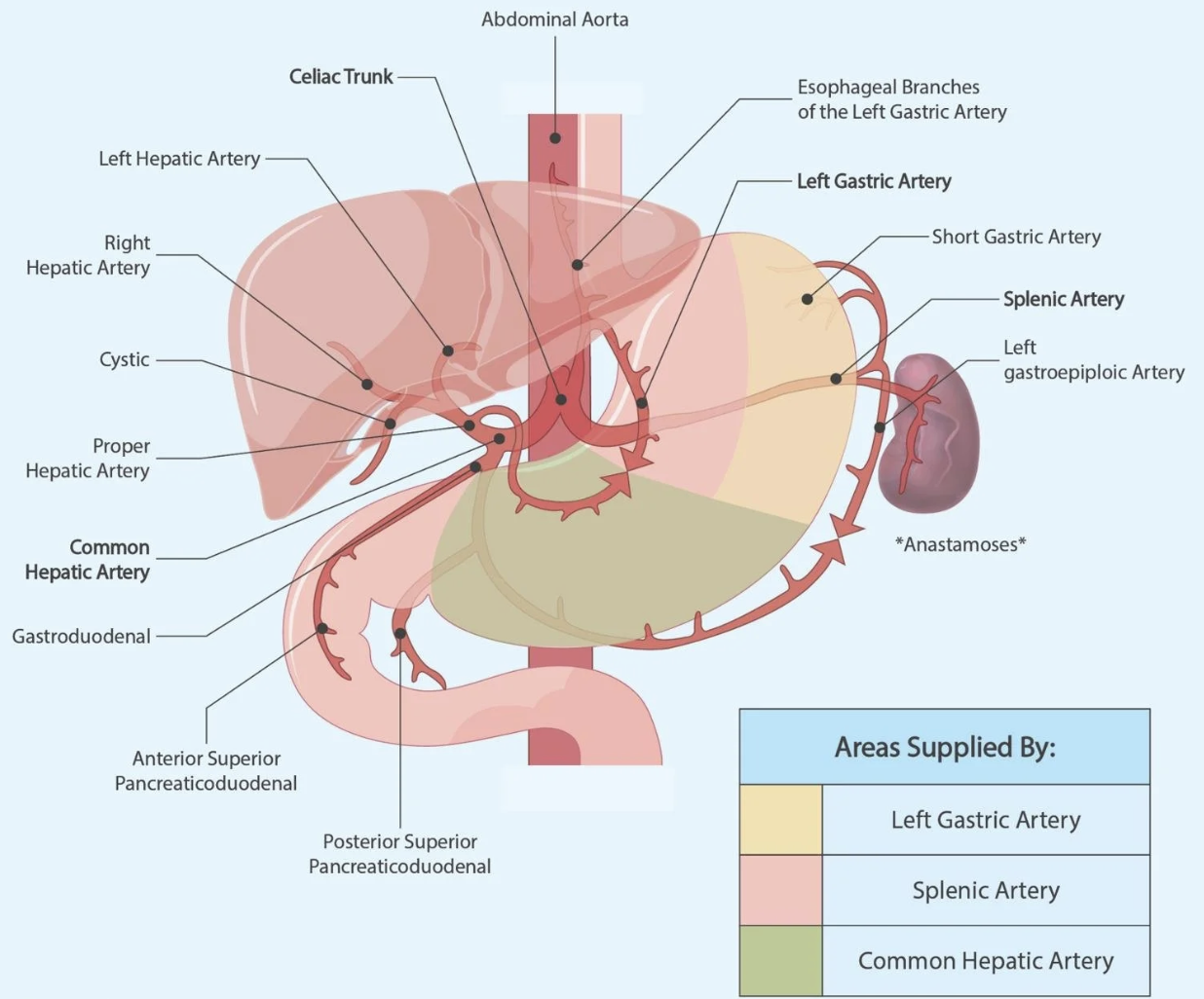
gastroduodenal artery (GDA)
branch of CHA
courses inferiorly
supplies right side of greater curvature of stomach and pancreatic duodenal area
proper hepatic artery (PHA)
branch of CHA (becomes PHA after GDA)
courses right laterally and superiorly; supplies liver via HAs
LHA supplies LLL and caudate
RHA supplies RLL and GB via (cystic artery)
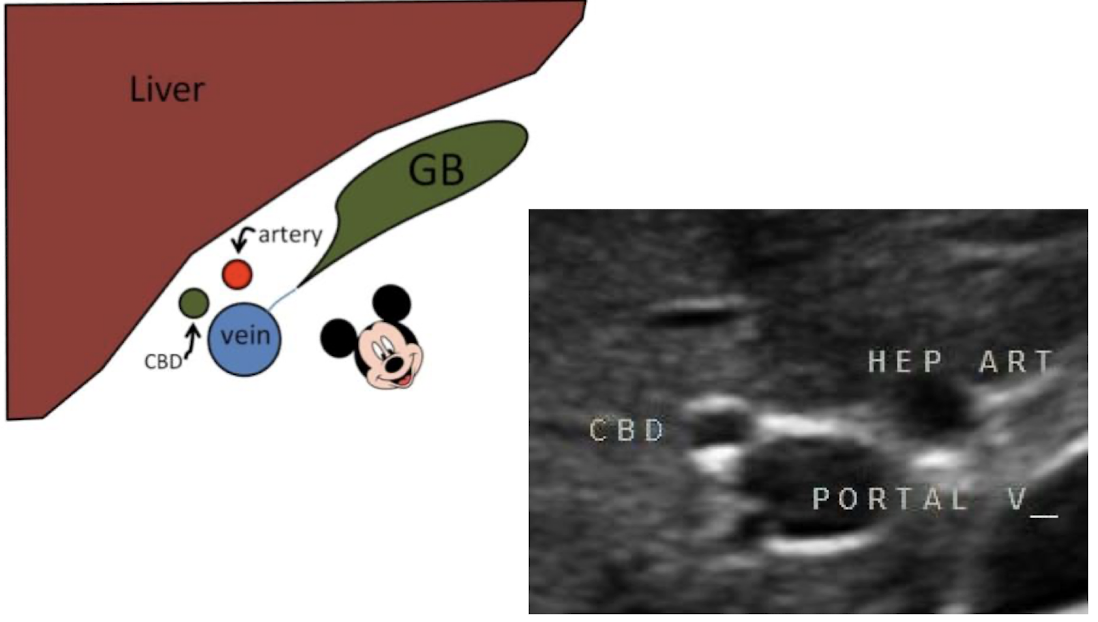
“Mickey Mouse” sign
consists of portal vein (head), hepatic or bile duct (right ear), and hepatic artery (left ear)
makes up the portal triad (in oblique TRANS)
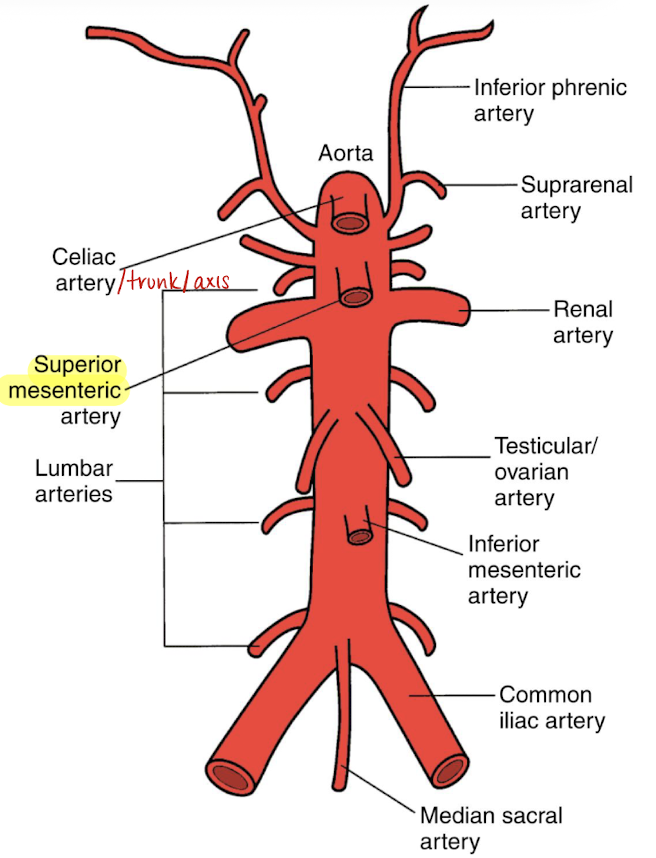
superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
2nd branch off AO
1 cm inferior to celiac trunk
follows anteroinferior course along AO and divides into several arteries
branches supply the small intestine, ascending colon, part of transverse colon, pancreatic head, and duodenal area
surrounded by echogenic fat (retroperitoneal fascia)
SONO in TRANS: circular structure posterior to pancreas and anterior to AO and left renal vein
SMA Doppler waveform
high resistant waveform (sharp brisk systolic upstroke; reduced diastolic flow)
no spectral broadening
ECA and post-prandial (changes to low resistant waveform after meals b/c body needs more blood for digestion)
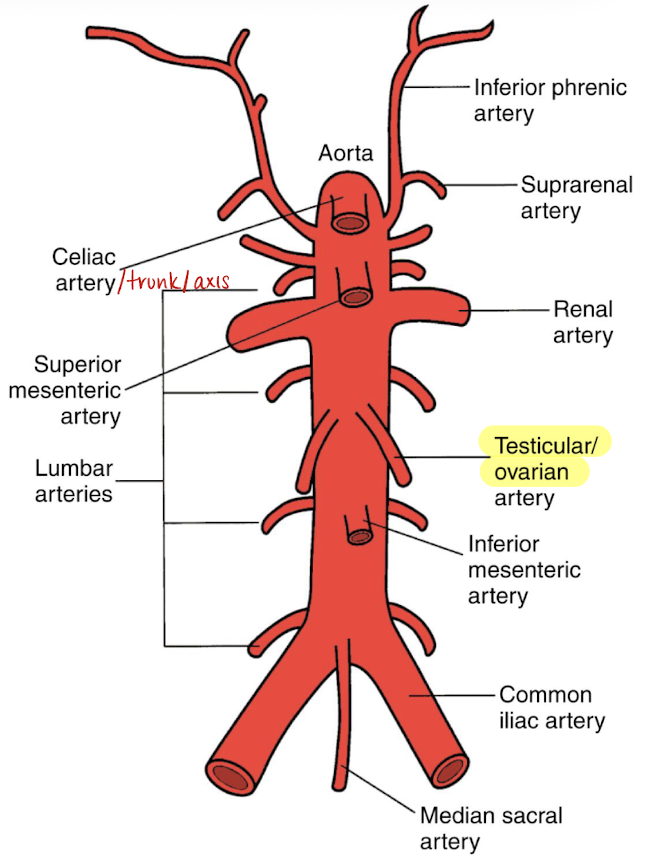
gonadal arteries (testicular or ovarian)
low resistance blood flow
courses inferiorly along the psoas muscle
inferior to SMA and renal artery
left gonadal artery originates a bit superior to right artery
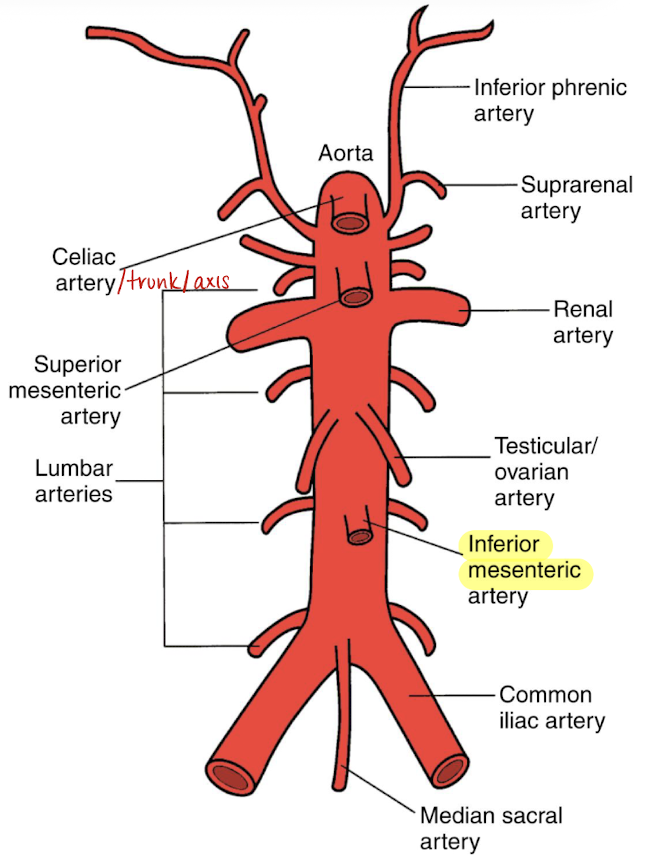
inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
courses anteroinferior to AO
divides into arteries that feed the transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum
SONO in TRANS: 1 o’clock dot on distal AO
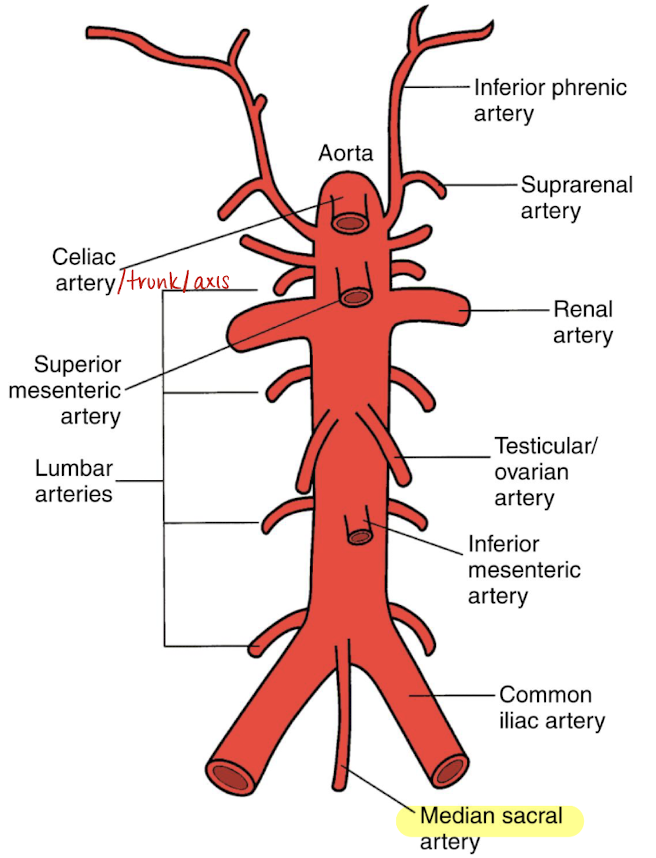
mid/median sacral artery
most inferior branch aside from iliacs
supplies the sacrum and rectum
aortic bifurcations
right and left common iliac artery that divide into external and internal iliac arteries
external CIA runs down the leg
supplies the pelvis and lower extremities
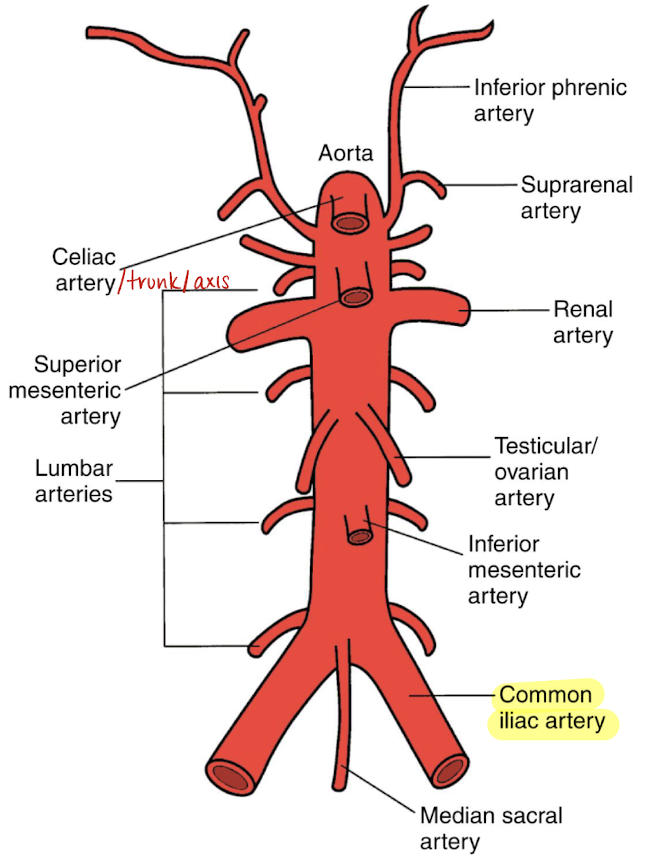
lateral branches of AO
phrenic arteries
suprarenal/adrenal arteries
renal arteries (RRA and LRA)
lumbar arteries
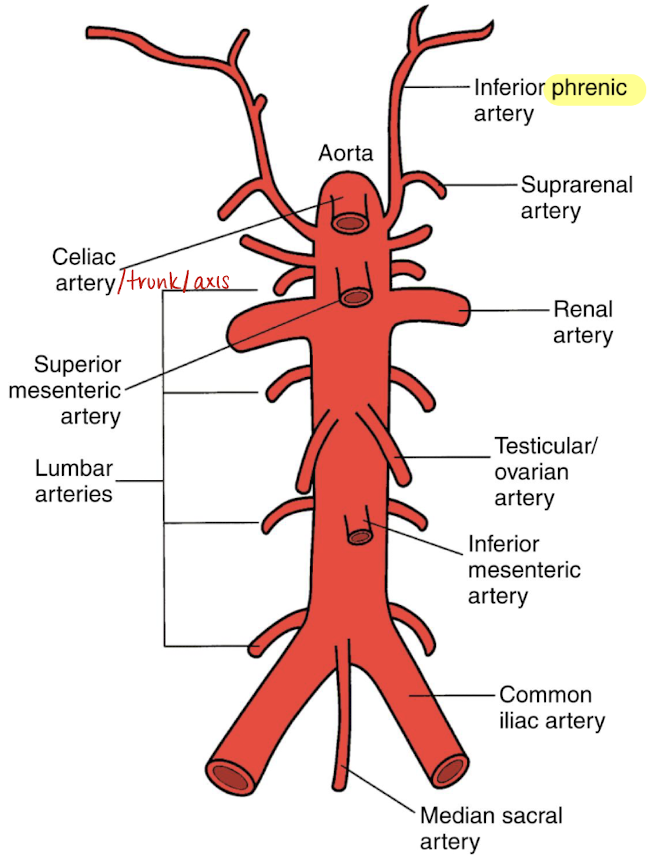
phrenic arteries
paired
supplies the undersurface of diaphragm
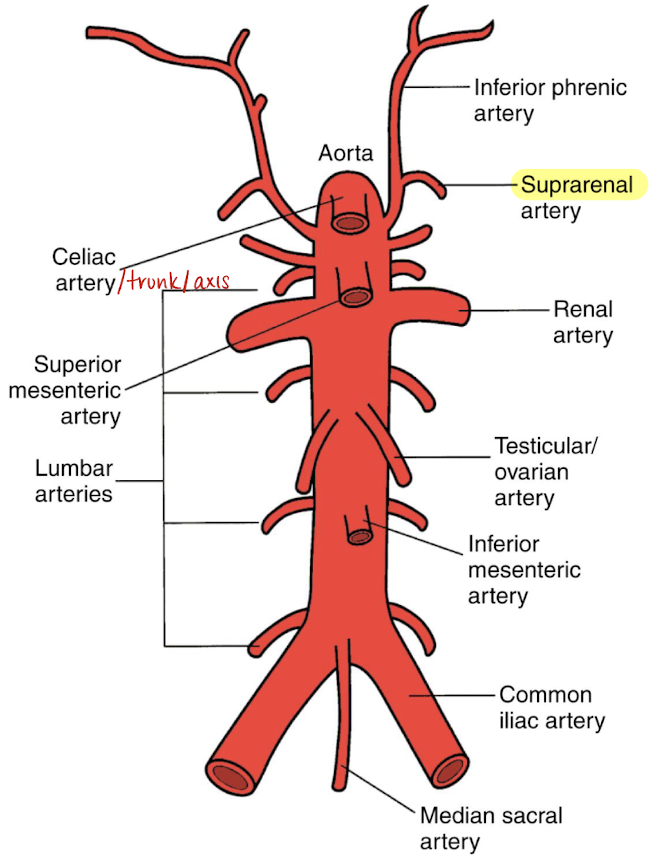
suprarenal/adrenal arteries
paired
supplies the adrenal gland
renal arteries (RRA and LRA)
inferior to SMA
courses horizontally to supply the kidneys
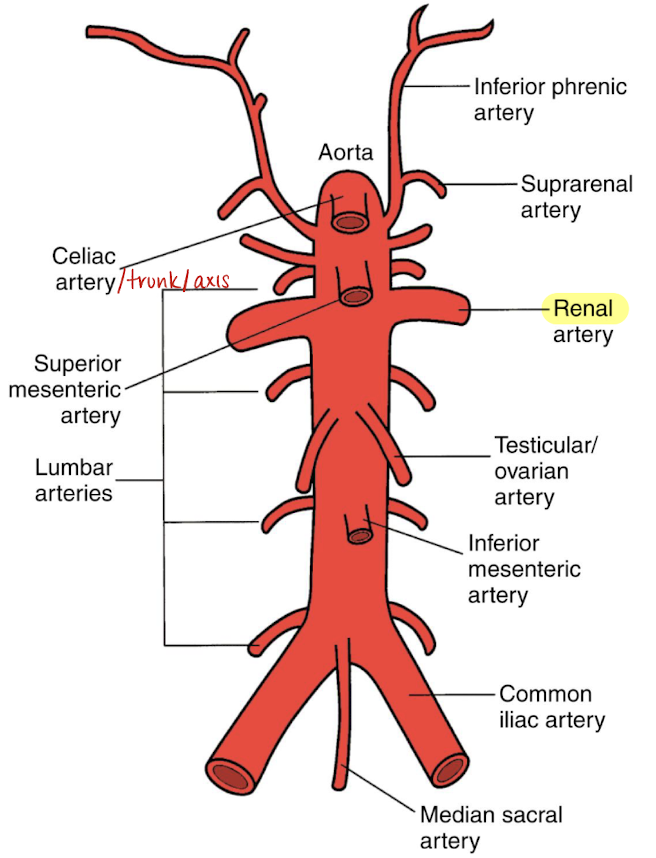
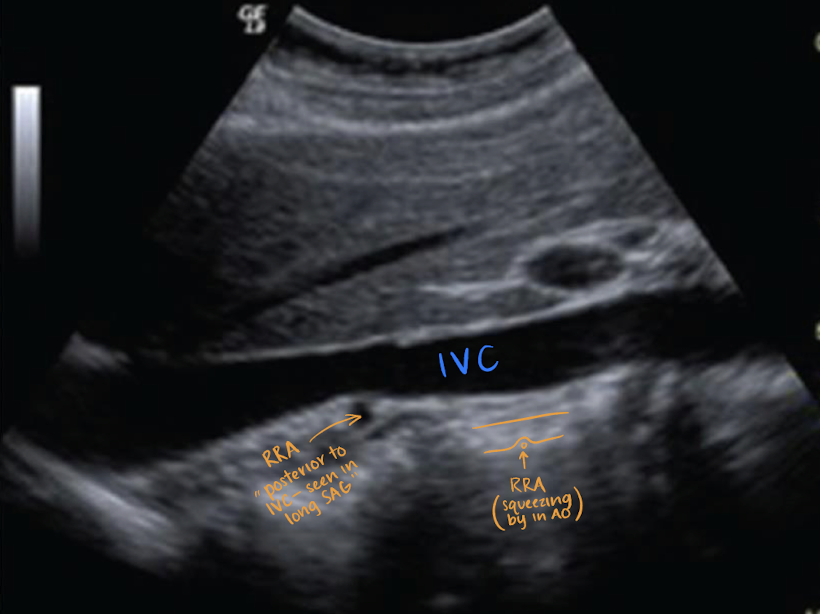
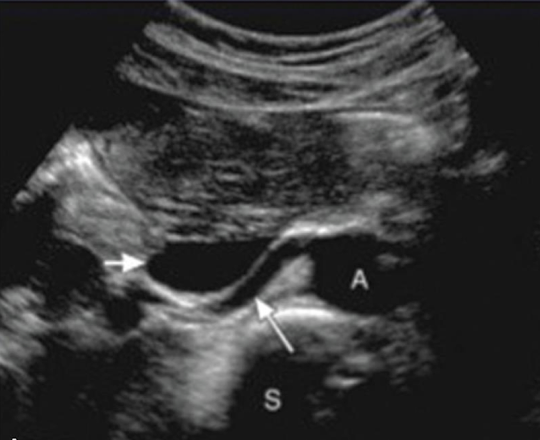
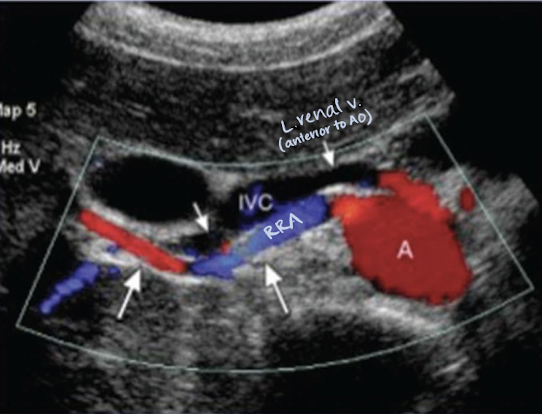
RRA
RRA is longer than LRA and courses posterior to IVC (goes excuse me under the IVC)
??
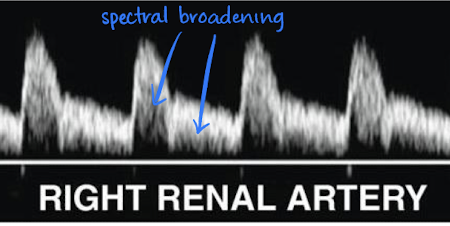
RA Doppler waveform
low resistant waveform (sharp brisk upstroke; significant diastolic flow)
had spectral broadening
lumbar arteries
4 pairs
posterolateral aspect of AO
supplies muscle, skin, bone, and spinal cord
arteriosclerosis
occurs when arterial vascular system becomes thick and stiff —> HTN due to blood flow constriction
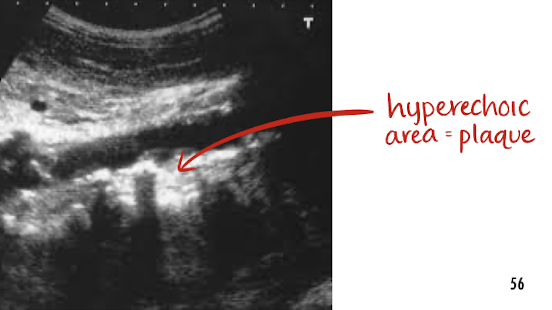
atherosclerosis
a form of arteriosclerosis
a buildup of plaque along arteries wall
must note in preliminary report if seen
abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
permanent localized dilation of AO when diameter is greater than 1.5x the proximal AO or is more than 3 cm
primary risk factors: dissection (3 types) and rupture
tx: surgical repair via graft placement
types of AAA
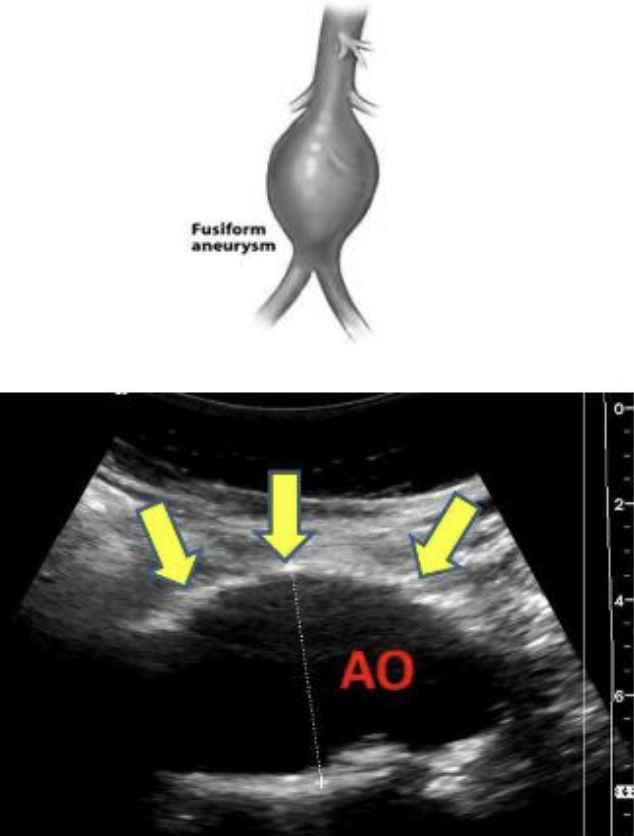
fusiform
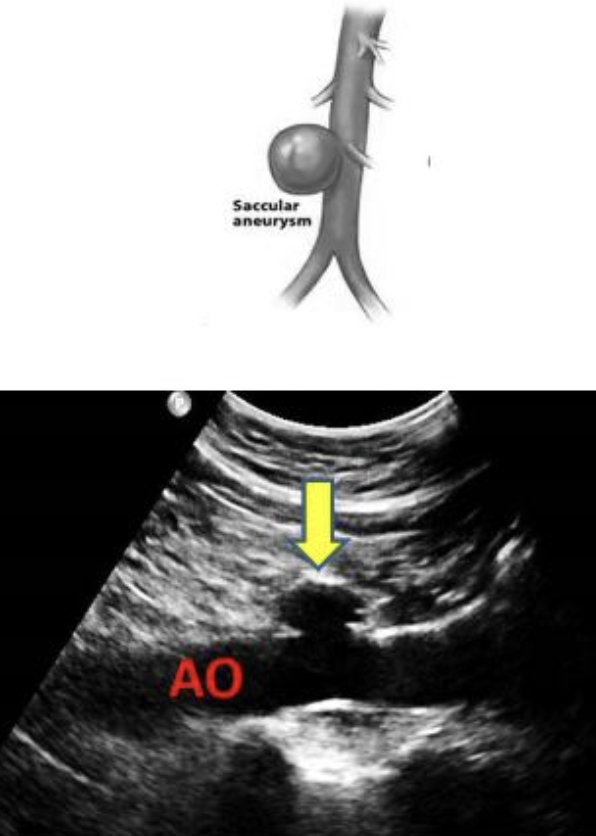
saccular
fusiform aneurysm
circumferential enlargement of vessel with tapering at both ends
resembles a football
saccular aneurysm
localized dilation of vessel
spherical structure connected by a vascular mouth
symptoms of AO rupture
excruciating abdominal pain
shock
expanding abdominal mass
mortality rate of 50%
s/s of AAA
asymptomatic
abdomen, back, or flank pain extending into groin, buttocks, or legs
Grey Turner sign (bruising of flanks)
become full easily
n/v
AAA locations
infrarenal (I)
juxtarenal (II)
pararenal (III)
suprarenal (IV)
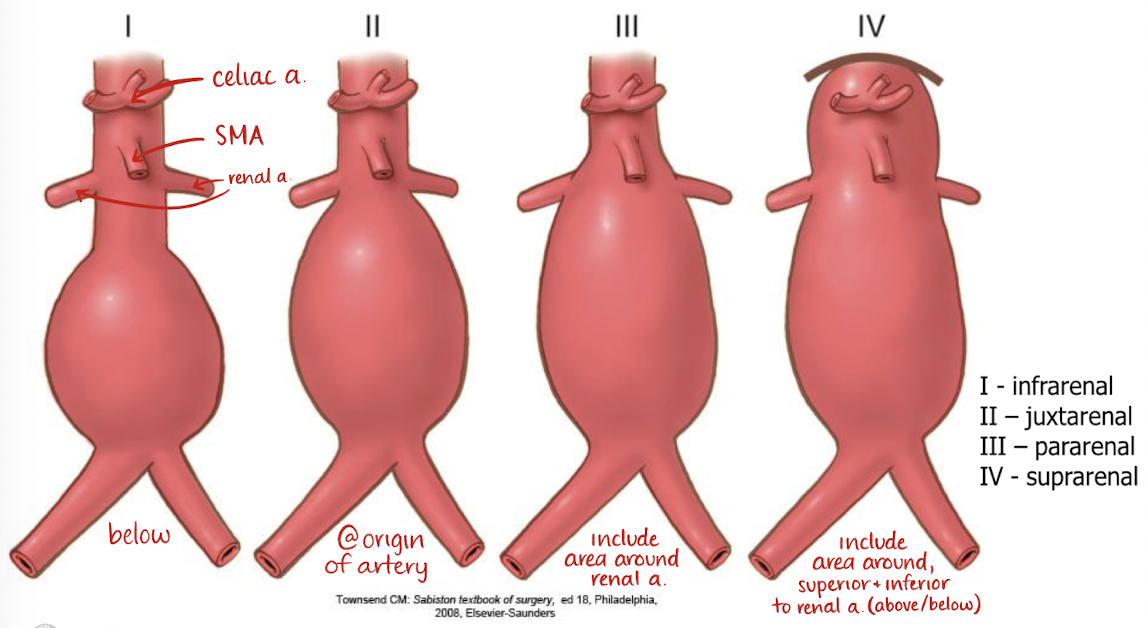
infrarenal AAA (I)
below RA
juxtarenal AAA (II)
just below, or at origin of RA
pararenal AAA (III)
involves area around RA
suprarenal AAA (IV)
involves area above and below RA
what should a sonographer note when they see a AAA?
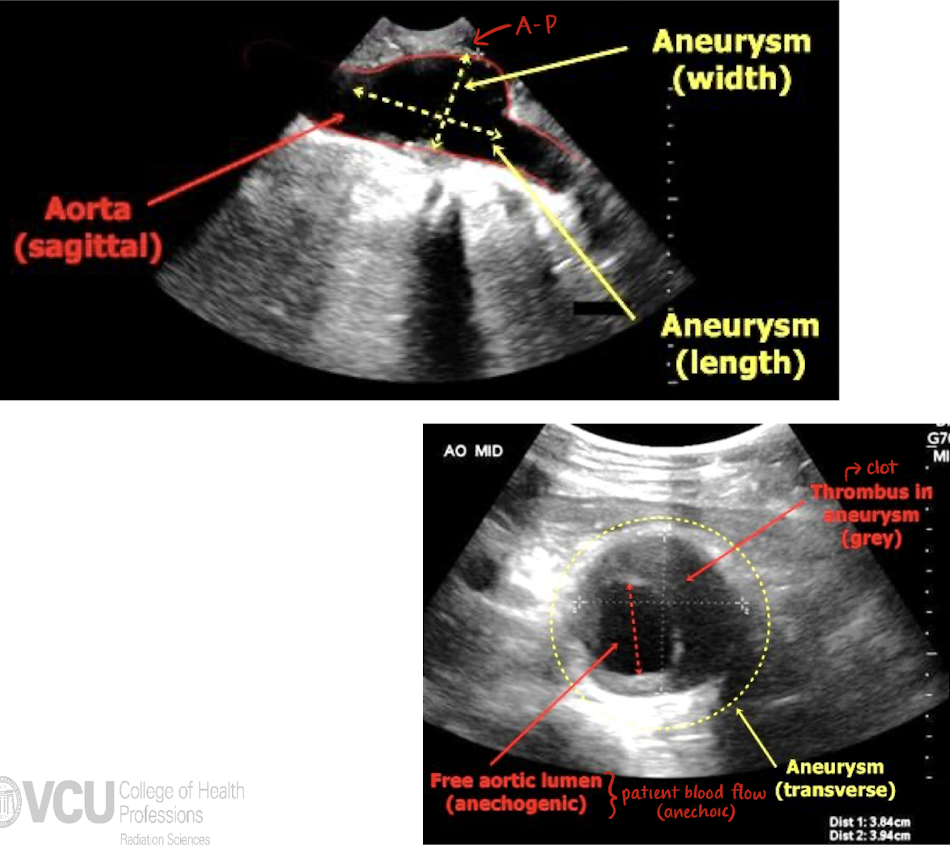
size (L x W x H in LONG and TRANS)
shape (fusiform or saccular)
location (infrarenal?)
is there wall thickening, calcification, blood flow, or plaque?
true aneurysm
lined by all 3 AO layer
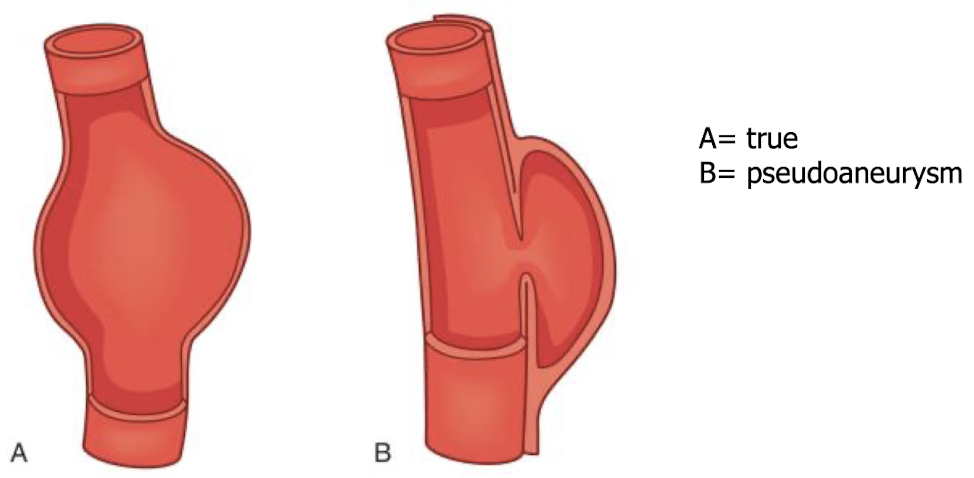
pseudoaneurysm
not lined by all 3 AO layers; blood is escaping from hole in intima layer —> outpouch and pseudo (“fake”) aneurysm
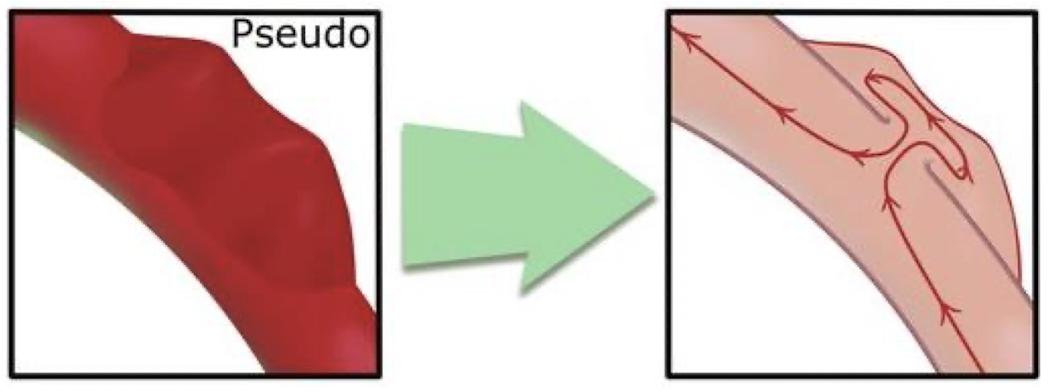
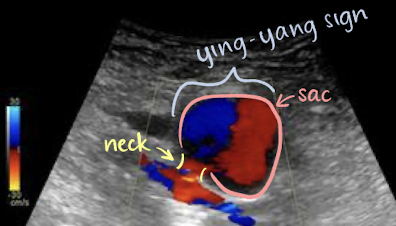
pseudoaneurysm with color Doppler
color appearance of “yin-yang” sign in sac (indicates pseudoaneurysm)
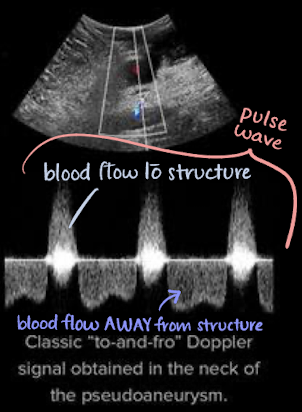
pseudoaneurysm with PW Doppler
classic “to-and-fro” Doppler signal obtained in neck of pseudoaneurysm
above baseline (positive)=blood going TO structure
below baseline (negative)=blood going AWAY from structure
where does the IVC originate from?
common iliac veins
where does the IVC drain into?
right atrium
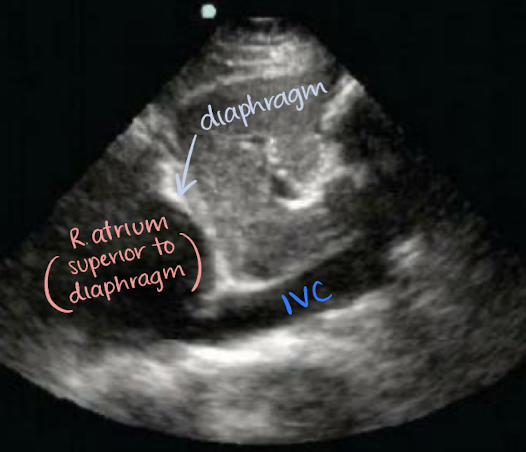
location of IVC
retroperitoneal
travels superiorly from the convergence of common iliac veins
to right of spine and AO
posterior to portal vein, intestine, liver
medial to RK
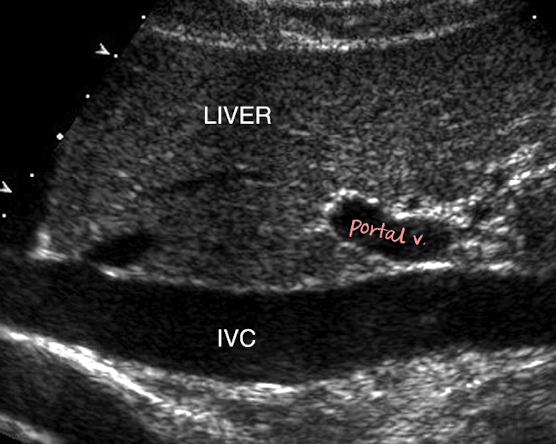
IVC info
tubular structure
collapsible with changes in respiration
many tributaries that empty deoxygenated blood into IVC
function of IVC
return deoxygenated blood to heart using valves in its low-pressure system
valves prevent retrograde or backflow of blood during diastole
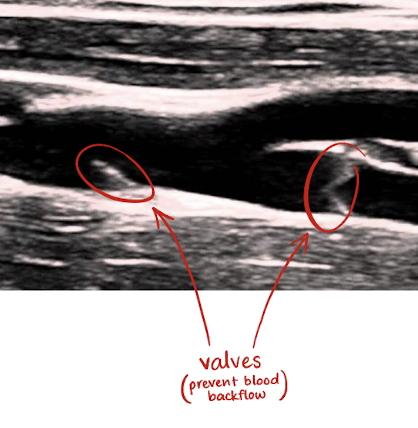
indications for imaging IVC
thrombus or tumor invasion
IVC filter placement assistance
IVC Doppler waveform
complex, spontaneous, above and below baseline
variations with respiration cycle
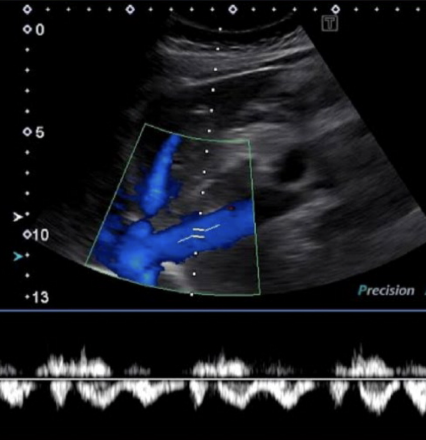
IVC normal varients
double IVC
left positioned IVC
absence of a portion (rare)
4 sections of IVC
hepatic (posterior to liver; HVs empty into IVC
prerenal (before renal veins)
renal (renal veins and other tributaries empty into IVC)
postrenal
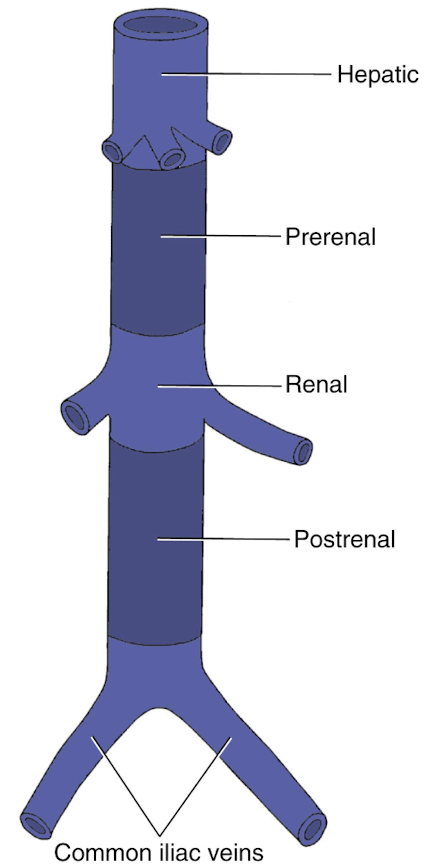
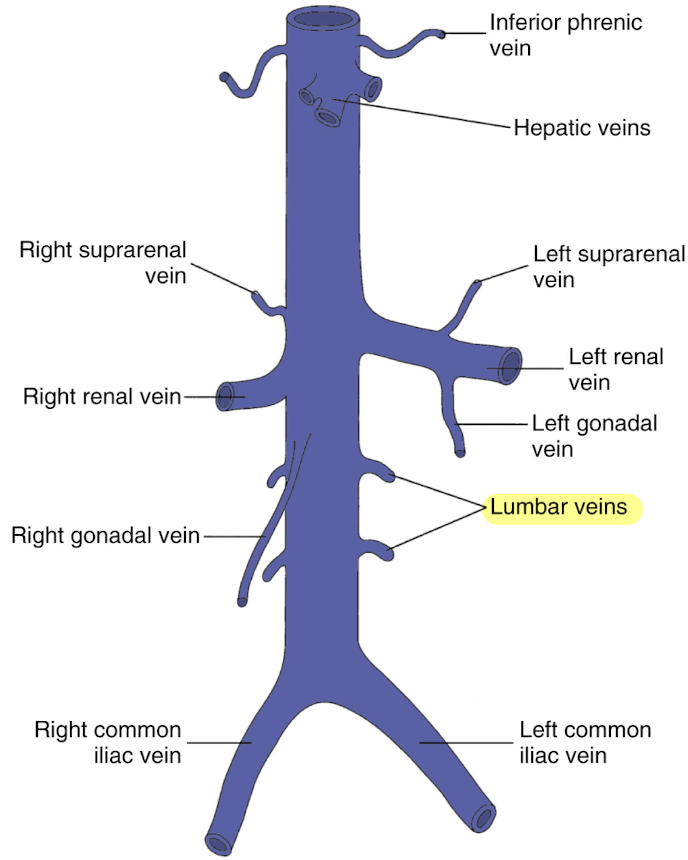
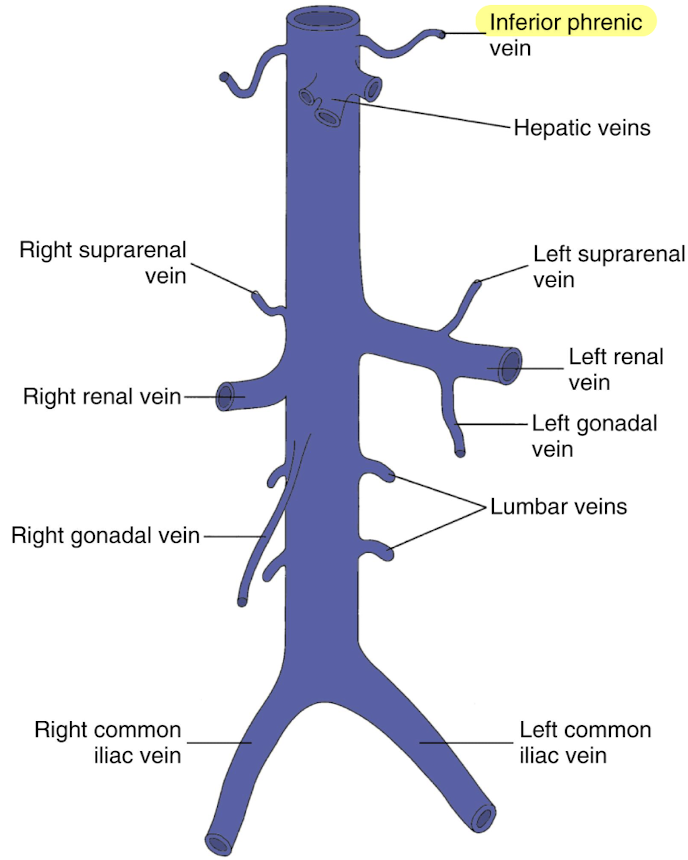
IVC tributaries from convergence
common iliac veins
lumbar veins
gonadal veins
renal reins (RRV and LRV)
suprarenal veins
hepatic veins (HVs)
inferior phrenic veins
common iliac veins
paired (right and left)
drains the pelvis and lower extremities
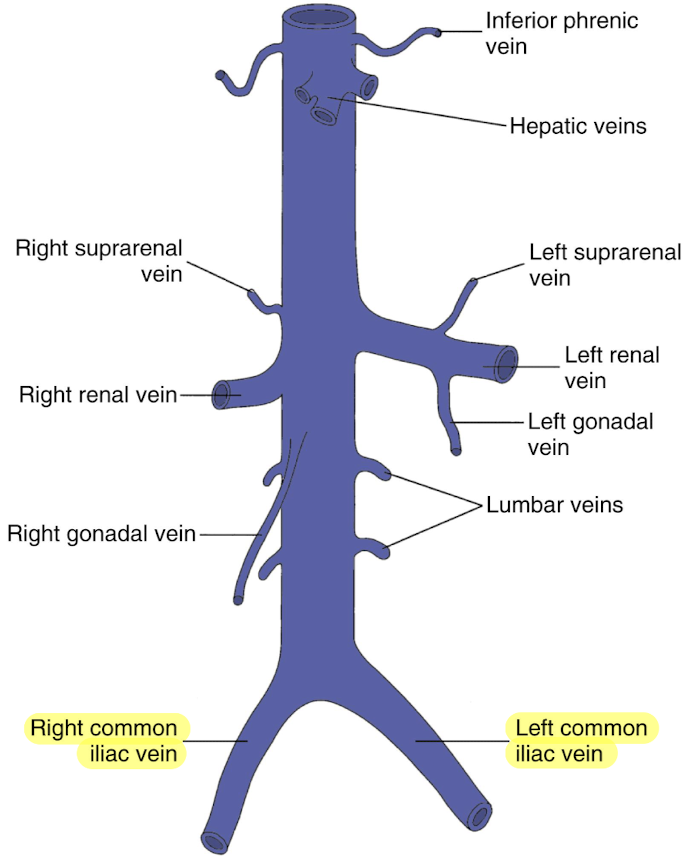
lumbar veins
4 pairs
drains posterior abdominal wall
empties into lateral aspect of IVC
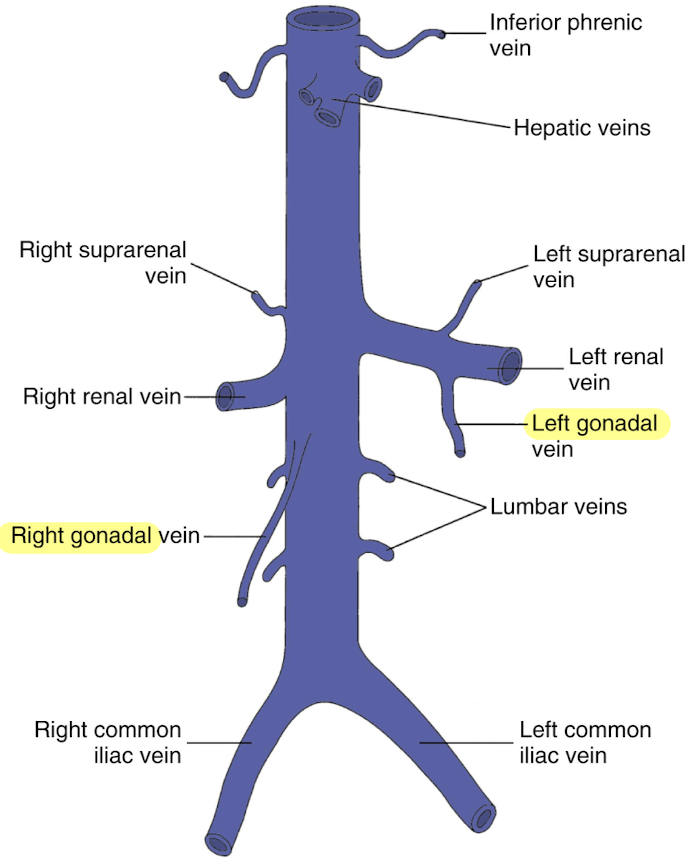
gonadal veins (testicular or ovarian)
courses parallel to IVC
left empties into LRV
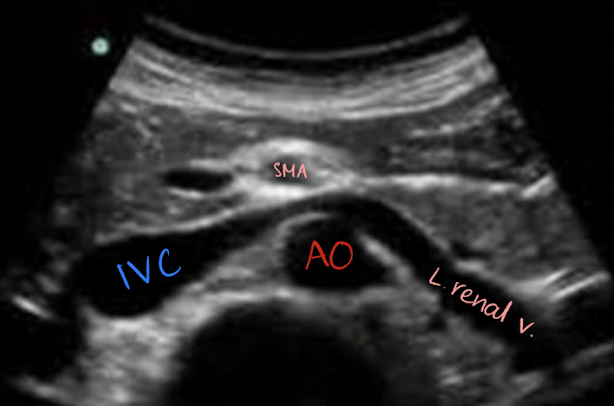
renal veins (RRV and LRV)
posterior to SMA
anterior to AO
LRV is longer than RRV
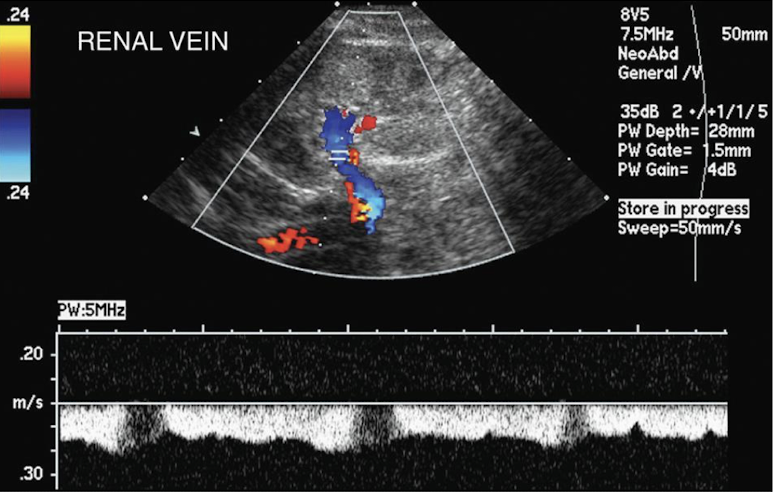
renal vein Doppler waveform
spontaneous and variable (similar to IVC)
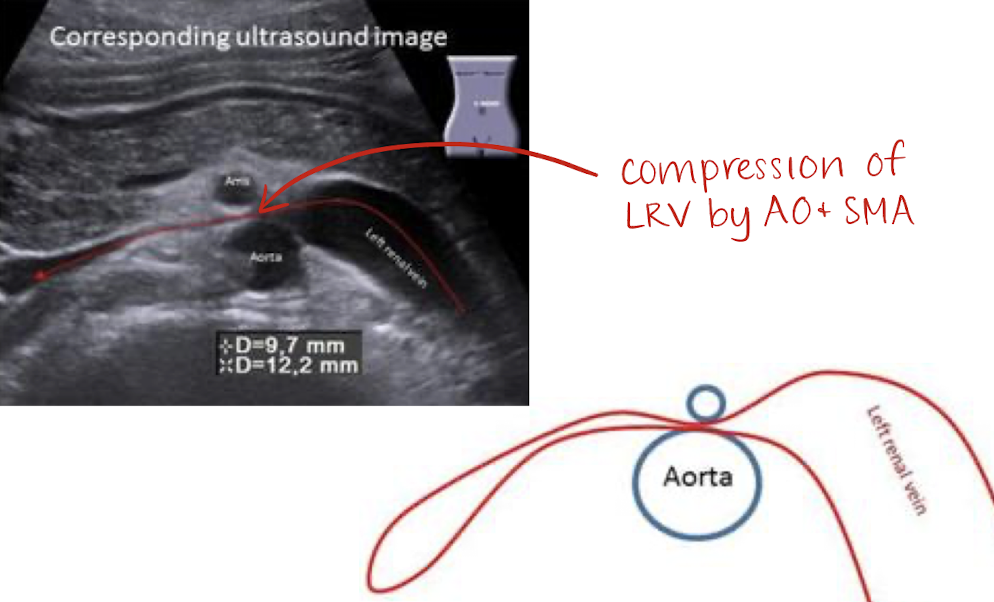
nutcracker syndrome
compression or LRV by AO and SMA
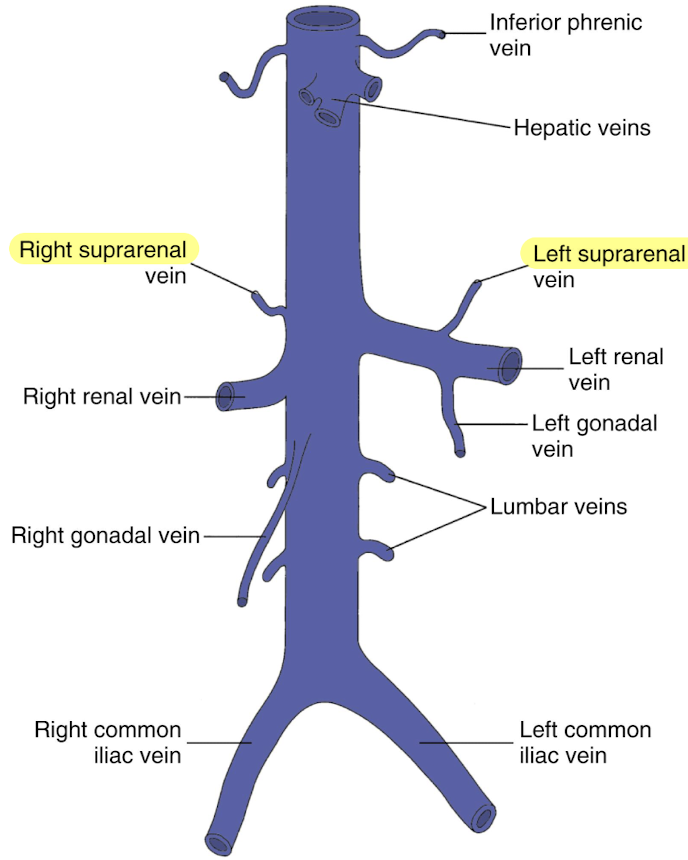
suprarenal veins
arise from suprarenal gland
right suprarenal vein drains directly into IVC
left suprarenal vein drains into LRV
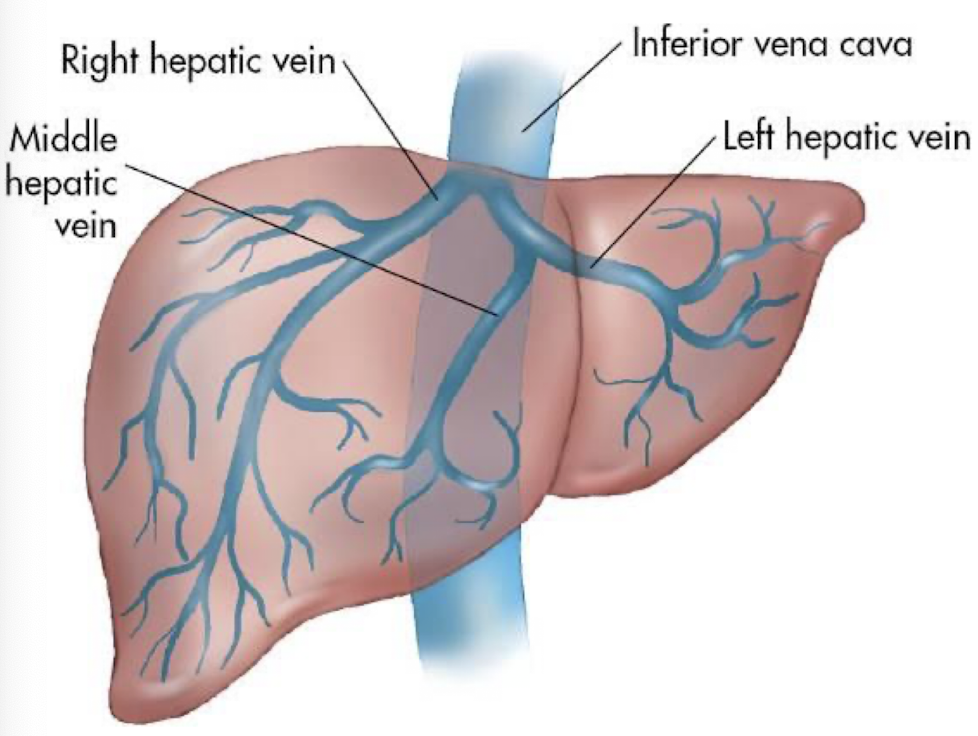
hepatic veins (HVs)
largest visceral tributaries of IVC
courses from inferior aspect of liver to superior aspect
3 HVs: left, middle, and right hepatic veins
drains liver posteriorly into IVC
thickens as it gets closer to IVC
function of HVs
returns deoxygenated blood from liver into IVC
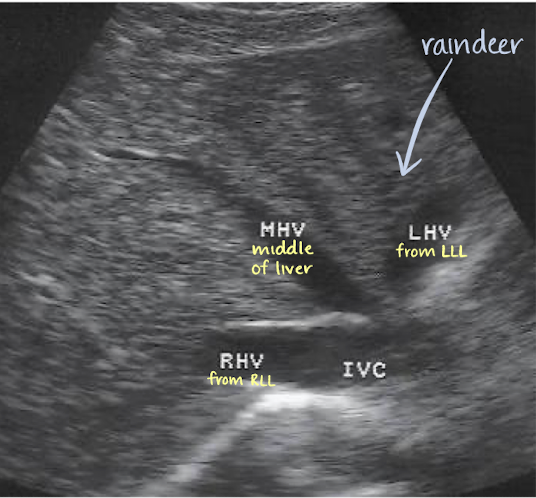
LHV drains blood from where?
left lobe of liver
MHV drains blood from where?
central (caudate) lobe of liver
RHV drains blood from where?
right lobe of liver
inferior phrenic veins
drains the diaphragm
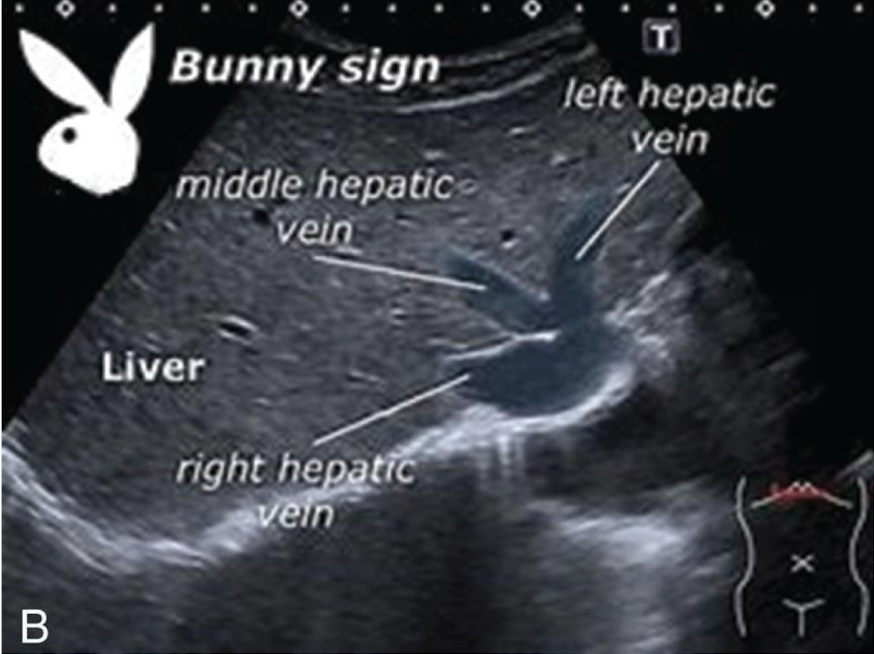
“reindeer” or “playboy bunny” sign
LHV, MHV, and RHV
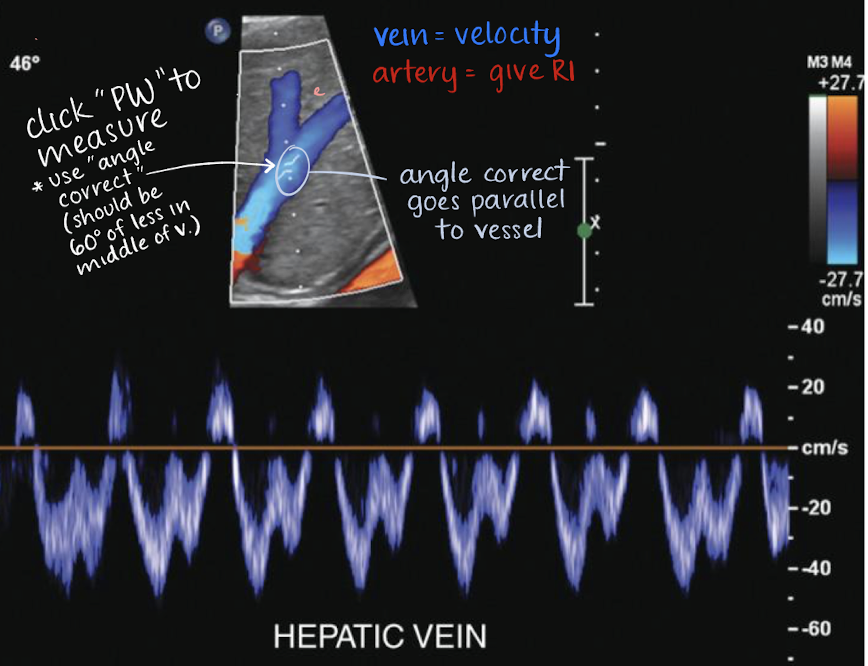
HVs Doppler waveform
complex, spontaneous, above and below baseline
variations with respiration cycle
hepatofugal
hepatofugal
flows AWAY from liver
hepatopedal
flows TOWARD liver
IVC pathology
right ventricular failure (causes IVC to not collapse during inspiration or expiration)
IVC and HV dilation
compression from pregnancy —> edema of feet and ankles and varicose veins
tumor or thrombus (heterogeneous mass looks the same in gray-scale, so use color Doppler)
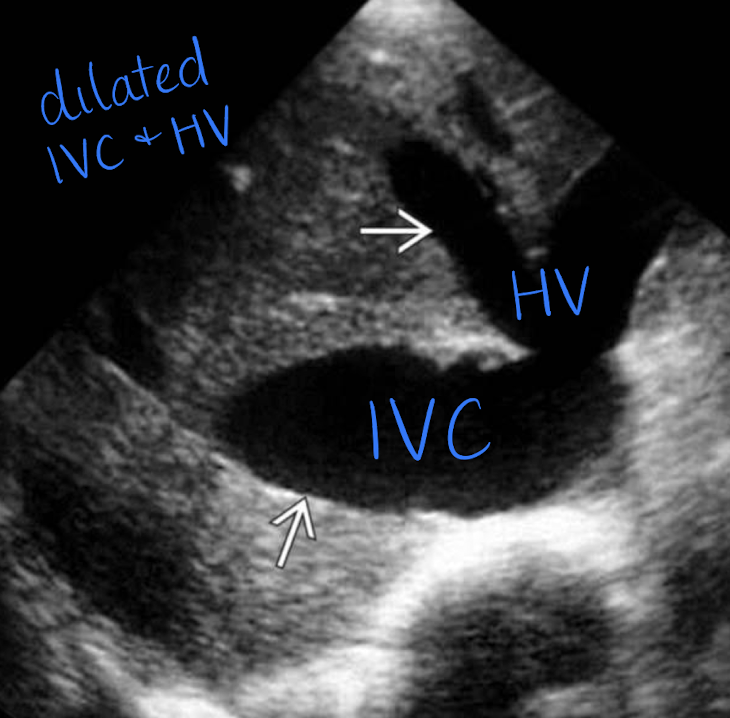
IVC tumor
has blood flow
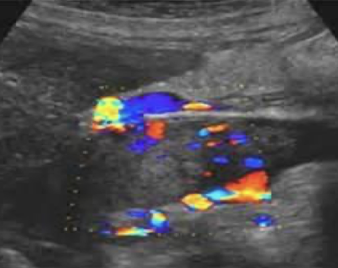
IVC thrombus
does not have blood flow