Lec 39
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:17 PM on 5/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
True or False, there are multiple factors affecting pain perception.
True
Gender, genetics, medication, anxiety, Age
Gender, genetics, medication, anxiety, Age
2
New cards
Acute Pain
Results from activation of pain receptors at the site of tissue damage
Cause: traumatic injury. surgery, inflammatory
Usually resolves in days to weeks
Serves as a warning signal to prevent further damage
Cause: traumatic injury. surgery, inflammatory
Usually resolves in days to weeks
Serves as a warning signal to prevent further damage
3
New cards
Chronic Pain
Results from abnormal processing of stimuli from nerve damage
Typically lasts over 3 months to years
Cause fatigue, sleepiness, anxiety, stress, depression
Typically lasts over 3 months to years
Cause fatigue, sleepiness, anxiety, stress, depression
4
New cards
Ascending/Afferent pathway
Carry signal from pain receptors to spinal cord and brain
“incoming nerves”
\
1)Tissue damage → release of mediators
2)Stimulation of nociceptors, generating an action potential
3)Impulse travels along peripheral afferent nerves
4)Travels to dorsal horn of spinal cord→ brain stem→thalmus→limbic system
5) message is processed as painful
“incoming nerves”
\
1)Tissue damage → release of mediators
2)Stimulation of nociceptors, generating an action potential
3)Impulse travels along peripheral afferent nerves
4)Travels to dorsal horn of spinal cord→ brain stem→thalmus→limbic system
5) message is processed as painful
5
New cards
A delta fibers
Afferent fibers
thinly myelinated
Associated with sharp, immediate pain and responsible for the pulling away reflex
thinly myelinated
Associated with sharp, immediate pain and responsible for the pulling away reflex
6
New cards
C fibers
Afferent fibers
unmyelinated
Responsible for slow, dull, longer lasting pain
unmyelinated
Responsible for slow, dull, longer lasting pain
7
New cards
Efferent/Descending pathway
Carry signal from brain and spinal cord to effector organs and muscles
“outgoing nerves”
“outgoing nerves”
8
New cards
Understand Gate Control Theory and the significance of the periaqueductal gray area.
Efferent pathway
\
Non painful stimuli can close the gate to painful stimuli in the Periaqueductal Gray Area
(ex: rubbing an bumped elbow reduces pain)
\
Stimulation of PAG activates enkephalin releasing neurons which modulates pain signal like volume control
\
Non painful stimuli can close the gate to painful stimuli in the Periaqueductal Gray Area
(ex: rubbing an bumped elbow reduces pain)
\
Stimulation of PAG activates enkephalin releasing neurons which modulates pain signal like volume control
9
New cards
Understand the SAR of the endogenous opioid peptides.
Endorphins and Enkephalins
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe
\
Phenol and amine functional groups are most important
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe
\
Phenol and amine functional groups are most important
10
New cards
Understand the message-address concept of the endogenous opioid peptides.
The N terminus of a peptide contains the message→ First 4 amino acids conserved and essential for binding to all opioid receptors (knows to go to opioid recetpor)
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe
\
The C terminus is the address, tells us what kind of opioid receptor
Additional amino acids in the sequence determine subtype specificity
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe
\
The C terminus is the address, tells us what kind of opioid receptor
Additional amino acids in the sequence determine subtype specificity
11
New cards
opioid receptors are….
inhibitory GPCRs and that stimulation of them hyperpolarizes the neuron and terminates pain signaling.
12
New cards
Know the effect of opioid receptor stimulation on adenylate cyclase, cAMP, potassium flux, calcium flux and phospholipase C.
Inhibit adenylate cyclase which drives down cAMP concentrations
Activate inwardly rectifying K+ channels towards resting potential (increases K+ efflux)
Closes Ca2+ channels
Stimulates phospholipase C
Activate inwardly rectifying K+ channels towards resting potential (increases K+ efflux)
Closes Ca2+ channels
Stimulates phospholipase C
13
New cards
Know that there are three classes of opioid receptors and their names.
Delta Opioid receptor→ enkephalins, B endorphin
Kappa opioid receptor→ Dynorphins, B endorphin
Mu opioid receptor→ Endomorphins, B Endorphin
Kappa opioid receptor→ Dynorphins, B endorphin
Mu opioid receptor→ Endomorphins, B Endorphin
14
New cards
What therapeutic action are mu-1 receptors associated with?
mediate pain neurotransmission
15
New cards
What side effect are mu-2 receptors associated with?
control respiratory depression
16
New cards
What would be the therapeutic advantage to the development of a selective kappa agonist?
Lack respiratory depression, constipation and physical dependence
17
New cards
Know the difference between tolerance and dependence
Tolerance: increasingly larger doses are required to produce the same degree of biological response
\
Dependence: Opioid is necessary to maintain physiologic and psychological functioning
\
Dependence: Opioid is necessary to maintain physiologic and psychological functioning
18
New cards
withdrawal and addiction.
Withdrawal: tremor, chills/sweats/increased blood pressure and heart rates, abdominal cramping
\
Addiction: Due to euphoric effects produced by mu opioids, addiction is a significant challenge, complicated by psychosocial and genetic components
\
Addiction: Due to euphoric effects produced by mu opioids, addiction is a significant challenge, complicated by psychosocial and genetic components
19
New cards
Know the challenges associated with the therapeutic use of opioids.
Euphoria/Dysphoria
Constipation
Cross tolerance (if swapping must be same type of opioid)
Metabolism
Combined alcohol consumption
Constipation
Cross tolerance (if swapping must be same type of opioid)
Metabolism
Combined alcohol consumption
20
New cards
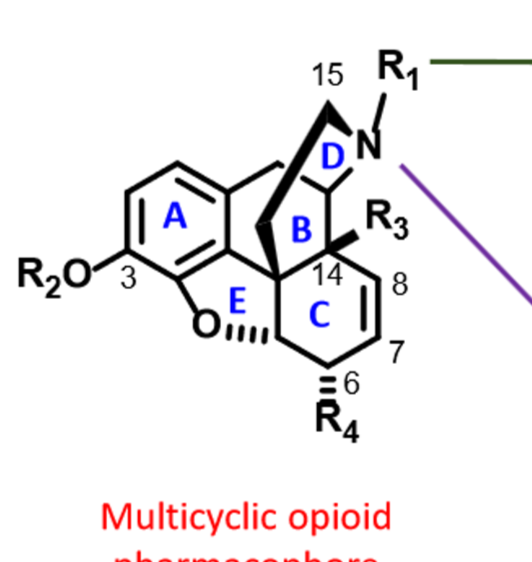
Know the SAR of multicyclic opioid AGONISTS.
R1 group dictates control of agonist or antagonist activity→ methyl group tends to be agonist, 3-5 carbon chains tend to be antagonists
\
\
Basic nitogren attached to R1 (tertiary amine)
\
R2 H or methyl
\
A ring is essential
\
R3 is H or OH
\
IMpact of R4 depends on presence of C7 and C8 double bond
\
\
Basic nitogren attached to R1 (tertiary amine)
\
R2 H or methyl
\
A ring is essential
\
R3 is H or OH
\
IMpact of R4 depends on presence of C7 and C8 double bond
21
New cards
What drug properties are relevant to choosing the appropriate opioid therapeutically?
Lipophilicity
Half life
Bioavailability
Excretion
Duration
Half life
Bioavailability
Excretion
Duration
22
New cards
heroin & morphine
Heroin is a prodrug that hydrolyzes into 6MAM which hydrolyzes to morphine
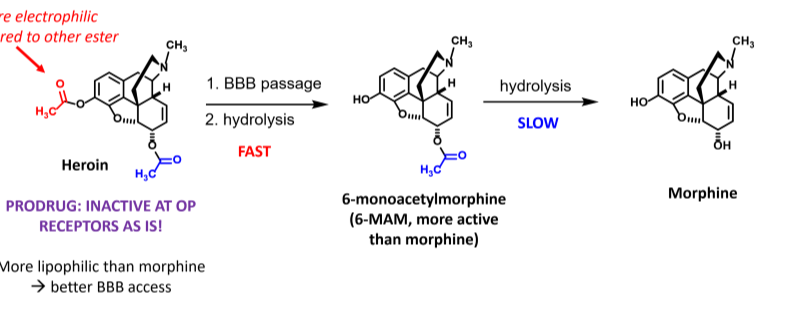
23
New cards
Can heroin cross the BBB?
Heroin is a prodrug, its active metabolite is morphine
Heroin is more lipophilic than morphine so it has better BBB access
Heroin is more lipophilic than morphine so it has better BBB access