Physical Oceanography Exam 1
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
The four branches of oceanography
Biological
Chemical
Geological
Physical
Pacific Ocean
The largest and deepest ocean with the most island. Has the average depth of 3,940 m
Atlantic ocean
Most land area drains into this ocean. It has an average depth of 3, 840 m
Indian ocean
Has the average depth of 3, 840 m (almost all south)
Artic ocean
Under debate on if it’s an ocean, smallest ocean. 3.4% of the ocean area, very shallow. Has an average depth of 1.117 m
Marginal sea
Partially enclosed sea adjacent to or widely open to the ocean at the surface but bounded by submarine ridges on the seafloor.
Temperature
A physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold
Temperature (thermodynamics)
The derivative of the internal energy with respect to the entropy
Temperature scales in regard to water
32 F - 212 F
0 C - 100 C
Importance of temperature
Effect on deep-ocean currents
Effect on storm formation
Effect on marine organisms and on us
Effect on climate
Surface temperature
Can measure by using a thermometer
Shade vs Sun
Wind vs no wind (wing cools water)
Is there metal nearby? (Metal can conduct heat)
Depth (top mm is the warmest)
Deep-water temperatures
Reversing thermometer
BT - less resistance = warm. More resistance = cold
xBT
Niskin rosette with CTD
BT = Bathythermograph
Temperature range in the ocean
-2 C - +36 C
28.4 F - 96.8 F
Surface temperature distribution
Warmest water at the equator
Coldest water at the poles
In the _____ ______ there is not a lot of change in temperature with depth
polar regions
In the ____________ the temperature does change with depth, but changes with seasons. How much of a change there is varies with seasons
Mid-regions
In the _______ ________ there is a definite change with depth, but it stays the same year round
Equatorial regions
Thermocline
Rapid decline of temperature
Mid-latitudes and low-latitudes have a _______
thermocline
High-latitudes / polar regions are ________
Isothermal
Salinity
The amount (in grams) of dissolved substances in one kilogram of seawater
What is seawater?
965 g of water and 35 g of dissolved substances
Atlantic salinity
34.92%
Pacific salinity
34.60%
Indian salinity
34.78%
Artic salinity
Lowest, varies with seasons
Distilled water salinity
0
Tap water salinity
0-5
Lake worth salinity
20-30
Typical seawater salinity
35
Bahamas salinity
40
Great Salt Lake, Utah salinity
50-270
Dead Sea, Isreal salinity
337
Salinity distribution in surface waters
In surface waters, the addition or subtraction of water is a major thing that changes salinity, not temperature
________ leads to water leaving the ocean. ______ is going to cause salinity to increase
Evaporation
_________ leads to water entering the ocean. ______ causes salinity to decrease
Precipitation
Water added =
decreased salinity
Water subtracted =
More salinity
Salinity distribution in deep waters
Generally, salinity is higher in deep waters than in surface waters
Salt makes the water denser, heavier, so it sinks to the bottom
Salinity distribution in water columns
Thermoclines and Haloclines are both controlled by the wind
Halocline
rapid change in salinity
Salinity distribution
Low salinities are typically low near land and rivers
SSS
Sea Surface Salinity
Lines connecting areas of equal saline are called _____
Isohalines
Reasons why high salinity water is a problem
Can’t drink
Corrosion
Many plants can’t tolerate it
Some animals can’t tolerate it
Reasons why high salinity water is a good thing
Source of salt for diet
Improves buoyancy of ships
Nothern harbors generally free from ice
Measuring salinity
Evaporation
Electronics (e.g., conductivity meter, CTD)
Refractometer
Residence Time
The average length of time that an element spends in the ocean
Density
Mass per unit volume
Depth (ft) Pressure (atm)
0 1
33 2
66 3
99 4
132 5
Salinity and temperature influence ______
Common density measurements
Object Density (kg/m³)
Freshwater 1,000
Seawater 1,020-1,030
Ice (in general) 920
Measuring density
Hydrometer
Electronic method
Surface distribution of density
Sigma + - density factor
Range 22-27
Density is ____ near the equator because of warm water and low salinity
Lower
Density is ______ at the poles because of cold water and high salinity
Higher
Density increases with _____
Depth
Pycnocline
Rapid change of density
Coastlines have _____ density water
Low
Artic has ____ density water
High
Importance of density
Drives deep-water currents
Increases buoyancy for ships
Important factor for subs
T-S Diagrams
A way of calculating density
Air Pressure
The pressure exerted by the weight of the air above
Average: 14.7 pounds/inch²
Air pressure is typically measured in ________, but the media uses inches of mercury
Millibars
Wind
The phenomenon where air moves horizontally
____ is the result of horizontal differences in air pressure
Solar radiation is the ultimate energy source
Wind is controlled by the following factors:
Pressure-gradient force
Coriolis effects
Friction
Pressure-gradient force
On a map, lines of equal pressure are connected by isobars
Coriolis effect
The deflective force of earth’s rotation on all free-moving objects
Friction
Only affects winds <6 km above the Earth’s surface
_______ (______) are centers of low pressure
Winds blow inward and counterclockwise
Lows (cyclones)
_______ (_________) are centers of high pressure
Winds flow outward and clockwise
Highs (anticyclones)
What creates wind?
The pressure-gradient force
What controls the direction of the wind?
Coriolis effect
What controls the direction and speed of wind?
Friction
North =
Right
South =
Left
Why study the Coriolis effect?
Winds
Ocean currents
Long range launches
Hurricanes
FCE =
2 w Sin0
w =
Rate of Earth’s spin (7.2921 × 10^-5 rad/s)
0 =
Latitude
R0 =
U / FCE L
U =
Velocity
L =
length of time object is in motion
Rossby # large =
Coriolis not important
Rossby # small =
Coriolis dominate
Laminar flow
Wind on ice
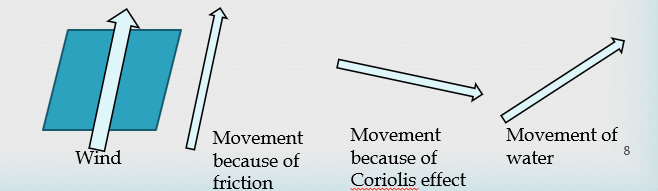
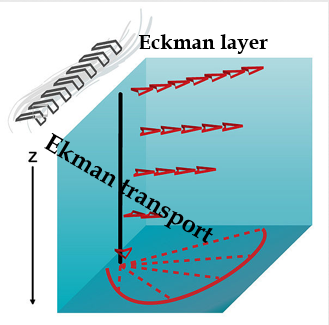
Ekman Spiral
Wind
Force from friction
Direction of water movement
Force from Coriolis effect
(Doesn’t do a complete spiral)
(Shallow, deepest found at 50 m)
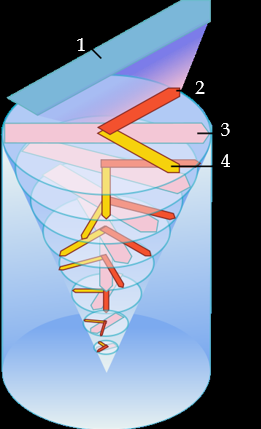
Ekman layer '/ transport
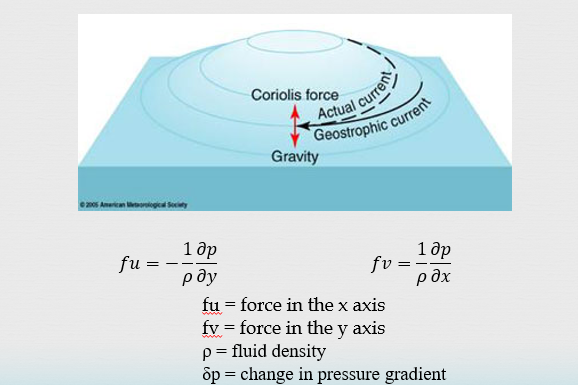
Geostrophic motion
Mound of water (Geostrophic flow)