2.5 Economic growth
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
The trade cycle
recession - animal spirits are low, consumers are saving, workers are unemployed.
recession - 2 or more consecutive quarters of negative economic growth. The part of the business cycle where real GDP is at its lowest.
Boom- part of business cycle where real GDP is at its highest,
Slump- the part of the business cycle where real GDP is decreasing.
Recovery- the part of the business cycle where real GDP is increasing.
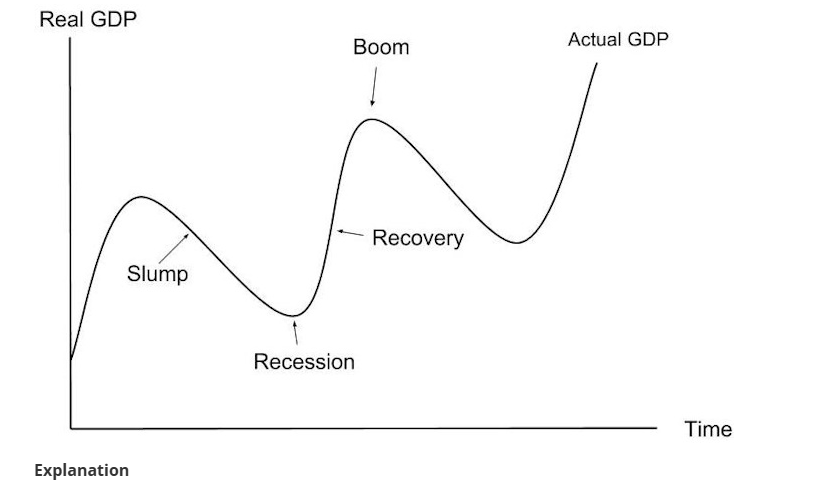
THE BUSINESS CYCLE
TREND POTENTIAL GROWTH
Long run improvements in technology increase the potential of an economy.

The business cycle
Negative output gaps
Actual GDP Below potential trend GDP is a negative output gap
The economy isn’t using its resources efficiently. - workers may be unemployed, factories may be vacant.
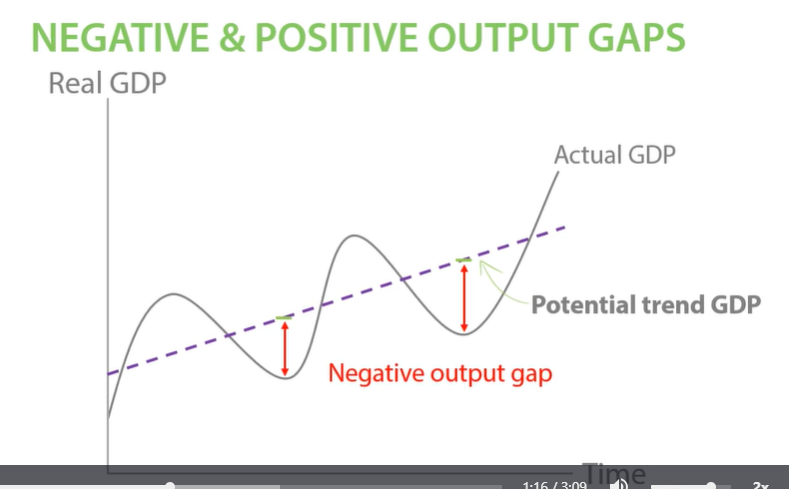
The business cycle
Positive output gaps
Positive output gap as actual GDP is above potential output gap.
The economy is producing above its resources. Overusing our resources. - not sustainable. Workers cannot work long hours.
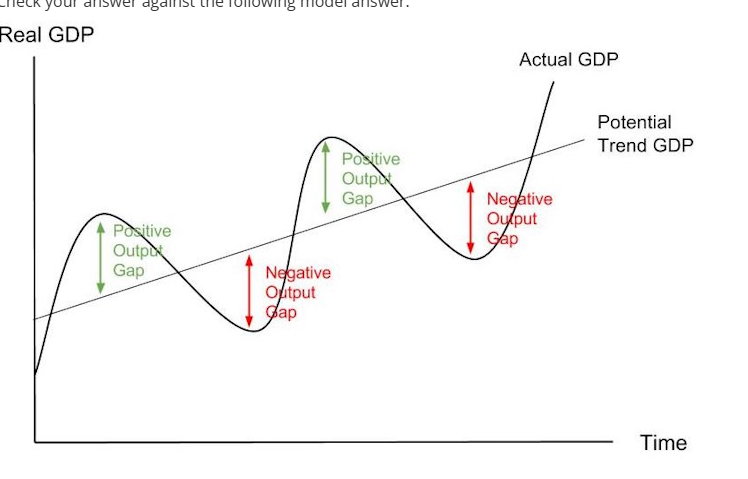
Definitions of potential trend GDP, negative output gap, positive output gap.
Potential Trend GDP- The sustainable rate of GDP growth caused by improvements in productive capacity overtime.
Negative output gap- when actual GDP is below potential trend GDP.
Positive output gap- when actual GDP is above potential trend GDP.
THE Business Cycle
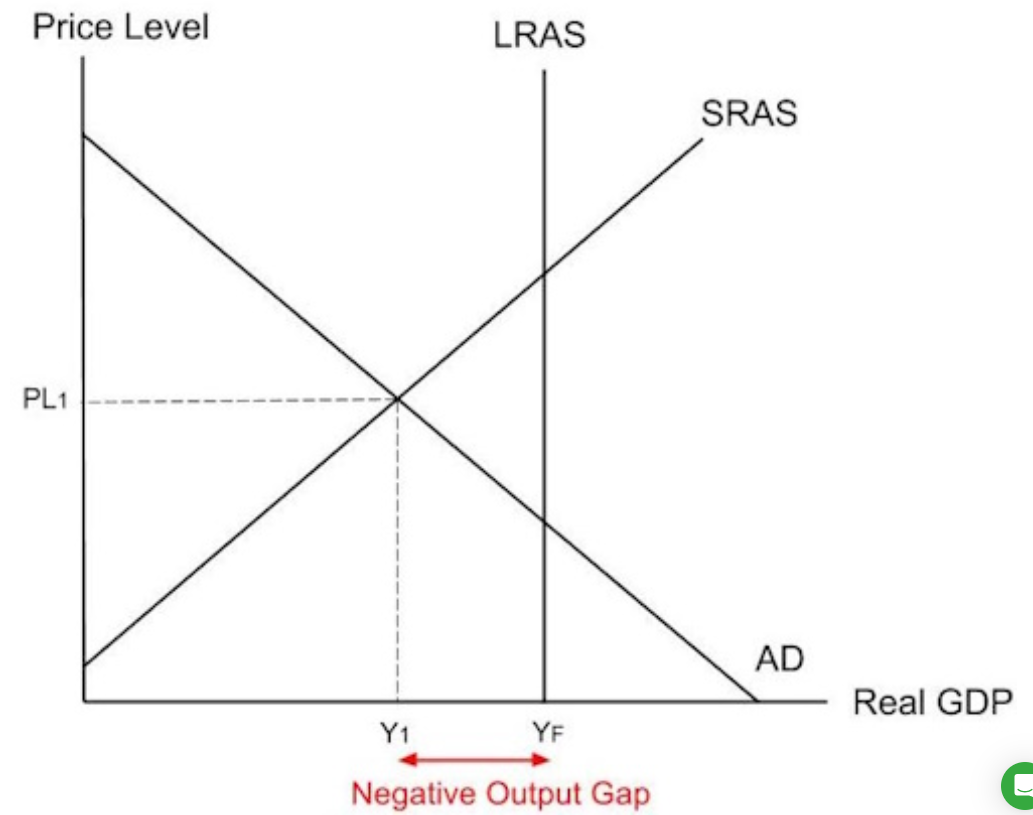
Neoclassical Short Run Output Gaps.
negative output gap
A negative output gap occurs when actual GDP is below potential trend GDP.
Neoclassic AS-AD diagram
LRAS is output at full employment.
In this economy, there is a negative output gap because actual output is below long run potential output.
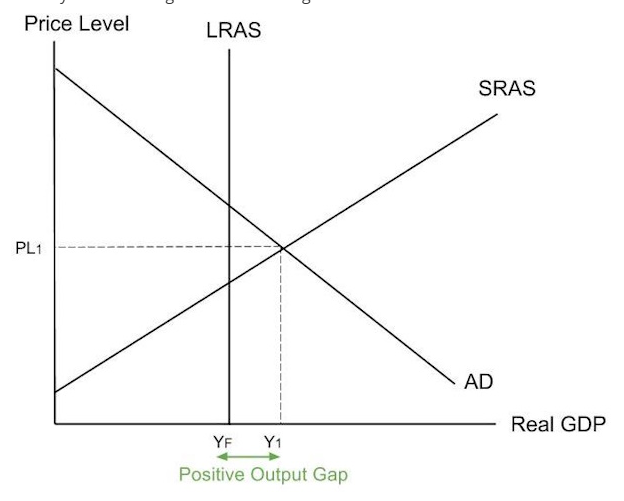
If short run equilibrium output is at Y1, below long run potential output, there is a negative output gap in the short run. There is a negative output gap at Y1YF. The economy is not using up resources efficiently.
The business cycle
Neoclassical short run output gaps.
positive output gaps.
There is a positive output gap as actual output Y1 is above long run potential output YF .
Economy is producing above its potential, workers are working overtime and overusing our machinery.
Neoclassical economics believe: Short run output gaps are possible but long run output gaps are impossible.
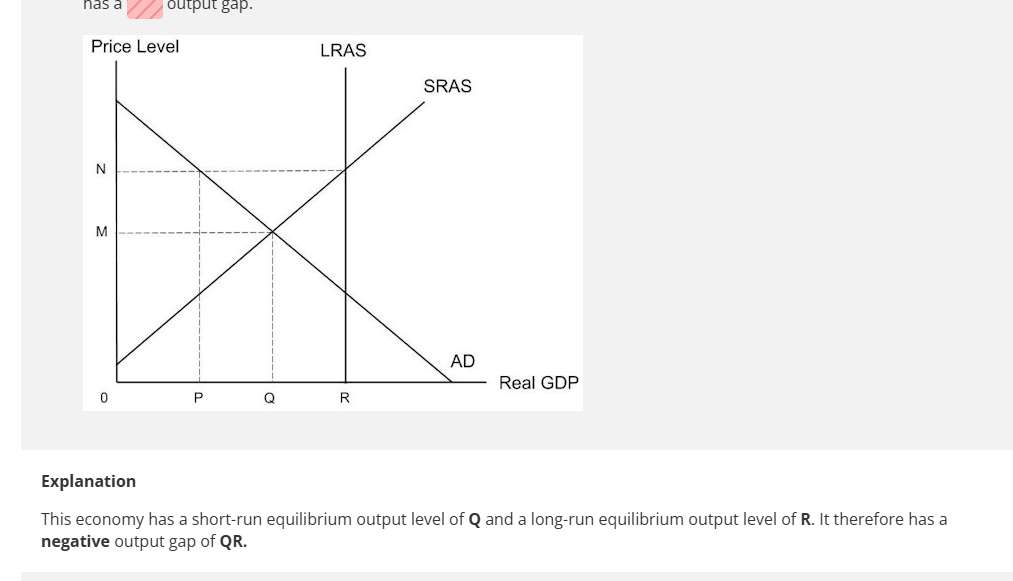
Neoclassical LRAS shows us our long run potential output at Yfe but if AD intersect short run SRAS at YR, there is a negative out put gap in the short run. However, in the long run we have to use long run LRAS, which intersects AD at full potential YFe. - no long run output gap.
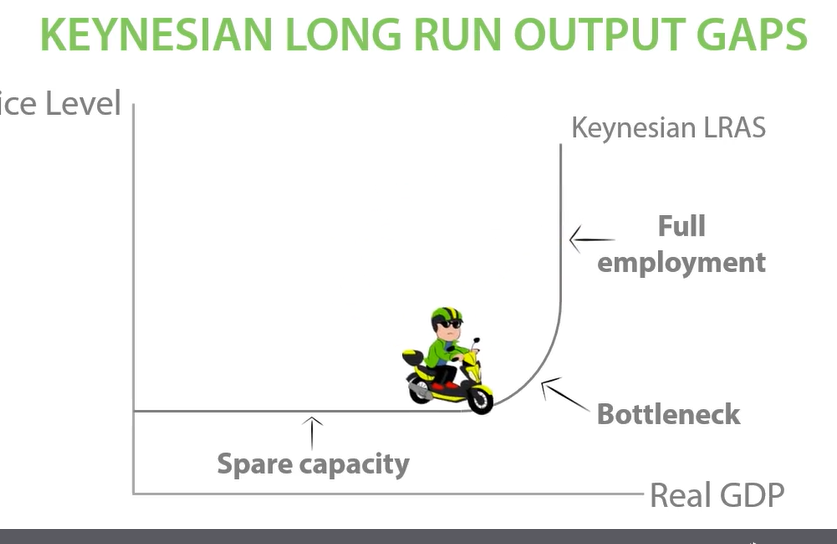
Keynesian LRAS
SIT BACK FLIP
Spare capacity, bottleneck, full employment. Full employment, YFe represents the full potential output of an economy.
Neoclassical long run output gaps
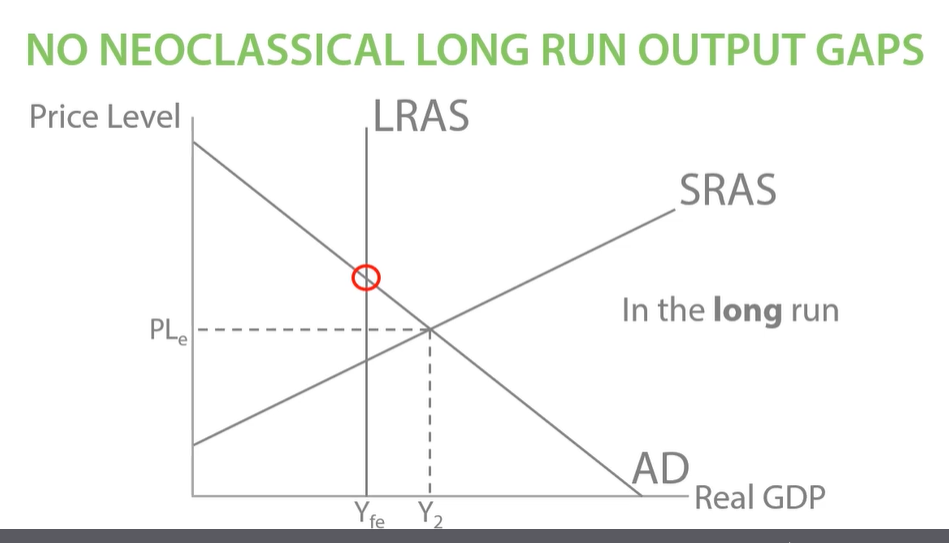
Even if we have a negative output gap in the short run, in the long run we have to use our long run LRAS at full potential Yfe. No output gaps in long run possible when using neoclassical LRAS.
No Neoclassical long run output gaps
In the short run we can have a positive output gap, we can force our workers to overwork and temporarily increase output however this isn’t sustainable. So will went up back at full employment YFe.
Neoclassical economists believe short run output gaps are possible but long run output gaps are impossible.
Keynesian long run output gaps
Producing at economy’s full potential, no more output gap.
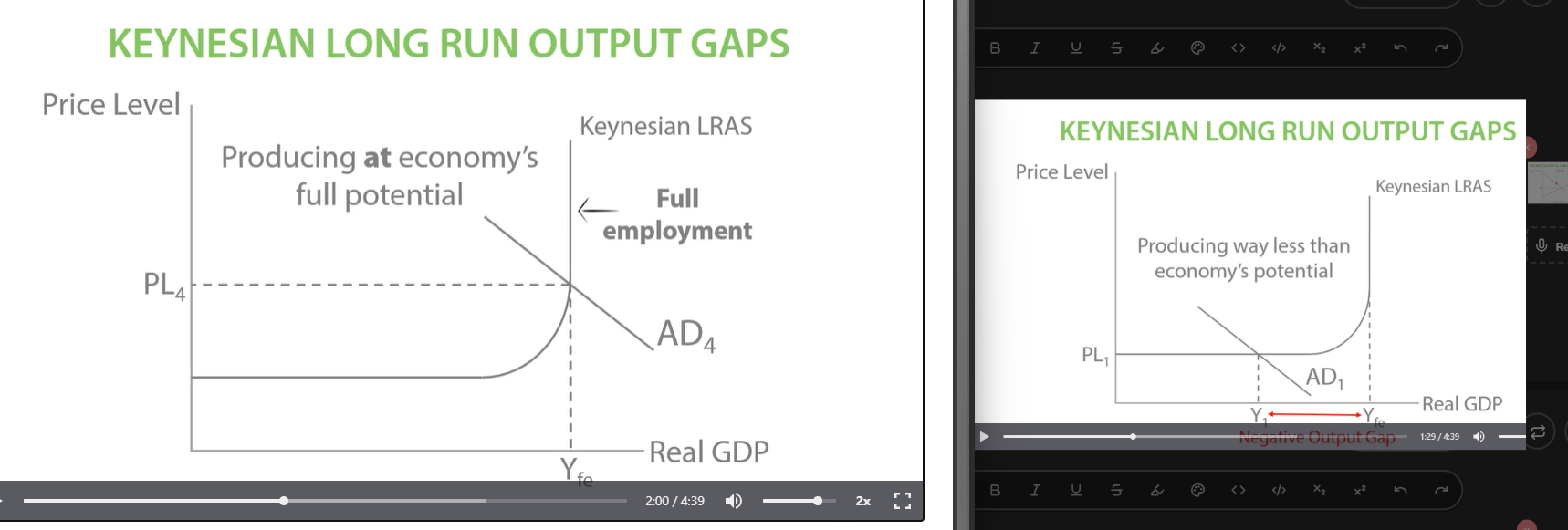
Keynesian long run output gap
Cant go past full employment as actual output can never increase past potential output.
Neoclassical LRAS and Keynesian LRAS
Neoclassical LRAS- No output gaps in the long run, always at full employment, full potential.
Keynesian can have negative output gap below Yfe. Can have no output gap at Yfe. Never a positive output gap.
Characteristics of a Boom
Characteristics of a boom:
High animal spirits:
Consumers and businesses feel confident about how the economy is doing. Consumption and investment will increase,
High economic growth:
AD will shift out, economic growth and increase in price level.
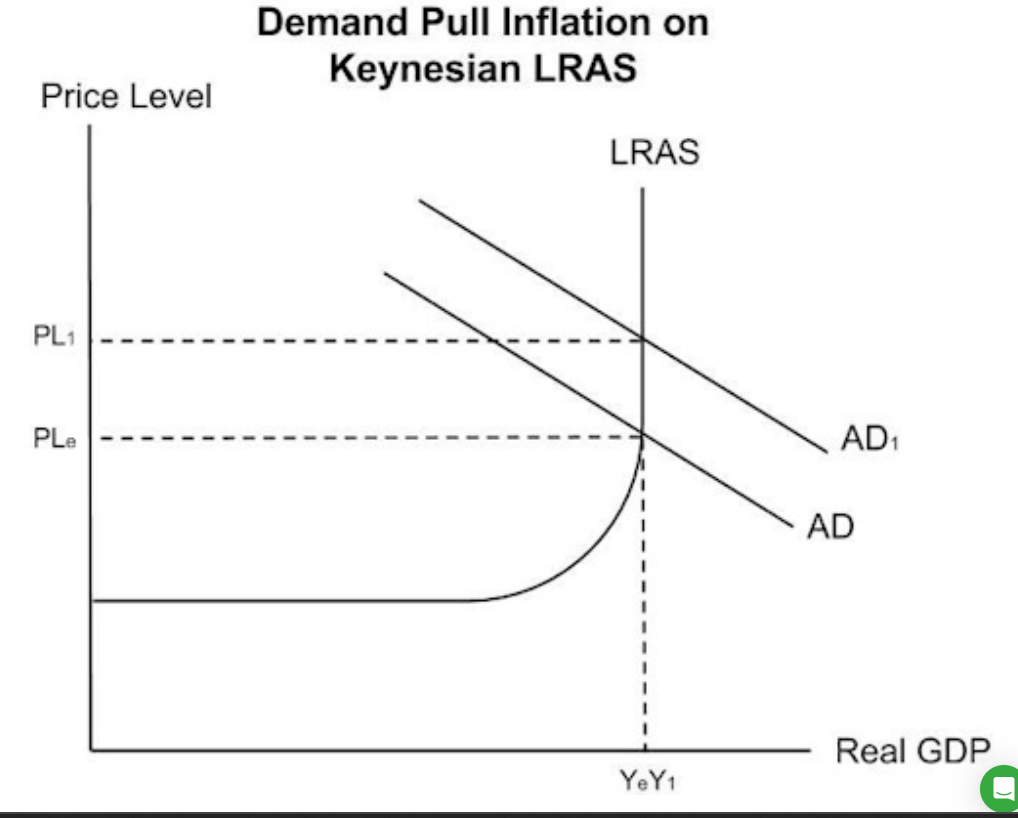
Demand pull inflation:
Price level increase from PL1 to PL2.
Derived demand for labour increase
As real GDP increases, firms need to increase output, derived demand for labour will increase.
Low unemployment.
5 Improved budget
If more people are in paid employment, government spending on benefits will decrease and income tax revenue will increase. This will decrease the budget deficit.
5 characteristics of a boom:
1) high animal spirits increase consumption and investment.
2)high economic growth, measured by an increase in real GDP.
3)demand pull inflation as the price level increases.
4)low unemployment as firms demand more workers
5) An improved budget as government spending decreases and tax revenue increases.
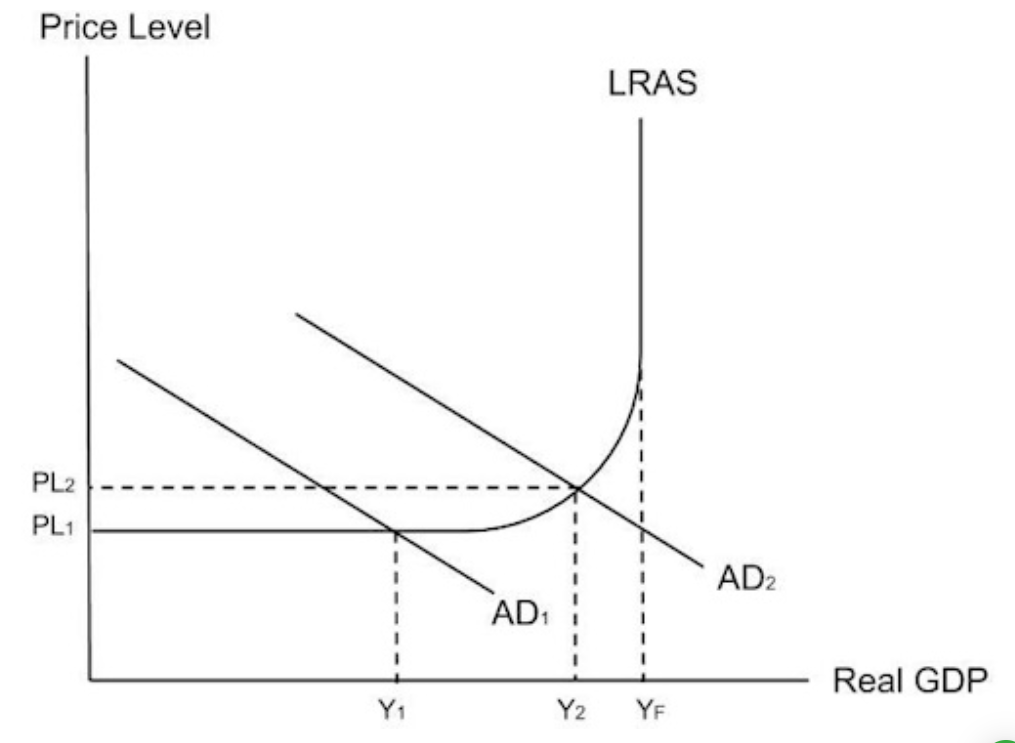
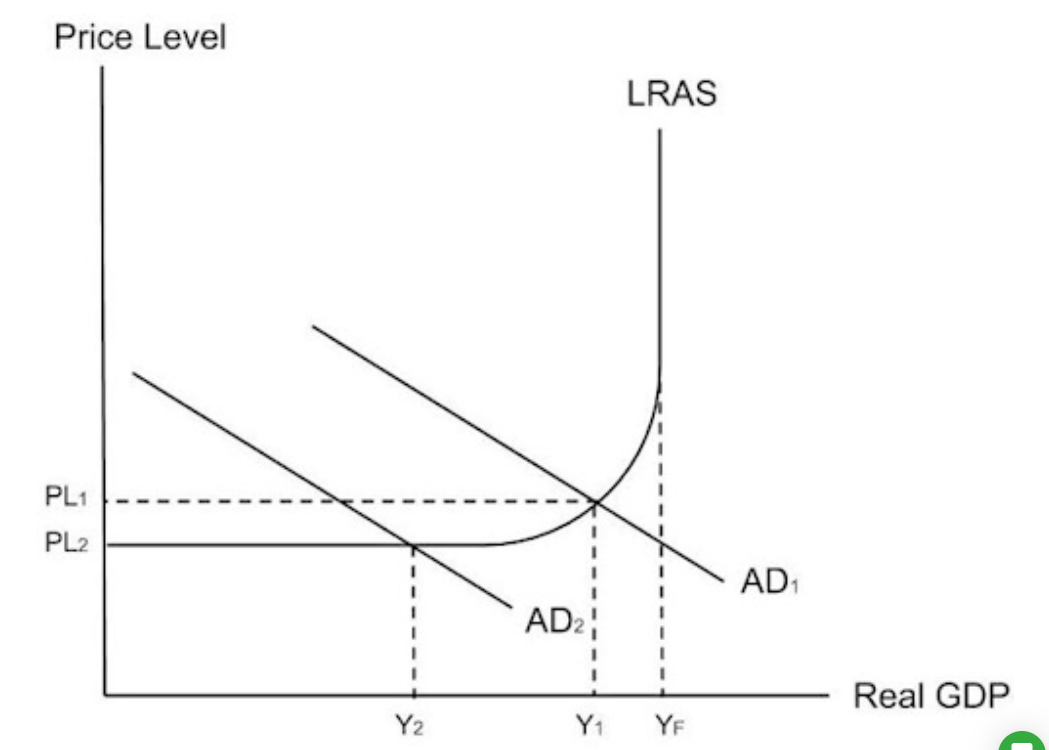
5 characteristics of a bust (recession)
If fewer people are in paid employment, government spending on benefits will increase and tax revenue will decrease, which will increase the budget deficit because the government has to borrow more money.
1) low animal spirits decrease consumption and investment
2)low economic growth measured by a decrease in real GDP
3) low inflation or deflation as the price level decreases.
4) high unemployment as firms demand fewer workers
5) a worsened budget as government spending increases and tax revenue decreases.
Causes of economic growth
increase in quality or quantity of one of the four factors of production, land, labour , capital, enterprise. Any factor that increases LRAS, will also increase economic growth.
Land: discovery of new resources e.g. oil will increase economic growth.
Labour: An increase in quality/quantity of labour will improve economic growth. Size of the workforce, more people of working age means more growth, raising the retirement age will increase the population of the working age, government can take action such as free childcare to encourage mothers to go back to work, increase participation rates.
Quality of the workforce: improving the quality of the labour, can be done through education, workers have more skills they need to be efficient, output per worker increases. More skilled workers, less likely to suffer from structural unemployment as they have greater occupational mobility, increase the output of economy, less unused resources. workers will contribute to change e.g. new technology, business ideas.
Capital: If a country receives sustained investment, they will be able to access or develop new technology which will enable country to improve productivity, more machines can be bought and used.
Enterprise: If government offer tax benefits and grants, this will encourage the development of business create jobs therefore more goods and services produced.
Technological progress: improved technologies means average cost of production is lower, because it is quicker to produce or less labour equipment is needed. creates new products for the market increases consumption MPC high new things to buy. Without increased spending, little economic growth.
Efficiency: Efficiency is important in bringing economic growth as less resources needed to produce each good, so more goods can be produced. One way government can ensure efficiency is to keep up competition, producers are forced to lower prices or increase quality so will have to improve efficiency to keep profits high.
International trade: Many economists argue that AD can affect economic growth, through export led growth, rise in AD through increased exports. Sustained high export levels will encourage or force firms to invest and increase demand for labour, lead to economic growth.