5. Random Variables
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Random Vairable
Numerical measurement of the outcome of an experiment
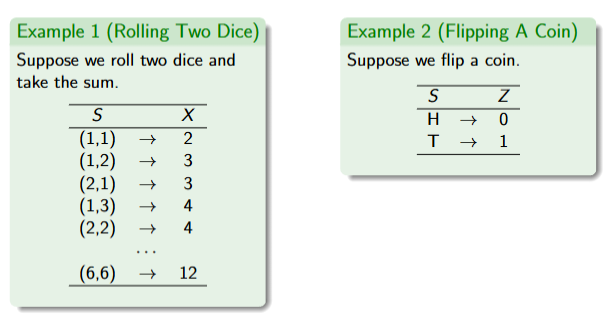
Probability Distribution
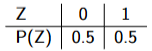
Discrete Random Variables
Random Vairable - X
Value - x
Plotted iwth Barplots
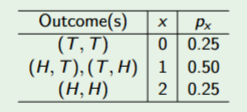
Mean of Discrete Random Variable
Weighted average of the values in the sample space, Expected value.
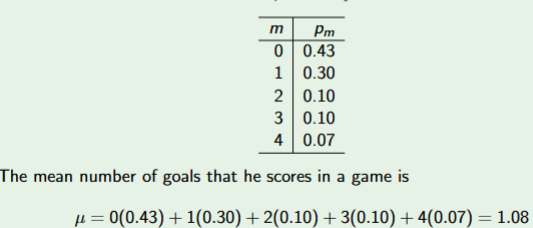
Properties of Mean
Linear Transformation
Multiple Random Variable Add Mean
Mean of random variables is mean

Variance of Discrete Random Variable
\sigma is the standard deviation of X
P is the probability
x is the value
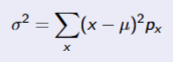
Properties of Variance
Multiplication
Random Variables Addition works
Mean variance of random variables is \sigma/ n

Continous Random Variable
Contains values that form an interval.
Probability Density function area should be less than 1.
Mean of Continous Random Variable
Expected value of X
Same properties as mean for discrete case
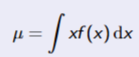
Variance of Continous Random Variable
Same properties as variance of discrete case
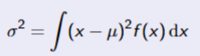
Quantiles of Continous Random Variable
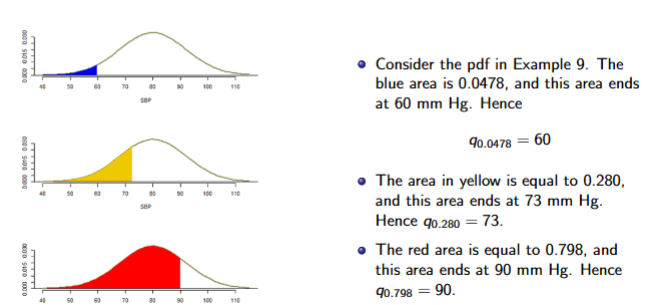
Binomial Distribution (X ~ Bin(n,p))
Strictly 2 outcomes
Constant probability of success
N Trails are independent
Mean = NP
Variance = NP(1-P)
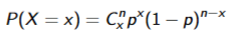
Binomial Distribution Example
Assuming Probability = ¼
N = 5
X = 10
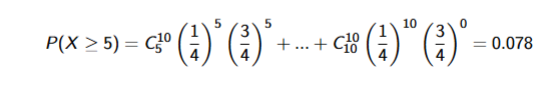
Poisson Distribution
\lambda is the expected number of events over time period t
Poisson can be use to accurately approximate binomial with large n and small p given mean = np
np almost equal to np(p-1)
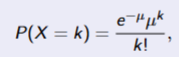
Poisson Distribution Example
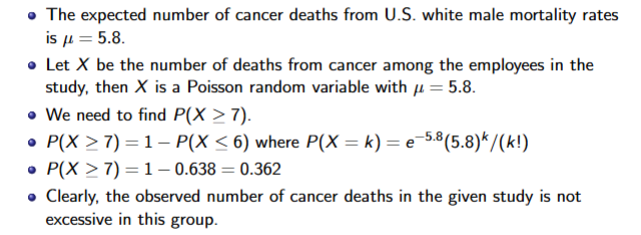
Normal Distribution
Symmetric, bell curved and characterised by mean and variance
Highest point is at mean
SD Diff: 68%, 95%, 99.7%
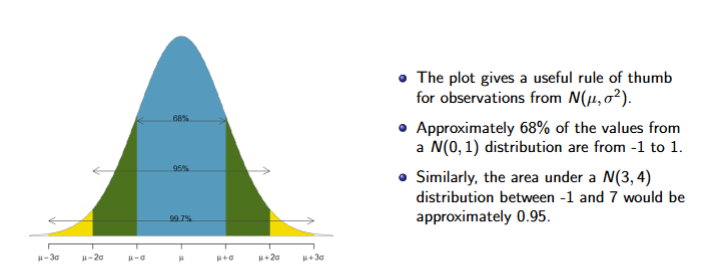
Linear Transformation of Normal Random Variables
Adding constants forms new variable
Sum of normal is still normal
Product of normal with constant is still normal
Adding Normal Varible

Mutiplying Normal Variable
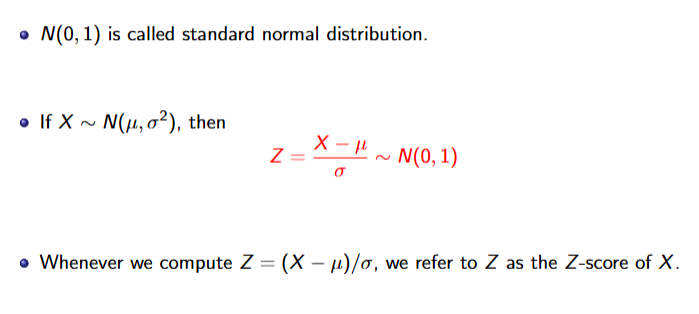
Standard Normal Distribution
N(0,1)
If Z-score is more than 3 or lesser than -3 its a outlier