TOPIC 8:ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the equation for gravitational field strength ?
g=GM/R^2
What is the equation for Electric field strength(3)
KQ/r^2
E = F/q
E=V/D
What is the equation for Electrostatic force
Fe=KQQ/r^2
What is the equation for Gravitational force
Fg=GMM/r^2
What is a Field
A field is an area of space that has an influence (force) on something
What is the graphical relationship/ representation of gravitational field strength
inverse square graph as gravity is inversely proportional to the r^2
What is flux density
The strength of a magnetic field.
what is an electric field
A region of space in which charged particles experience either an attractive or repulsive force depending on the charge of the particle and direction of the field
What is a magnetic field
A region of space in which magnetic materials and moving electric charges feel a force.
What does a positive symbol signal in an electric field
Repulsion
what does a negative symbol signal in a electric field
Attraction
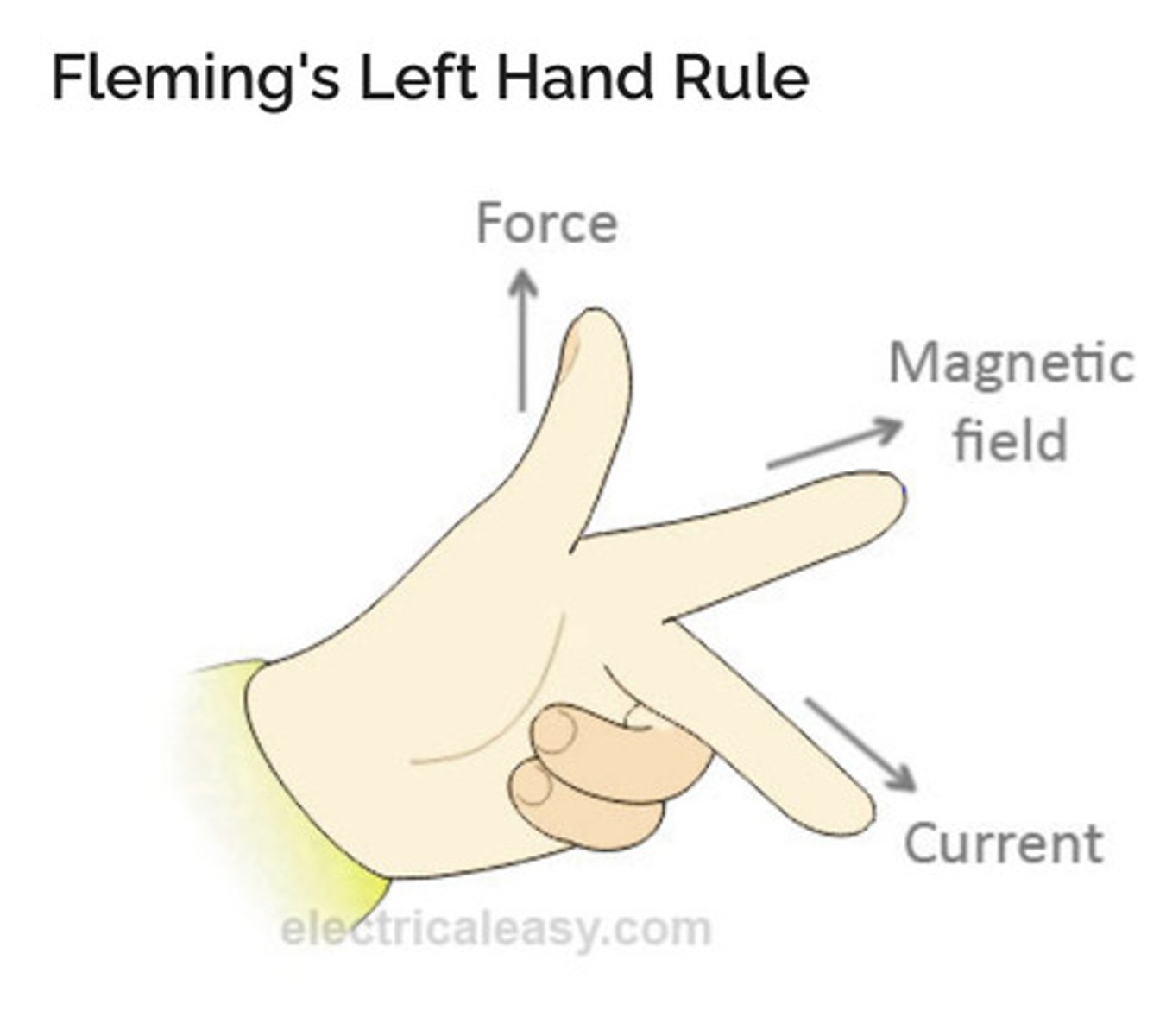
Explain Fleming left hand rule
The relative direction of motion(force), field direction and current direction in the motor effect.
Explain the magic wand experiment in relation to
Electric Fields
Coulomb's Law
The size of the force that acts between two point charges is proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation
Define capacitance
The ratio of the charge stored in a capacitor to the potential difference between the two sides of the capacitor.
Why is the symbol for gravitational Force always negative
It is always negative because it is an Attractive force
Explain Columb's Law for Attractive and repulsive forces mathematically
opposite charges
+ & - = -
-=attraction
opposites charges attract
Like charges
- & - =+
+ & + = +
+= repulsion
like charges repel
What are Electric Field Lines
A way of representing an electric field in a diagram
In What direction do electric field lines point.
They point in the direction that a positive charge would experience a force, point positive to negative.
What is Electric Potential.
Defined at a point. The work done moving a unit positive charge from an infinite distance away to that point.
What is Electric Potential Difference
The work done per unit positive charge in moving between two points
What is the equation for Electric Potential
V = kQ/r
Why is KQ/r^2 not the generic equation for eletric field strength
it only applies to eletric field strength at a distance of r from Q
What is the equation for the electric field strength acting between two plates
E=V/D
Explain the semolina experiment in terms of electric fields
The potential difference generated between the two plates creates an electric field which creates a force that acts on the charge of the semolina powder causing them to accelerate back and forth between the plates as they pick up and lose charge.