EXSS 4000 Final Exam (Philips)
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
Muscle Structure
-Tendon
-epimysium surrounds muscle
-perimysium surrounds groups of fascicles
-endomysium surrounds fibers which contain myofibrils that are made of actin and myosin
Muscle proteins
actin and myosin
Cross-bridge cycling (Sliding Filament Theory)
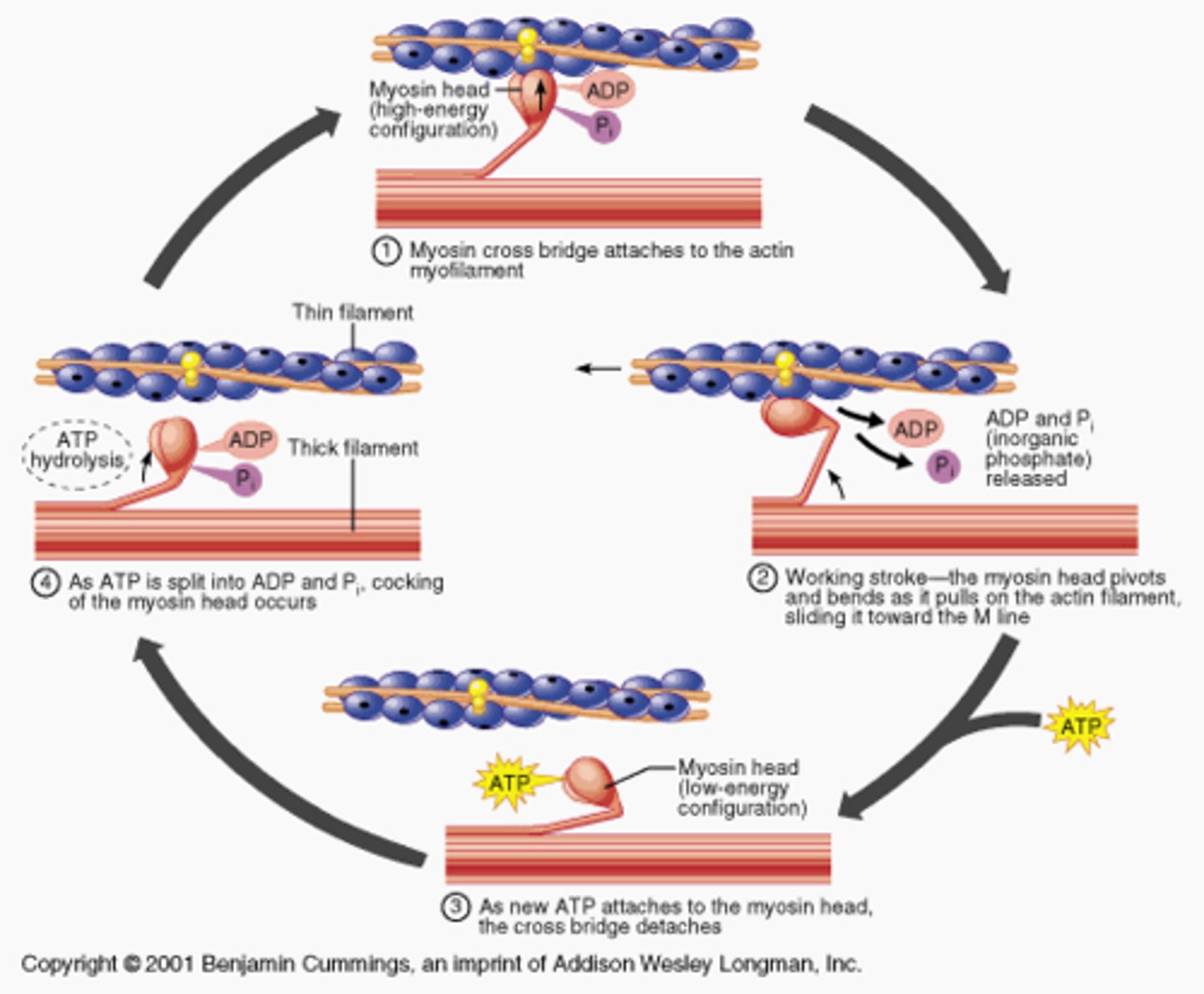
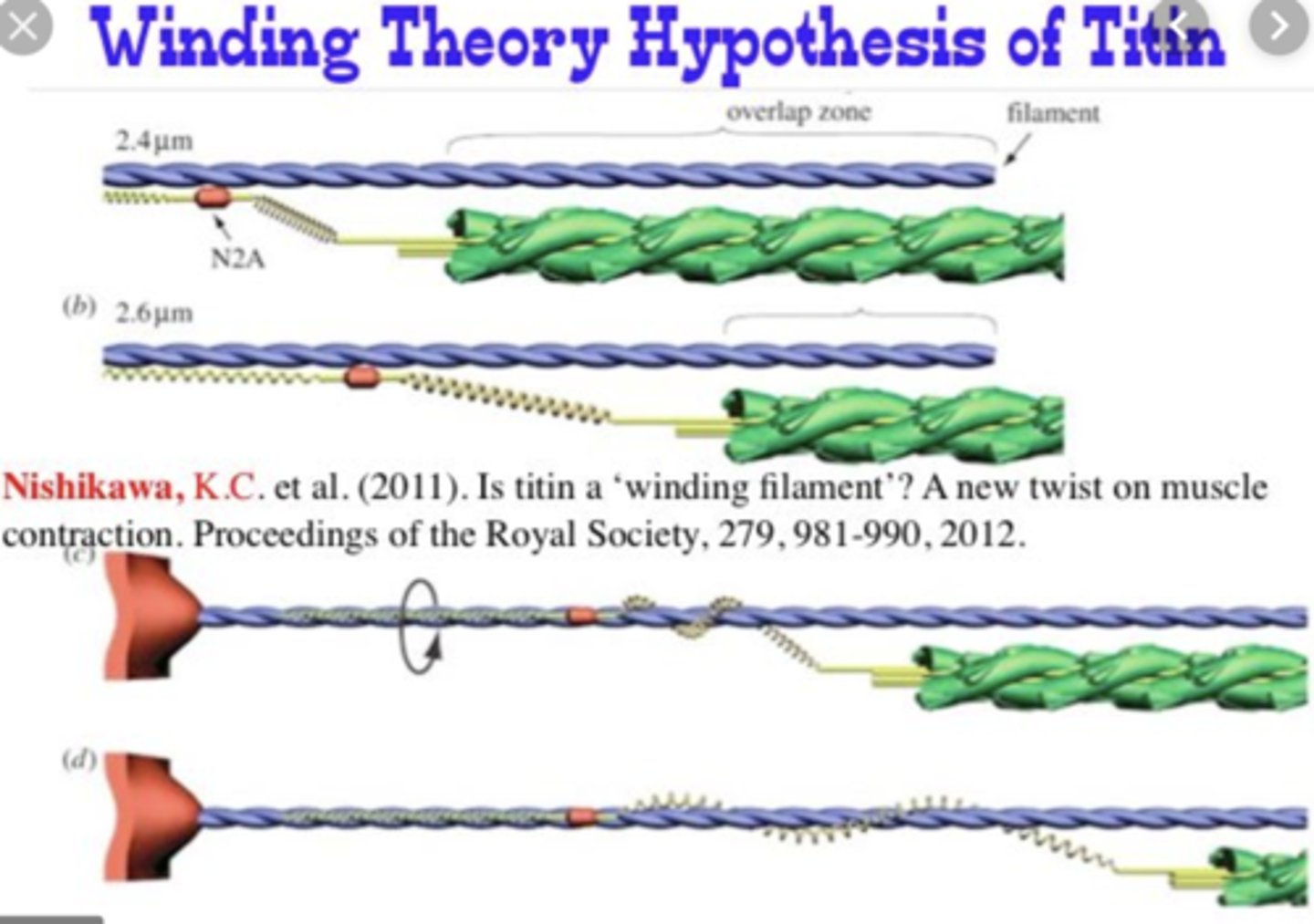
Winding Filament Theory
-new theory
-calcium binds to troponin AND titin
-titin winds around actin filament causing contraction
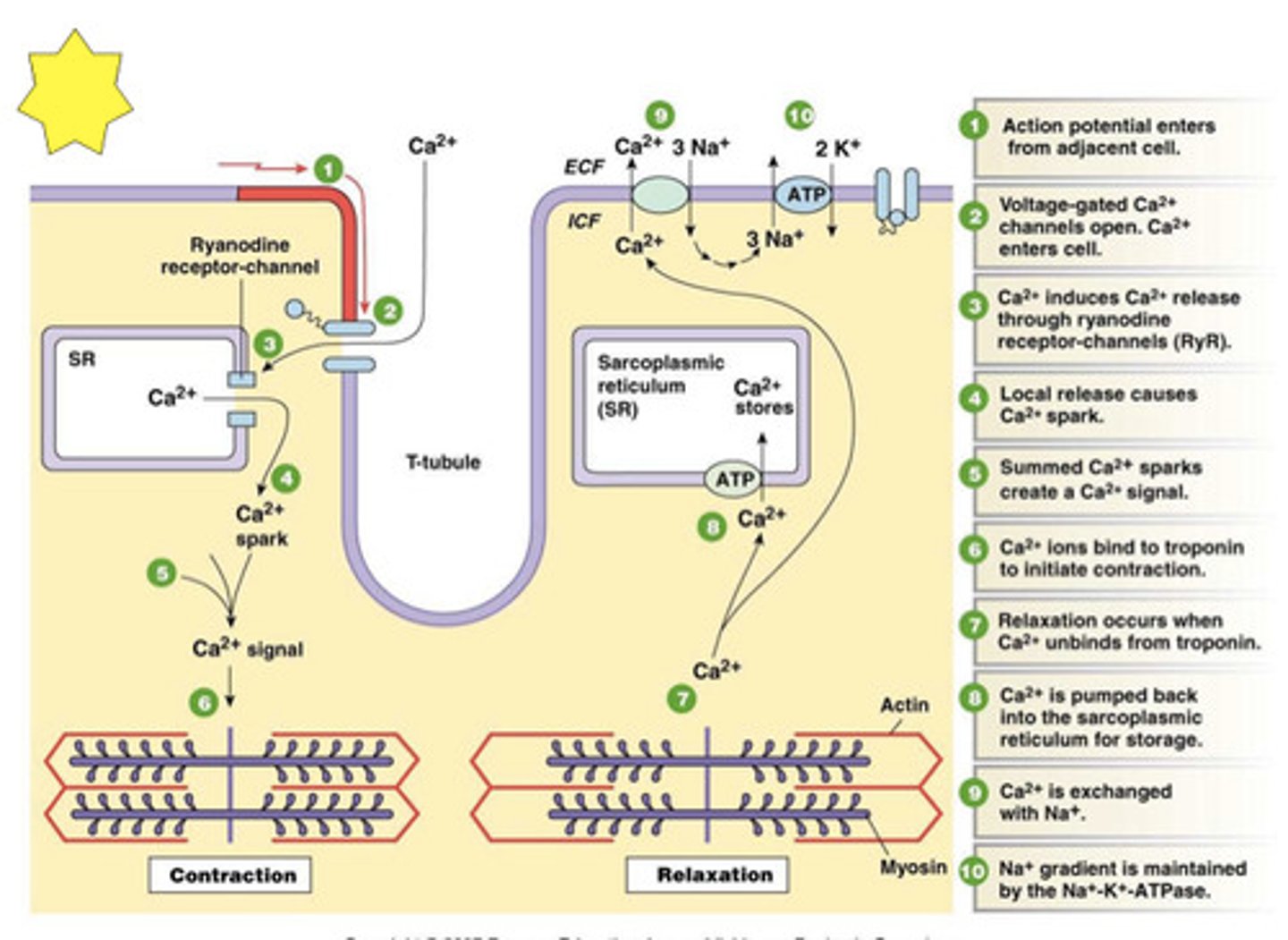
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
connection between muscle fiber stimulation and muscle contraction
All-or-none principle
Refers to the fact that the action potential in the axon occurs either full-blown or not at all.
Factors That Affect Force Production
-cross-sectional area
-pennation angle
-distribution of muscle fiber type
-muscle length
-muscle length relative to its resting length
-contraction velocity
-cross bridge formation (# of MUs recruited and fibers per MU, joint angle, muscle architecture)
Slow-twitch (ST, Type I, oxidative)
-small motor neuron
-first to be recruited (smaller threshold)
-slow conduction velocity
-smallest fiber diameter
-less SR dev
-high mitochondria
-high capillary density (more oxygen)
-high myoglobin (oxygen reserve in cell)
-<300 fibers per motor neuron
-low phosphocreatine stores
-low glycogen stores
-high triglyceride stores
-low ATPase
-low glycolytic enzyme
-oxidative enzymes
-twitch time 110
-slow relaxation
-low force prod
-high energy efficiency
-high fatigue resistance
Fast-twitch a (Type IIa, oxidative/glycolytic)
-large motor neuron
-second to be recruited
-fast conduction velocity
-large fiber diameter
-more SR dev
-high mitochondria
-medium capillary density
-medium myoglobin (oxygen reserve in cell)
->300 fibers per motor neuron
-high phosphocreatine
-high glycogen stores
-medium triglyceride stores
-high ATPase
-high glycolytic enzyme
-high oxidative enzymes
-50 twitch time
-fast relaxation
-high force prod
-low energy efficiency
-low fatigue resistance
Fast-twitch b (Type IIbx, glycolytic)
-large motor neuron
-last to be recruited
-fastest conduction velocity
-largest fiber diameter
-most SR dev
-low mitochondria
-low capillary density
-low myoglobin (oxygen reserve in cell)
->300 fibers per motor neuron
-high phosphocreatine
-high glycogen stores
-low triglyceride stores
-high ATPase
-high glycolytic enzyme
-low oxidative enzyme
-50 twitch time
-fast relaxation
-high force prod
-low energy efficiency
-low fatigue resistance
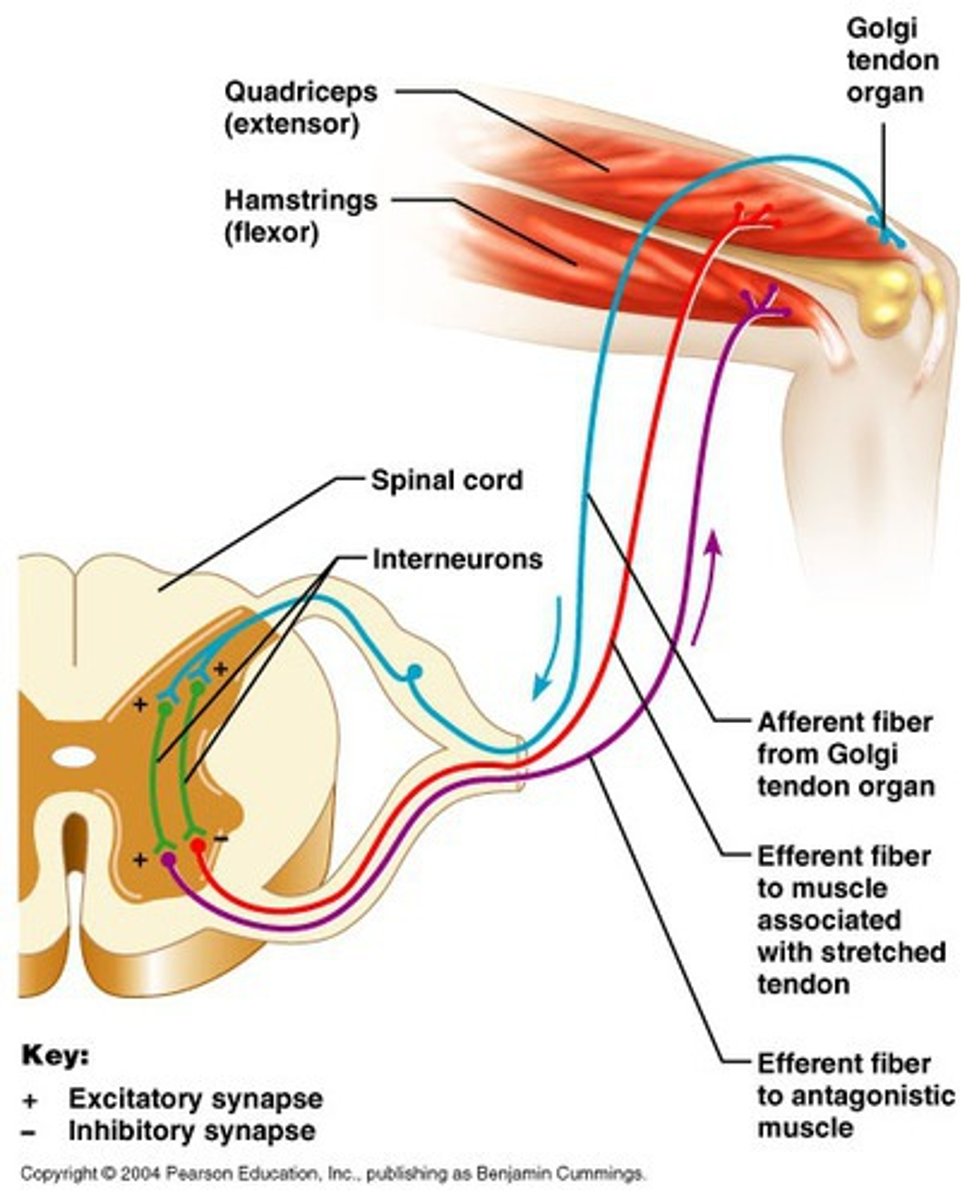
Autogenic inhibition
The process by which neural impulses that sense tension are greater than the impulses that cause muscles to contract, providing an inhibitory effect to the muscle spindles.
Orderly Recruitment Principle
(size principle) because the size of alpha motor neuron. As size increases, twitch increases.
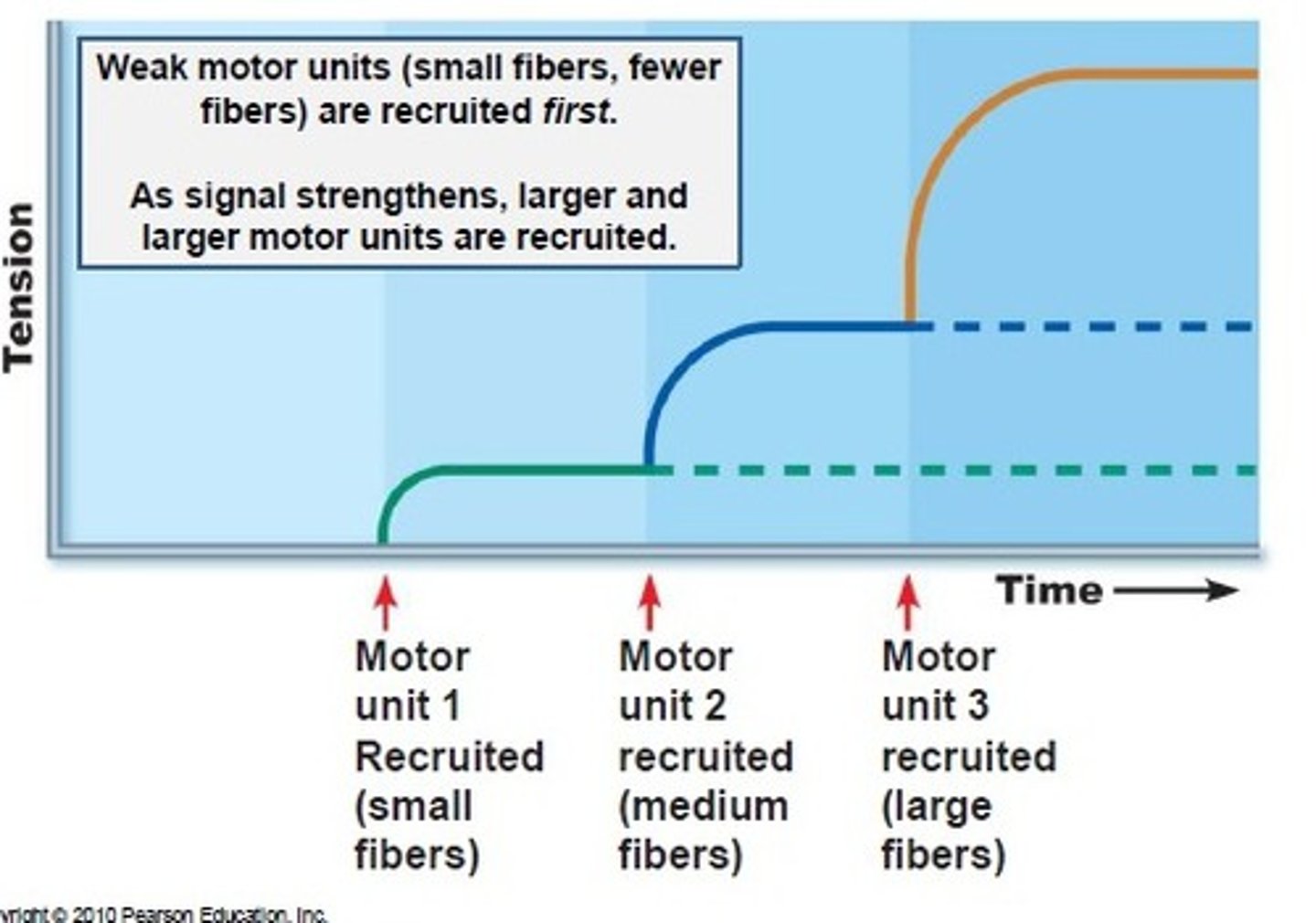
Factors that impact skeletal muscle force development
Types of Muscle Action
concentric (shortening), eccentric (lengthening), isometric (no change)
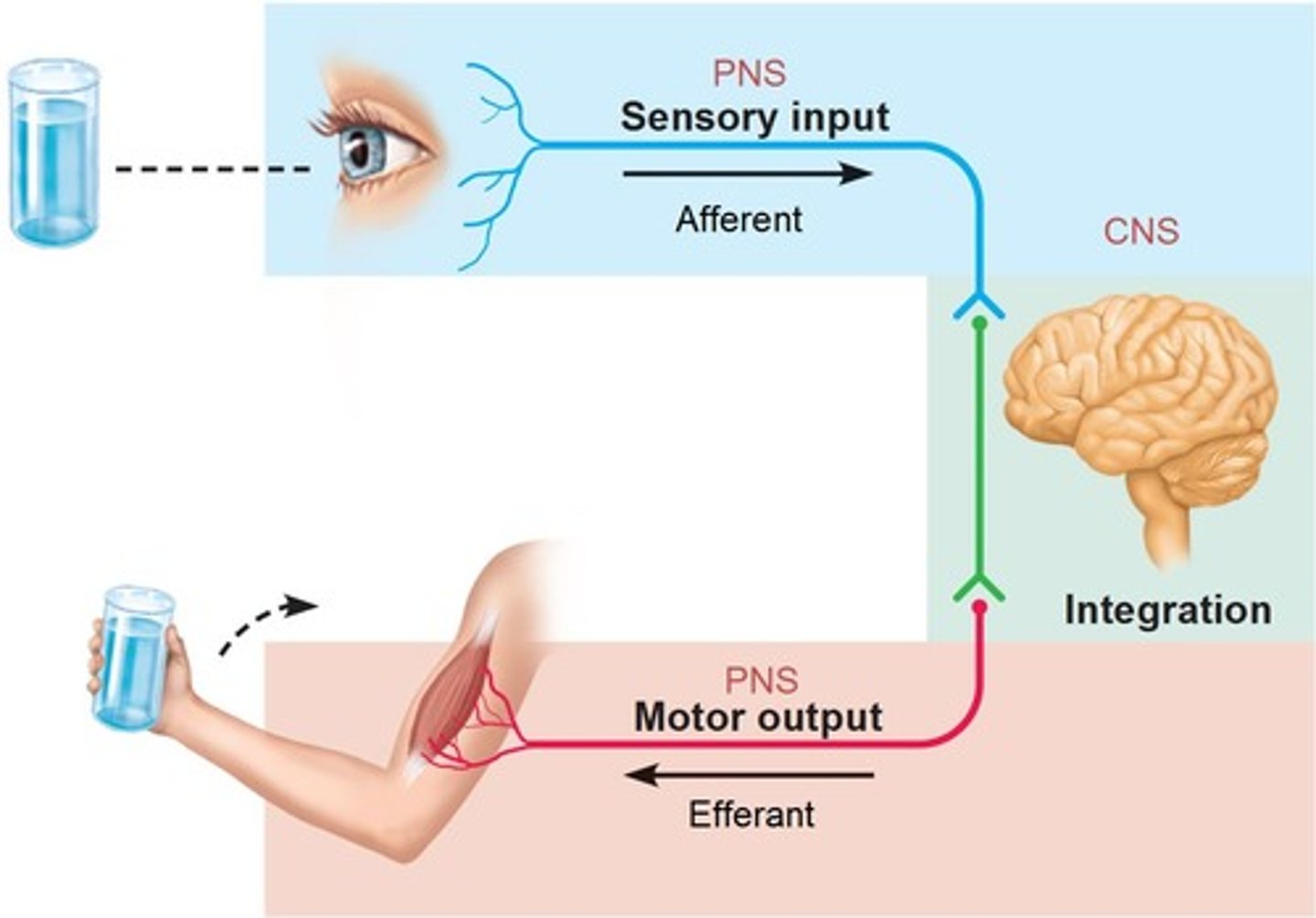
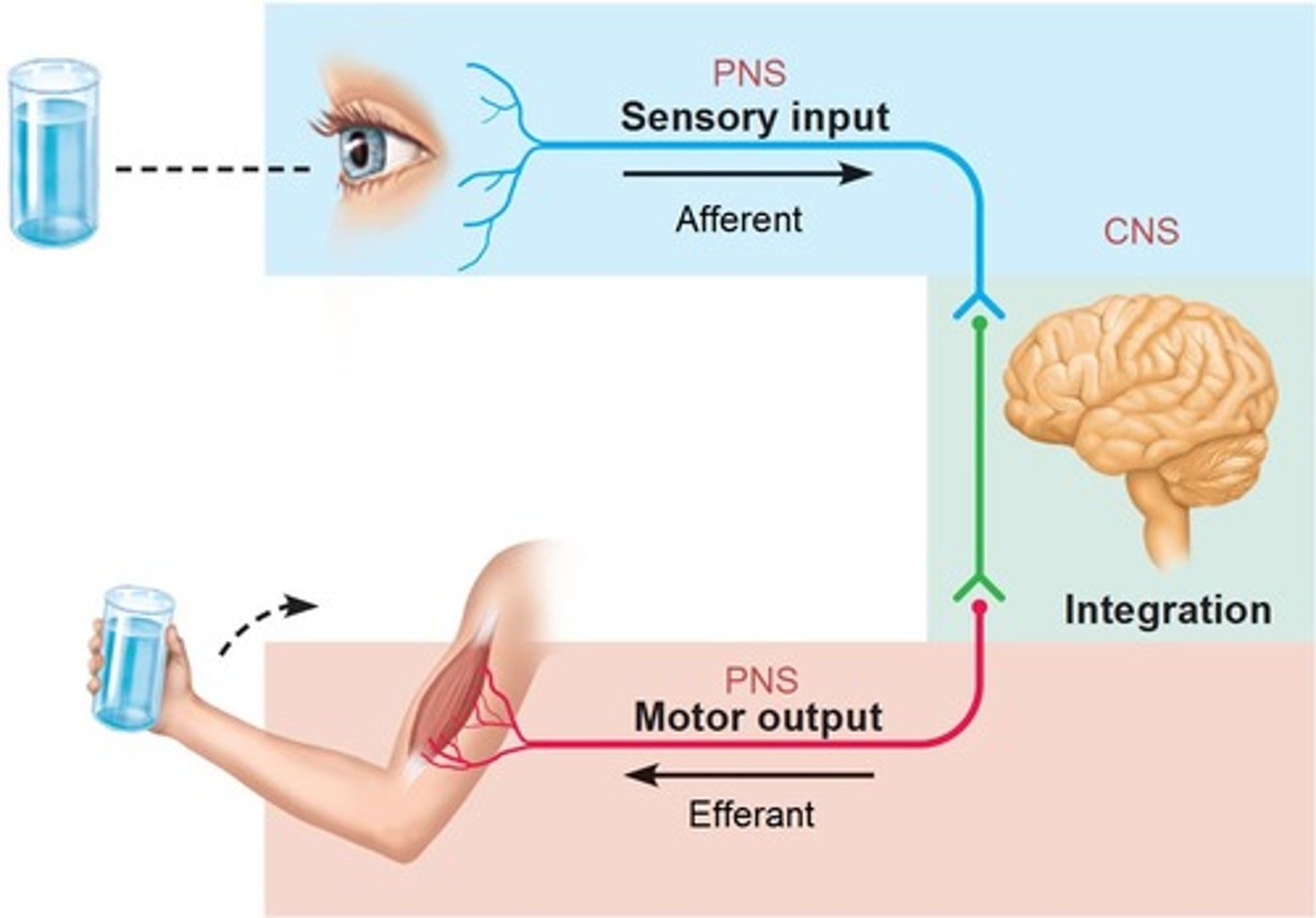
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
Sensory (afferent) division
-somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers
-conducts impulses from receptors to the CNS
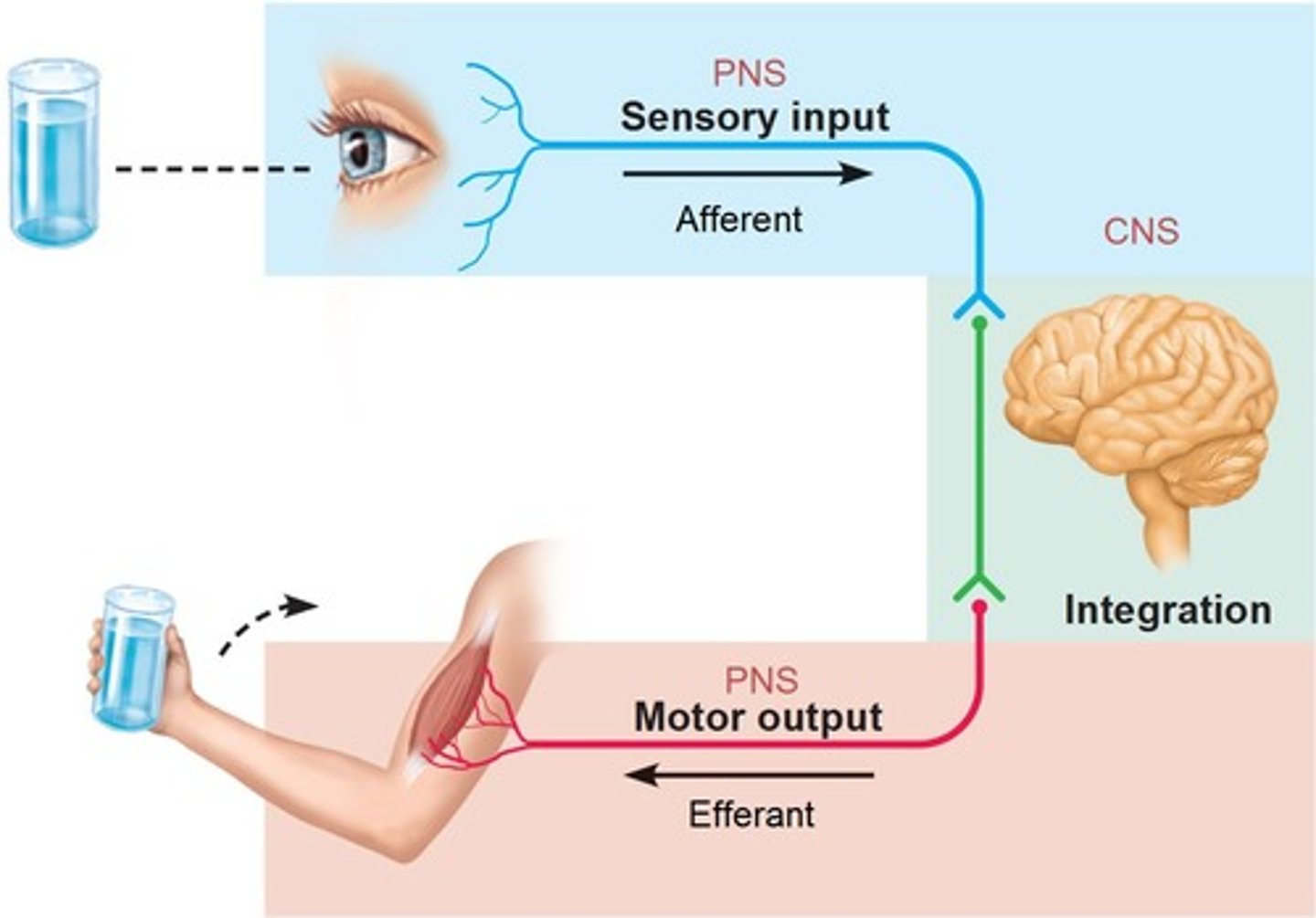
Motor (efferent) division
Transmits impulses from the CNS to effector organs
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
-ACh, amino acids, biogenic amines, neuropeptides and others
Absolute refractory period
The minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin.
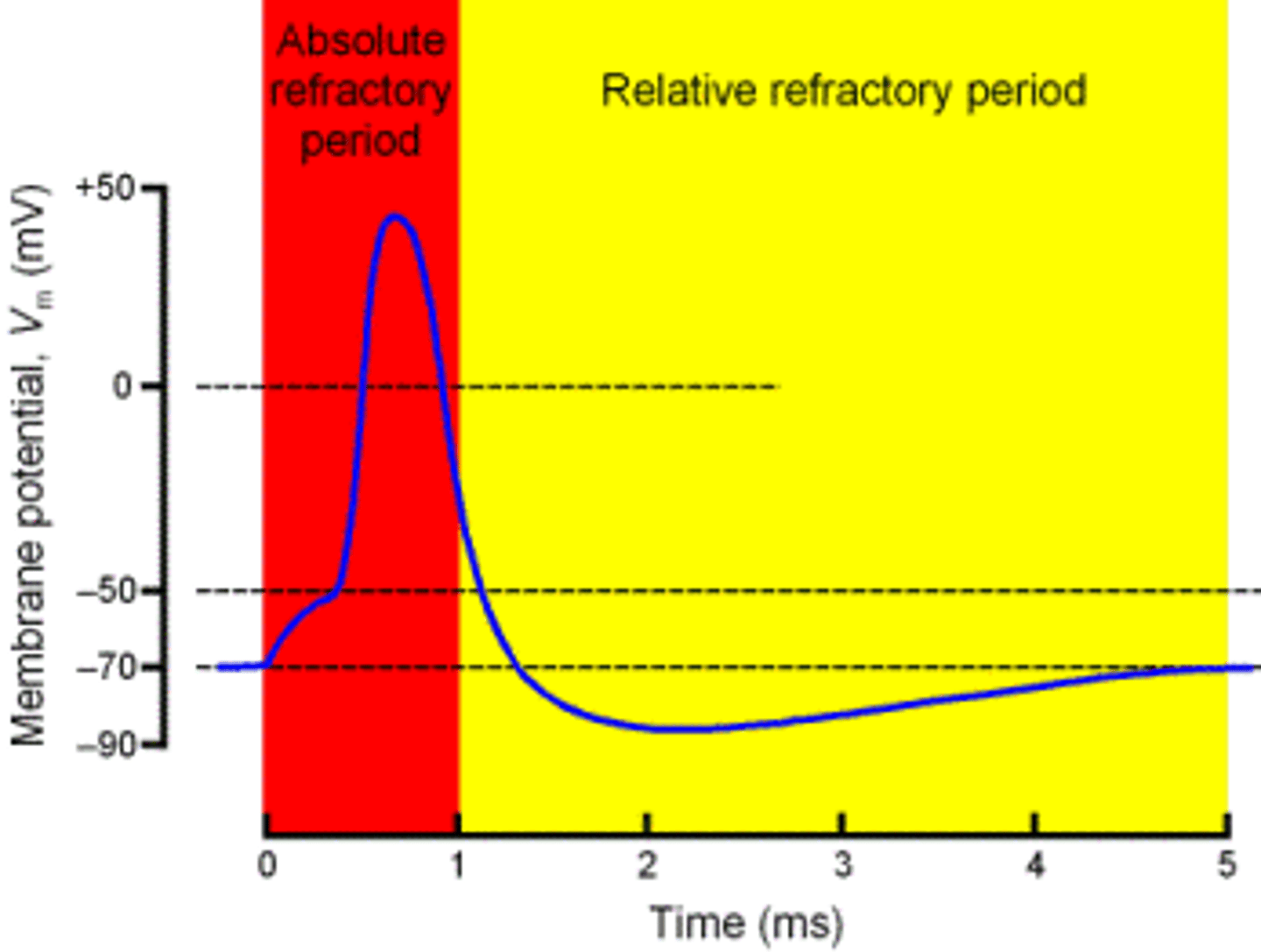
Relative refractory period
A period after firing when a neuron is returning to its normal polarized state and will fire again only if the incoming message is much stronger than usual
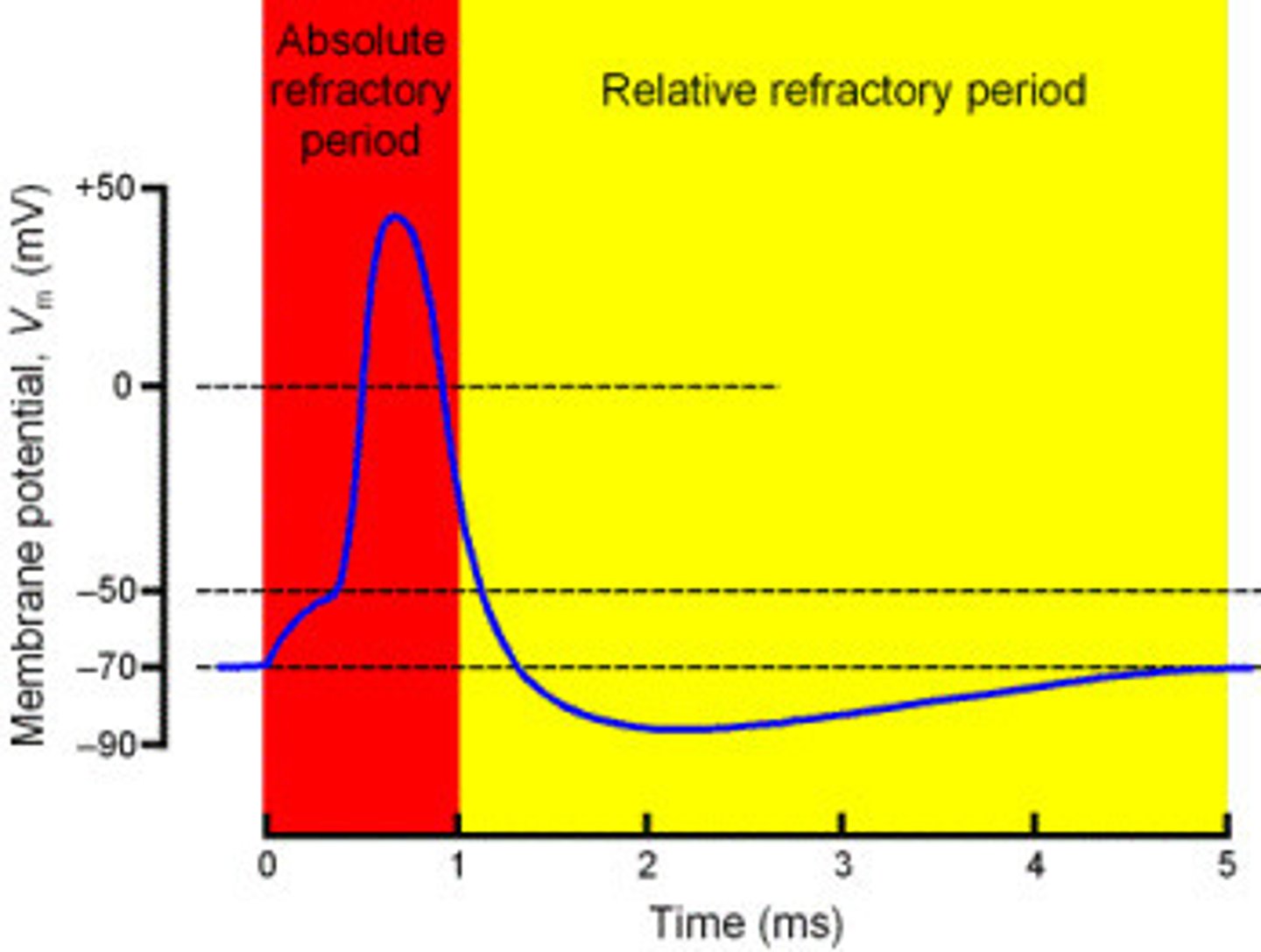
Excitatory postsynaptic potential & Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
EPSP: brings voltage closer to threshold (more positive-depolarization)
IPSP: brings voltage farther from threshold (more negative-hyperpolarization)
Primary Motor Cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement
-1ST
-not filtered signals
Basal ganglia
structures in the forebrain that help to control movement, posture and learned activities
-2ND
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination
-integration of sensory impulses
-3RD
Brain stem - Reticular formation
maintains cerebral cortical alertness, filters out repetitive stimuli, helps regulate skeletal and visceral muscle activity
-4TH
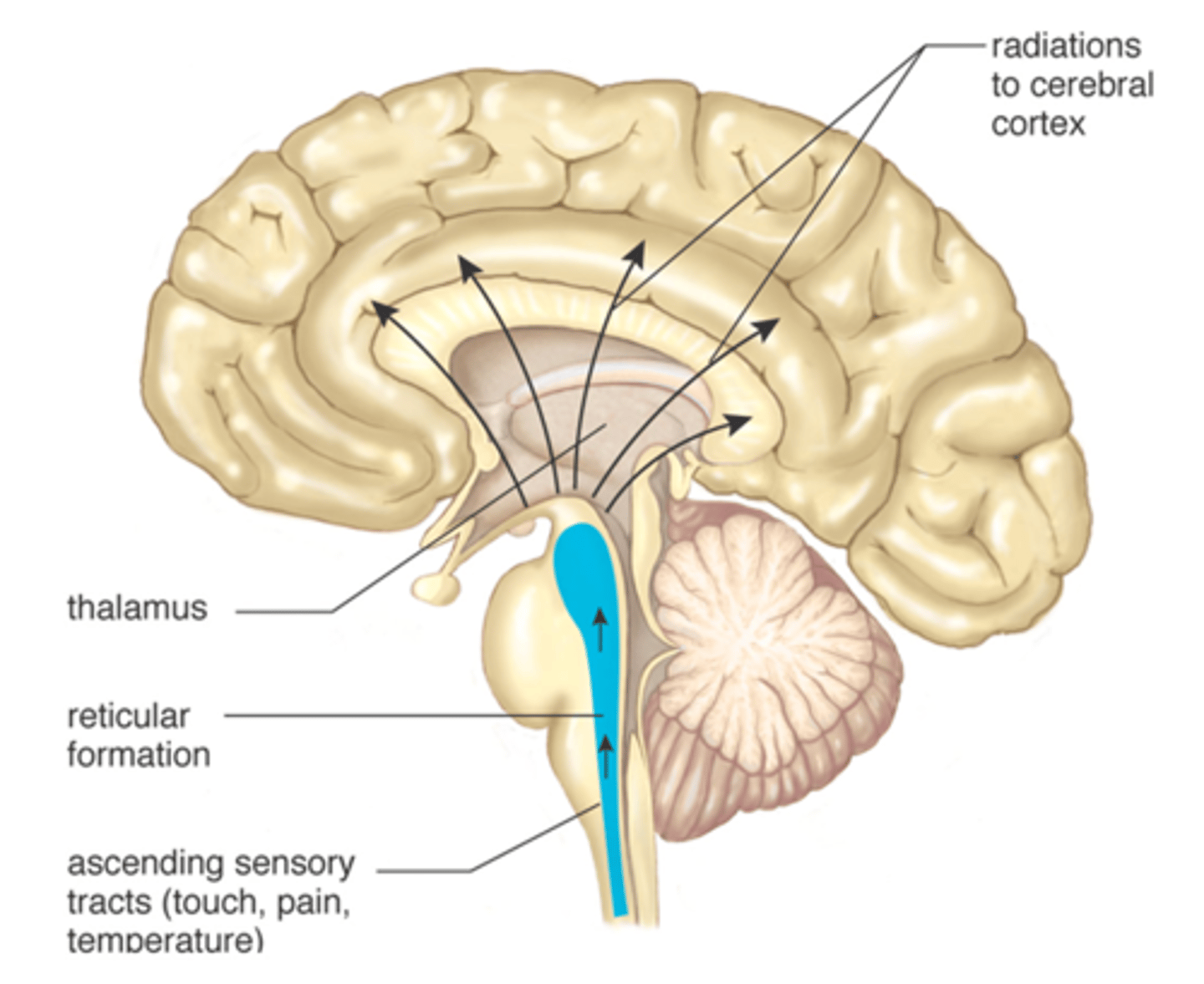
Spinal Cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
-5TH
Sensory division
transmits impulses from sense organs to the central nervous system
Reflex vs complex response
-reflex only goes to the spinal cord
-complex reaches the brain and back
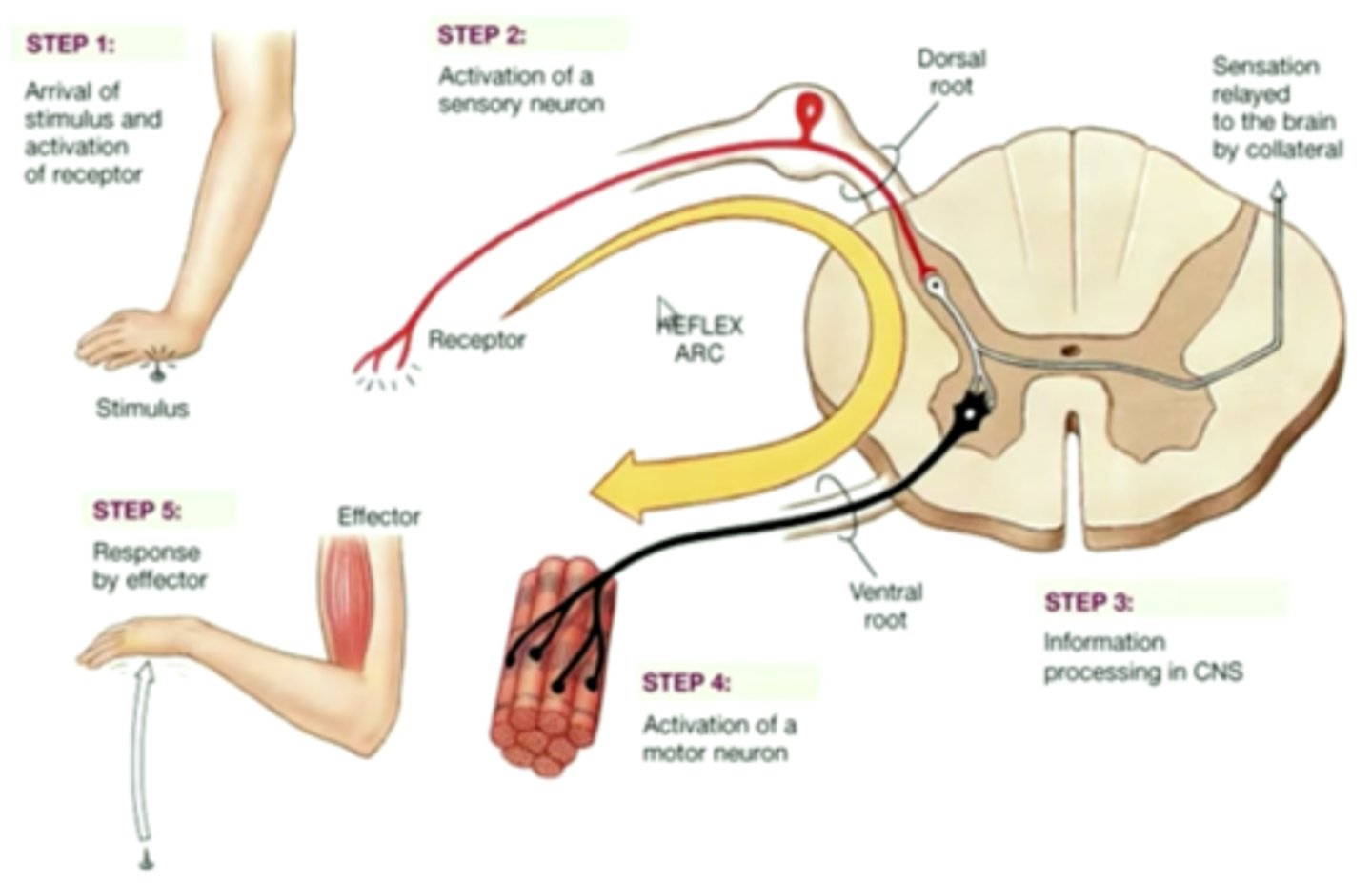
integration
To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed
Motor Division
carries signals from the CNS to gland and muscle cells that carry out the body's responses
Sensory - Motor integration
the process by which the sensory and motor systems communicate and coordinate with each other
Muscle spindle
a sensory receptor located in a muscle that senses its tension
-responsible for reciprocal inhibition
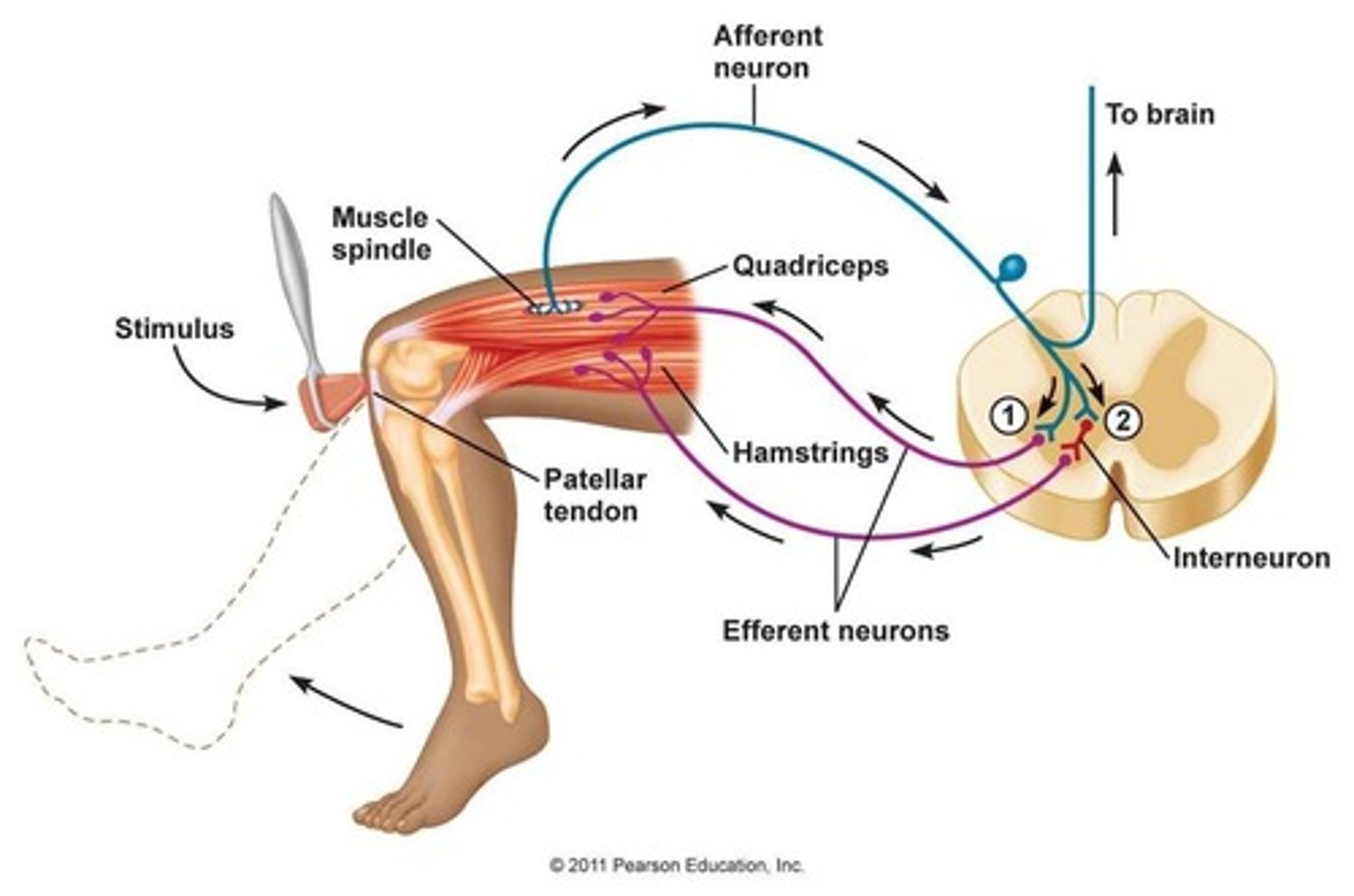
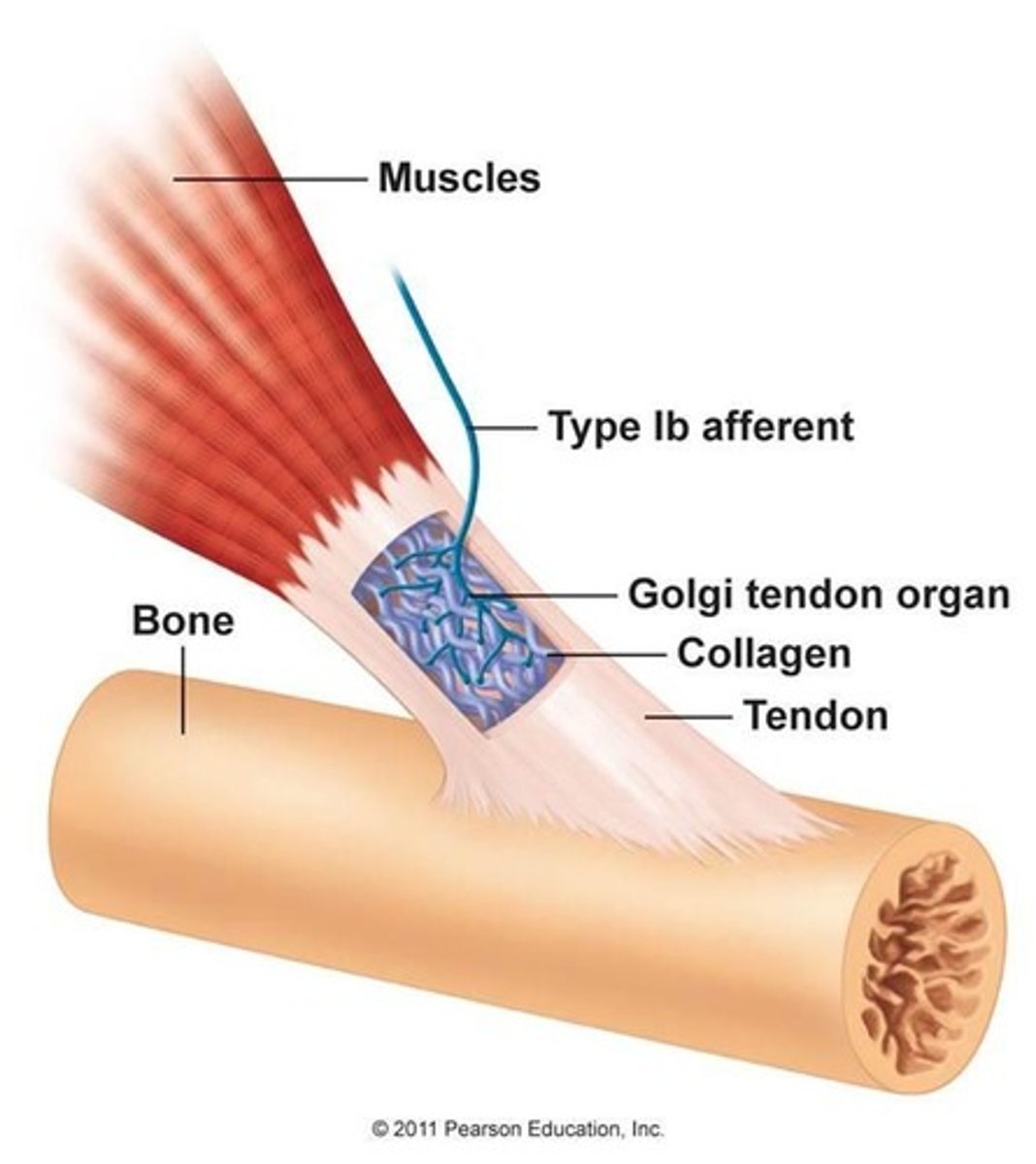
Golgi tendon organs
Receptors sensitive to change in tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
-responsible for autogenic inhibition
Sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
The component of the autonomic nervous system that responds to stressful situations by initiating the fight-or-flight response.
-adrenergic receptors
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
Division of the autonomic nervous system that slows down body functions, activated when you relax or when SNS stimulated too long.
-muscarinic receptors
Neurological change with resistance training
1. motor unit recruitment synchronization (more firing at once gives us greater strength)2. reduced autogenic inhibition (protective mechanism)3. reduced coactivation (anything detrimental to force production)4. increased synergistic muscle activation5. change in rate coding (higher volley of impulses)6. change in neuromuscular junction morphology7. increase muscle spindle activity
Chronic hypertrophy mechanisms of change
-structural changes
-more myofibrils, actin & myosin, sarcoplasm
-more connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber
Hyperplasia
the enlargement of an organ or tissue because of an abnormal increase in the number of cells in the tissues
Hypertrophy Transient mechanisms of change
the "pumping up" of muscle that happens during a single exercise bout, resulting mainly from fluid accumulation in the interstitial and intracellular spaces of the muscle (edema)
mechanism from chronic hypertrophy
1. increase cross sectional area of existing fibers
2. muscle protein synthesis (continual flux)
3. decreased degradation
4. INCREASE SYNTHESIS VS DECREASED DEGRADATION
5. satellite cells
Anabolic hormones & hypertrophy
-testosterone: 2nd sex characteristics
-growth hormone: fat, muscle, bone growth and metabolism (A PEPTIDE- not lipid soluble)
-promotes secretion of IGF
-fiber type specific effect
Fiber Type Alterations with Training
-if you cross innervate motor neurons then you can change the fiber type
-ex: old ppl don't stim type II fibers as much, so the fibers will die and be absorbed and contribute to type I fiber type
-fibers consist on a continuum
Qualitative Changes in Muscle Tissue with Resistance Training
morphology, muscle architecture, and muscle function in elderly postoperative patients
Changes in Muscle Tissue with Disuse/Atrophy
decrease in muscle mass, one limb being smaller than the other, and numbness, weakness and tingling in your limbs
Acute Muscle Soreness
-mechanical disruption of tissues
-caused by eccentric movements
-occurs during and immediately after exercise and is due to the accumulation of lactate, decreased oxygen (ischemia), and tissue swelling within the muscle (edema)
Delayed onset muscular soreness (DOMS)
day or two after exercise.
1. Disruption of connective tissue or muscle damage
> inflammatory process.
• Metabolites/Ca released:
• Neutrophils (inflammation)
• Macrophages/intercellular contents stimulate nerves:
these all lead to...Edema
2. Edema -> build up of fluid. More long term build up of fluid.
Cramping - Heat Related and Fatigue Related (Treatment & Prevention)
heat cramps- electrolyte distubances (fluids and ice)
fatigue related- overuse or underconditioned (rest and stretching)
Aerobic metabolism
-more than 3 mins
-oxygen
-carbs and fats as energy
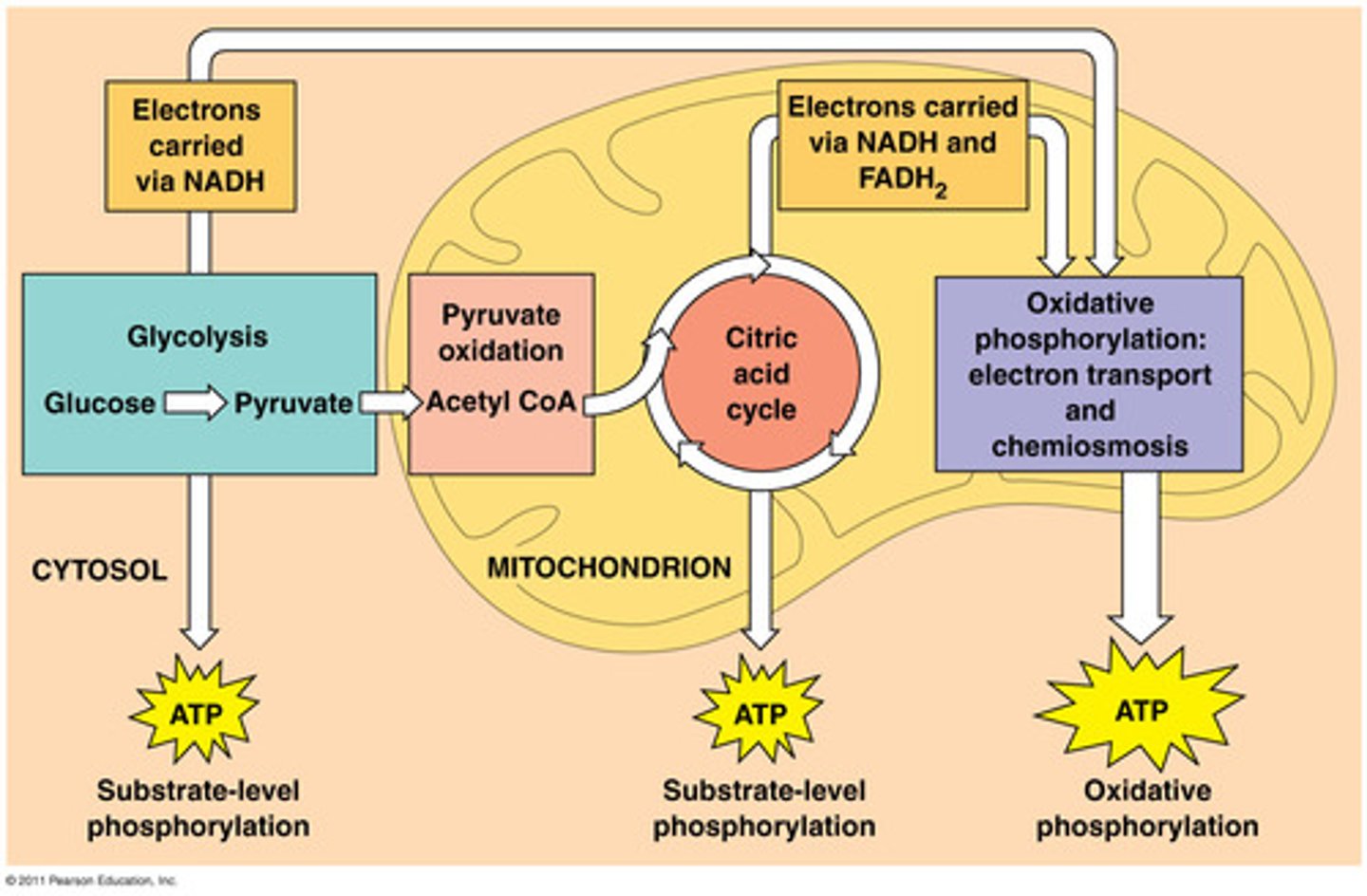
Anaerobic metabolism
-10 sec to 3 mins
-carbohydrate use
-Short-term energy source for moderate-high intensity activities
Direct calorimetry
measurement of heat production as an indication of metabolic rate
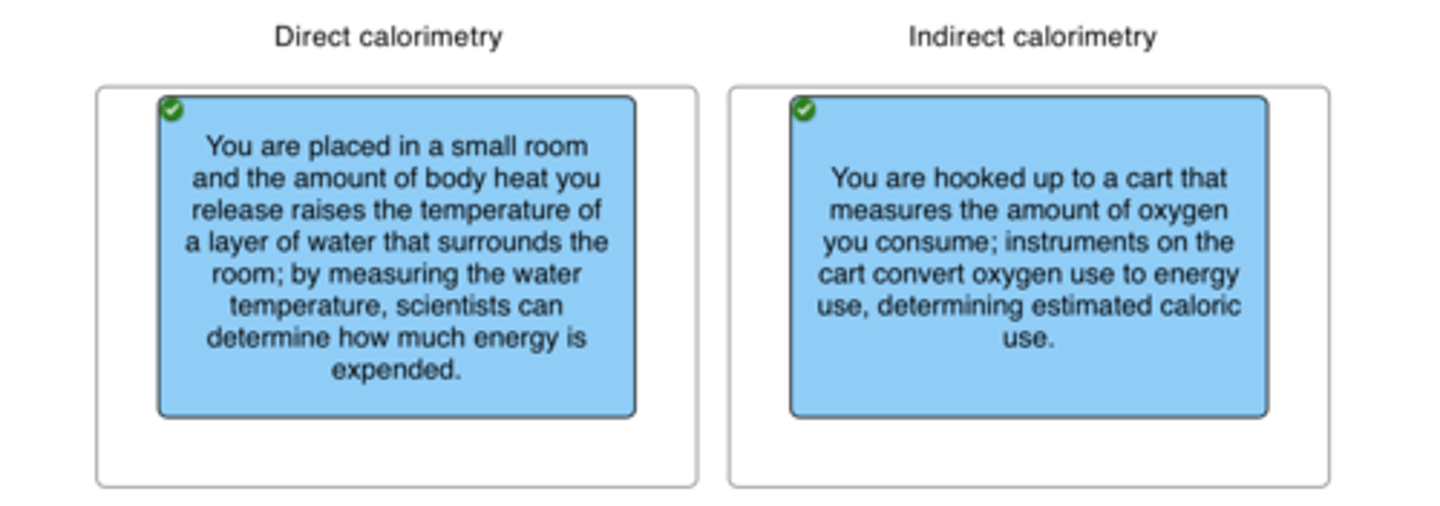
Indirect calorimetry
measurement of oxygen consumption as an estimate of resting metabolic rate

Respiratory exchange ratio (RER)
The amount of carbon dioxide produced relative to the amount of oxygen consumed-glucose = 1.0-fat = 0.7
-low RER indicates better fitness than a high RER
CHO vs Fat use relative to VO2
-the more CHO youre using, the more CO2 youre giving off
-more fat= less CO2
-more CHO means RER closer to 1 and higher intensity
-more fat means lower RER and lesser intensity
-training can allow you to use fat better and delay CHO usage, allowing you to exercise longer and at a higher intensity
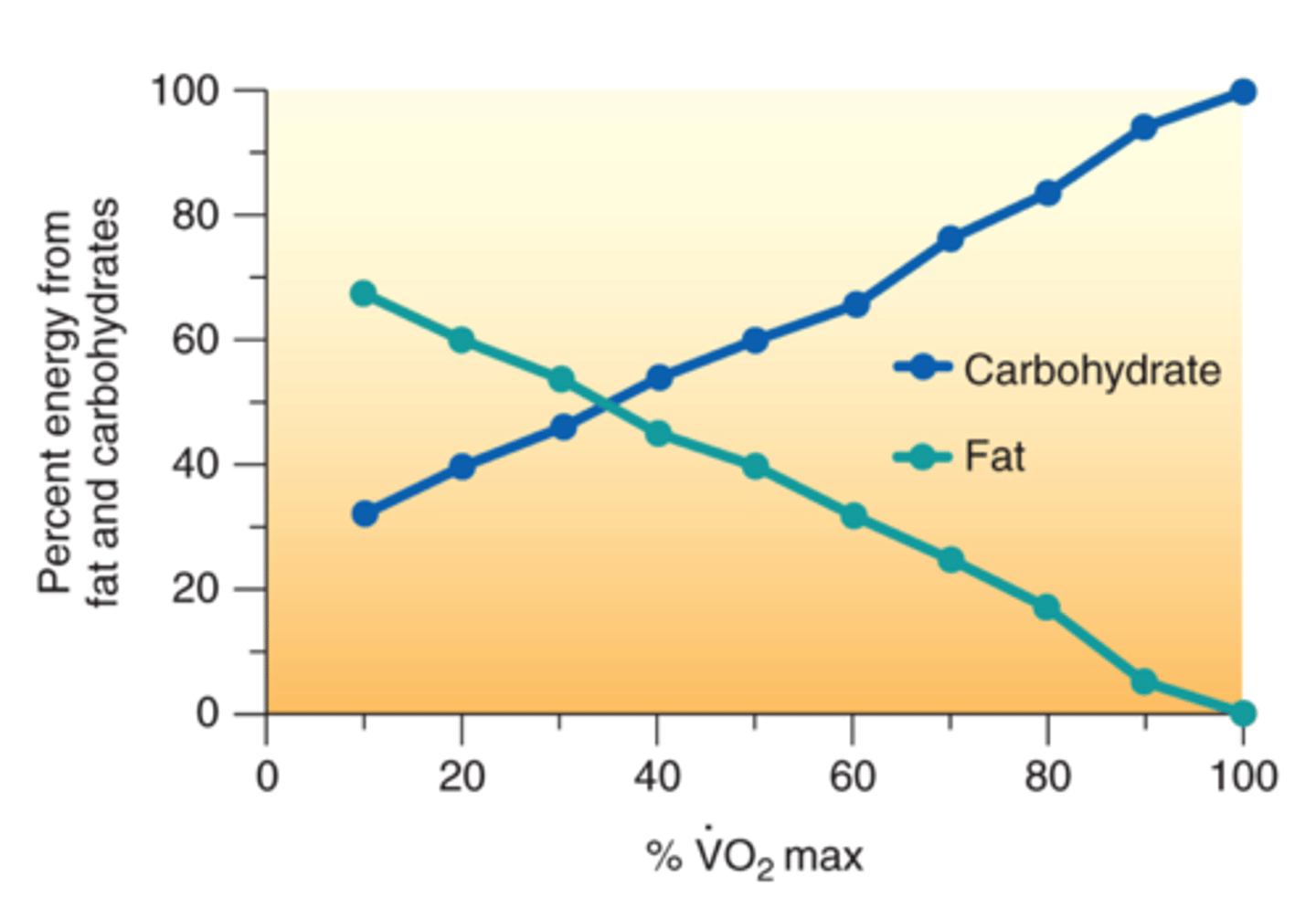
Energy expenditure (VO2) from rest-transition to exercise-submaximal (economy)
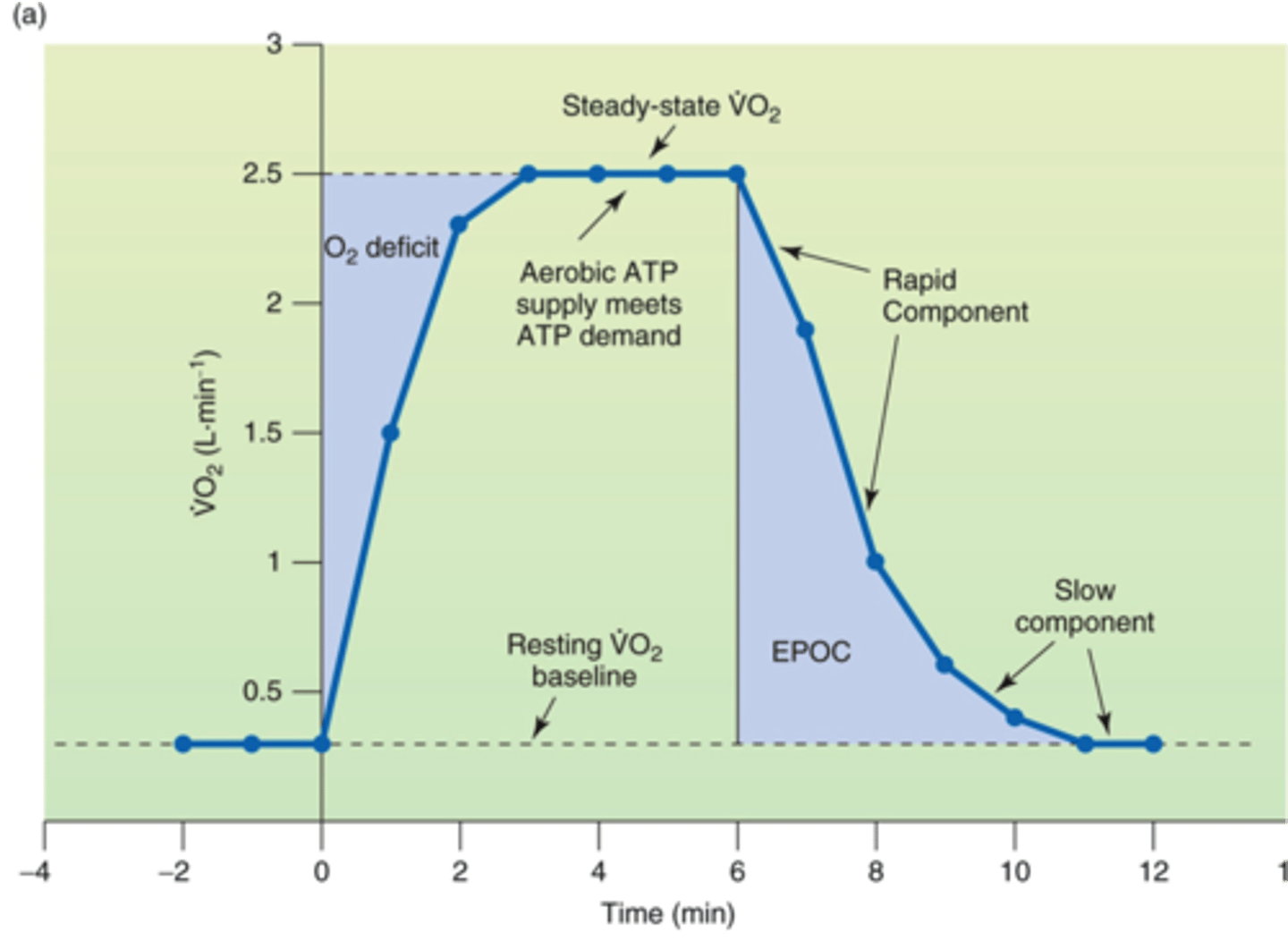
EPOC
excess post-exercise oxygen consumption; another term for oxygen debt
what is happening:
-lactic acid and CO2 removal
-restore PCr and myoglobin/ Hb O2
-Q10
-reestablished RMP
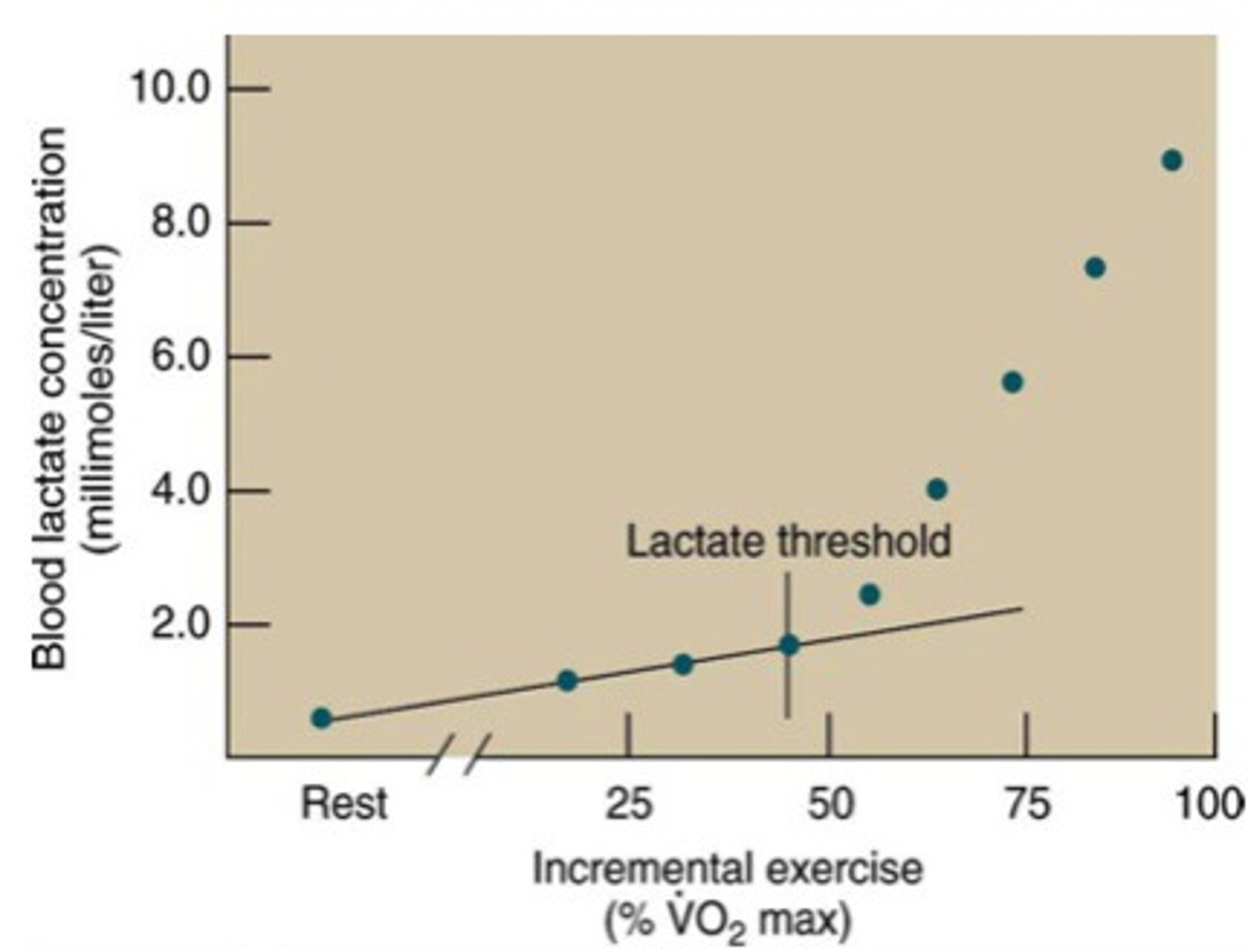
Lactate threshold
point at which lactate increases substantially above resting
-onset of anaerobic metabolism
-rate of lactate prod exceeds lactate clearance
-about 80% of max HR in LESS trained
-about 90% of max HR in well trained
Peripheral fatigue
problems with the neuromuscular junction between the motor nerve and muscle or problems within the muscle cell at the level of the sarcomere
Central nervous system fatigue
Perceived inability to do muscular work
Steroid vs Nonsteroid Hormones
steroid enter cell and act on DNA
Nonsteroid stay at cell surface, use AMP
Factors that dictate a given hormones response
-concentration of hormones (more [ ] = greater effect)
-concentration of receptors (2,000-10,000 per cell- up and down regulation)
-sensitivity, resistance and affinity
Pituitary gland
GH, ADH
Thyroid gland
T3/ T4 - calcitonin
Adrenal glands
Catecholamines - Cortisol -Aldosterone
Parathyroid gland
Parathyroid hormone
Pancreas
- Insulin -Glucagon
Kidneys
Renin- Erythropoietin
Regulation of glucose metabolism during exercise
Prolonged moderate intensity exercise of moderate duration
- Blood glucose remains steady (insulin is not needed)
- Liver's glucose release closely matches muscle's uptake until liver glycogen depleted
- Then, muscle glycogen & blood glucose get low & fatigue occurs
Regulation of Fat Metabolism During Exercise
- FFA mobilization and fat metabolism critical to endurance exercise performance
* Glycogen depleted, need fat energy substrates
* In response, hormones accelerate fat breakdown (lipolysis)
Hormonal Effects on Fluid and Electrolyte Balance During Exercise
-hemoconcentration increases w the onset of exercises (10%)
due to more fluid leaving the plasma into the tissues vs electrolytes
-this is due to increased osmotic pressure, increased BP and sweating
-decreases by 5-15% (sweating)
-SIGNALS RENIN and THEN ALDOSTERONE and ADH
Muscle fiber type & size aerobic
-increase size of slow twitch fibers by 25%
Capillary density aerobic
more capillary density with aerobic training
Myoglobin content aerobic
more myoglobin with aerobic training
Mitochondrial function aerobic
more mitochondrial function with aerobic training
Oxidative enzymes aerobic
more oxidative enzymes with aerobic training
QO2 aerobic
# of microliters of O2 taken up per mg of dry weight tissue per hour
-related to training volume
-lactate threshold allows for you to run faster as VO2 max maxes out
-increases w aerobic training
Purpose of adaptations of aerobic training
-minimal relationship to VO2 max
Carbohydrate stores aerobic
-glycogen utilized during exercise
-after exercise, ingest carbs to replenish glycogen stores
Fat stores aerobic
increase muscle TG stores by 2 fold with aerobic training
-beta oxidation enzymes increase
-more FFA mobilization allows us to not utilize glycogen as much to reduce depletion
Volume & Intensity Aerobic System
-ideal volume is individualistic (due to genetic window)-can increase with both frequency and duration-must be specific to activity
-intensity relative to individual-more intensity means shift to utilizing more CHO-more intensity = less volume
ATP-PCr adaptations Anaerobic Training
-training 79 legs of men separately
-both legs increases in strength
-15- 30 sec legs - increase in creatine phosphokinase and myokinase
- 5-6 sec legs - no increase in creatine phosphate or myokinase, but does increase strength
Muscle Fibers Anaerobic Training
increase fast twitch fibers
-increase in type IIa and decrease in type I
Glycolytic system adaptations Anaerobic Training
increase in enzymatic action in PFK, succinate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase, and LDH and phosphorylase
Other adaptations Anaerobic Training
-improvement of bicarbonate system
-lactic acid tolerance (temporary buffering of lactate production)
-beta-alanine and bicarbonate loading (sodium citrate)
-increase in force production
VO2 max Anaerobic Training
increases
Blood lactate Anaerobic Training
-reduced production and increased clearance
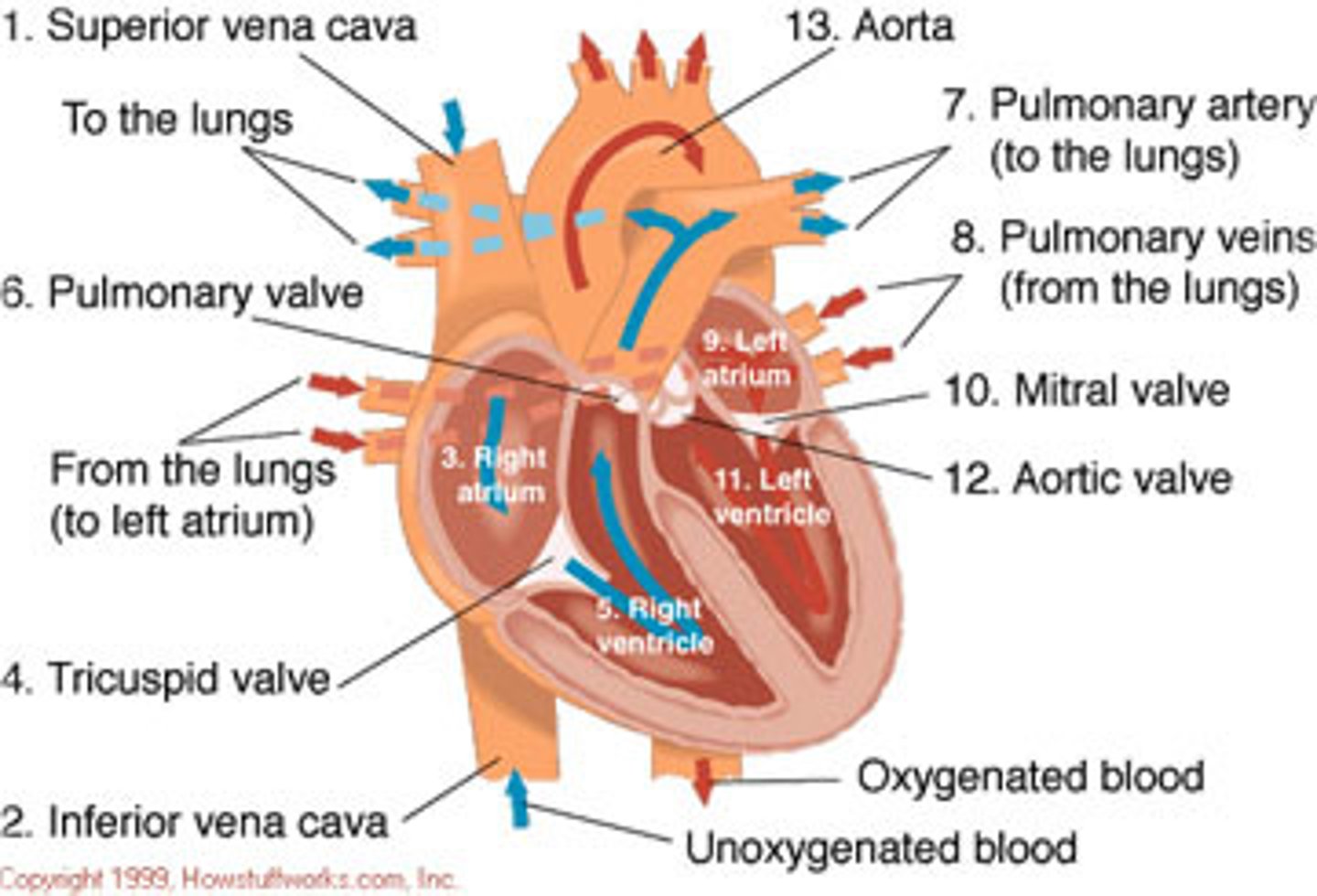
Blood flow through heart
From body -> Superior/Inferior vena cava -> Right Atria -> Tricuspid Valve -> Right ventricle -> Pulmonary valve -> lungs -> Left Atria -> Mitral Valve -> Left ventricle -> Aortic Valve -> Aorta -> body
Intercallated disks - desmosomes
Inside cardiac muscle.
Intercalated disks contain gap junctions and contract as a unit
Desmosomes resist stress
Synctium
The individual cells of the myocardium that collectively function so that the heart contracts as a unit
Ca++ handling in heart
Ca++ comes through Dyhydropyridine C++ channels on T-Tubles. Then travels to Ryanodine receptors to be released through Ca++ release channels in the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Torsional contraction
twisting of ventricles during contraction
Coronary Arteries
blood vessels that branch from the aorta and carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle
Automaticity (spontaneous rhythmicity) of heart
the property of cardiac cells to generate spontaneous action potentials
ECG
electrocardiogram
External measure of electrical activity of the heart
Phases of Depolarization
P wave- Atrial Depolarization
PR segment- AV nodal delay
QRS complex- Ventricular Depolarization
QT segment- ventricular systole
T wave- ventricular repolarization
TQ interval- Ventricular diastole
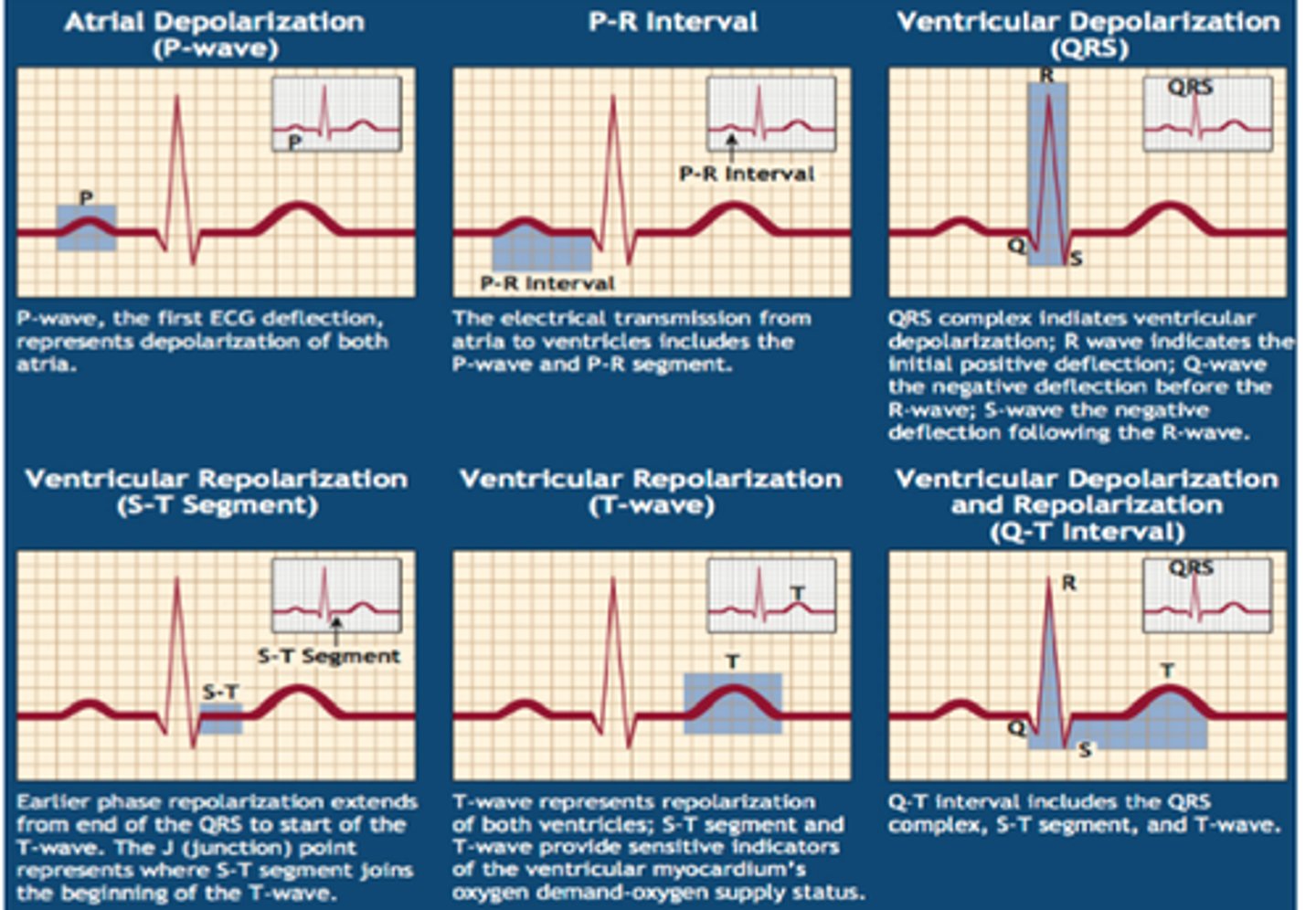
Absolute/Effective Refractory Period
Absolute- the time during which another stimulus given to the neuron will not lead to a second action potential
Effective- the longest S1-S2 interval that fails to capture or depolarize the tissue of interest
Relative Refractory Period
the interval of time during which a second action potential can be initiated
Extrinsic control - PNS & SNS & Endocrine
SNS- increased sympathetic activity through nerves or epinephrine -> B1 receptors in SA node -> increase open state of If and calcium channels -> Increase rate of spontaneous depolarization -> Increased HR
PNS- Increased parasympathetic activity (vagus nerve) -> Muscarinic/Cholinergic receptors in SA node -> Increase open state of K channels and closed state of Ca+ channels -> Decrease rate of spontaneous depolarization and hyperpolarized cells -0> decreased HR