Histology and Micturition
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is erythropoietin?
Hormone produced by the interstitial cells of the kidney, it stimulates erythropoiesis (formation of RBCs)
How is erythropoietin regulated?
Not regulated by the number of RBCs but by the oxygen levels in the tissue. Regulatory feedback route:
- Hypoxia leads to increased release of EPO
- EPO increased erythropoiesis which increase RBC formation
- Increaced RBCs lead to normoxia (normal level of oxygen), therefore less EPO
What are the layers that make up the excretory passageways?
Mucosa: luminal sheet of epithelium (mostly transitional) and lamina propria (loose to moderately dense FECT)
Sub-mucosa: usually merged with the lamina propria
Muscularis Externa: Usually 2-3 layers of smooth muscle, inner layer is longitudinal
Adventitia or Serosa: Loose FECT +/- mesothelium
What is the structure of transitional epithelium?
Balloon shaped, nuclei don't line up, fairly round shape at rest, when stretched the cells (especially the surface ones) become flattened - almost giving the appearance of stratified squamous.
What is the structural organisation of the ureter?
smooth muscle tube with transitional epithelium
What makes up the mucosa layer of the bladder? Submucosa? Muscle? Serosa?
Mucosa: luminal sheet of epithelium
Sub-mucosa: usually merged with lamina propria
Muscularis Externa: Three layers of smooth muscle bundles- inner layer is longitudinal, middle is circular, outer longitudinal. Muscle is heavily bundled with loose to moderate dense FECT between bundles.
Serosa: Loose FECT +/- mesothelium
What is the structure of the male urethra?
Mucosa is folded longitudinally, epithelium varies from T.E to stratified at urethral orifice, lamina propria (loose to moderately dense FECT) +/- muscularis mucosa.
Muscle layer is only 2-3 layers, with the inner longitudinal layer being sparse and the outer circular region is surrounded by skeletal muscle in the sphincter regions
(other layers same as generic excretory passageways)
How does horses urine differ from other domestic species?
In most animals, urine comp does not change between collecting ducts and the bladder. However horses glands in the renal pelvis and upper ureter that secrete mucus. Equine urine is therefore quite viscous.
Define micturition
urination
What muscles control the outflow of urine and what type of muscles are they?
- Detrusor muscle- smooth muscle
- Internal urethral sphincter - smooth muscle
- External urethral sphincter - striated muscle
What sort of nervous supply do the muscles that control outflow of urine receive?
Detrusor and Internal sphincter are controlled by ANS, External sphincter controlled by somatic NS
What is the trigone of the bladder?
Triangular area of smooth muscle inside the dorsal wall of the bladder neck- attached the ureters to the bladder neck and urethra
What effects do the sympathetic nervous system have on the bladder?
- relaxation of detrusor muscle
- contraction of internal sphincter
What effects do the parasympathetic nervous system have on the bladder?
contracts detrusor
What are the effects of the somatic nervous system of the bladder?
Controls the external sphincter as it is skeletal muscle, so can prevent bladder emptying, even when autonomic control attempts to bring about urine discharge.
Which part of the spinal cord do these sympathetic nerves originate from?
Inner sphincter sympathetic fibres and somatic fibres from outer sphincter originate from lumbar region
What causes bladder filling? (Sympathetic effects and somatic motor effects)
- Sympathetic effects: relaxation of the detrusor muscle and contraction of the internal sphincter
- Somatic effects: continuous excitation of the external urethral sphincter muscle
What receptors supply the sympathetic and somatic stimulation to the muscles?
- Sympathetic via noradrenaline acting on β-2 receptors on the detrusor muscle and ⍺-1 receptors on internal sphincter muscle
- Somatic motor effects come about via acetylcholine acting on nicotinic receptors
What occurs when filling is sufficient enough to stretch the smooth muscle? Picture and flow chart
- Myogenic reflex contraction of the detrusor, sensory nerves carry this info to the spinal cord, where there are two reflexes:
- Activation of parasympathetic motor nerves to the bladder
- Inhibition of the somatic motor drive to the external sphincter
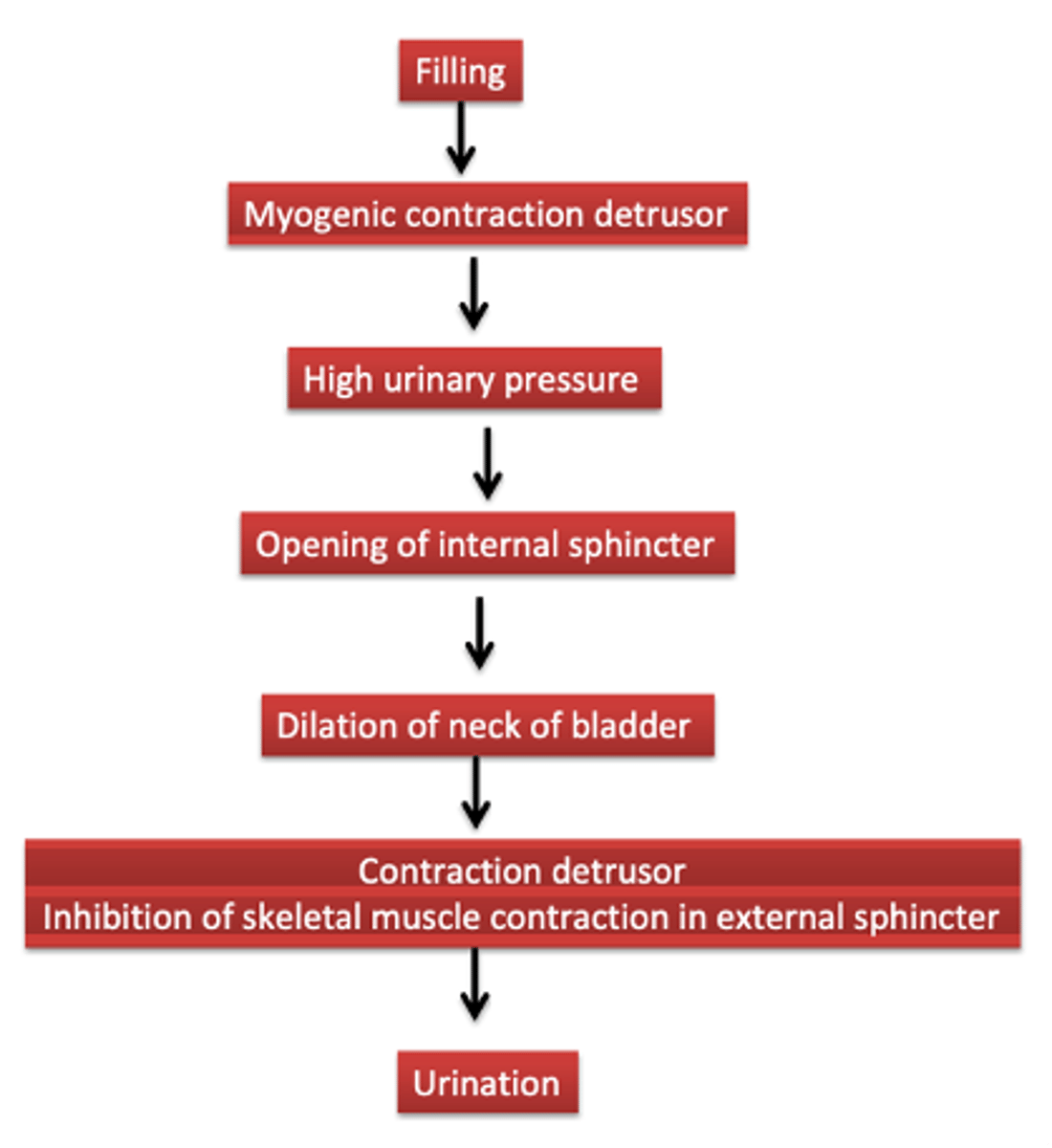
What are the parasympathetic and somatic motor effects upon bladder emptying?
- Parasympathetic effects: contraction of detrusor muscle (acetylcholine acting on MUSCARINIC receptors)
- Somatic motor effects: Inhibition of continuous excitation (inhibition of acetylcholine acting on nicotinic receptors)
How is bladder emptying controlled?
- Under voluntary control (somatic nerves supply external sphincter)
- Used for chemical communication
- Stretch signals from the bladder pass to the brain- so conscious of full bladder and CNS can override local reflexes so can up to a point deliberately inhibit bladder emptying
How is bladder emptying different in newborns?
Spinal reflex in new-borns so they can't control it
What nerves supply motor function to the bladder? What is their function
- Hypogastric nerve: sympathetic motor to internal sphincter (contracts) and detrusor (relaxes)
- Pelvic nerve: parasympathetic motor to detrusor (contracts)
- Pudendal nerve:somatic motor tonic contraction of external sphincter
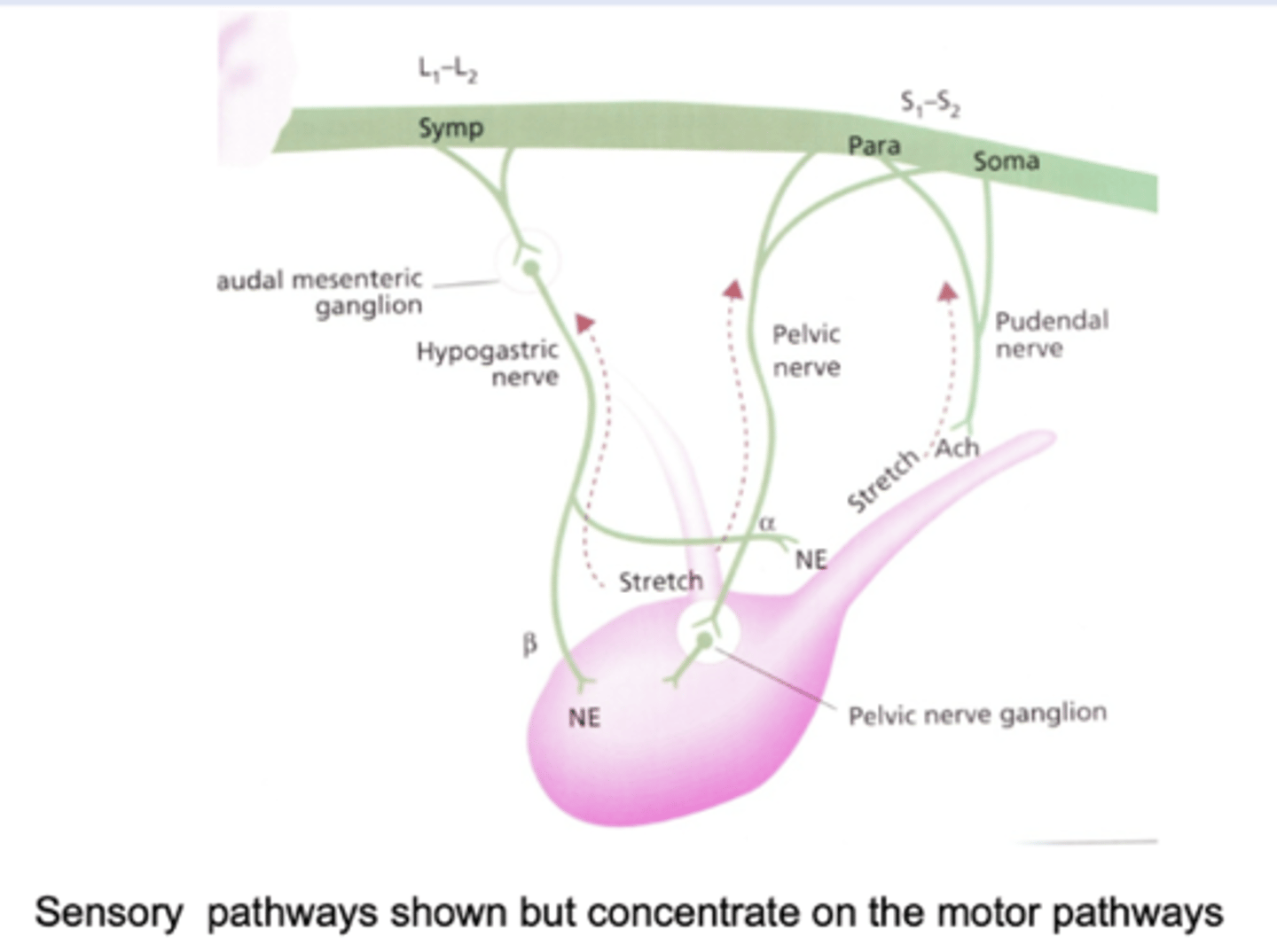
What would happen if the pelvic nerve was damaged?
Lack of parasympathetic motor neurones to the detrusor- prevents bladder emptying- bladder will contain urine but will have to be manually expressed (sphincters still working)
What would happen if there was a spinal lesion in the sacral segment of the spinal cord?
Loss pelvic and pudendal nerve
Lack of parasympathetic supply to detrusor and loss of external sphincter, bladder would be full but easy to express
What would happen if there was damage to the pudendal nerve?
Detrusor reflex ok- can void urine, however sphincter lacks control so urine leaks.
What will stimulate increased tone in the internal sphincter of the bladder?
Increased activity of the sympathetic nerve fibres to the sphincter muscle.