Lecture 29: Recap - bioavailability, dissolution and membrane transport
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what is pharmacodynamics?
what the drug does the to body
what is pharmacokinetics?
what the body does to the drug
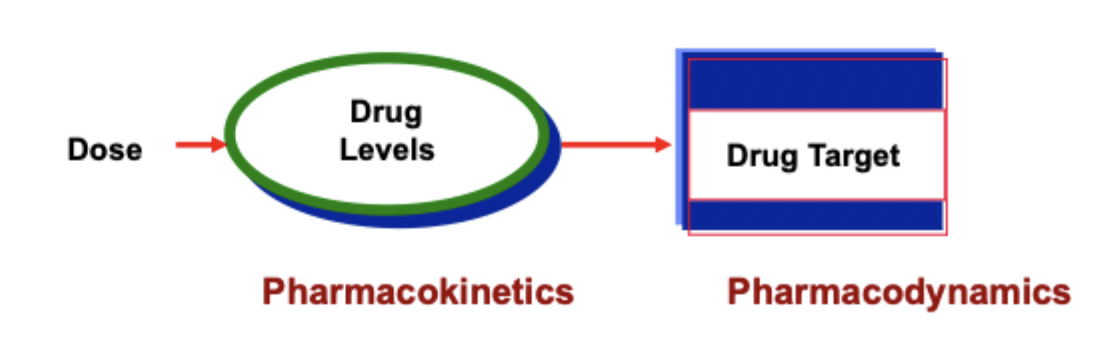
what is bioavailability?
a measure of the amount of drug that reaches its site of action and the rate at which it gets there
important for comparing dosage forms
what are the determinants for pharmacokinetics?
Liberation(release from dosage form)
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
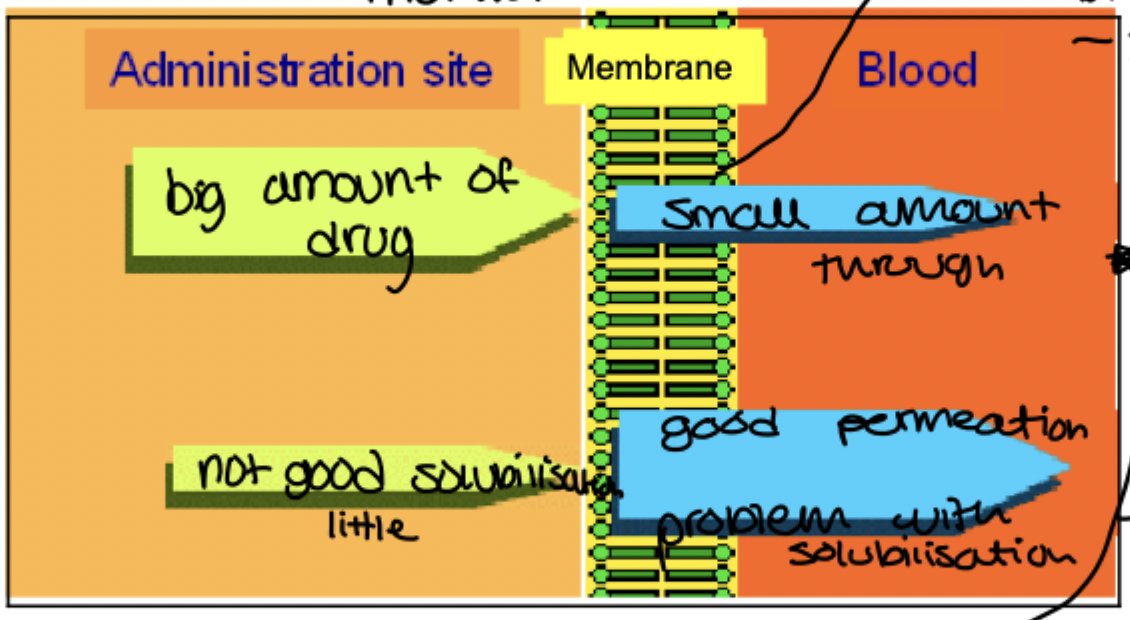
After extra vascular administration, what are the 2 steps the drug appearance in blood demands?
release: drug dissolves at administration site
absorption: drug crosses biomembrane to reaach blood
slowest step controls overall rate of absorption
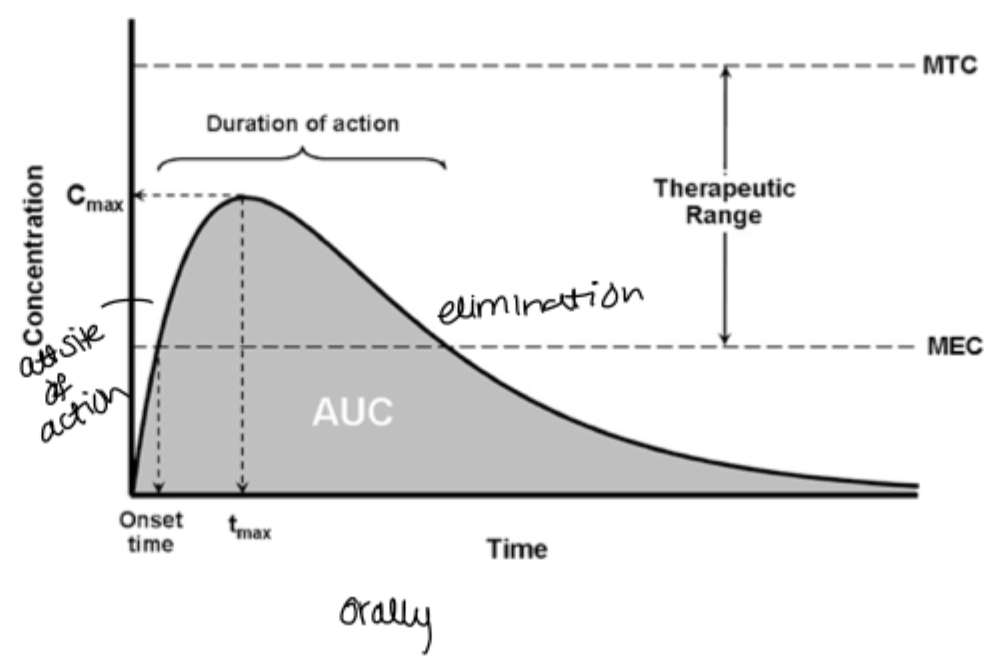
Explain what is shown on the graph here
drug is rapidly released but only a small amount passes through the membrane so its typically hydrophilic molecules. permeation is the limiting factor
drug is poorly soluble but has good permeation which is typical for lipophilic molecules
what does the process of dissolution of a solid crystal in a liquid involve?
solvation of a drug at crystal surface to create a stagnant layer of saturated solution
diffusion of dissolved molecules across this layer into bulk solution
observed rate depends on slowest step
what is the overall rate of dissolution at constant temp equation?
Noyes-whitney equation
S= surface area of particle

how can the solubility(Cs) of a weakly acidic drug be predicted?
pH of solution
pKa
Solubility of free Unionised form of drug(So)
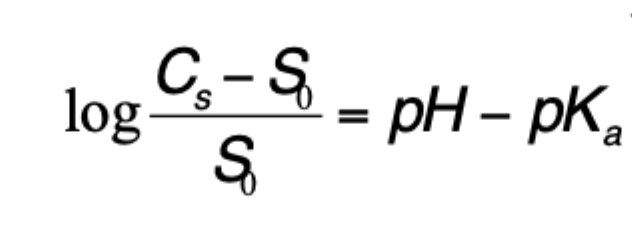
how can the solubility(Cs) of a weakly basic drug be predicted?
pH of solution
pKa
solubility of free unionised form of drug(So)
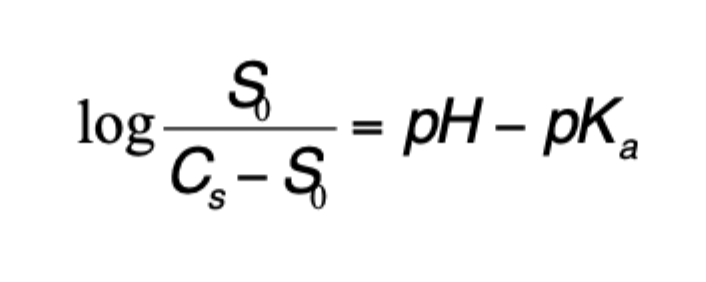
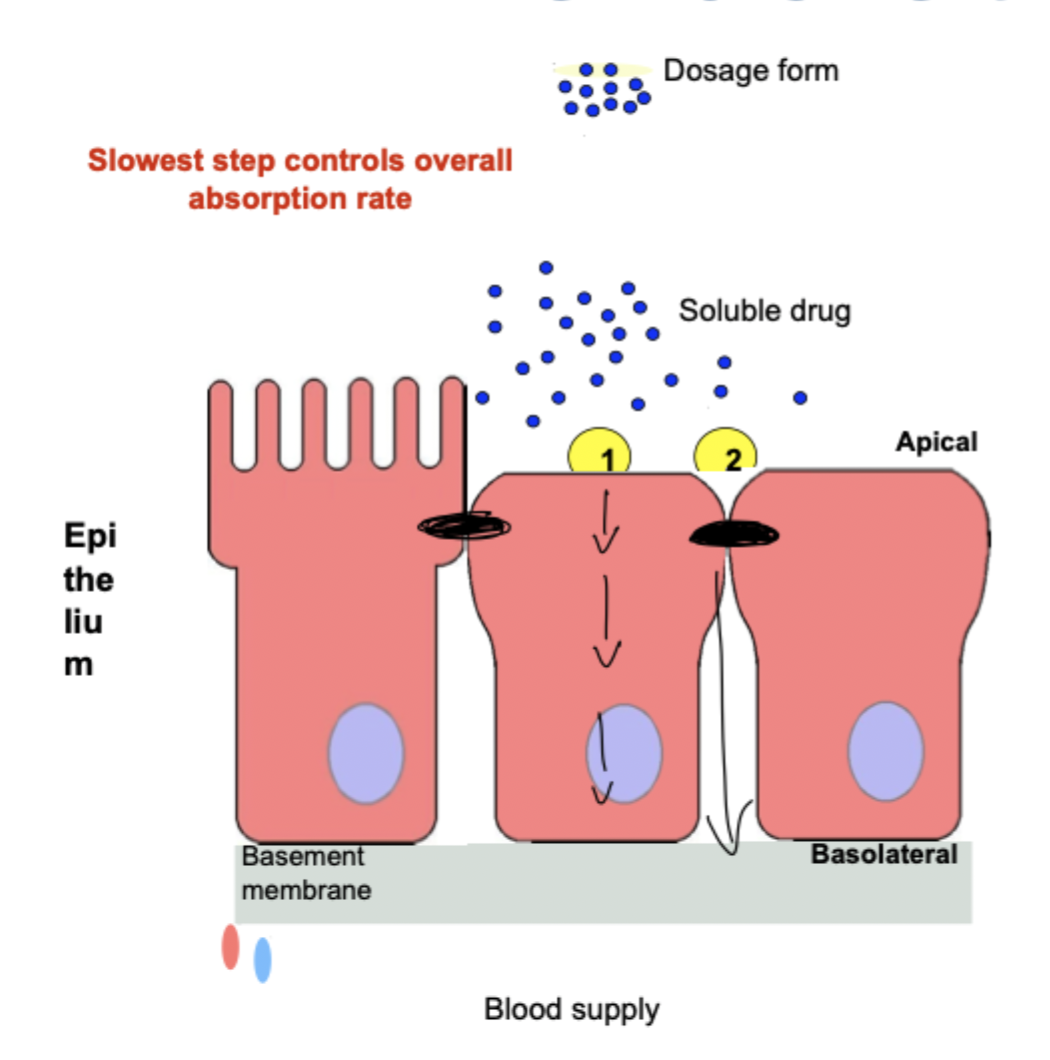
what are the 2 methods of membrane transport of drug?
transcellular pathway
paracellular pathway
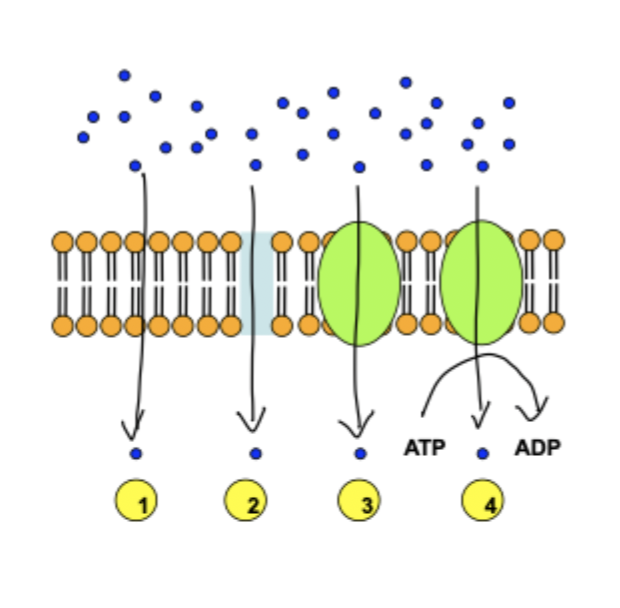
what are the 4 pathways of transcellular absorption(Major)?
passive diffusion
aqueous pore
facilitated diffusion
active transport
how does passive diffusion take place in transcellular absorption?
main pathway of drug absorption
solutes diffuse down a conc gradient
must partition into the lipid bilayer and out into cytoplasm
how do solutes move across aqueous pores in transcellular absorption?
continuous
hydrophilic channel created by aquaporin proteins
allows transport of small neutral solutes such as urea and glycerol
how does facilitated diffusion take place in transcellular absorption?
selective
carrier mediated transport of drug down conc gradient
how does active transport take place in transcellular absorption?
selective
carrier mediated transport of drug down or against conc gradient
needs energy from ATP
what happens to drug molecules not in equilibrium?
it moves towards equilibrium which means flow(flux) must occur
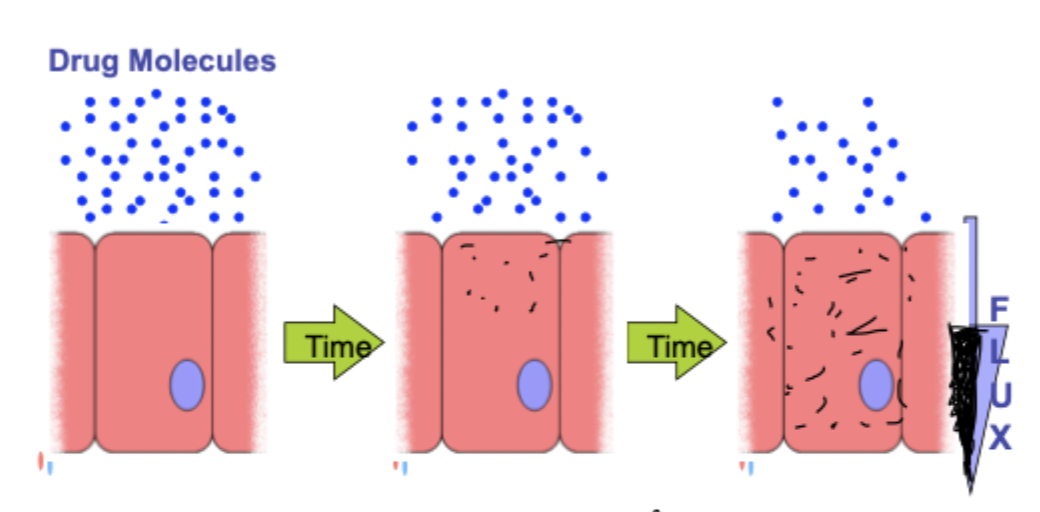
what is the formula for flux
F= C x V x A
conc
velocity
area
what is ficks first law equation?
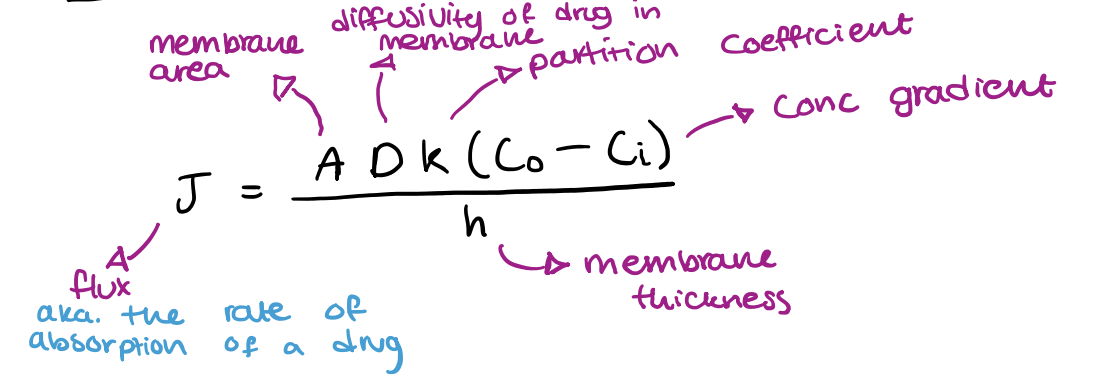
what happens to flux as surface area increases (A)?
flux increases
what happens to flux as membrane thickness increases (DeltaX)?
flux decreases(inversely proportional)
what happens to flux as conc gradient increases (C1-C2)?
flux increases(directly correlated)
ficks first law of diffusion:
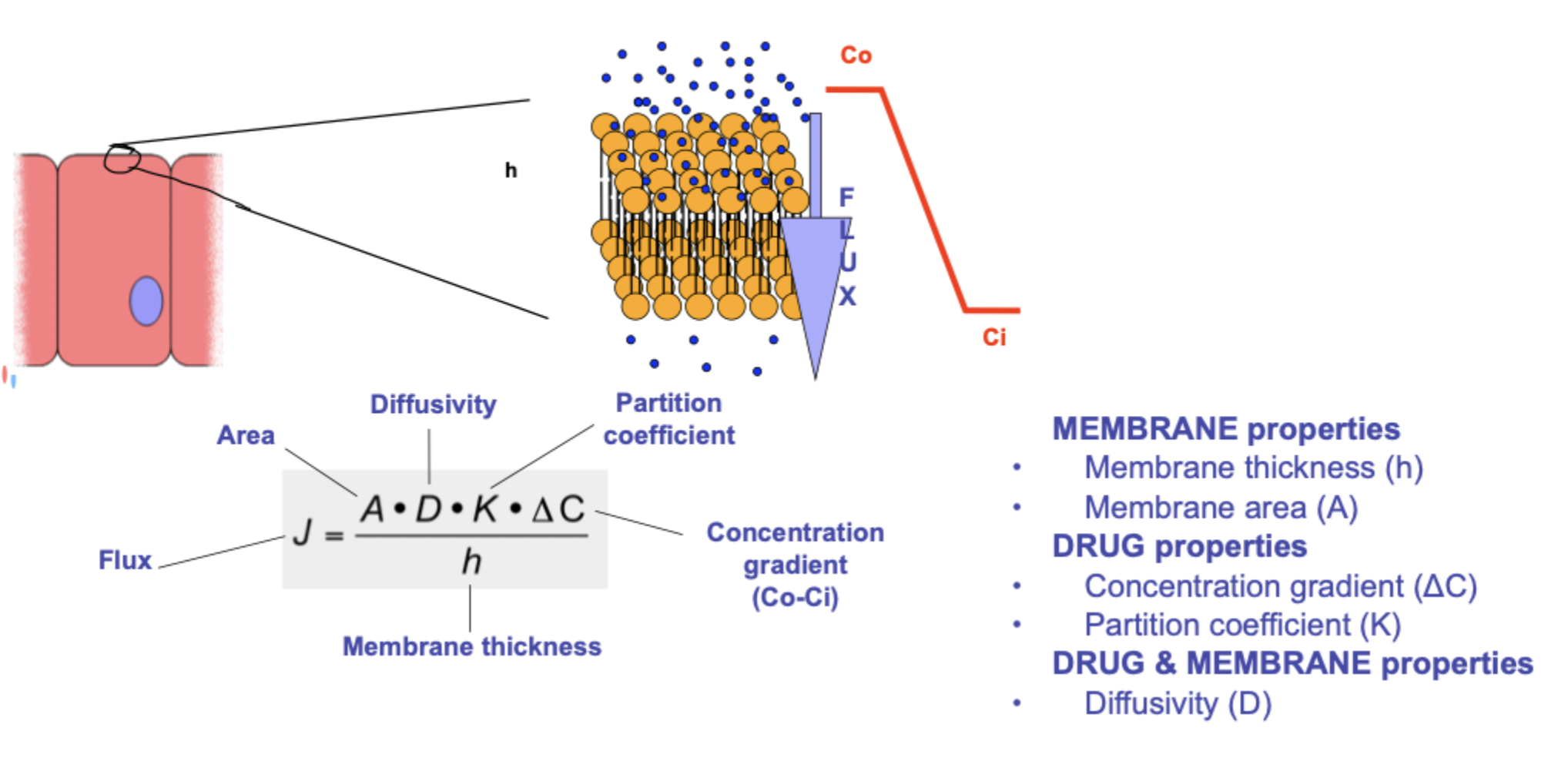
what is the partition coefficient?
it quantifies the distribution of drug between membrane and aqueous phases which it separates
octanol-water partition coefficient(Log P) is often used to characterise a drugs lipophilicity
K=Coil/Cw
K= drugs relative affinity for oil compared to water
how does a drugs lipophilicity affect its ADE?
has to be lipophilic to cross cell membranes
too lipophilic may be deposited in fatty tissues
features of the octanol water partition coefficient:
e.g conc of drug is 10x more soluble in octanol than water if P=10 and logP=1

most drugs are weak acids or bases so they exist in a solution as an equilibrium of unionised and ionised forms depending on the pH of the environment and the pKa of the drug
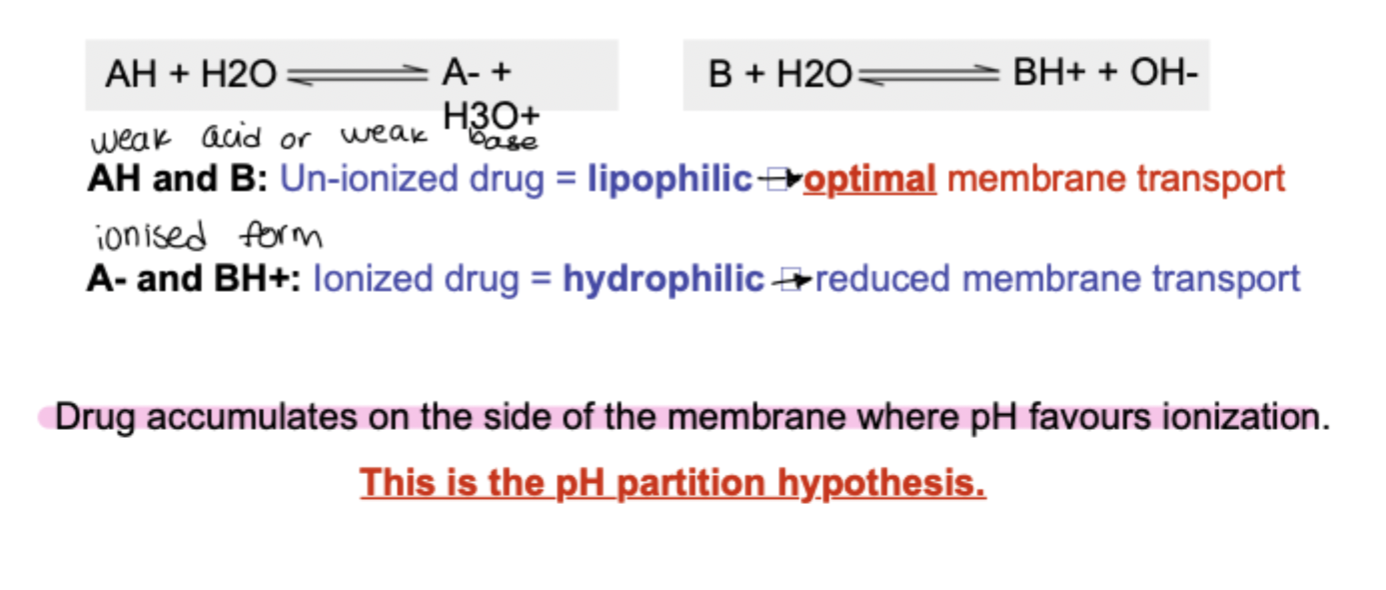
what are the pH partition hypothesis limitations?
doesnt take into account:
type of epithelium
surface area of absorption site
active transport of drugs
what is lipinskis rule of 5
predicts good oral bioavailability
molecular weight</500
log P </ 5
no more than 5 H bond donors
no more than 10 H bond acceptors