orgo unit 1
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
organic chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
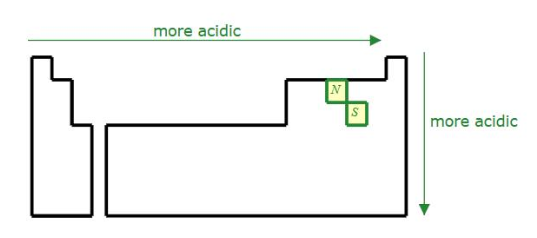
Acidity Trend on the PT
To the right and down (higher E- which is more stable when the H leaves)
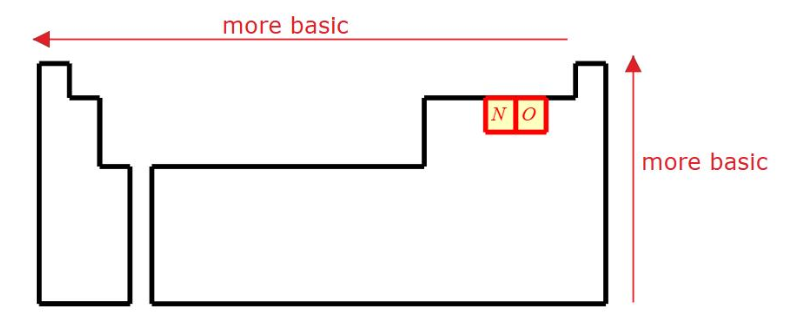
Basic Trend on the PT
To the left and up (lower e-neg which holds on tighter to its H)
Basic sites
Will have lone pairs, and generally have the ability to gain an H atom
Acidic Sites
Will generally have an H on an e-neg atom that can be donated/ will be fine/stable without it.
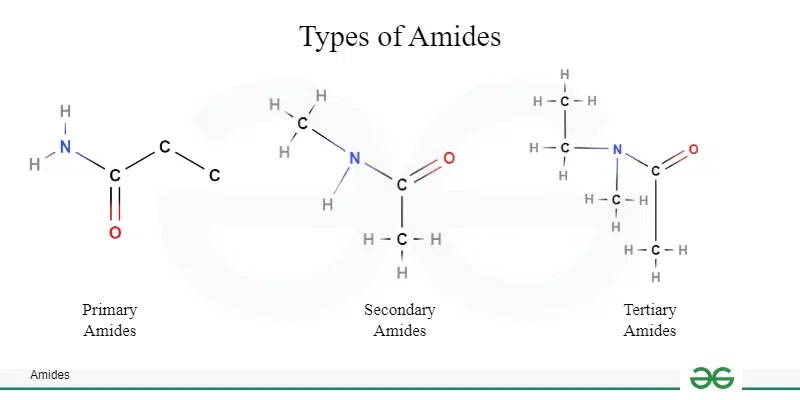
What makes an amide, an amide?
In an amide the N atom is directly bonded to a carbonyl =CO carbon. |
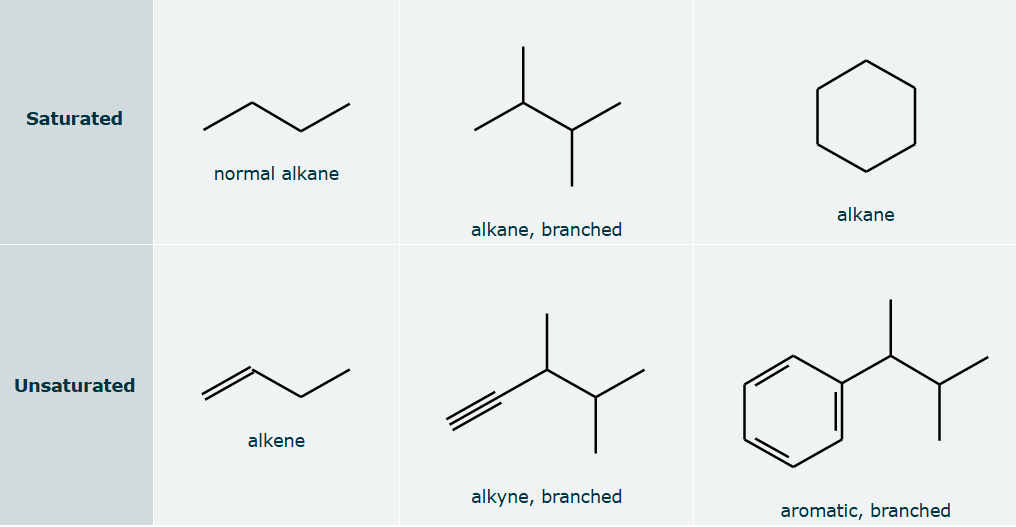
Hydrocarbon Rules
Hydrocarbons with no double or triple bonds are called alkanes. We also say that these compounds are saturated.
Hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds are called alkenes, and hydrocarbons with one or more triple bonds are called alkynes. We also call both alkenes and alkynes unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Alkanes with a carbon skeleton that can be drawn as just one straight line of bonded carbon atoms are called normal alkanes.
Hydrocarbons with a carbon skeleton containing a main chain and one or more side chains are called branched hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons that contain benzene rings are called aromatic.
axial bonds are
first, directed vertically parallel to the axis of the ring
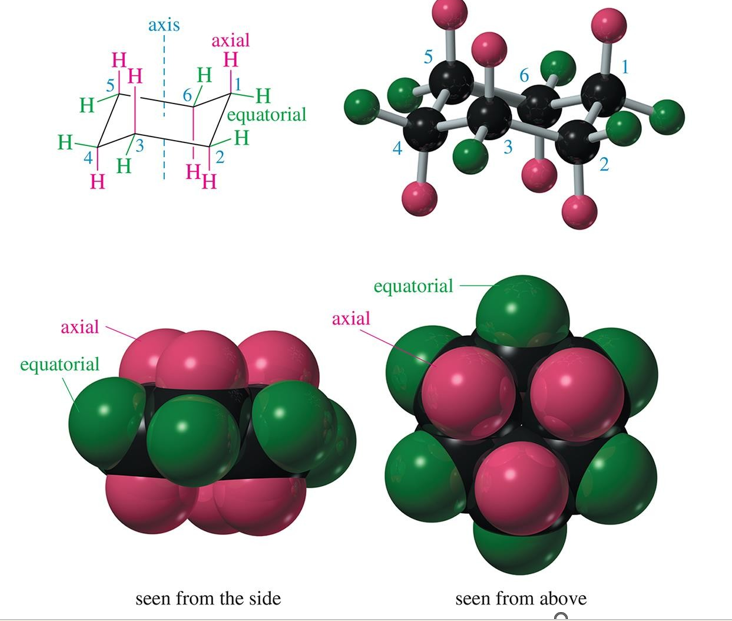
equatorial bonds are
second, directed outward toward the equator of the molecule
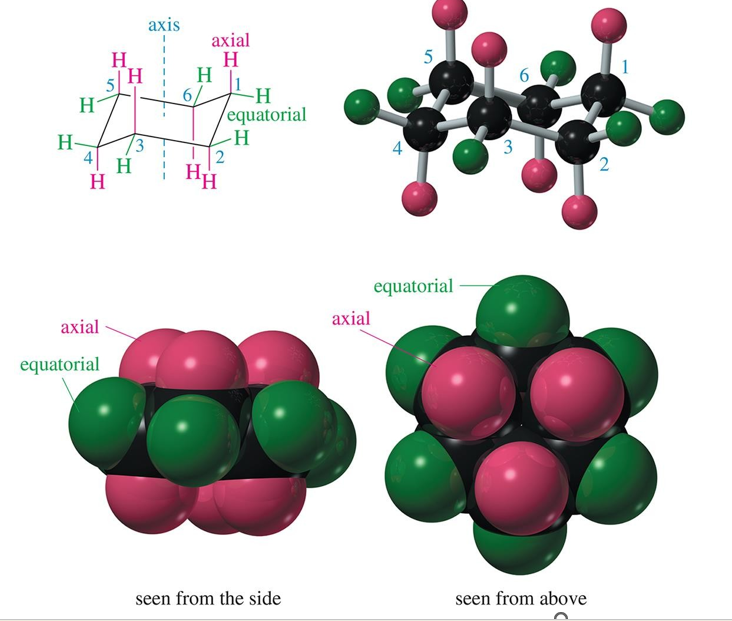
what happens to axial and equatorial bonds because of a chair conversion?
the axial and equatorial bonds become one another. (half chair is a boat?)
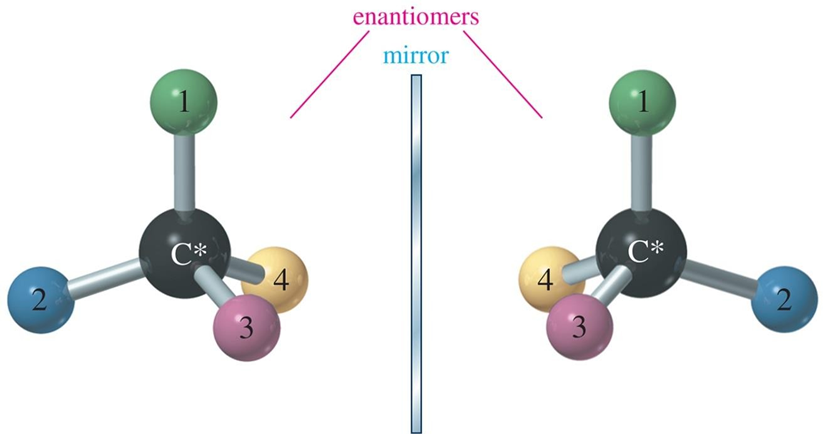
chiral
mirrored image is different of the image (all stereoisomers) (ur hands)(nonsuperimosable)
achiral
mirrored image is the same (mittens or socks) (cis/trans, z/e)
Stereoisomers
molecules with the same molecular formula and connectivity but different spatial arrangements of atoms. enantiomers, nonsuperimosable. any chiral molecule must have an enantiomer (nonsuperimosable part)
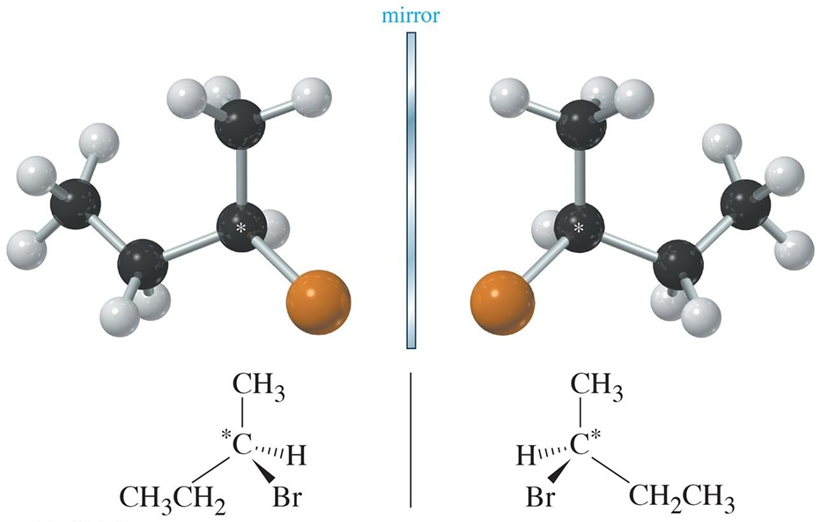
chiral carbon atom
asymmetric carbon atom, bonded to 4 DIFFERENT groups (chiral).
must be tetrahedral (sp3 hybridized).
the mirror image will be a diff compound (enantiomer).