The Diencephalon & The Cerebellum: Test 4
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are the 4 divisions of the brain?
cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brainstem
The ________________ is located in the center of the brain and is hidden almost completely by the cerebral hemispheres in an external view. Consists the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus
diencephalon
The _______________ consists of two-oval shaped masses and acts like a “gateway” for signals traveling to the cerebral cortex.
thalamus
The ______________ is shaped like a funnel and is located anterior and inferior to the thalamus. it plays an important role in homeostasis and regulating the endocrine system.
Hypothalamus
The ______________ is not pat of the diencephalon, it is anatomically and functionally linked to the hypothalamus. It is connected to the hypothalamus by a short stalk called _________________. The hypothalamus regulates the activity of the pituitary gland.
pituitary gland
infundibulum
The ____________ is an endocrine organ that produces the hormone melatonin
pineal gland
The _____________ is located at the posterior and inferior portion of the brain. Functions include coordinating muscle movements.
Composed of two hemispheres that are connected by a __________.
The ridges in the cerebellum are called __________ ________.
White matter called __________ __________ connect the cerebellum to the brainstem and information flowing into or exiting the cerebellum travels along the fibers of the peduncles.
cerebellum
vermis
folia
arbor vitae
cerebellar peduncles
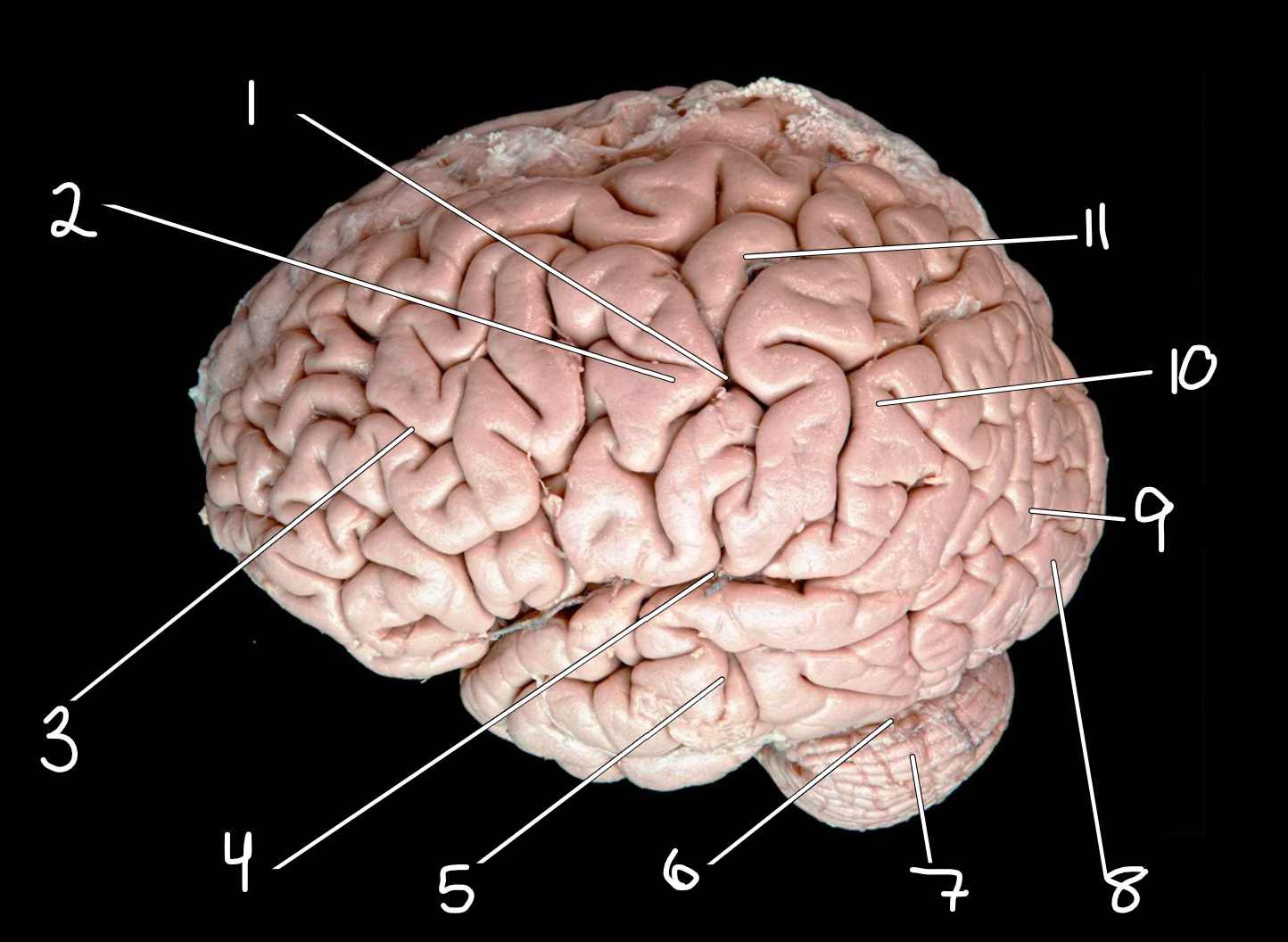
Left Cerebrum and cerebellum: lateral view
1.central sulcus
2.precentral gyrus
3.frontal lobe
4.lateral sulcus
5.temporal lobe
6.transverse fissure
7.cerebellum
8.occipital lobe
9.parieto-occipital sulcus
10.parietal lobe
11.postcentral gyrus
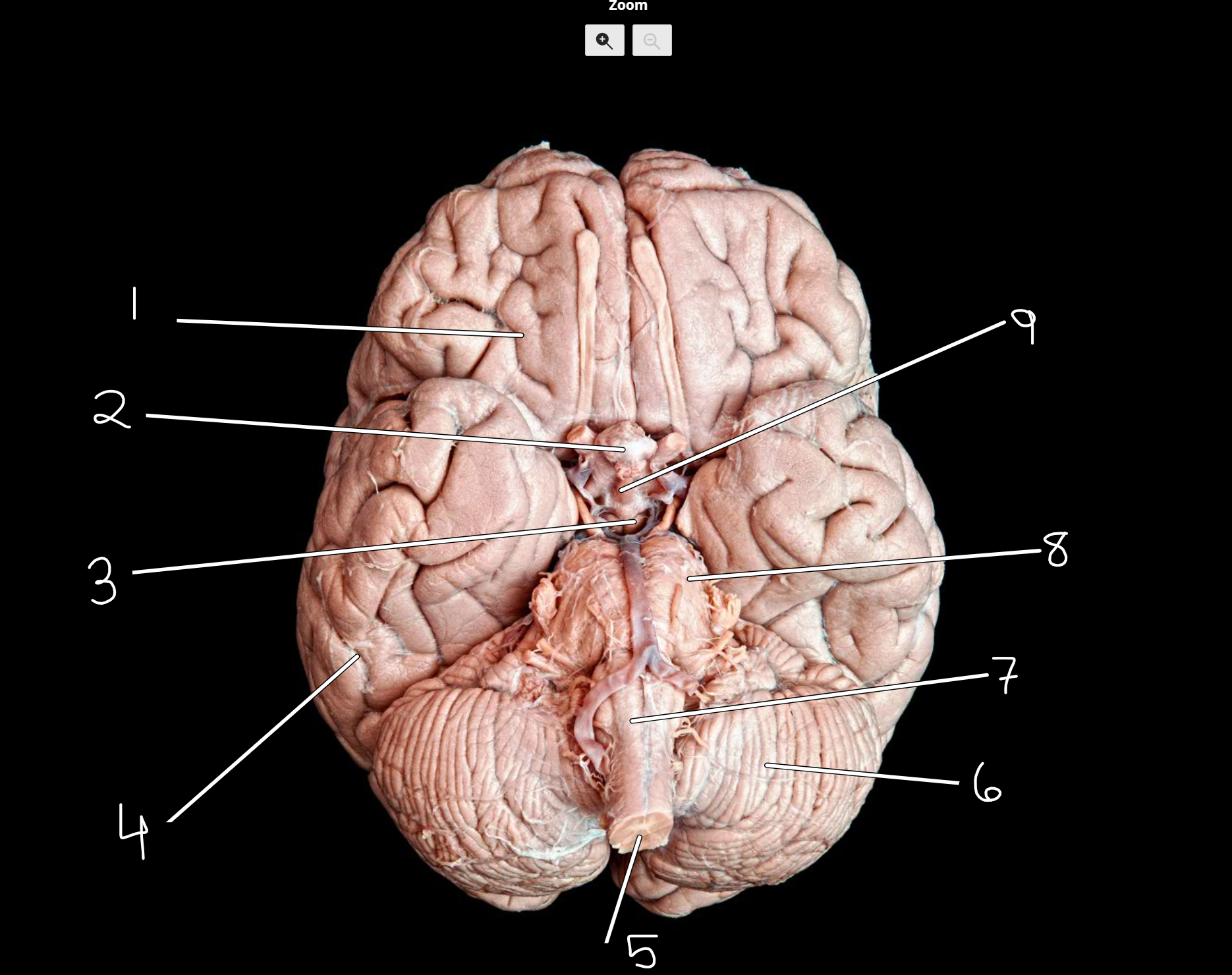
Brain structures: inferior view
1.frontal lobe
2.pituitary gland (hypophysis)
3.mammillary bodies
4.temporal lobe
5.spinal cord
6.cerebellum
7.medullar oblongata
8.pons
9.infundibulum
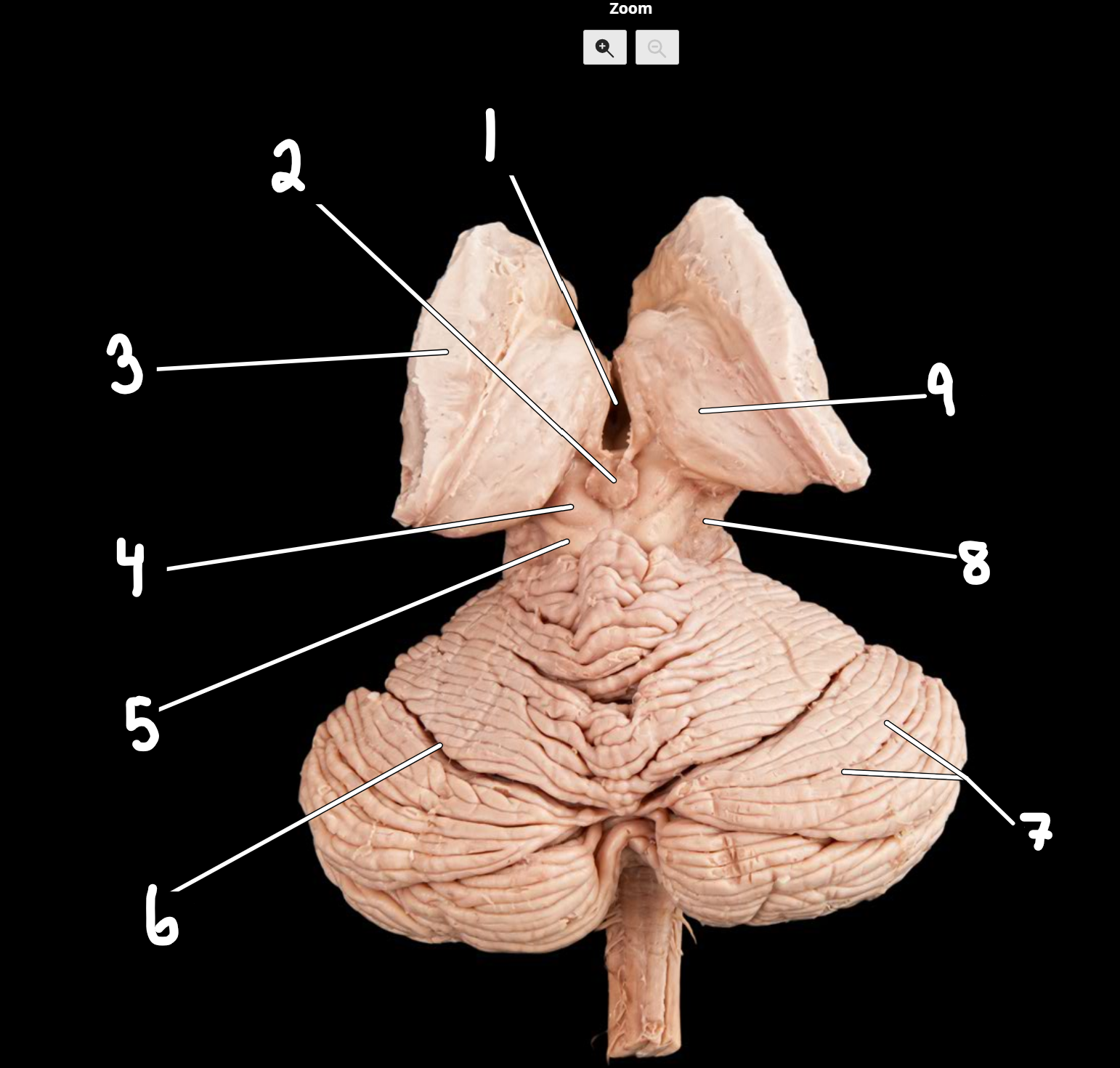
Thalamus: midbrain: cerebellum: posterior view
1.third ventricle
2.pineal gland
3.lentiform nucleus
4.superior colliculus
5.inferior colliculus
6.cerebellar fissure
7.folia
8.cerebral peduncle
9.thalamus
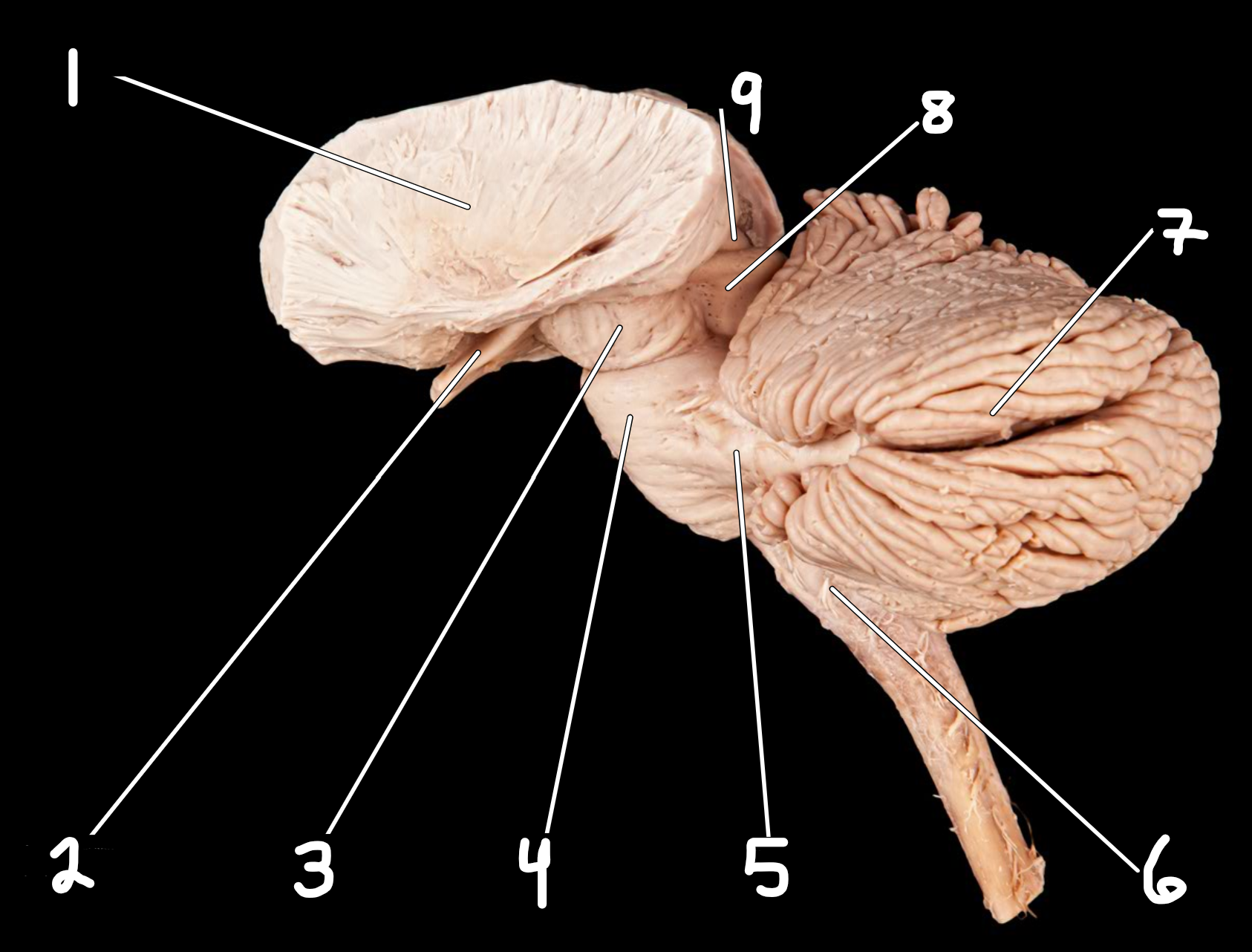
Midbrain and cerebellum: lateral view
1.internal capsule
2.optic nerves and tracts
3.cerebral peduncle
4.pons
5.middle cerebellar peduncle
6.olive
7.cerebellum
8.superior cerebellar peduncle
9.inferior colliculus
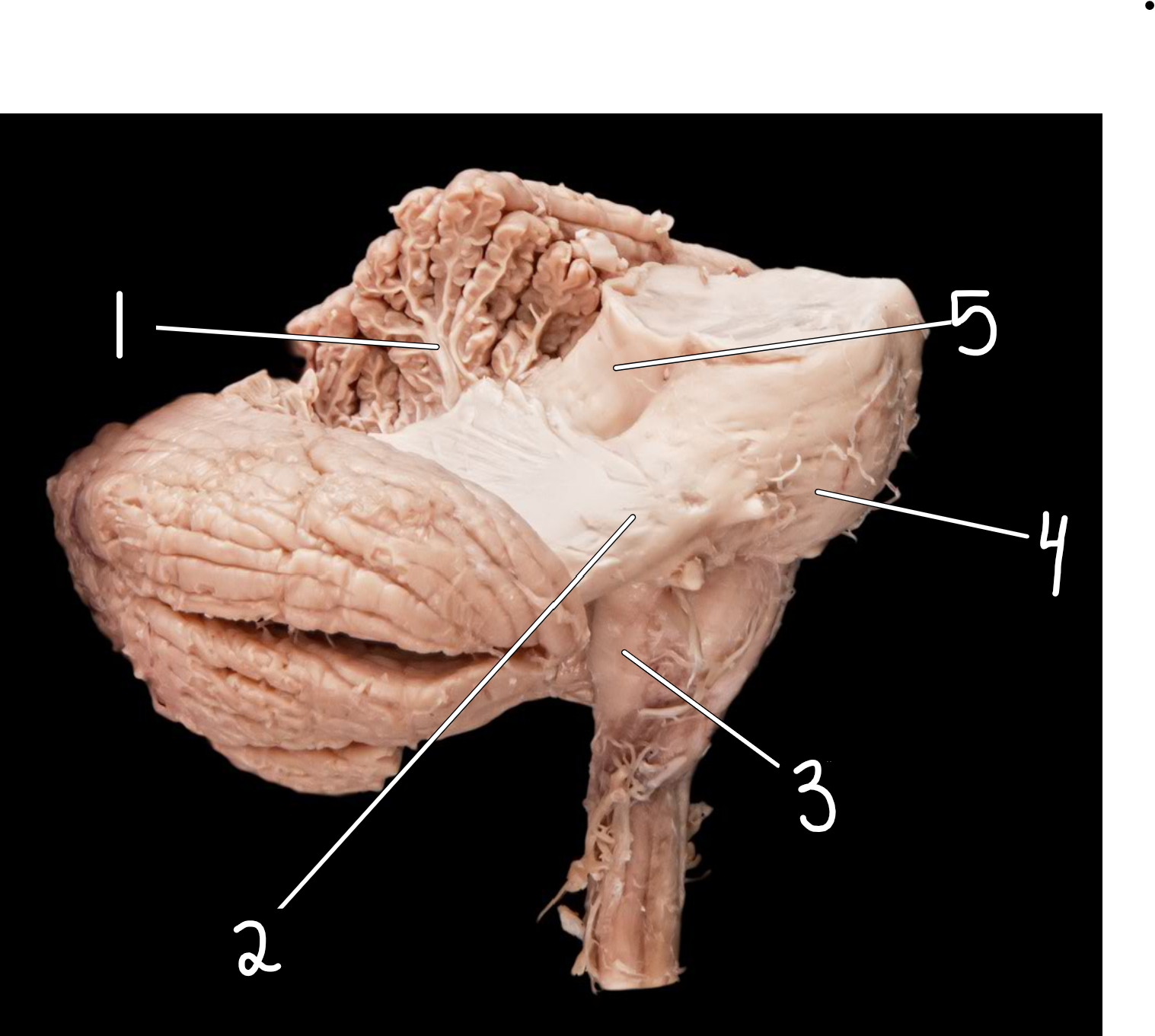
Cerebellar peduncles: lateral view
1.arbor vitae
2.middle cerebellar peduncle
3.inferior cerebellar peduncle
4.pons
5.superior cerebellar peduncle
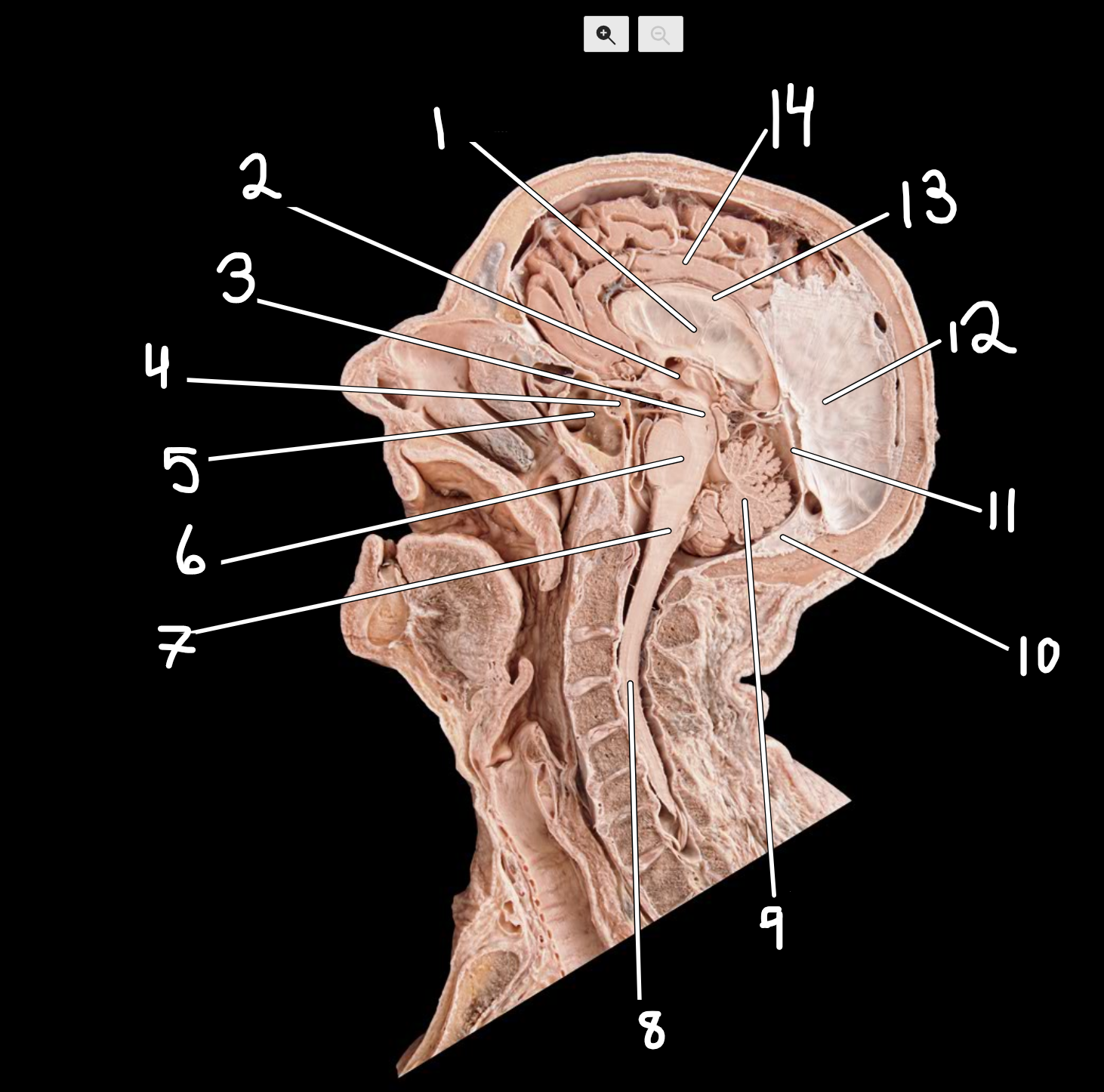
Midsagittal head
1.septum pellucidum
2.diencephalon
3.midbrain
4.pituitary gland
5.sphenoid sinus
6.pons
7.medulla oblongata
8.spinal cord
9.cerebellum
10.falx cerebelli
11.tentorium cerebelli
12.falx cerebri
13.corpus callosum
14.cerebrum
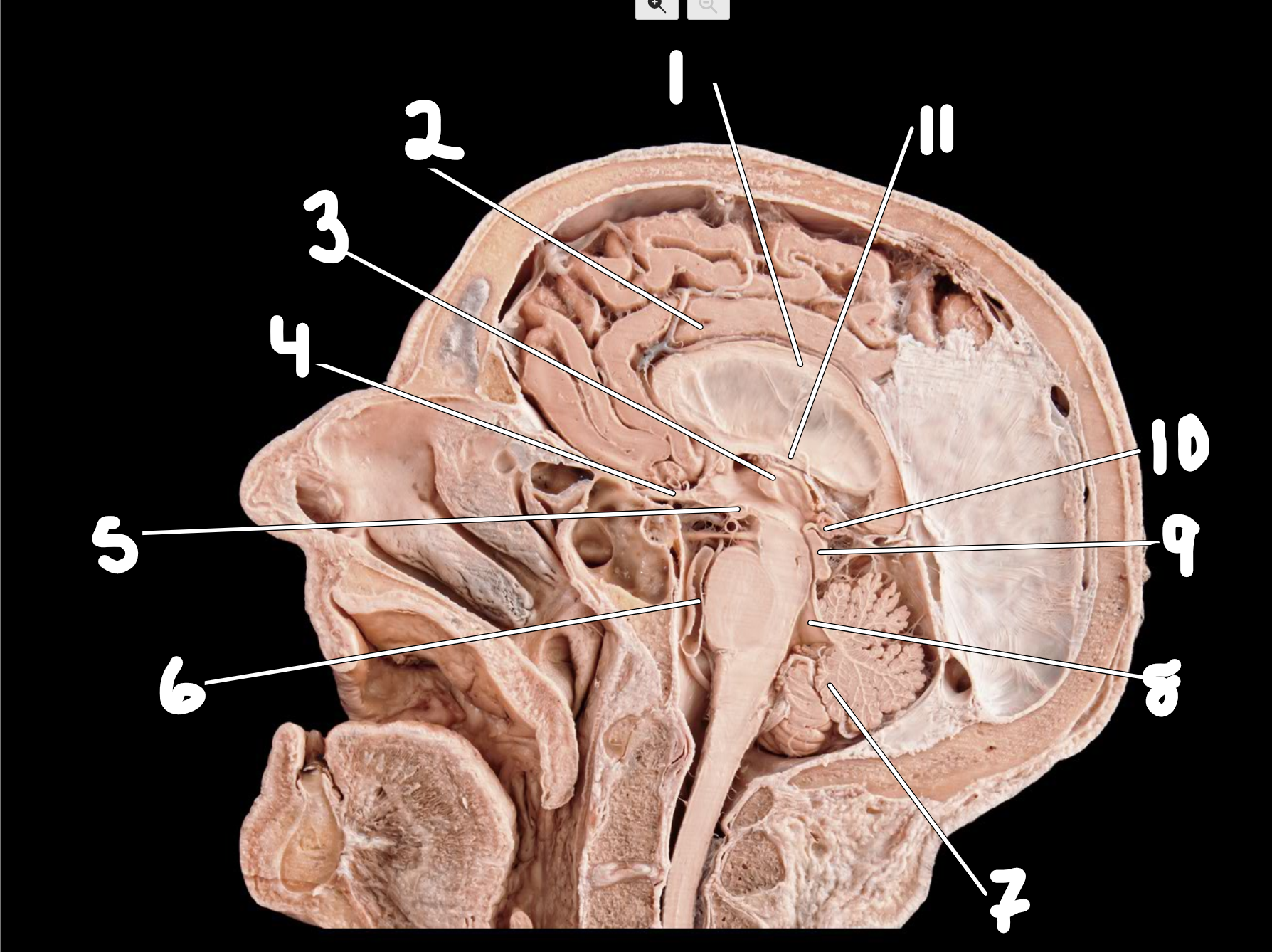
Midsagittal head
1.corpus callosum
2.cingulate gyrus
3.thalamus
4.optic nerve
5.mammillary body
6.basilar artery
7.cerebellum
8.fourth ventricle
9.corpora quadrigemina
10.pineal gland
11.fornix
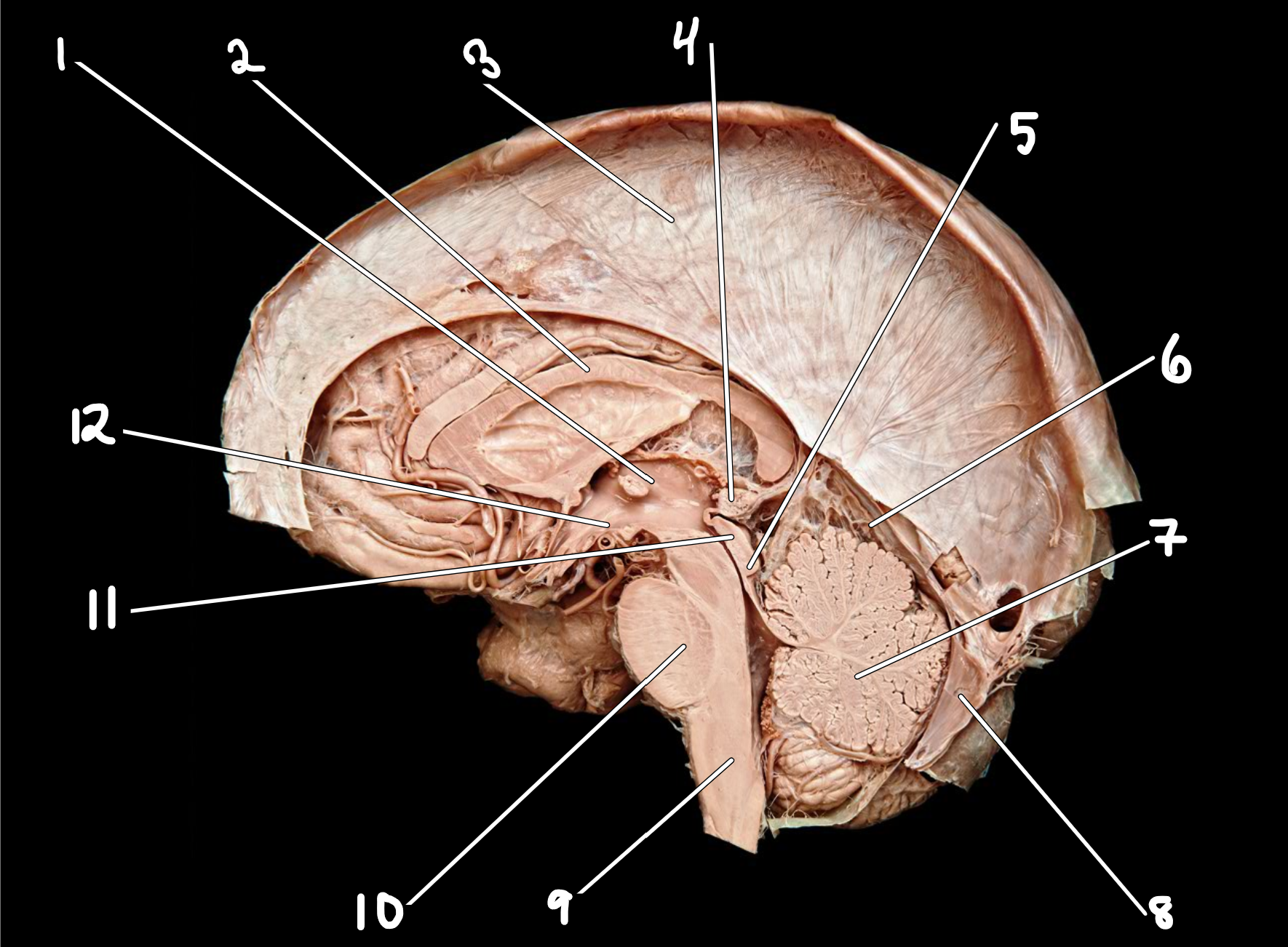
Midsagittal brain with dura mater
1.thalamus
2.corpus callosum
3.falx cerebri
4.pineal gland
5.inferior colliculus
6.tenroium cerebelli
7.cerebellum
8.falx cerebelli
9.medulla oblongata
10.pons
11.superior colliculus
12.hypothalamus
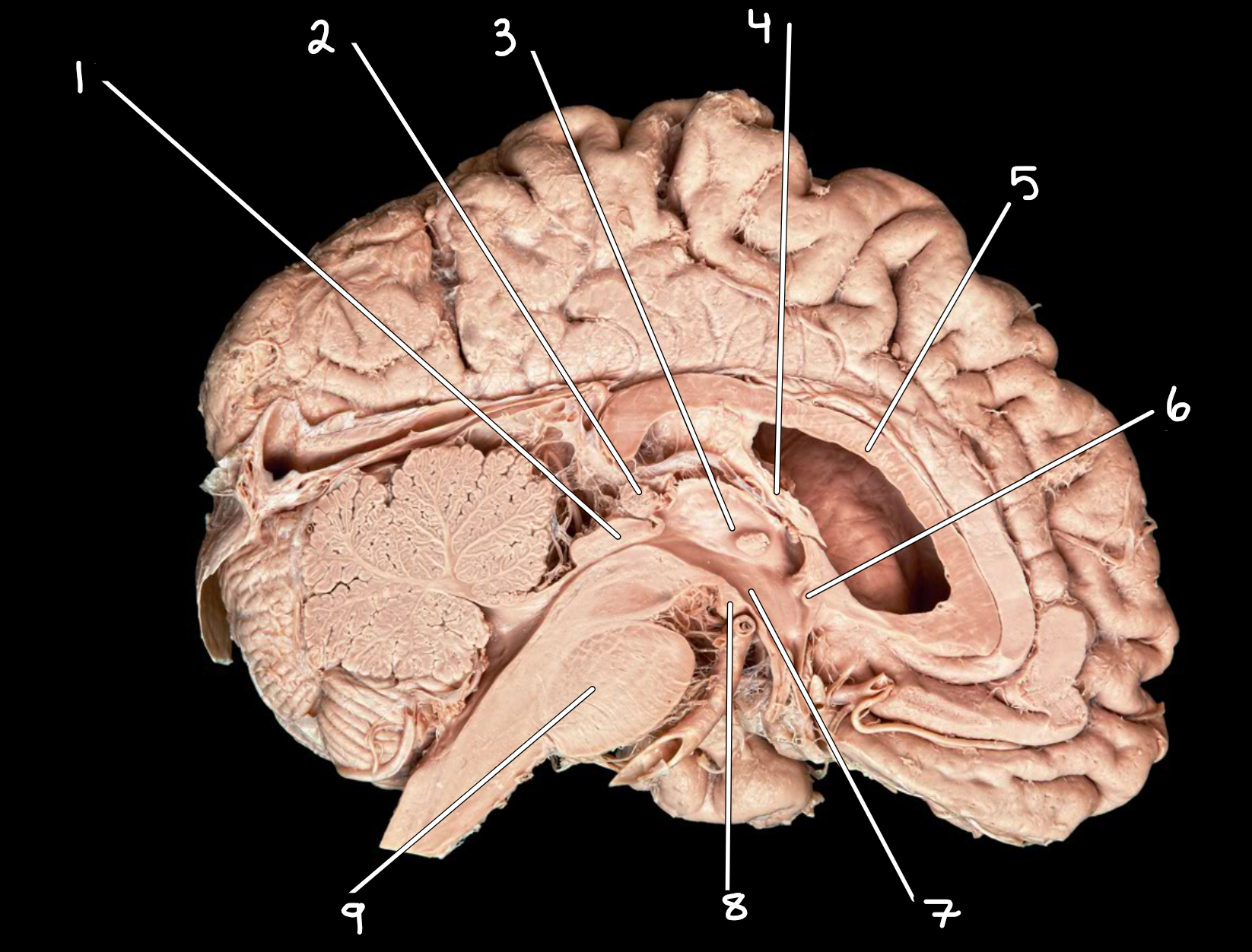
Midsagittal brain: left side
1.corpora quadrigemina
2.pineal gland
3.thalamus
4.fornix
5.corpus callosum
6.anterior commissure
7.hypothalamus
8.mammillary body
9.pons
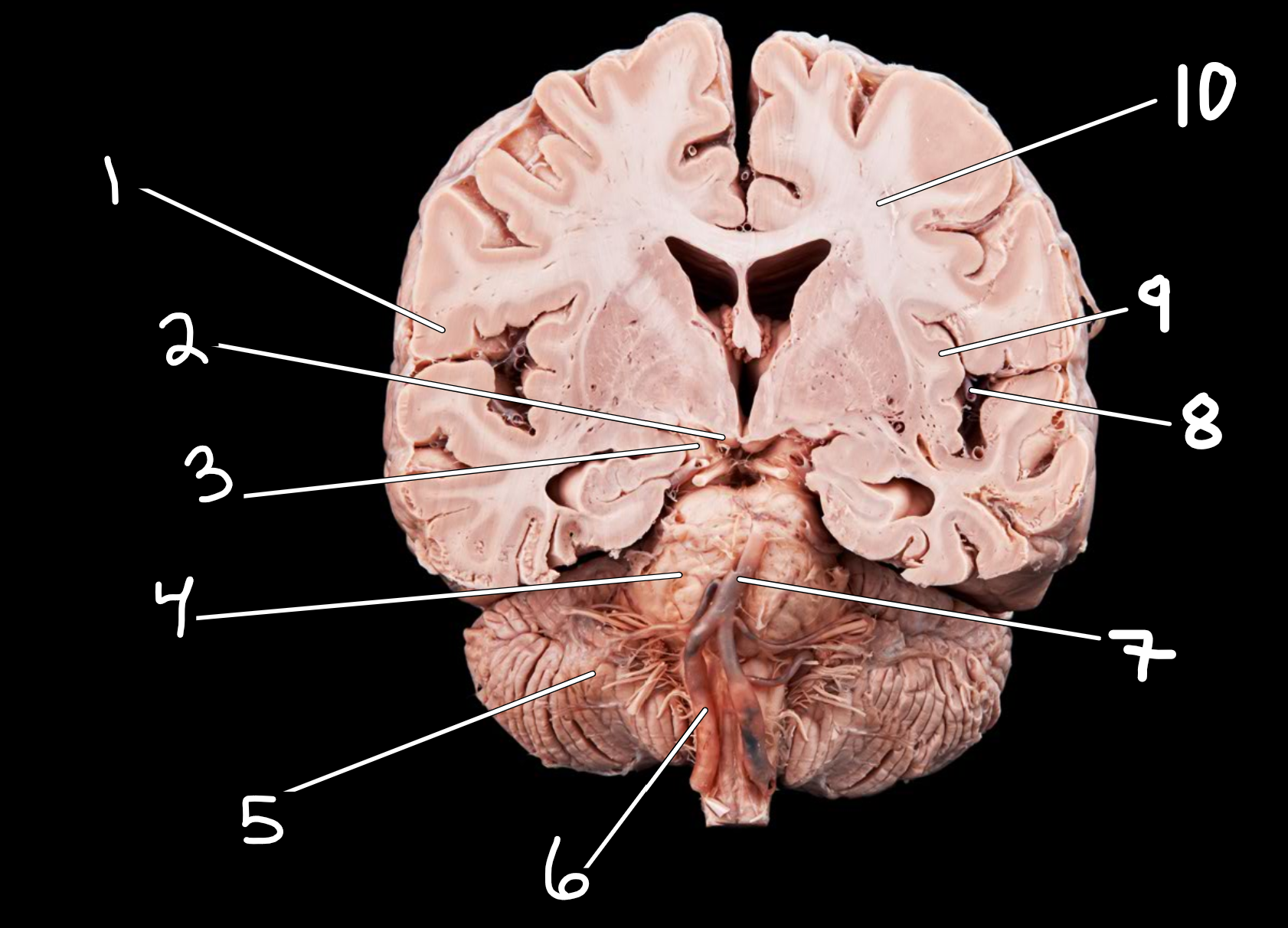
Midsagittal brain: left side
1.cerebral cortex of frontal lobe
2.mammillary bodies
3.cerebral peduncle
4.pons
5.cerebellum
6.vertebral artery
7.basilar artery
8.lateral sulcus
9.insula
10.white matter
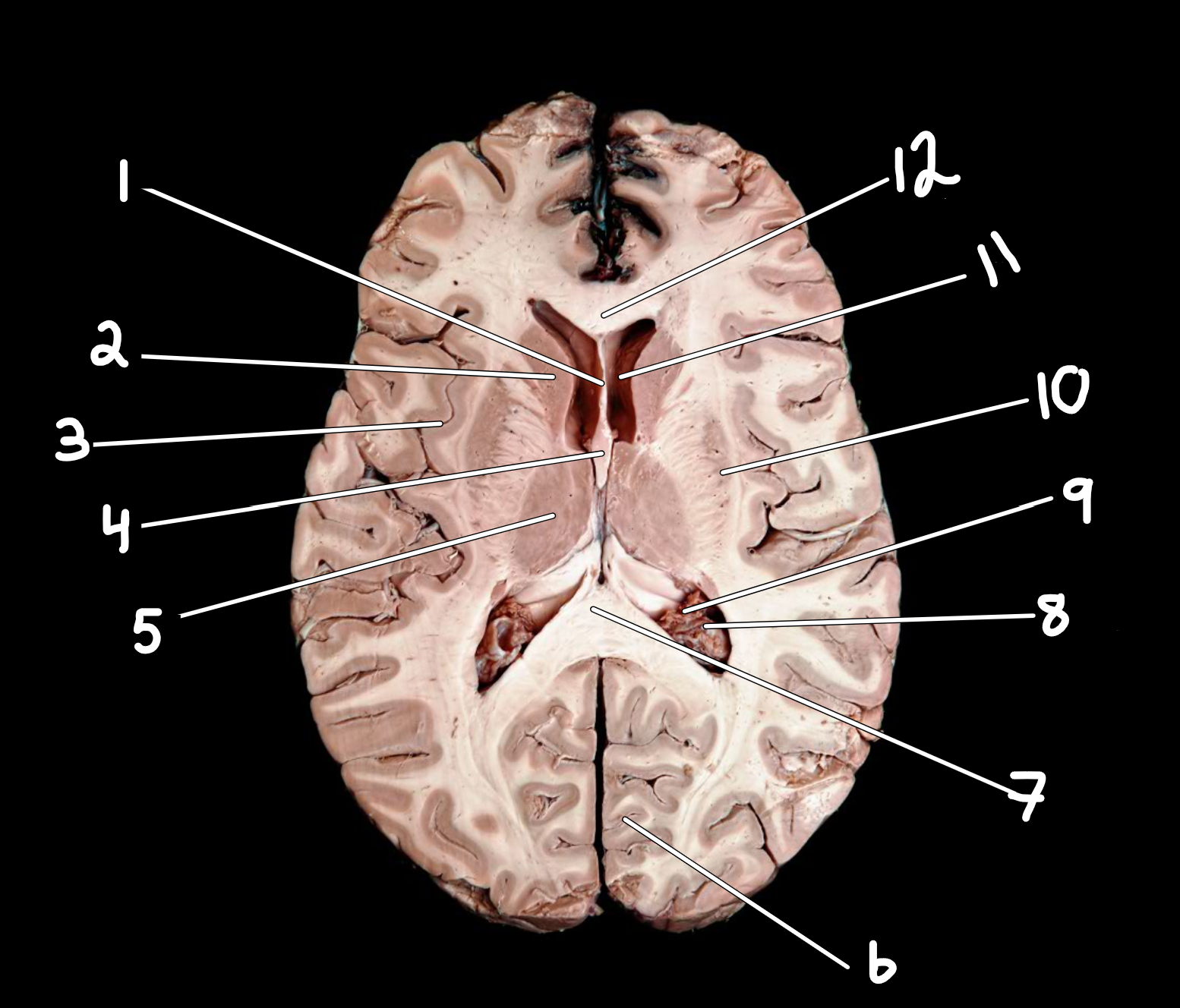
Brain: transverse section
1.septum pellucidum
2.caudate nucleus
3.insula
4.fornix
5.thalamus
6.cerebral cortex
7.splenium of corpus callosum
8.posterior horn of lateral ventricle
9.choroid plexus
10.lentiform nucleus
11.anterior horn of lateral ventricle
12.genu of corpus callosum
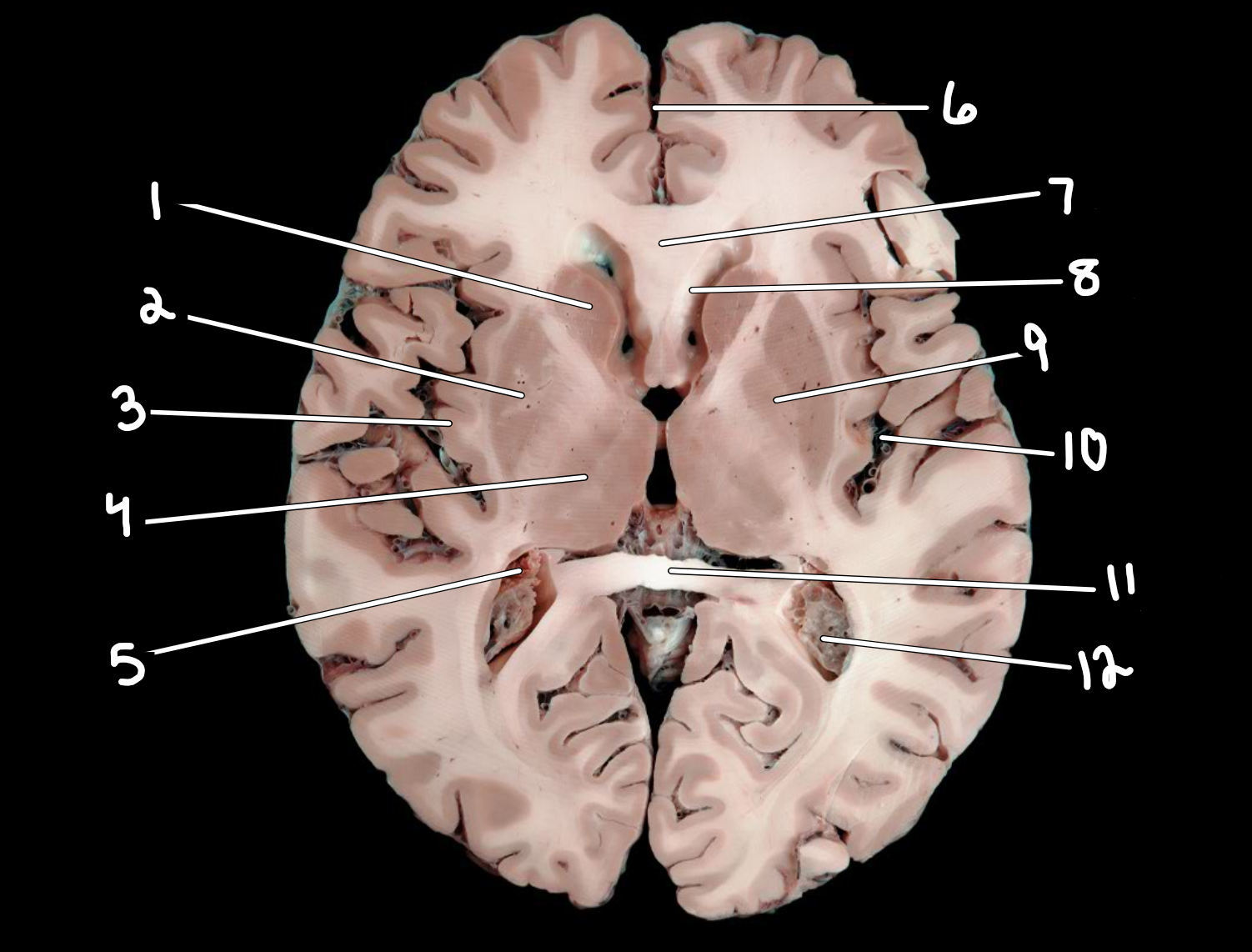
Brain: transverse section
1.caudate nucleus
2.putamen
3.insula
4.thalamus
5.choroid plexus
6.longitudinal fissure
7.genu of corpus callosum
8.anterior horn of lateral ventricle
9.globus pallidus
10.lateral sulcus
11.splenium of corpus callosum
12.posterior horn of lateral ventricle
What hormone is secreted by the pineal gland?
melatonin
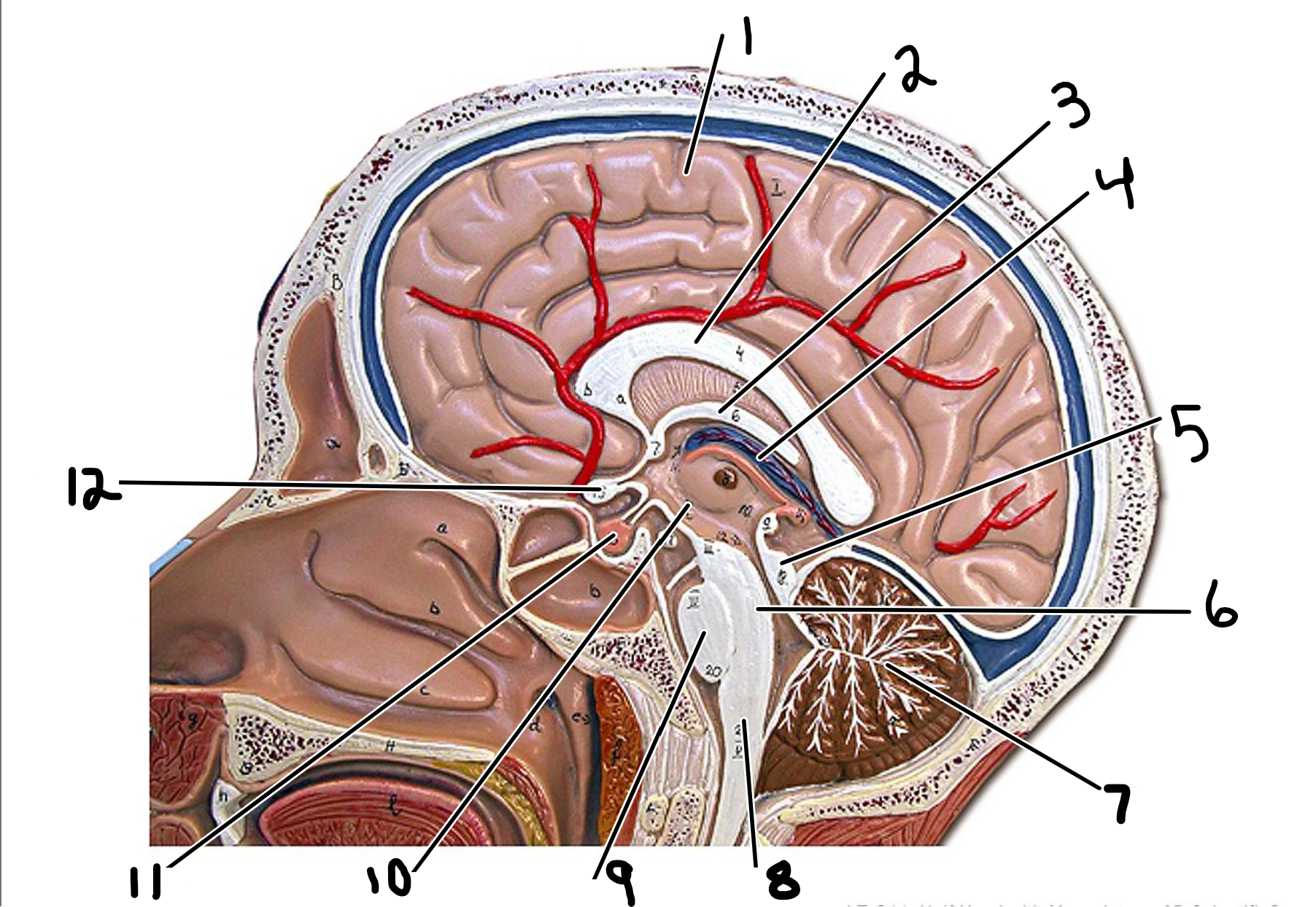
Brain: midsagittal view
1.cerebrum
2.corpus callosum
3.fornix
4.choroid plexus
5.corpora quadrigemina
6.midbrain
7.cerebellum
8.medulla oblongata
9.pons
10.diencephalon
11.pituitary gland
12.optic chiasm
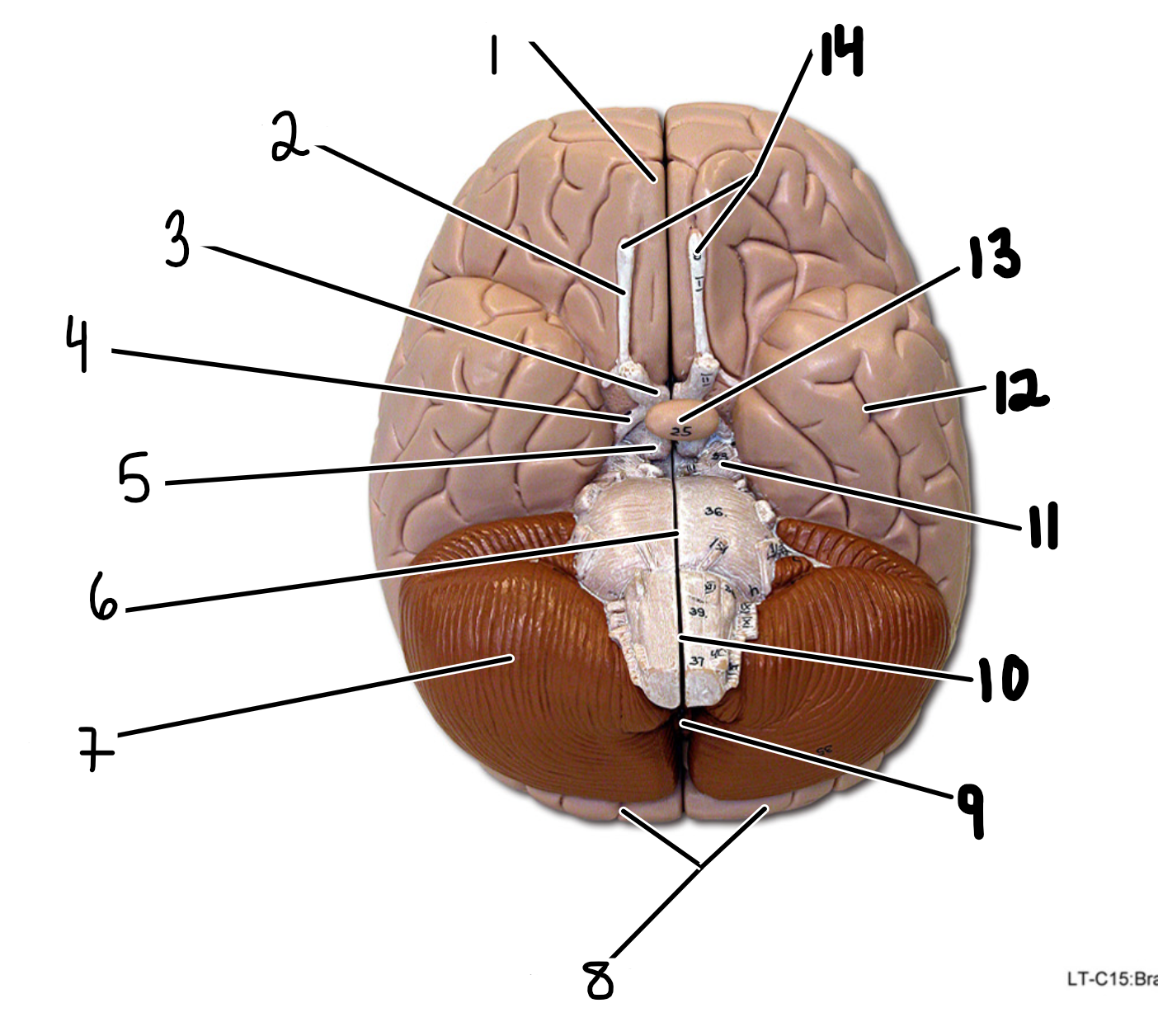
Brain: inferior view
1.cerebrum
2.olfactory tract
3.optic chiasm
4.optic tract
5.mammillary body
6.pons
7.cerebellum
8.occipital lobes of cerebrum
9.vermis of cerebellum
10.medulla oblongata
11.cerebral peduncle
12.temporal lobe of cerebrum
13.pituitary gland
14.olfacotry bulbs
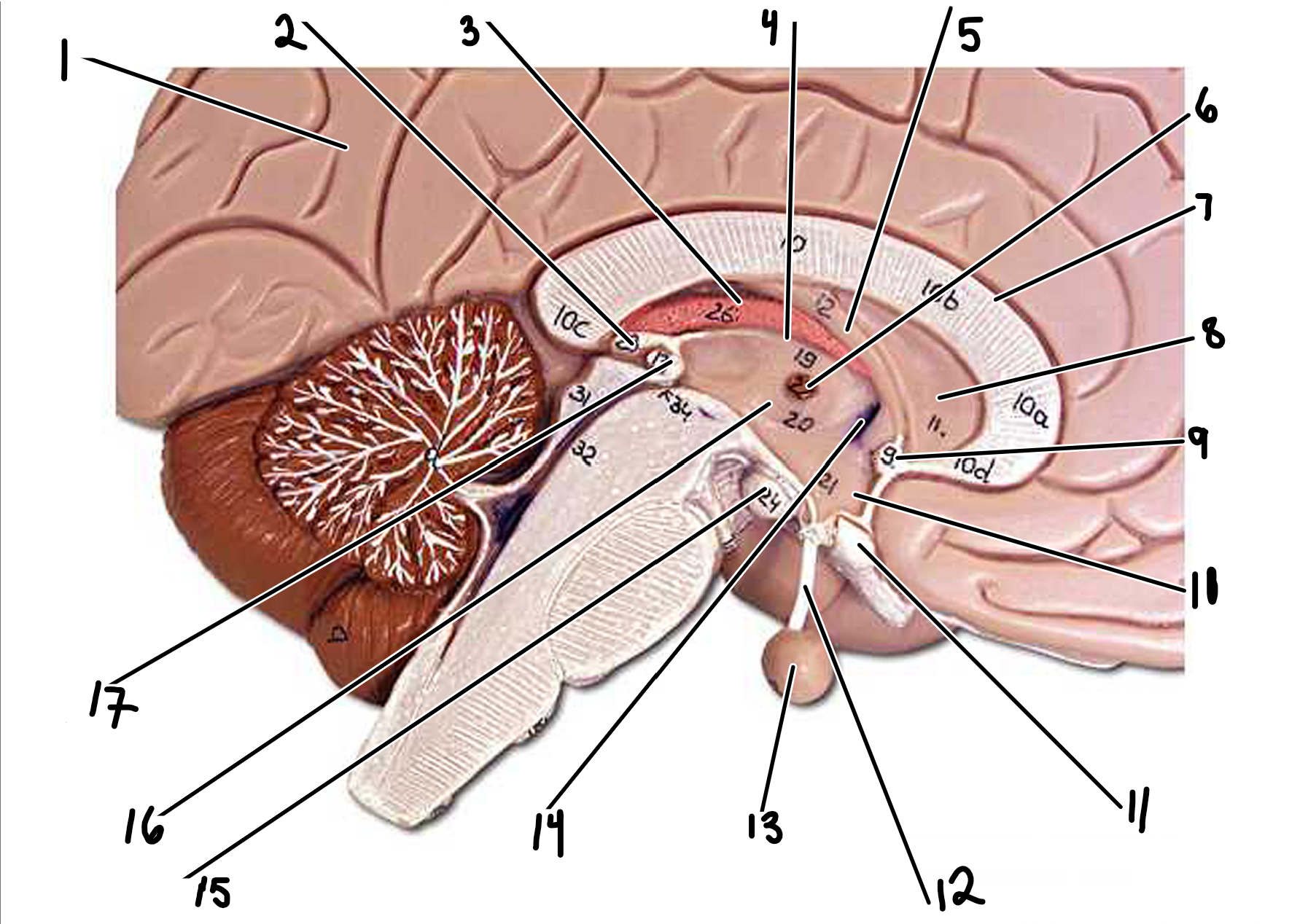
Forebrain: medial view
1.cerebrum
2.pineal gland
3.choroid plexus
4.epihalamus
5.fornix
6.interthalamic adhesion
7.corpus callosum
8.septum pellucidum
9.anterior commissure
10.hypothalamus
11.optic chiasm
12.infundibulum
13.pituitary gland
14.interventricular foramen
15.mammillary body
16.thalamus
17.posterior commissure
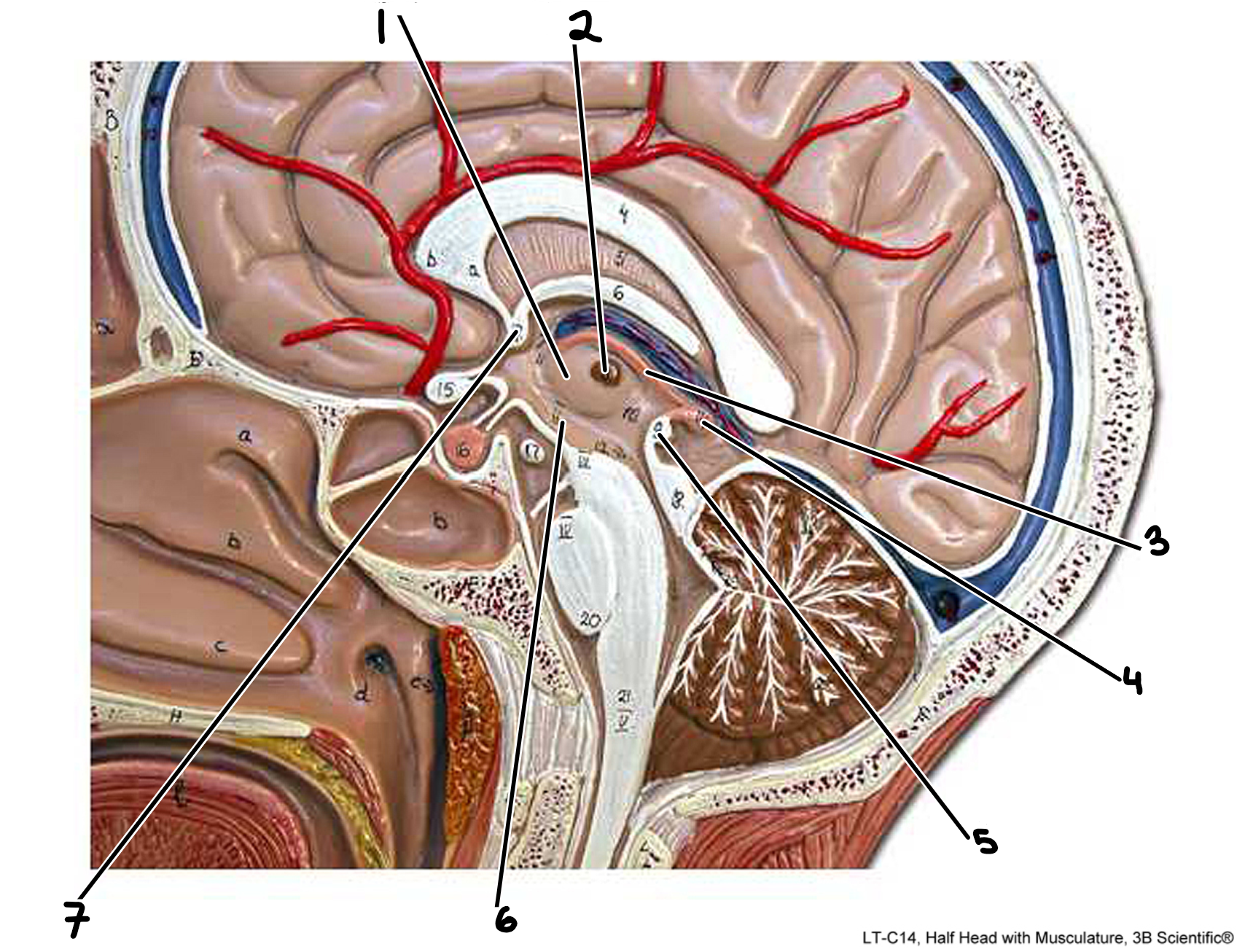
Diencephalon: medial view
1.thalamus
2.interthalamic adhesion
3.epithalamus
4.pineal gland
5.poserior commissure
6.hypothalamus
7.anterior commissure