lecture 6- equine limb vessels, nerves, and distal limb blocks
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pimentel
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
where is the brachial plexus found
C6-T2
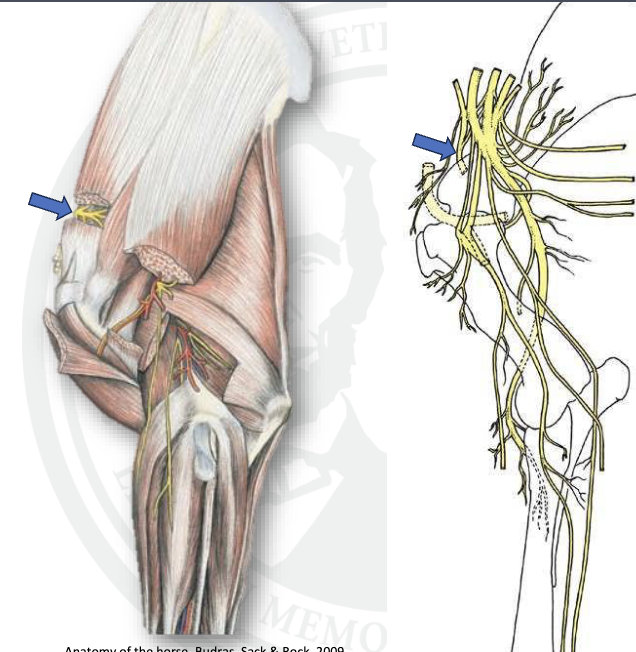
what is this
suprascapular
what is sweeny shoulder
damage to suprascapular nerve not uncommon in horses
results in atrophy of supra and infraspinatus, shoulder instablity, and shoulder “slip”
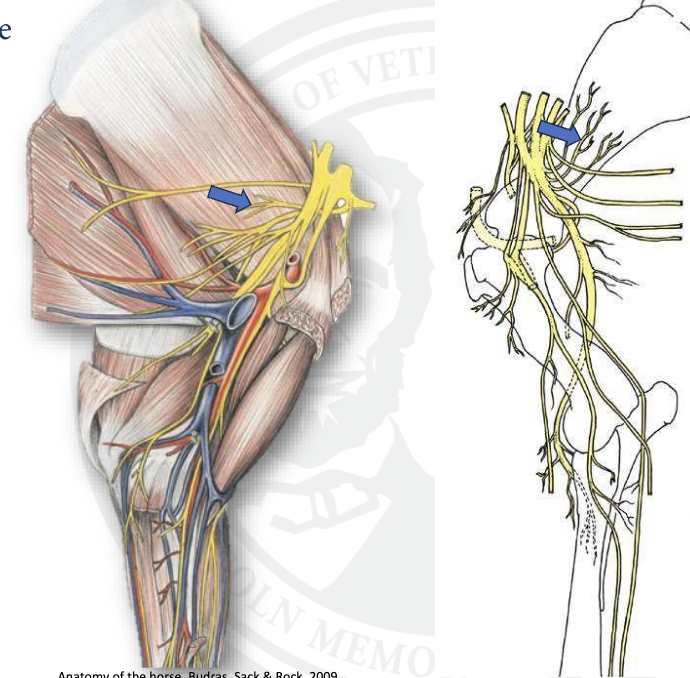
what is this
subscapular n.
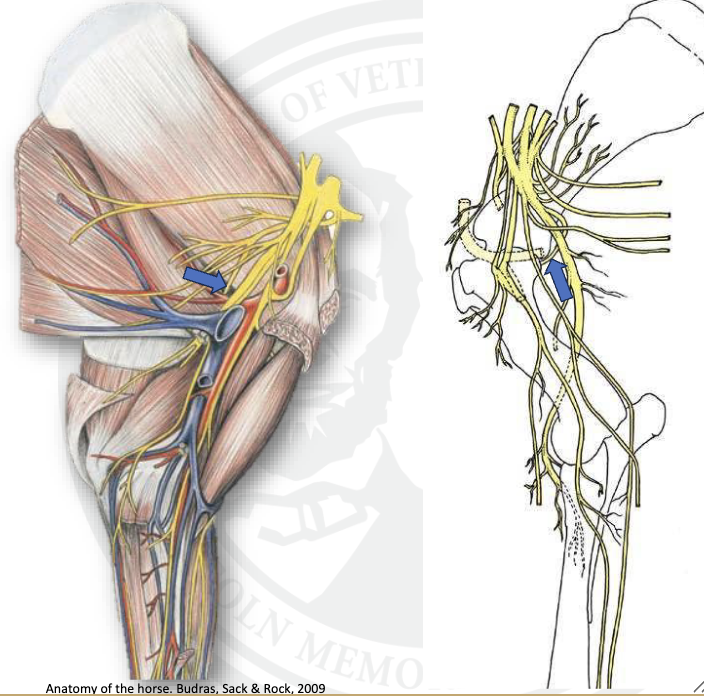
what is this
axillary nerve
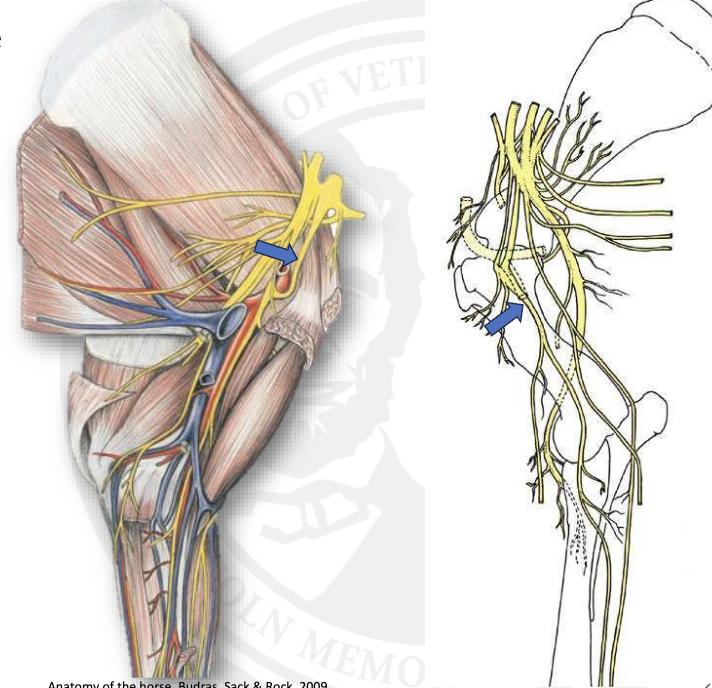
what is this
musculocutaneous n.
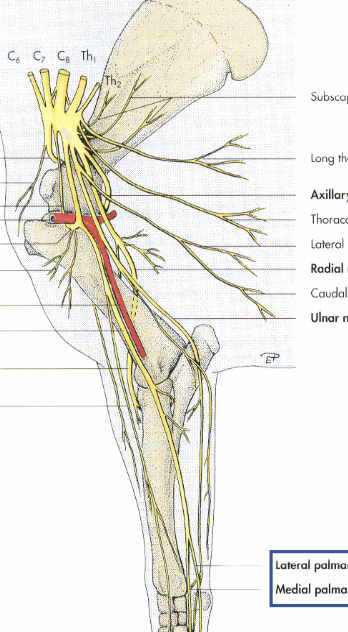
what is the main nerve in this image that we are seeing going down the limb
median n.
what is this
ulnar n
where is radial autonomous zone
lateral portion of brachium
where is ulnar innervation
ventral region of antebrachium AND brachium
where is musculocutaneous innervation
medial/dorsal region of brachium
whta is the cutaneous innervation of the craniomedial antebrachium
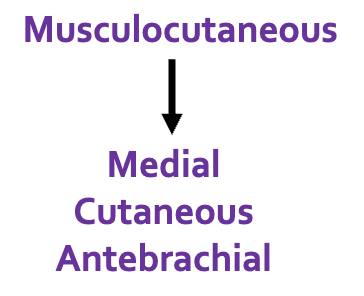
explain the breakdown of the cutaneous innervation for the fore digit of the caudal antebrachium and medial antebrachium
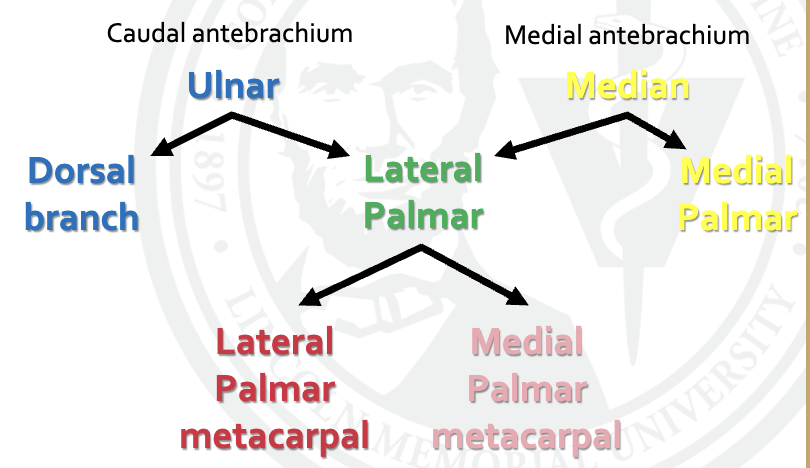
what are the parts of the median nerve
communicating branch
medial palmar
medial digital palmar
dorsal branch
what are the branches of ulnar nerve
dorsal branch
what are the branches of the lateral palmar nerve
lateral digital palmar
what are the branches off the lateral digital palmar n
dorsal branch
medial palmar metacarpal
lateral palmar metatarsal
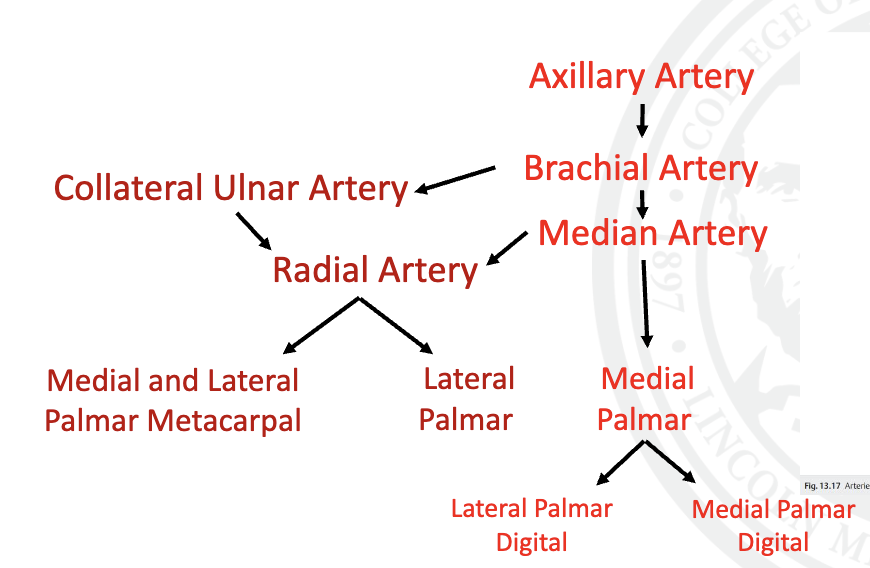
explain the blood supply of the thoracic limb
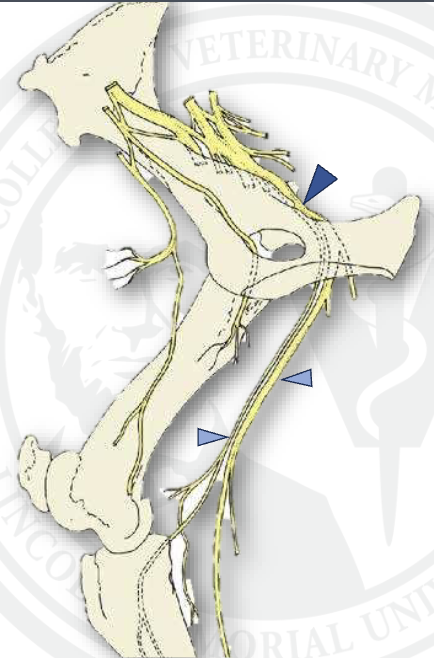
where is the LS plexus found
L4-S2

what is the dark blue arrow
femoral n.

what is the light blue arrow
saphenous

what is this
obturator n.
what is the union between the median and musculocutaneous n.
ansa axillaris
what is the top dark blue arrow
sciatic n.
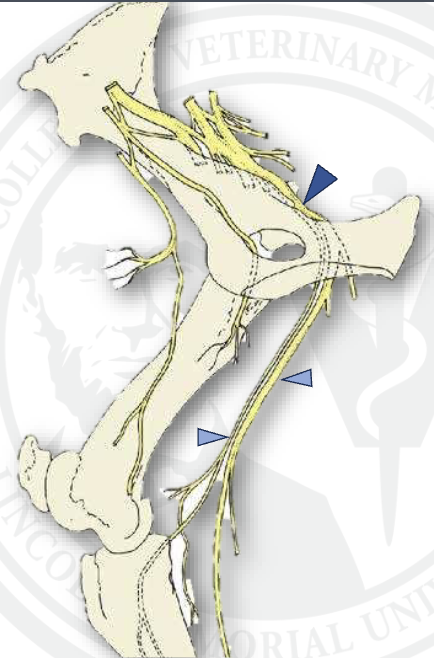
what is the middle light blue arrow
tibial
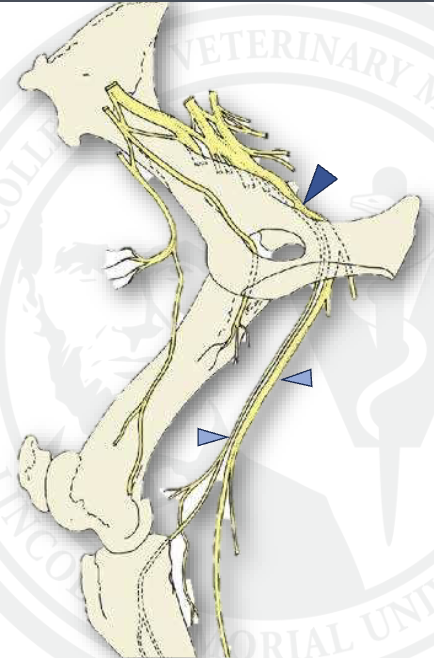
what is the bottom light blue arrow
common fibularis
where is tibial innervation
caudal portion of leg
where is saphenous innervation
medial thigh
where is peroneal innervation
lateral portion of shin
what is the cutaneous innervation of the hind digit of the craniomedial tibia
saphenous
what are the cutaneous innervation of the hind digit at the cranial tibia level and what are the branches
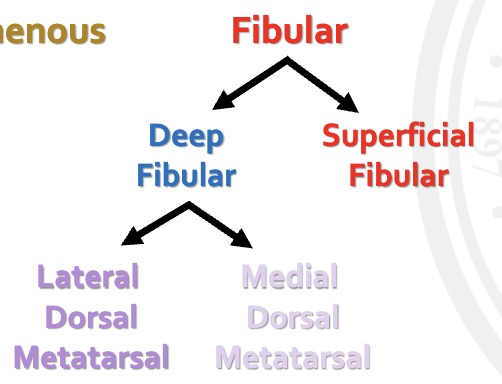
what nerve innervates the most distal part of the thoracic limb
median
what are the cutaneous innervations of the hind digit at the caudal tibia
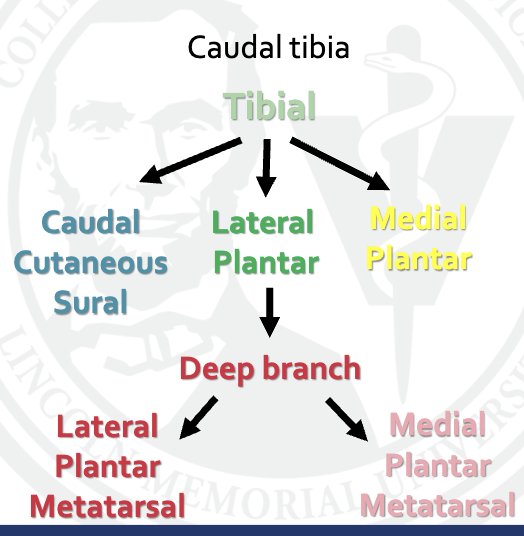
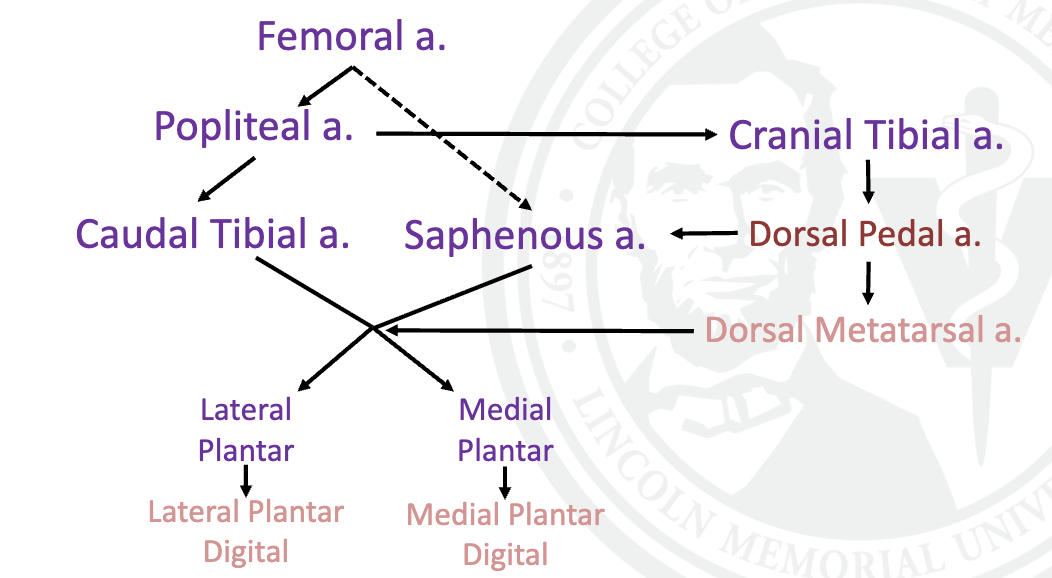
explain vasculature of the pelvic limb
w
regional anesthesia useful, fast, affordable, efficient
distal limb blocks
what are the 4 types of distal limb blocks
1. Palmar/plantar digital
2. Abaxial sesamoid
3. Low 4 points
4. High 4 points
technique for palmar digital nerve block
• Insert the needle subcutaneously over the neurovascular bundle.
• Close to the proximal border of the ungular cartilage.
nerves blocked by palmar digital nerve block
palmar digital nerves
VAN
what will palmar digital nerve block affect
• Facies solaris (Sole)
• Navicular Apparatus
• Distal interphalangeal joint (Coffin)
• Distal flexor tendon sheath
• Distal sesamoidean ligaments
• Loss of skin sensation at the heel
technique for abaxial sesamoid nerve block
• Insert the needle at the abaxial surface of the sesamoid at the caudal edge of the neurovascular bundle.
• Point needle distally
nerves for abaxial sesamoid nerve block
palmar digital nerves
main areas affected by abaxial sesamoid nerve block
• Distal phalanx
• Middle phalanx
• Proximal and distal
interphalangeal joints (Coffin and pastern)
• Distal SDF and DDF
• Distal sesamoidean ligaments
• Digital annular ligaments
• +/- Metacarpo/tarsophalangeal
joint (Fetlock)
technique for low 4 point (low palmar) block
• Insert the needle distal to the head (button) of the II and IV metacarpal/tarsal (splint) bones.
• Drive the needle subcutaneously between the interosseous ligament and the DDF tendon
nerves affected by low 4 point block
• Palmar metacarpal/metatarsal nerves (medial
to metacarpal/metatarsal bones)
• Palmar nerves (between interosseous and
DDFT)
pelvic limb performing a low 4 point block
• Performed the same as the thoracic limb.
• Will not reliably anesthetize the skin dorsally
• Important for suturing a laceration
• Less important for a lameness work up
• Can do a dorsal ring block to anesthetize the skin
high 4 point block thoracic technique
• Inject subcutaneously on dorsal surface of the DDFT through the fascia (retinaculum flexorum) just distal to the carpo-metacarpal joint
• Flex the limb and insert the needle along the metacarpal bones II and IV pointing at palmar MC3
high 4 point block thoracic nerves
medial and lateral palmar nerves
medial and lateral palmar metacarpal nerves
high 4 (6) point block of hind limb technique
• 1.5in needle inserted 1cm distal to tarso-metatarsal joint on either side and
hit the back of Metetarsal bone III
• 25g 5/8in needle – deposit 3-5ml through the fascia over the DDFT on
medial and lateral side
• 2cm distal to the TMT at 10 and 2 o’clock positions on the dorsal aspect od
the metatarsal bone III.
nerves of high 4 point block of hind limb
• Medial and lateral plantar nerves
• Medial and lateral plantar metatarsal nerves
• Dorsal metatarsal nerves