Idk if this is actually unit 4 this is what our teacher taught us
Intelligence
the cognitive ability to think, reason, and act purposefully & effectively as to manipulate one’s environment and meet goals in a rational manner
ability to learn from experiences
ability to apply knowledge to new sitations
ability to solve problems
ability to adapt / respond
Biological mechanisms of intelligence
brain anatomy
cerebral cortex, frontal lobe, cerebrum, corpus callosum, both hemispheres
neurology
neural plasticity
number of synaptic connections
genetics & heredity
characteristics are a product of one’s DNA
Francis Galton
came up with the idea of eugenics
Eugenics
attempts to biologically engineer the human gene pool by breeding superior people
Charles Spearman
came up with the theory of general intelligence (g)
intelligence is composed of a single, cognitive ability
General intelligence (g)
statistical factor analysis that indicates an individual’s overall mental capacity is based upon a singular cognitive skill set
level of academic intellect typically transcends across multiple curricular disciplines
led to creation of standardized tests
Louis Thurston
stated intelligence is a list of “primary mental abilities” → human intelligence consists of 7 different abilities (NSAWVIP)
his theories led to the creation of modern intelligence tests
Primary mental abilities
Numerical abilities
Spatial relations
Associative memory
Word vocabulary
Verbal comprehension
Inductive reasoning
Perceptual processing speed
Raymond Cattell
he revised Spearman’s theory of general intelligence
described g (general intelligence) as being composed of 2 factors
Crystallized intelligence (gc)
knowledge acquired and solidified through lifelong learning experiences; “book smarts”
Fluid intelligence (gf)
flexibility of reasoning abilities, speed & efficiency of information processing; “street smarts”
Howard Gardner
came up with the “Theory of Multiple Intelligences”
his theories revolutionized the modern education system
Theory of multiple intelligences
described intelligence as unique individual learning abilities and develop according to cultural influences
described 8 learning abilities (LLMBSNII)
logical / mathematical
linguistic (reading, writing, speech)
musical
bodily (kinesthetic)
spatial relations
naturalistic
interpersonal
intrapersonal
Interpersonal
social skills & communication
Intrapersonal
self perception & metacognition
Robert Sternberg
came up with the “Triarchic Theory of Successful Intelligence”
Triarchic Theory of Successful Intelligence
intelligence is displayed through practical problem solving
focuses on the process of problem solving, not the final product
3 abilities
Analytical intelligence
Practical intelligence
Creative intelligence
People with high intelligence effectively synthesize all three forms
Purposes / Clinical applications for intelligence testing
used to assess cognitive development for psychological / scientific research
used as diagnostic indicators to identify potential learning disabilities or gifted learners
used forensically to evaluate legal competency
Achievement test
measures information learned / retained over time
Aptitude test
measures specific skills, talents, and natural abilities
Intelligence test
measurement of one’s ability to learn based upon multiple cognitive skills and problem solving abilities
Alfred Binet
he collaborated with Theodore Simon to create the Binet-Simon Intelligence Test
Binet-Simon Intelligence Test
foundation of the modern intelligence assessment
first test to measure multiple cognitive abilities that was not a measurement of aptitude or achievement
the scoring was flawed because this test was originally made for children
not the first IQ test
Lewis Terman
developmental psychologist
adjusted Binet’s test and revised the scoring calculation to identify cognitive disabilities in children
created the Stanford Binet Intelligence Scale
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale
first clinically used intelligence test
standardized a classification system to label various degrees of intellectual disabilities in children
calculated the intelligence quotient (iq) formula
score of 100 (mean) = average human intelligence
Stanford-Binet IQ calculation
IQ = (mental age / chronical age) × 100
Wechsler Test of Intelligence
most commonly used series of IQ tests
considered the clinical standard for intelligence measurement
WAIS-III → adults
WISC-IV → children
instead of comparing test scores to one’s age, these tests are normally distributed according to statistical averages
Standard deviation
measures how close the numbers within the dataset are in relation to the mean
Wechsler IQ Bell Curve ranges
85-115 → 68% of the population
70-130 → 95% of the population
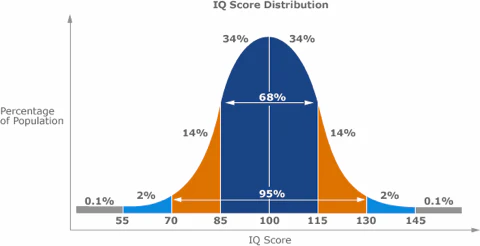
Genius
Wechsler IQ score of 145 - 200 (0.1%)
Gifted
Wechsler IQ score of 130 - 145 (2%)
Above Average
Wechsler IQ score of 115 - 130 (14%)
Below Average
Wechsler IQ score of 70 - 85 (14%)
Intellectually Disabled
Wechsler IQ score of 55 - 70 (2%)
Profoundly Mentally Disabled
Wechsler IQ score of 0 - 55 (0.1%)
Intellectual disabilities
psychometrically defined by IQ scores < 70
85% of the intellectually disabled population is considered mild
Savants
people with cognitive deficiencies yet are gifted in specific areas such as math, memory, music, art, etc.
Causes of intellectual disabilities
genetics (down syndrome, PKU)
prenatal teratogens (birth defects, FAS)
physical brain injuries
environmental factors (neglect, language deprivation)
Cognition
a system of multiple mental processes that allow for human introspection and evaluation of thought
perception
memory / learning
problem solving / decisions
language
conceptualization
Conceptualization
developmental classifications for a collective group of objects, stimuli, etc. that share similar characteristics
identifying / placing stimuli into schemas
Schema
mental categories based upon cognitive similarities
constantly evolve & redefine as mind develops
Assimilation
inclusion of a stimulus into an existing schema
fitting in when similarities > differences
Accommodation
mental adjustments made when the differences > similarities
3 ways
redefine parameters of the schema
place new item into a different schema
create new schema
Natural concepts
understanding the characteristics that define the schema and representing it with a prototype
Prototype
model examples that contain all essential features / characteristics of the schema by which new stimuli are compared to
Artificial concepts
defining the characteristics of the prototype & comparing new stimuli not to the model example but to a defined list of it’s features
if a majority of the characteristics of the mental checklist are in common, new stimuli can be assimilated
Hierarchical concepts
prioritizing metal checklists into a ranked order of the most important features
Step 1 of problem solving
Preparation
often skipped (why humans aren’t the best problem solvers)
understanding the situation / problem
identify & familiarize yourself with relevant data & discard irrelevant information
explicitly define the goal
Step 2 of problem solving
Production
developing hypotheses and producing solutions
Algorithms
step-by-step procedures that if properly used will always produce a correct solution
Heuristics
“short cut” strategies; typically algorithms modified through experience; requires less time but may be prone to error
Step 3 of problem solving
Evaluation
final analysis of solutions
does the solution answer the questions?
Is the solution correct in all cases / scenarios?
Mental set
tendency for previous successful experiences to become reliant and complacent; failure to learn new / alternative strategies
Functional fixedness
general inabilities to recognize alternative uses for manufactured objects other than the designer’s intended purpose
Anchoring bias
tendency for people to base decisions, attitudes, and opinions solely upon the first information that is presented to them
Confirmation bias
selectively picking / choosing information and data that supports your preconceived opinions and ignoring information that contradicts your beliefs
Belief perseverance
tendency to cling to beliefs and positions despite new information that firmly discredits and contradicts your opinions; inability / unwillingness to admit mistakes
Selective perception bias (self-serving bias)
our perceptions of reality are based upon our self motivated interests / experiences; reality blinded by emotion / personal point of view
Dunning-Kruger Effect
tendency for people with below level abilities to inaccurately exaggerate their own competence and to assume superior intelligence
Imposter Syndrome
self perceived doubt in one’s abilities making them believe they are not as qualified, skilled, or talented as others
Hindsight bias
tendency to reevaluate and unpredictable event after time has passed and information is made available that was not originally known
Framing / wording effect
tendency to influence or manipulate our thoughts and perceptions based upon how the information is presented
Availability Heuristic ★
tendency to assume or exaggerate the likelihood of events based upon the frequency and availability of information; biases based upon familiarity
Representative Heuristic ★
tendency to make judgements and evaluations based upon conceptual schemas with characteristics that draw upon generalizations; based upon stereotypes
Analytical Intelligence
ability to evaluate situations and apply knowledge
Practical Intelligence
intelligence to perform everyday tasks
Creative Intelligence
ability to adjust in response to new, changing situations
3 elements of creative intelligence
Originality
Fluency
Flexibility
Originality
ingenuity to create unique ways to solve problems
Fluency
ability to produce multiple correct solutions to a problem
Flexibility
ability to interchange various methods of problem solving and make judgements when circumstances dictate
Divergent thinking
problems intended to have multiple solutions; brain storming
Convergent thinking
multivariable problems that direct thinking to one correct solution; conventional thinking
Heritability
the portion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
Epigenetics
studies part of the dynamic biology of genetics & experience
Growth mindset
a focus on learning and growing rather than viewing abilities as fixed
Fixed mindset
the view that intelligence, abilities, and talents are unchangeable even with effort
Stereotype threat
a self-conforming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
Factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a test used to identify different dimentions of performance
Cattel-Horn-Carrol Theory
the theory that our intelligence is based on g as well as specific abilities (gc, gf)
Grit
passion or perseverance in pursuit of long term goals
Emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
Mental age
a measure of intelligence test performance; the level or performance typically associated with children of a certain chronological age
Intelligence quotient (IQ)
defined originally as the ratio of mental age to chronological age multiplied by 100
Standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group
Normal curve
the bell shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical / psychological attributes
Flynn effect
the rise in intelligence test performance over time and across cultures
Reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results
Validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it’s supposed to
Content Validity
the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest
Construct validity
how much a test measures a concept or trait
Predictive validity
the success that a test predicts the behavior that it is designed to predict
Executive functions
cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organize, plan, and implement goal-directed behavior
Insight
a sudden realization of a problem’s solution
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct
Nudging
framing choices in a way that encourages people to make beneficial decisions
Metacognition
thinking about thinking
Language
our agreed upon systems of spoken, written, or signed words and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning
allows for sophisticated exchange of thought
promotes social identity and cultural unity
foundation of human cognitive development
allows for introspection
Phoneme
the smallest distinctive sound unit (in language)
Morpheme
the smallest unit that carries meaning (in language)