Exam 3 Psych 1
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Sigmund Freud
1856-1939
Doctor in 1881
Interested: physiology and psychodynamic movement
Focus: Bio mech. behind thought + behaviors
Research: + Jean Charcot = treating people with hypnosis and other approaches = understanding unconscious
developed own pyschodynamic institute
created psychodynamic theory
Freud inspired interest
physiology and psychodynamic movement <- Ernst Wilhelm Ritter von Brucke
psychodynamic theory
personality based on interplay of conflicting forces within individual
explains individual diff (personality) and abnormal
consscious vs unconsciou
conscious
thoughts and experiences where we are aware of that impact on our behavior
unconscious
thoughts and experiences where we are unaware of that impact on our behavior
source of forces
id
superego
ego
id
unconscious force that constantly seek SATISFACTION of basic needs
(survival, sex, thirst, hunger, sleep)
"it" (instincts) = 'devil'
superego
preconscious force that's only goal is to push us to do what is RIGHT via society standards
superego tries to balance out id but superego gets pushed under the surface
"super" "I" (moral compass) = 'angel'
ego
conscious force that we develop in social world and operates on reality principle seeking to SATISFY ID and SUPEREGO's desires in REALISTIC ways
"I" (mediator)
source of forces mountain
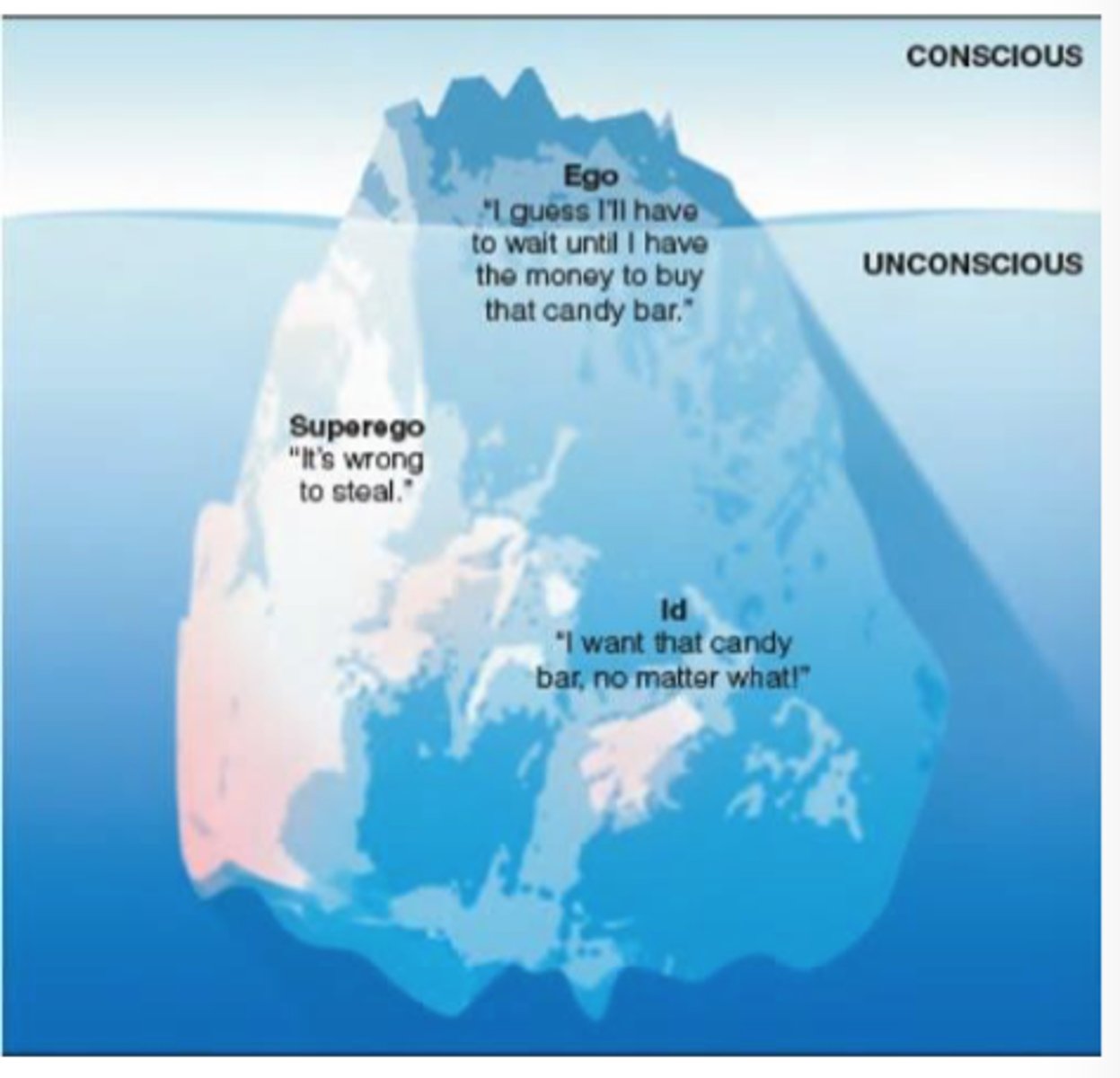
psychodynamic theory relation to psychology
personality came from interaction of sources (id, superego, ego) throughout life
suggested unmet needs or traumatic experiences that can --> abnsormal behavorial/thoughts if unaddressed
psychodynamic theory result
clincal work
emphasize: hypnosis
freud clincal work
focus: accessing unconscious traumas/needs that had to be addressed to understand person
brought unconscious UP to change personality or address the abnormal
psychoanalysis
hypnosis
free asociation
dream interpretation
"freudian slips"
psychoanalysis
clinical work
used to get into unconscious
hypnosis
clinical work
suggestions
person highly susceptible and not really help as evidence
free association
clinical
rattle things that come in mind (unconscious thoughts?) in a stream of consciousness
dream interpretation
clinical
report dream --> freud decode it with own code --> conclude meaning of dream
manifested content in dream = relates to something/symbolization
freudian slips
clinical
person says things that they mix up of the tongue
freud thinks this represent real feelings/unconsciou feelings
trend of freud + mental health
1) freud believed mental health issues were mental, not a disease = help stigma
2) freud believed mental health issues were from sexual trauma/fustration = blacklash
freud's focus on sexual trama/fustration
argues that we all have sexual drive --> problems in life
libido
oral stage
anal stage
phallic stage
latency
genital stage
Freud's psychosexual stages is "Old Aged People Love Grandchildren"
libido
psychosexual energy
different orogenetic zones in psychosexual staes that were stimulated at diff ages to explain behaviors/actions
ex// chewing gum bc mouth centered stimulation in oral stage
oral stage
0-18 months
mouth centered stimulation
oral fixation
anal stage
18-36 months
potty training focus
anal retentiveness
phallic stage
3-6 yrs
genetal/gender exploration
penis envy, gender intensification, castration fear
ana freud = daughter = went back to change penis envy for women --> child-bearing envy for men
latency
6 to puberty
no libido
genital stage
puberty +/- maturation of sexual interest
sexual issues
sources of freud's theories
personal insights
cited evidence
- case studies: ann O (bertah pappenheim) = client of one of freud's friend where freud lied about doing therapy session with her and made positive evidence
lack of empirical work (never used surveys or exp)
questions about whether case studies were actually true
complaints on freud
His attempts to link disorders like schizophrenia, depression, and others = childhood trauma --> to a lot of undesirable outcomes
resulted in exploration in this fiend in less scientific way
not really study sex bc Freud intersected childhood experience w/ sex despite not really good research + stigma around mental health
appreciative things about freud
Caused Personality and clinical psychology
Mental health views transitioned (Medical view as disease to psychological concerns)
Appreciation of complexity of desires/drives
Consideration for childhood
Discussion of the impact of sexual life in our behaviors and mental health
Exploration of LEVELS of consciousness
Note: Differences between Freud's unconscious vs current version of subconscious (implicit mental life)
carl jung
1875-1961
formation of personality
Theory: Analytical Psychology
Key Concepts: Collective unconscious, archetypes, individuation.
Mnemonic: "Jung's Journey of the Jungian mind."
car jung accepted freud's beliefs
accepted freud's belief
- personality formed from conscious and unconscious forces
- past experience impact personality
car jung disapproved freud's beliefs
disaproved freud's belief
- personal unconscious did NOT CONTAIN the basic instincts (id) from Freud
Wanted to look at future + strive for goals = important
spiritual component to personality (archetypes, collective unconscious)
spiritual component to personality
archetypes: shifting the way we saw us and others = shape our perception and experience of the world
collective unconscious: all humans share a common, INHERITED layer of the unconscious mind = contains universal patterns of thought and instinct called archetypes
superiority theory
alfred adler
"Adding over and over again to be cool"
early student of freud = broke away because freud was too focus on sex
individual psychology
individual psychology
main force BEHIND thoughts and behaviors is FOCUSED on US and the underlying attempt for SUPERIORITY
--> want to be suprior person and not less than other individuals
striving for superiority
inferiority complex
striving for superiority
desire to seek personal excellence and fulfillment
inferiority complex
exaggerated feeling of weakness, inadequancy, and helplessness due to assessing lack in a skill
carl rogers
1902-1987
formed an HUMANISTIC appraoch to personality and clinical psychology
actual self
ideal self
self-efficacy
self-actualization
the (S)elf
Theory: Humanistic Psychology = want person to understand self
Key Concepts: Client-centered therapy, unconditional positive regard, self-actualization.Mnemonic: "Rogers Regards Respect and Realization."
humanistic appraoch
approach to psych. and assumes POSITIVE aspects of individuals and examins attempts to OVERCOME hardship and despair
actaul self
person that we are
ideal self
person that we want to be
self-efficacy
belief in ability to ACCOMPLISH goal/task
self-actaulization
achievement of one's full potential
results in GREAT accomplishments + obtained through alignment of selves
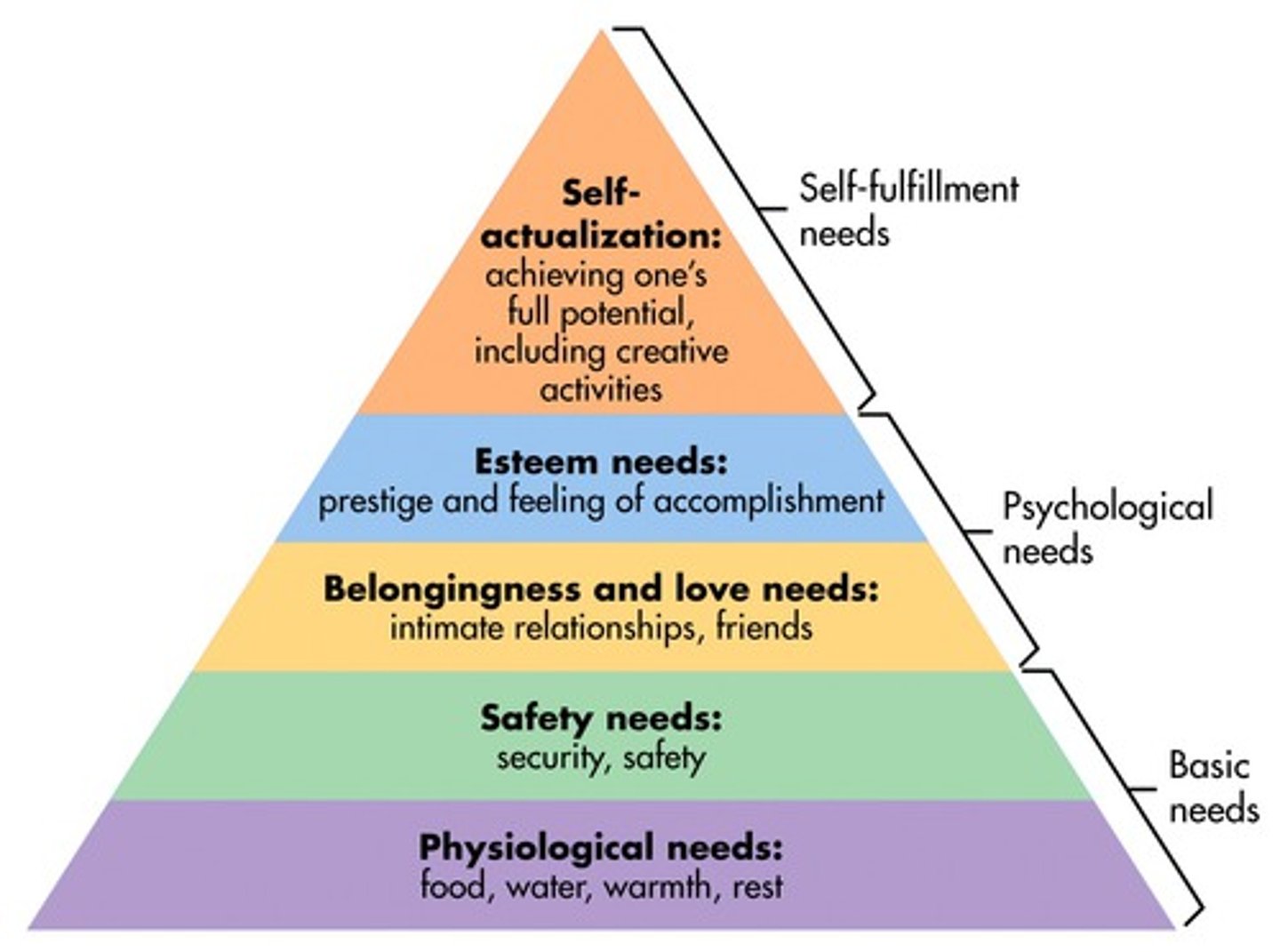
hierarchy of needs
abraham maslaw (colleage of rogers) = Maslow's Mountain of Needs."
needs that need to be obtained
Psychological: food, air, water, shelter, sex, clothing, comfort = primary drivers
Safety: personal and financial security, health, law, protection from elements
Love/belonging: friendship, love, intimacy, family, ecommunity, belonging, relationship
Esteem : self-esteem, achievement status, confidence, prestige, recognition, mastery, independent
Self-actualization: not really reached here = peace, knowledge, self-fulfillment, personal growth, realization of personal potential
no data/evidence
did try to look for quantifying clincal results, but similar to how freud got his info
social cognitive model
byproduct of social encounters and what we learn
branch of personality
personality
byproduct of learning
learning
effect on social intxn
focused on:
How to SEE different environments?
What to EXPECT out of those environments?
What to WANT from situations?
How to OBTAIN what we want?
Albert bandura
social cognitive
how we learn to develop personality related behavior
modeling = process of developing behaviors BASED on OBS. of others and outcomes experienced
--> BOBO DOLL EXP.: Bobo doll experiment: Kid watched the model play with the Bobo doll (one plays with it, the other beats the doll up). The kid is put in a different room where the Kid plays/beat the doll depending on what the Model did
Theory: Social Learning Theory
Key Concepts: Learning through observation and imitation, Bobo doll experiment.Mnemonic: "Bandura Believes in Behavioral Imitation." = Bobo
walter mischel
focus: research on cognitions developed that FORM personality
expectations of results from behaviors
interpretations of situations
competency: skill sets available to deal with social situation
--> extrovert vs introvert = diff types of thinking dictates personality
Known: delay of gratification = the ability to resist the temptation of an immediate reward in favor of a more valuable one later
==> trying to figure what made you who with quantifying results and correlation = Marshmallow test
personality and behavior summary
All of the theorists:
- looked for explanations for why each of us are unique and consistent in our behaviors (Correlation)
- stressed the past and our focus on the future shape our personality
- Only a few researchers stressed the need for research when generating their ideas
assessing personality
Barnum Effect,
Reliability and Validity,
Objective Personality Measures
Projective Personality Measures
Barnum effect
tendency to accept GENERALIZED personality desc. as accurate desc. of one's unique personality
effect of authority
ex/ vague + positive + mostly true = "You have a tendency to be critical of yourself."
experiment: Gave a mass murderer's horoscope to multiple people and they believed that it applied to themselves mostly
reliability and validity
scaling personality
validity = test accurate (target)
reliability = variable free from random error = similar results (clumped)
ex/ off by 5lbs all the time = reliable but not valid
objective personality tests
self reported tests
standardized personality tests: likert scale (1 to 5) + gather a lot of paper = bell curve
middle = most people = average person
more extreme scores = less, not frequence
if person is close to mean or not = normal range?
Big5 = NEO Pi-R
TIPI
MMPI
MBTI
Big 5
NEO personality inventory-revised
1) dictionary (Allport + Odbert) = looked in dictionaries = found every word in English language related to personality
(18000 words)
2) compared words for syn/ant (cattell) = rid of redundant words (nice+friednly, nice + mean)
(35 traits)
3) conducting "FACTOR ANALYSIS" (overlapp in response frequency) to see which reamining words/traits emerged = five factor model of personality (costa and mccrae) --> 5 traits
OCEAN
- Openness: enjoy new exp. + intellectual exp.
- C: conscientiousness: discipline + ambition
- E: extroversion: sociable, adventurours, + emtoion, taking risks
- A: agreeableness: compassionate, + social relationship, less prejudiced
- N = neuroticism: neg. emotions
likert scale = mean responses
measure general vs clinical population
90% reliable
correlate in behavior in real life
limitations of big 5
not good predictor with other cultures = big 5 based on english dictionary
- most cultures do have overlap
might have too few variables (religious levels, humor, etc?)
might have too many variable (+ corr. E and O, - corr. N and E/O)
potential of (GROWTH) merging/alignment of traits as a person grows older
might not be good predictor of specific behaviors = CAP on predictive value of BIg 5
TIPI
ten item personality inventory
self reproted data
I ese myself as ... (1-5)
MMPI
minnesota multiphasic personality inventory
Assesses personality traits and psychopathology - used most widely in clinical settings = protected psychological instrument
--> VALIDITY SCALES: catch exaggerated symptoms or covering up sympotms for personal GAIN
~300-600 True/False items (10 Clinical Scales)
= EMPIRICALLY (not theoretically) → if answers correspond to people with disorders who answered SIMILARLY
Limitation: culture + MMPI (single test measure personality for all people), high intercorrelations (overlap between scales vs Big 5's clustered questions), misleading/outdated terms (hysteria, schiz., musc/fem)
MBTI
myers-briggs type
workpalce + schools
categorize into 16 types (combo of 4 traits)
limitations: categorization vs continuum perspective =MEDIAN split scoring (49 50 = diff info)
not capture ALL Big 5 traits (no Openness)
E/I
Sensing (facts/specificity), Intuitive (exploring/recognizing connections) = how obtain info
T/F = decisions on logicial/emotional
Judging (planning/analyzing)/Perceiving (spontaneity)
projective technqiues
+ specificities that come with this technique (pro/con)
projecting info of yourself to an IMAGINARY person to ASK questions about that person
Protected: answers analyzed by trained psychologists
Ambiguous: Ambiguous stimuli promote personal exploration
Open to interpretation: results can be interpreted differently by different people
rorschach inkblot
low relaibility + potential low viability
= almost no mental disorders that cannot be identified (except for schizophrenia,)
= people who talk more may score higher
= Created for Western population → minoirty groups may score higher
TAT
thematic Apperception Test
- Morgan and Murray (1935)
- Projective test made up of 30 pictures that show people in black and white engaged in ambig. activities
- widly used projective test
write a story of an image --> psych. relate story to certina disorders/personalities
less abstract than Rorschach
early theories on traits
cause of individual differences
specific information --> broader terms (personality and traits) to understand how traits impact your choices in life
personality (combo of…)
combo of characteriesitcs/qual. --> inidivddual distinctive character
traits
distinguishing character/quality = describe consistent behaviors in individual
Gordon allport
1987
first true personality psych.
Theory: Trait Theory of Personality
Key Concepts: Focus on individual traits and patterns in personality = transformational = CONCERN how to measure traits --> Big 5
Mnemonic: "Allport's Array of Attributes."
1) 1. When considering graduate work in psychology, he decided to travel to Vienna and meet with Sigmund Freud at his Psychodynamic Institute ("breakthrough moment")
2. Decided to attend graduate school at Harvard and earned his PhD at the age of 24 (in 2 years of schooling)
3. Presented his theories of personality (from his graduate work) to his colleagues at his dissertation talk = REJECTED to some extent
Focus:
SURFACE traits to describe a person but 'traits'
= rejected by people who wanted to study abnormal personalities
Personality Traits: Their Classification and Measurement (1921)
Gordon allport
why first TRUE psych
on healthy individual and inidiv. diff (not abnormal prsonality)
traits = heart of personality
explored bio basis of traits
physiology
genetic inheritance
nuances of traits = analysis of frequency (occurances), intensity (strength), and range (situations eliciting occurences) of the TRAITS
challenge to Allport's theory
Allport believed understanding traits = explain individual differences and research = crucial to personality psychology
difficult to explore:
Unique trait combinations of individuals
VARIATION in the number of traits needed to DESCRIBE a person
Focus on the ways that traits can manifest themselves DIFFERENTLY across situations
sourcing traits
causation of traits = genetics, unshared environments
theory of traits
allport
social interactions and identity SHAPE personality traits and our interpretation of them
Cliques/Memberships
Anchoring effects
historical perspective of mental health
Phillipe Pinel's work in 1793 at the Parisian hospital system = Insisted that abnormal thoughts were not transmissible and were NOT DISEASES
Sigmund Freud's impact in the early 1900s = Looked at the mental side of mental health (consciousness, archetypes, etc)
Bio-psycho-social model
ABNORMAL behavior and/or thoughts is the RESULT of biological, sociocultural, and/or psychological factors that combine and interact
Diathesis-stress model:
BIO predispositions and ENV STRESS are both NECESSARY components for the manifestation of ABNORMAL behaviors or thoughts
Ways to Address the Biological
Psychosurgery
Medication
Psychosurgery
based on the idea that abnormality is caused by physical abnormalities of the BRAIN or NERVOUS SYSTEM
historical =focus on identifiable causes
Electro-Convulsive Shock Therapy (ECT): shocking/frying parts of brain or rebooting the brain with electricity
Lobotomies: go through naval cavaty and snip away parts of the brain
Medication
assumes that there is a CELLULAR/NEUROchemical link to certain disorders and mental issues
Benefits:
- Quick results and powerful reduction of symptoms
- Wide range of symptom applications
Cons:
Overmedication
Addiction
Tolerance effects
Long term value concerns (waning effects and no end): not finding the correct thing to fix + temporary effects
Concern over what's being "fixed" (car analogy) rather then the source
Ways to Address the Psychological
Psychotherapy = a treatment of psychological disorders and mental issues through methods that include an INTERACTIVE relationship between a trained therapist and a client or clients
- belief = source of mental health issues = thought-based
- main goal = addressing mental sources of mental health issues
ex/ psychoanalysis, behavioral approach, CBT, Humanistic appraoch
brief therapy, group therapy, self-help groups, integrative psychotherapy (eclectic therapy)
Psychoanalysis
Developed and introduced by Sigmund Freud
Based on his psychodynamic theory
A very interactive, expensive, and long process
- explores present and past
- diff tech. (talk, hypnosis, dream interp., etc)
!! primary attempt: IDENTIFY unconsciou thoughts, memories, and meotions that are dISTURBING --> bring into conscious --> addressed
CBT
cognitive behavioral appraoch
Attempts to address cognitions, emotions, and actions in attempts to HELP an individual
= gold standard = EFFICACY RESEARCH across wide range of disorders
Rational-emotive behavior therapy
CBT that assumes that PROBLEMS are result of INAPP./IRRAT. emotional rxn to situations
Albert Ellis
Look at situation + what emotional reactions/thoughts are causing that situation ==> Changing these thoughts to overcome those emotional and behavioral problems
ex/Negative emotions of shyness and guilt are from telling yourself of those emotions
The Behavioral Approach
Focus is on ADJUSTING actions to eventually change the mind
- effective as treamtent w/ several disorders ((substance abuse, phobias, and some eating disorders))
1) begins with clear well defined goals
2) attempts to achieve goals through diff. LERANING TOPICS + strengthening behavioral CONNECTIONS
- classical and operant conditioning
ex/ systematic desensitization
= exposure therapy of snakes
The Humanistic Approach
Carl rogers
Assumes mental health issues are a PRODUCT of disliking, misperceiving, or generating an incongruence of SELVES (MISMATCH between a IDEAL self and ACTUAL self)
= Assumes that "CLIENTS" are the only ones that can DETECT what is required to REACH their full potential (self-actualization) and ADDRESS the reasons for why they sought therapy in the first place
person or client-centered therapy: therapeutic approach = therapist incorp. TOTAL ACCEPTANCE AND UNCONDITIONAL POSITIVE REGARD TO CLIENT
- mirroring and client directed convo rather than teherapist directed = + supportive environment to lead to self-actualization
opiod epidemic
Increased because prescription cut off
Addiction
Inability to manage behavior around a certain area, and it causes trouble in your life
Tolerance
either
1) need MORE of substance to achieve the DESIRED effect
2) a DIMINISHED effect with continued use of the SAME amount
Withdrawal
negative physical and psychological effects that develop when a person STOPS taking a substance or REDUCING the amount, or RECURRENTuse of drug to relieve/AVOID withdrawal
Clinical Diagnosis (DSM-V)
Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders
Substance Use Disorders (DSM-V) (substance abuse)
- not addiction
Addiction (gambling)
- gambling disorder
Substance Use Disorder Symptoms:
Problematic pattern of use that impairs functioning. Two or more of symptom present for >=1yr
rate via rating scale
1) Impaired control over substance
- taken in larger amounts or for longer than intended
- • Persistent desire/unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control use
• A great deal of time spent to obtain, use, or recover from effects
- • Craving or strong desire or urge to use
2( social impairment
• Failure to fulfill obligations at work, school, or home
• Continued use despite relationship problems
• Big social/occupational/recreational acts given up or reduced
Risky Use
• Repeated use in physically DANGEROUS situations (e.g., driving)
• Continued use despite problems (physical or psychological)
Pharmacological Effects
• Tolerance
• Withdrawal
two interrelated types of dependence
physical: BIO Dependence and Body's GROWING tolerance of drug leading to WITHDRAWAL if drug is removed
Psychological: Neurochemical Dependence and Prsencen of antecedents cue the brain to STRONAGLY anticipate and DESIRE the substance and its reinforcing consequences
phyiscal dependence
growing tolerance to the drug
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms: irritability, anxiety, depression, fatigue, shakenness
Incentive-sentsitization theory
Psychological dependence
Liking (PLEASURE obtained by taking the drug)
Wanting (CRAVING for drug) --> Addiction = strengthened wanting
Dopamine system becomes SENSITIVE to the drug and cues associated with drug (e.g., needles, rolling papers, etc.) = EXCITEMENT
dopamine from psych. dependence
Using the substance stimulates dopamine receptors in nucleus accumbens
Housed in nucleus accumbens = brain's "attention and habit center" --> MORE!!
devleopment of dependency
Monkey respond to cue gets rewarded
Should not only depend on Dopamine released because some of them do not increase dopamine as much = not really as correlation
Perhaps how quick dopamine releases but not strong predictor
Drugs that block dopamine release but does not eliminate reward value of dopamine
Genetic and environmental influences on drug consumption
Usually with twin studies
Gene that effects liver's ability to metabolize alcohol = very SLOW to convert alcohol to acetaldehyde = slow accumulates ACETALDEHYDE so feel sick so avoid alcohol
Addiction and Treatment: nicotine
Nicotine replacement source(nicotine patch, gum, lozenges, or Rx options)
Counseling to support quit attempt
Addiction and Treatment: Alcohol
Inpatient (DETOX)
Alcoholic anonymous (AA)
Medications (Eg Antabuse)
Harm REduction
Cotingency Management
Relapse Prevention
Addiction and Treatment: Opiates (and others)
Narcotes Annonymous (NA) - all substances
Substitiute (eg. methadone for opiates - weekly taking it and also weed off this as well)
Contingency Management
DSM
diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders
classify disorders
- anxiety/depressive disorders are similar
- Depression, Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), Persistent Depressive Disorder, and Bipolar Disorder =affective disorders
Anxiety Disorders:
intense experience of anxiety
impact life (school, work, relationships), are PERSISTENT, and are often UNDESIRED by those suffering
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Panic Disorder
Phobias
GAD
symptoms + diagonisis
prevalence
treatment
Involves a pervasive and free-floating anxiety
continuously tense and jittery, and usually SFFER from sleeplessness (tired/withdrawn)
least 6 months for diagnosis
Found in 2-3% of the population at any given time (more in women 2-3x, lower income, relationship issues)
treatment: antidepressant medication, CBT, INABILITY to taper off drugs