light dependent reactions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
location of light independent reactions
takes place in the stroma of chloroplast
location of light dependent reactions
occurs in thylakoid membrane, requires chlorophyll
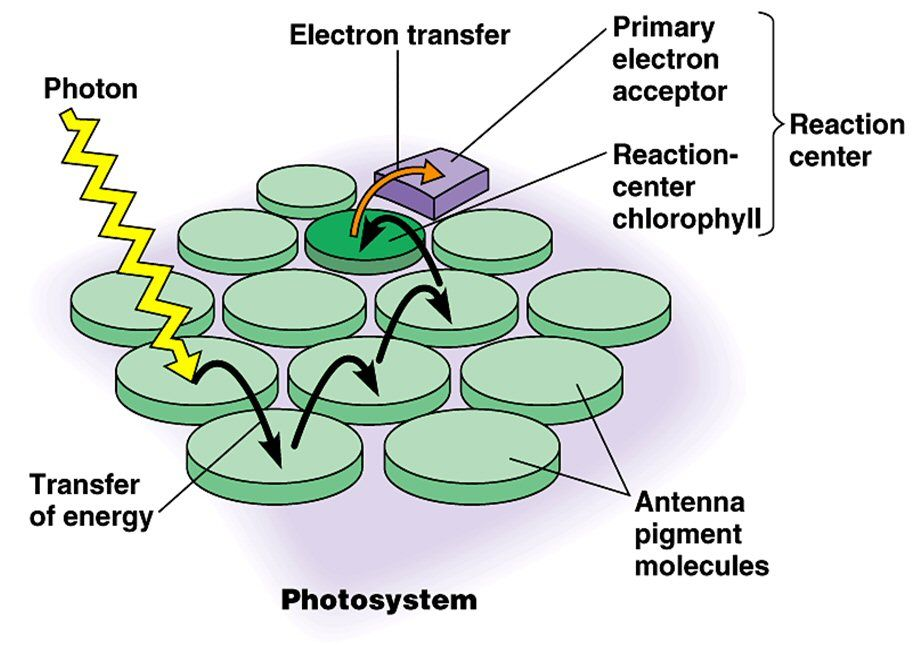
photosystems
photosystems are clusters of pigments embedded in the thylakoid membrane
photosystem is made of 2 chlorophyll a molecules (reaction molecules) and surrounding accessory pigments (antenna complex)
antenna complex harvests the light and passes it to the reaction center
types of photosystems
photosystem I (P1) → P700, absorbs up to 700nm wavelengths
photosystem II (P2) → P680, absorbs up to 680nm in wavelength
reaction centers are identical but accessory pigments are different, so they absorb slightly different wavelengths
NADPH
electron carrier used in photosynthesis and is involved in anabolic reactions
NAPH has P group
light reactions
when light strikes the thylakoid membrane, photo systems absorb a photon, that energy is passed from pigment to pigment in the antenna complex until it reaches the reaction center
energy from the photo eventually excites the electrons in the chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center
5 components of light reactions (in order)
photosystem II
cytochrome complex
photosystem I
NADP+ reductase
ATP synthase
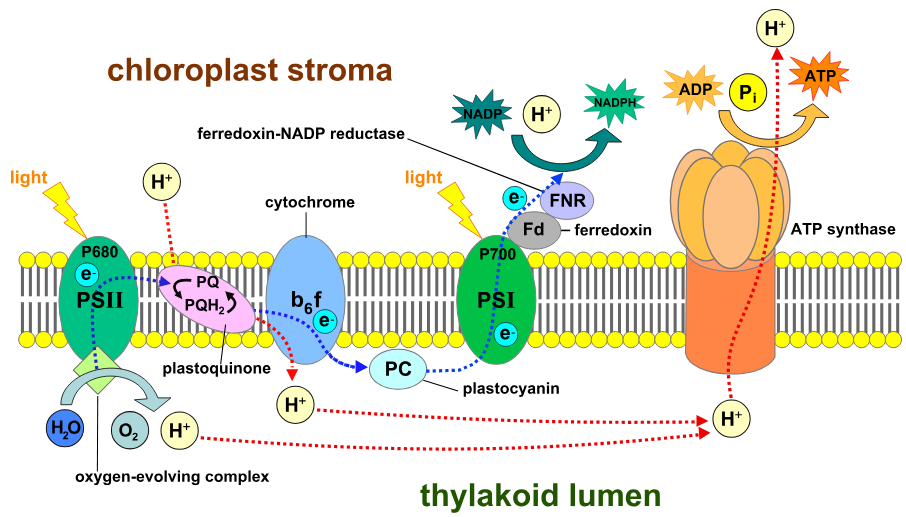
non-cyclic — step 1 (photoexcitation)
electrons excited by photons (antenna complex), photosystem II
energy is passed until it reaches P680
P680 is excited and leaves PS2 to pheophytin (primary e acceptor of PS2)
photoexcitation happens in PS1 as well, electron of P700 is excited and goes to ferredoxin (primary electron acceptor in PS1)
split water into O, 2H+, 2e by Z protein, provides electrons (O is waste product)
non-cyclic — step 2 (ETC)
Q cycle: some energy in the electron is used by the cytochrome complex to pump H+ into the lumen to make an electrochemical gradient
non-cyclic — step 3 (photoexcitation)
PS1 accepts electron, replaces electron that was previously there
photon absorbed by PS1 and re-excites the electron that just arrived
non-cyclic — step 4 (ETC)
electrons (P700) re-excited by photon
ferredoxin brings the electron to another ETC (Calvin cycle) where it reaches NADP+ reductase
NADP+ reduced to NADPH
in the Calvin cycle, electron goes back to cytochrome
non-cyclic — step 5 (photophosphorylation)
cytochrome complex pumps H+ into the thylakoid lumen
H+ gradient (H+ lumen > H+ stroma)
H+ moves through ATP synthase into the stroma, making ATP
cyclic electron flow
happens when there’s low O2, low levels of NADP+, low ATP : NADPH ratio
only PS1 used, P700 donates its electron to ferredoxin, go to Q cycle and BACK to P700
makes a proton gradient for ATP synthesis but doesn’t release electrons to get NADPH