Integumentary and Immune System
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
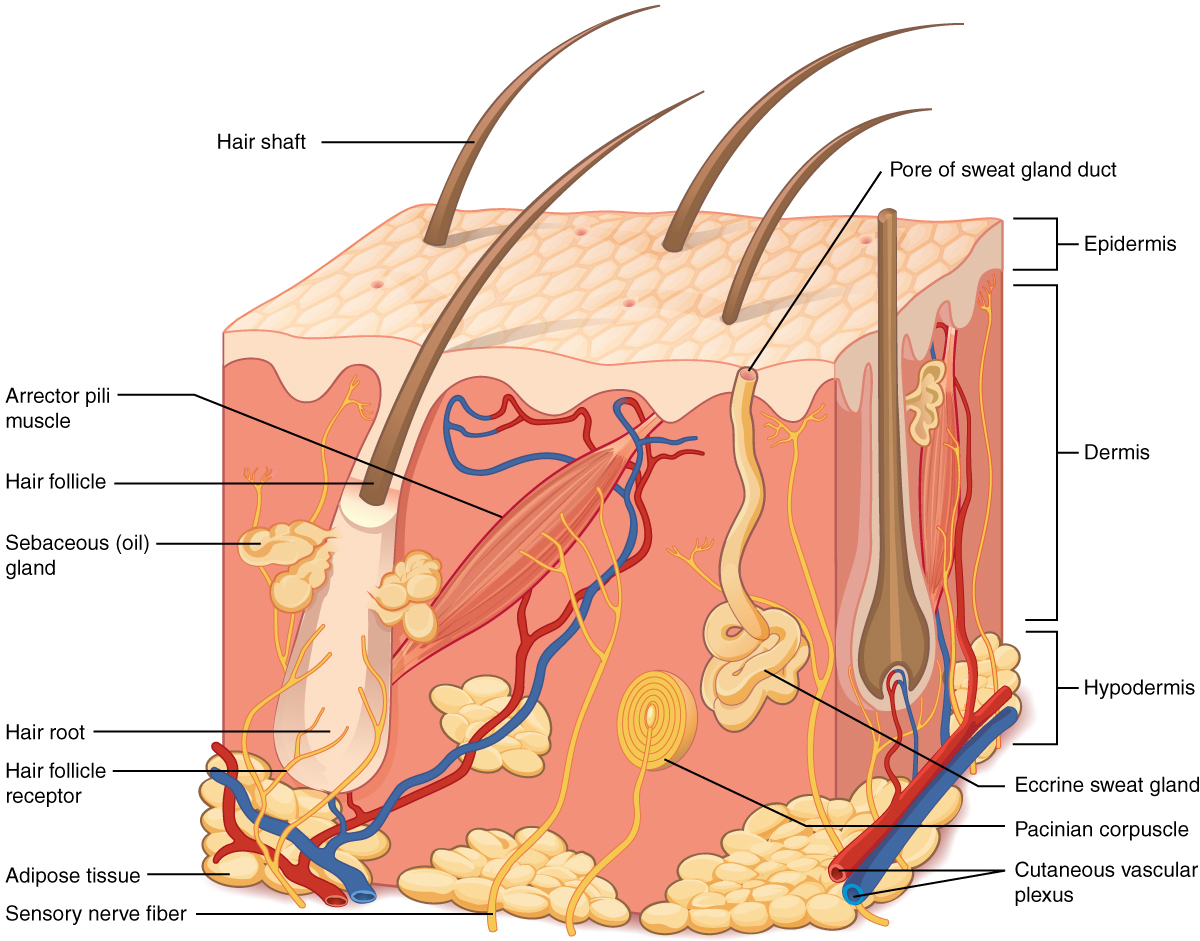
Skin (Cutaneous Membrane)
Definition: The body's outer covering made of epithelial and connective tissue.
Importance: Protects internal organs, regulates temperature, and provides sensory input.
Function: Acts as a barrier, regulates heat, synthesizes vitamin D, and detects stimuli.
Location: Covers the entire body.
Quick Tip: Skin is your first line of defense — treat it gently and moisturize regularly.
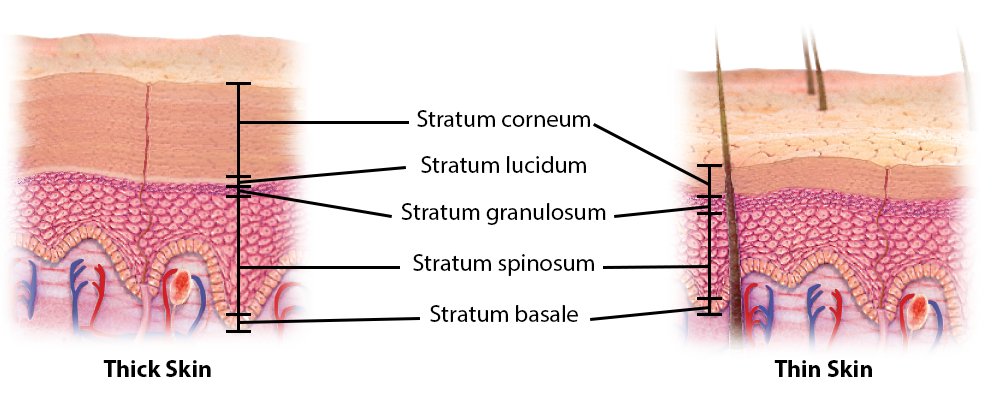
Thin Skin
Definition: Type of skin that grows hair and lacks dermal ridges.
Importance: Provides flexibility and sensory input.
Function: Covers most of the body and allows hair growth.
Location: Found everywhere except palms and soles.
Quick Tip: If it grows hair, it’s thin skin.
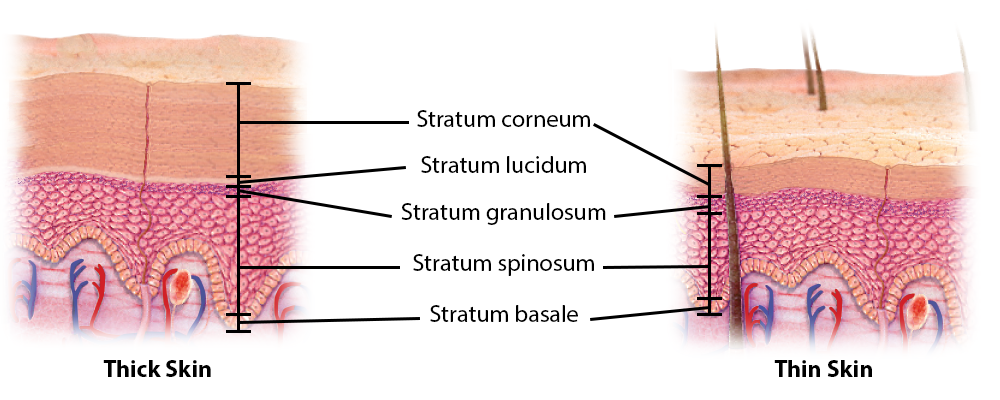
Thick Skin
Definition: Hairless skin with dermal ridges designed for friction resistance.
Importance: Enhances grip and protects high-friction areas.
Function: Prevents damage in areas of frequent contact.
Location: Palms of hands and soles of feet.
Quick Tip: Fingerprints come from thick skin’s dermal ridges.
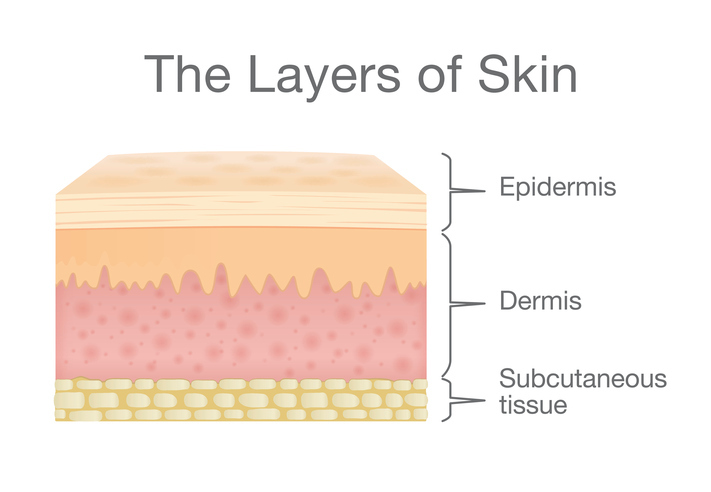
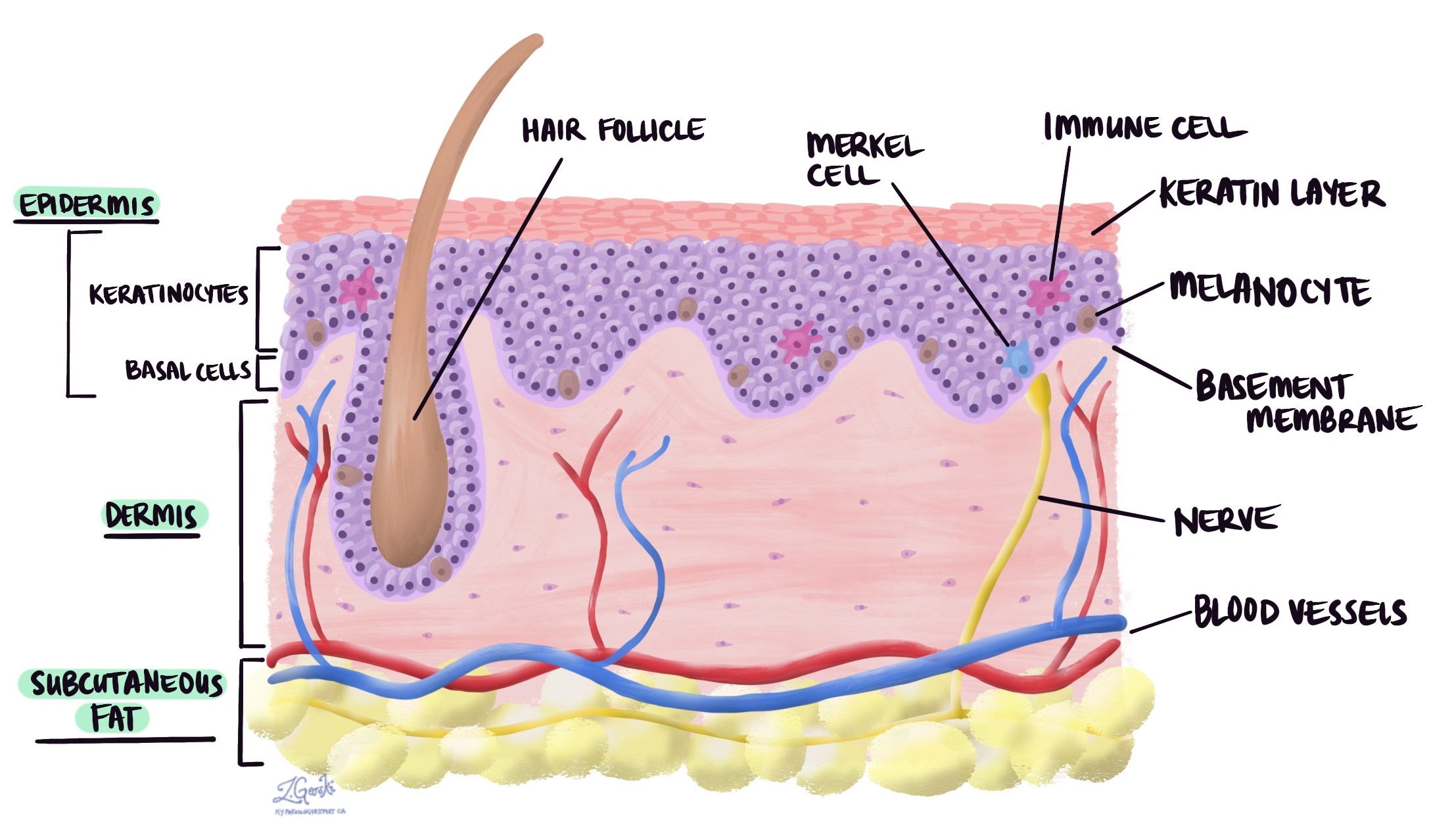
Epidermis
Definition: The outermost layer of skin made of stratified squamous epithelial tissue.
Importance: Provides waterproof protection and regenerates quickly.
Function: Shields against dehydration, UV rays, and pathogens.
Location: Superficial layer of skin.
Quick Tip: The epidermis is avascular — it gets nutrients from the dermis below.
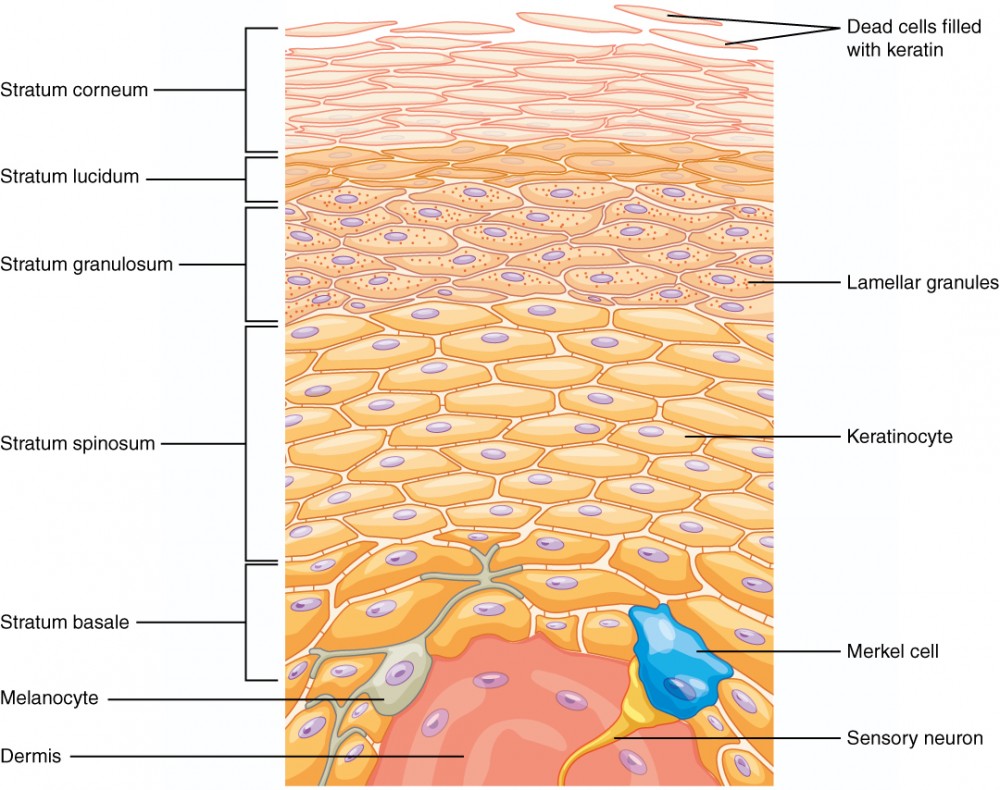
Stratum Corneum
Definition: Top layer of epidermis made of dead keratinized cells.
Importance: Acts as a tough, protective barrier.
Function: Prevents water loss and blocks pathogens.
Location: Outermost layer of epidermis.
Quick Tip: This is the layer that flakes off when your skin peels.
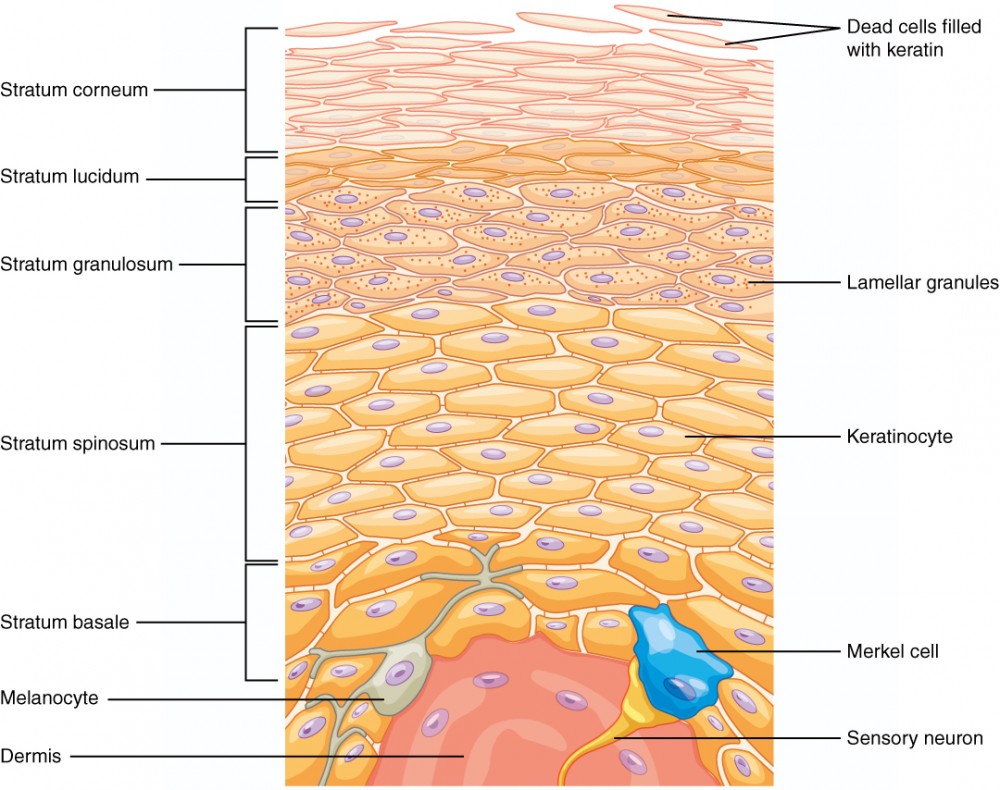
Stratum Lucidum
Definition: Clear layer found only in thick skin.
Importance: Adds extra protection in high-friction areas.
Function: Enhances durability of thick skin.
ABSENT IN THIN SKIN
Location: Palms and soles.
Quick Tip: If it’s not on your palm or sole, it’s not lucidum
Surface Film
Definition: A thin layer of sweat, oil, and dead cells on the skin.
Function: Protects, hydrates, and prevents infection.
Location: On the outermost skin layer (stratum corneum).
Importance: Keeps skin healthy and balanced.
Quick Tip: “Sweat + oil = skin shield” It’s your body’s natural armor—keeping moisture in and germs out.
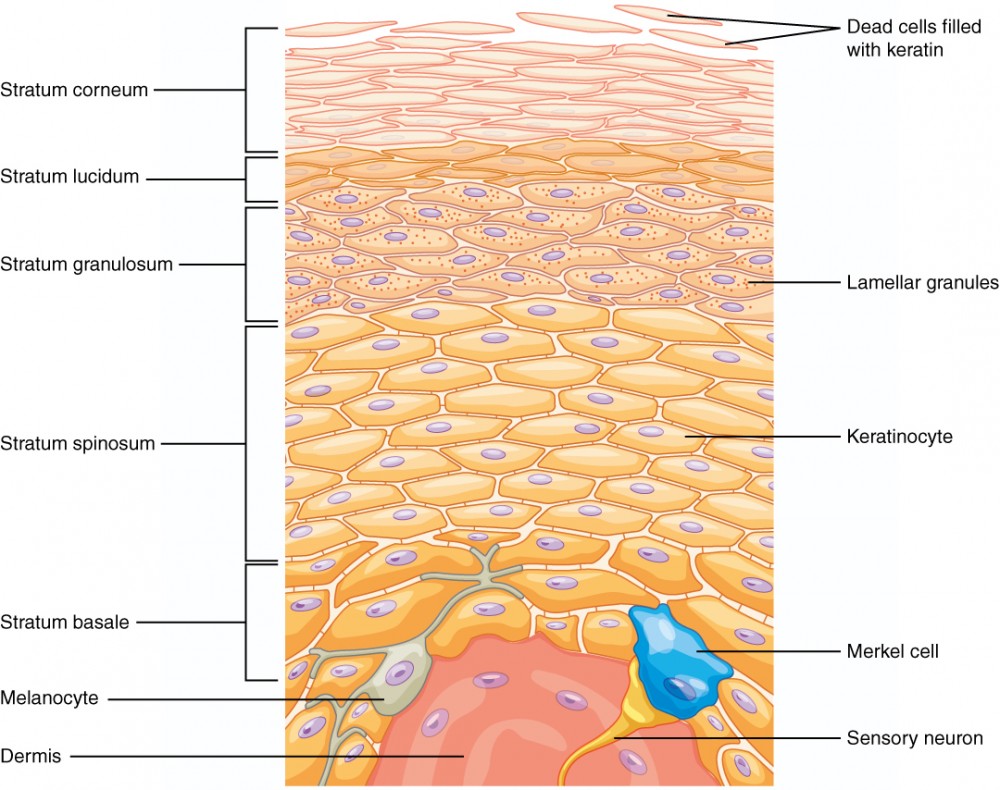
Stratum Granulosum
Definition: Layer where cells begin to die and keratinize.
Importance: Prepares cells for protective outer layer.
Function: Transitions living cells to dead protective cells.
Location: Middle layer of epidermis.
Quick Tip: This is the skin’s “prep zone” before cells die.
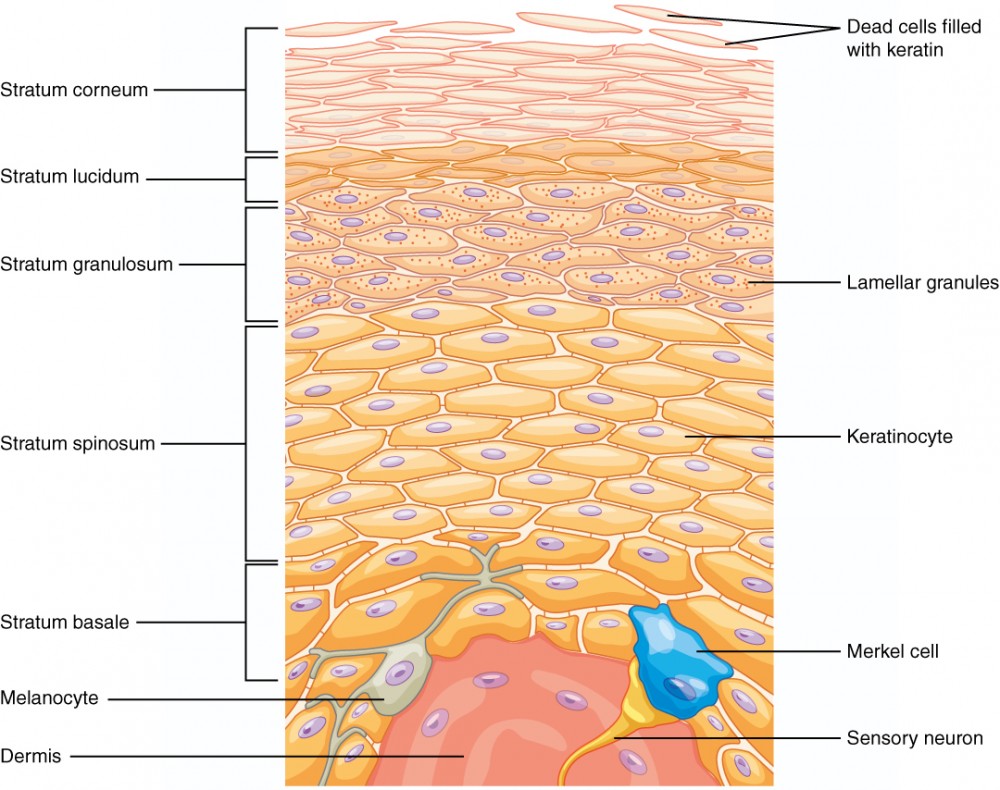
Stratum Spinosum
Definition: Layer where cells are held together by desmosomes.
Importance: Provides structural integrity.
Function: Supports skin strength and some cell division.
Location: Just above the stratum basale.
Quick Tip: Desmosomes = skin’s Velcro.
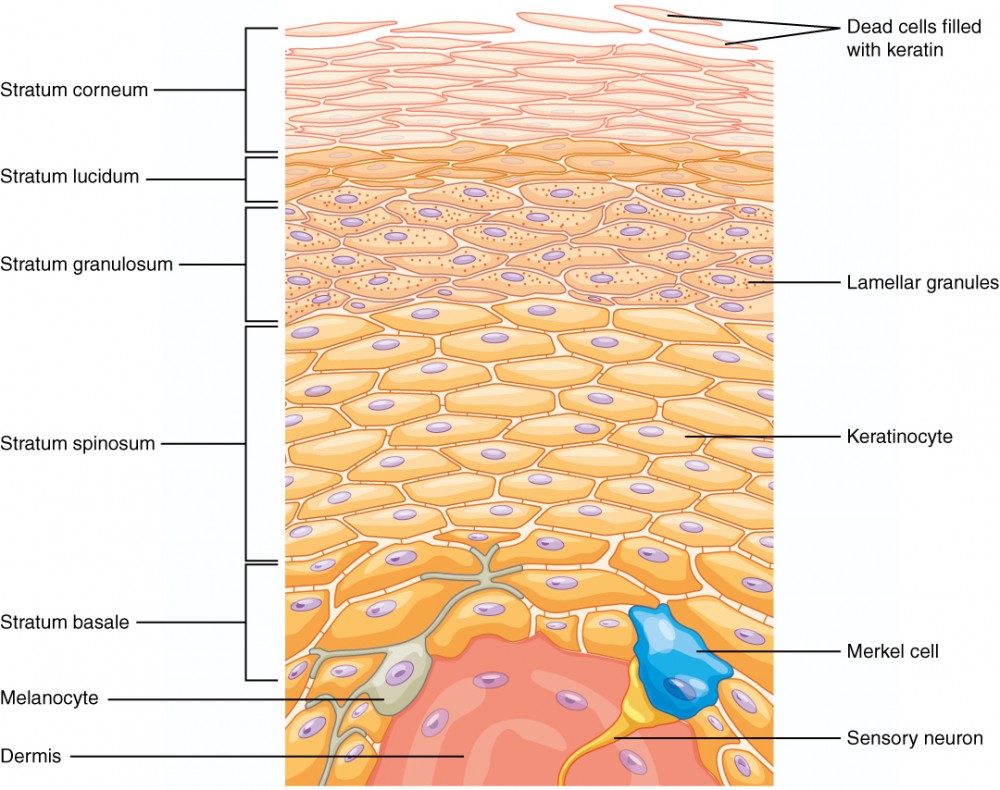
Stratum Basale
Definition: Deepest layer of epidermis with high mitotic activity.
Importance: Generates new skin cells.
Function: Replaces dead cells with new ones.
Location: Base of epidermis.
Quick Tip: Skin regeneration starts here.
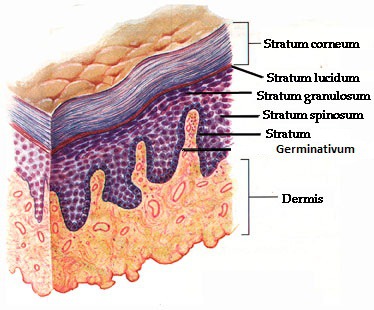
Stratum Germinativum
Definition: Combined term for stratum basale and stratum spinosum.
Importance: Site of active cell division.
Function: Produces new epidermal cells.
Location: Lower layers of epidermis.
Quick Tip: Germinativum = growth zone.
5 Layer Epididermis (Superifical to deep)
Stratum corneum
Composed of dead, flattened keratinocytes.
Acts as a tough, protective barrier.
Stratum lucidum ✨ (only in thick skin like palms and soles)
Thin, clear layer of dead cells.
Adds extra protection and thickness.
Stratum granulosum
Cells begin to die and accumulate keratohyalin granules.
Helps waterproof the skin.
Stratum spinosum 🕸
Contains living keratinocytes connected by desmosomes.
Provides strength and flexibility.
Stratum basale (germinativum) 🌱
Deepest layer, where cell division occurs.
Contains melanocytes and stem cells for regeneration.
(Come, lets, get, sun, burnt)
Keratinize
Definition: When skin cells produce keratin, a tough protein, and become part of the outer protective layer.
Function: Makes skin strong, water-resistant, and protective.
Location: Happens in the epidermis, especially in the stratum corneum.
Importance: Shields your body from germs, injury, and dehydration.
Quick Tip: Think of it like “armor-building”—your skin cells toughen up as they rise to the surface
Keratinocytes
Definition: Cells that produce keratin.
Importance: Waterproofs and protects skin.
Function: Form the bulk of the epidermis.
Location: Throughout epidermis.
Quick Tip: Dry skin often means keratinocytes need support.
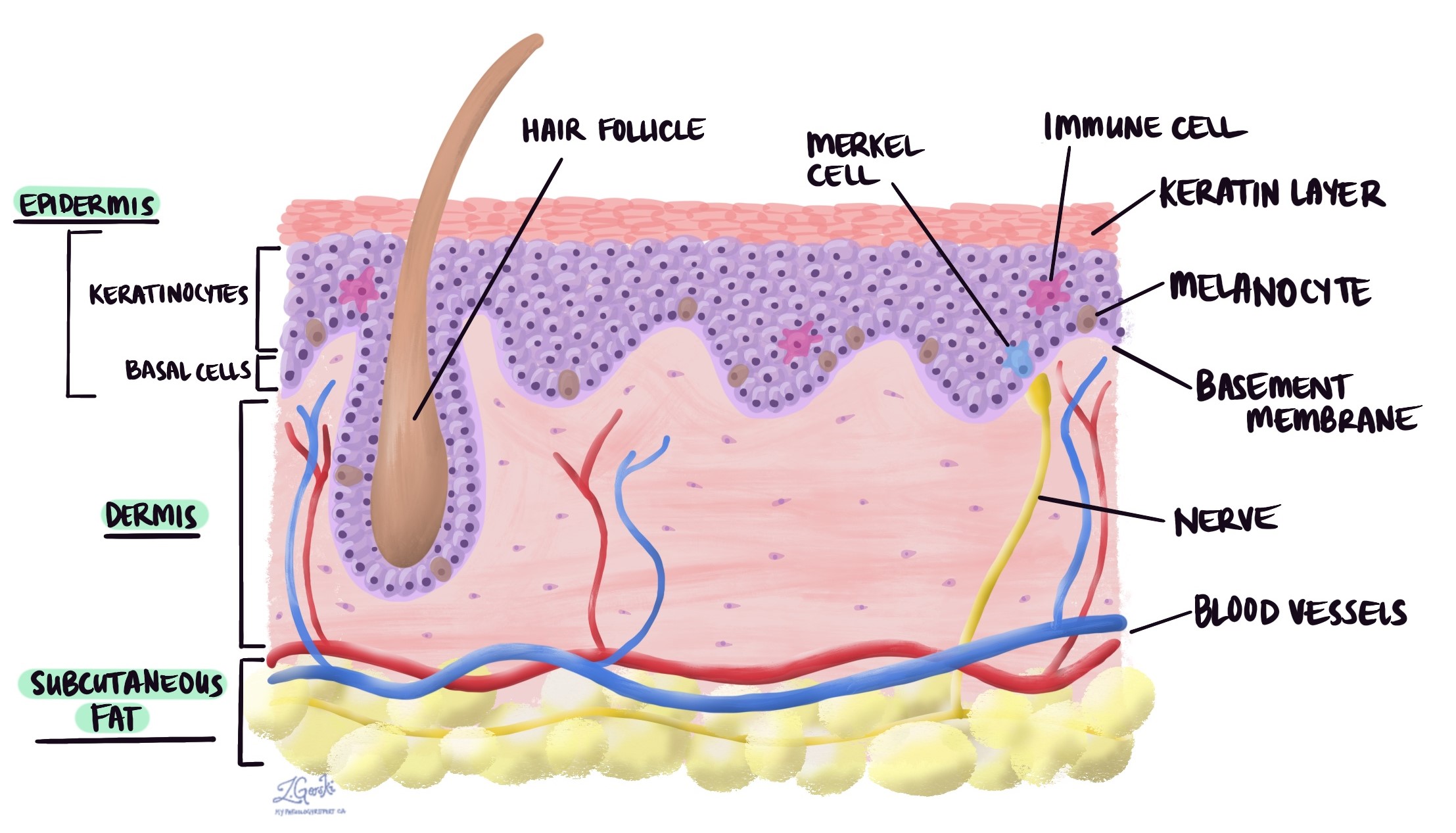
Melanocytes
Definition: Cells that produce melanin pigment.
Importance: Protects DNA from UV damage.
Function: Absorbs UV light to prevent mutations.
Location: Stratum basale.
Quick Tip: More sun = more melanin = darker skin.
Dendritic Cells
Definition: Immune cells that respond to skin damage.
Importance: First responders to infection.
Function: Trigger immune response.
Location: Epidermis.
Quick Tip: Scratches activate these defenders.
Merkel Cells
Definition: Sensory receptors for touch.
Importance: Detect light pressure.
Function: Relay tactile information.
Location: Stratum basale.
Quick Tip: Sensitive areas like fingertips have more Merkel cells.
Dermoepidermal Junction
Definition: Basement membrane between epidermis and dermis.
Importance: Anchors skin layers together.
Function: Prevents separation and supports skin structure.
Location: Between epidermis and dermis.
Quick Tip: Blisters form when this junction is disrupted.
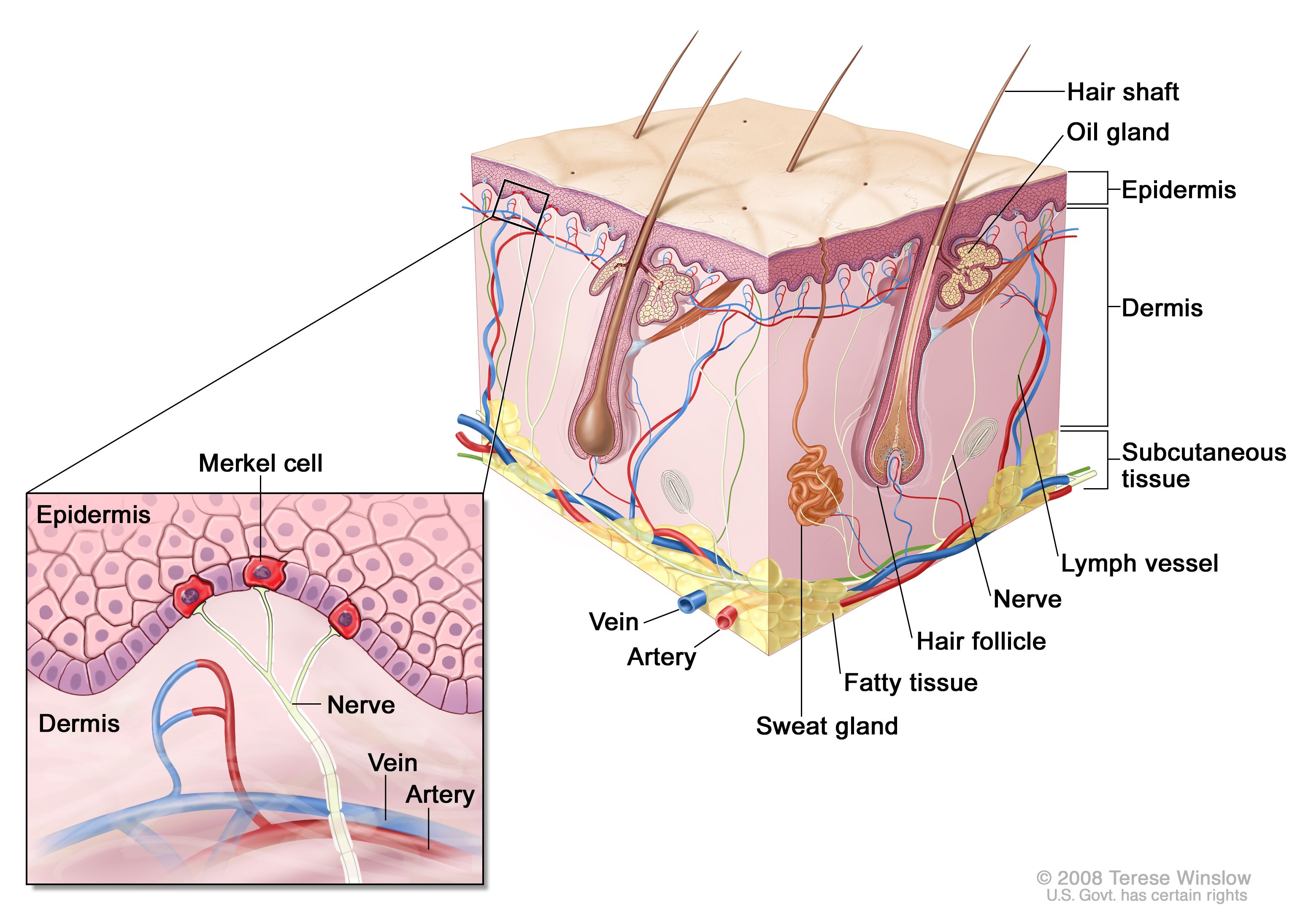
Dermis
Definition: Thicker, vascular layer beneath epidermis.
Importance: Supports skin with blood supply and strength.
Function: Nourishes epidermis and provides elasticity.
Location: Beneath epidermis.
Quick Tip: Scar tissue forms here due to low mitosis.
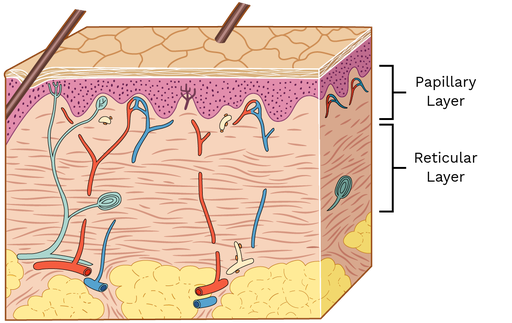
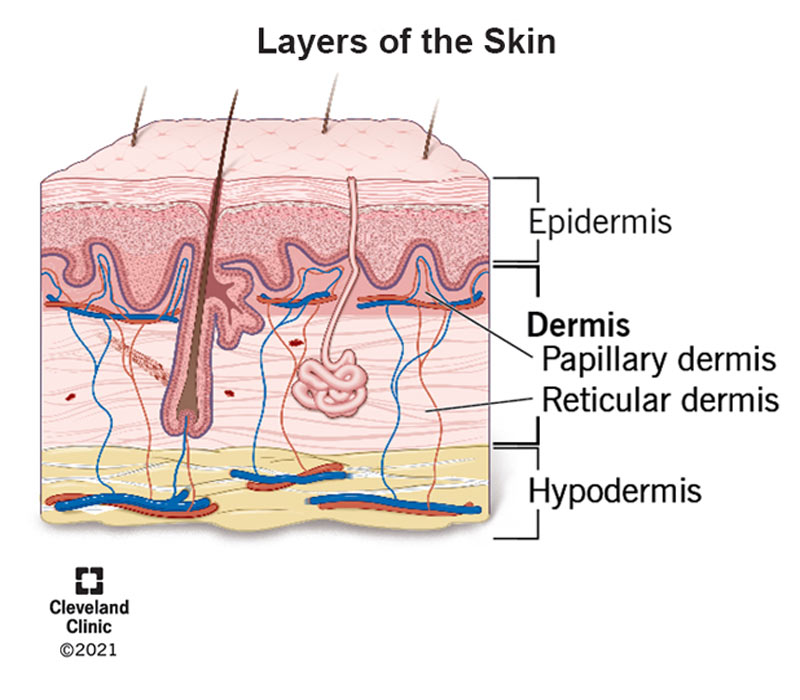
Papillary Layer (Superficial dermis layer)
Definition: The upper layer of the dermis, just beneath the epidermis.
Function: Supplies nutrients to the skin, supports temperature regulation, and helps with touch sensation.
Location: Directly under the epidermis, part of the dermis.
Importance: Contains capillaries and nerve endings—key for feeling and skin health.
Quick Tip: Think of it as the “support crew” for your skin’s surface—feeding it and helping you feel touch
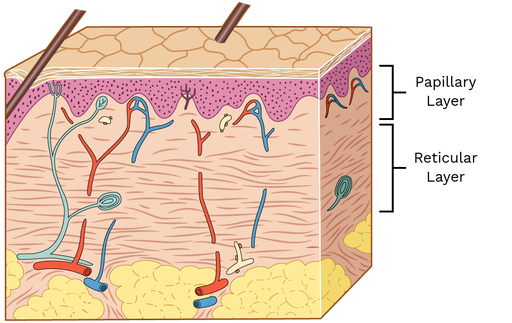
Reticular Layer (Deep dermis layer)
Definition: The deeper, thicker part of the dermis.
Function: Provides strength, elasticity, and houses structures like sweat glands, hair follicles, and blood vessels.
Location: Beneath the papillary layer, part of the dermis.
Importance: Supports skin structure and anchors important skin functions.
Quick Tip: Think of it as the “foundation layer”—strong, stretchy, and full of working parts.
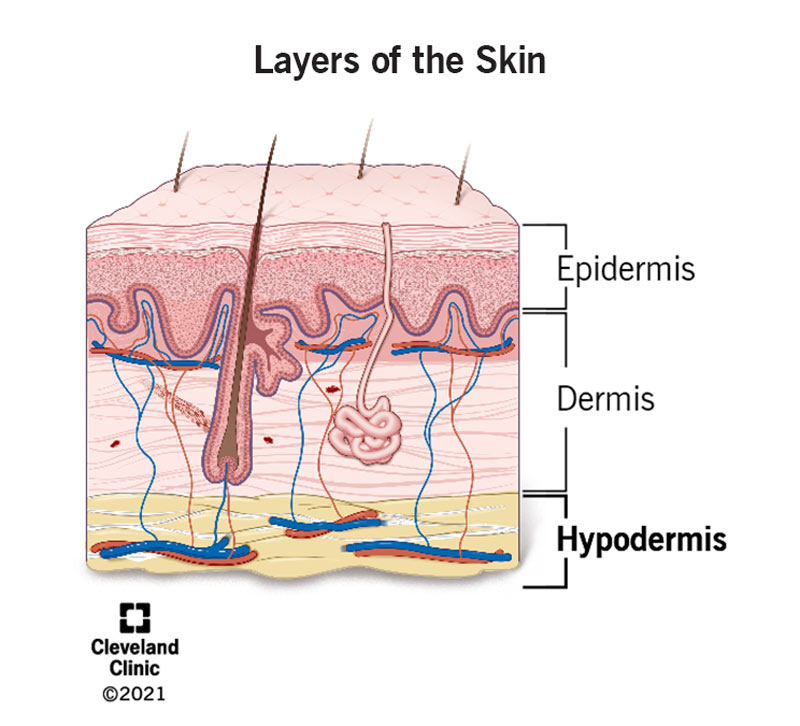
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)
Definition: Fat-rich layer beneath dermis.
Importance: Insulates and cushions the body.
Function: Stores energy and regulates temperature.
Location: Deepest skin layer.
Quick Tip: Pinch your skin — the squishy part is hypodermis.
Hair
Definition: Keratinized shaft growing from follicle.
Importance: Protects and senses environment.
Function: Detects touch and regulates temperature.
Location: Thin skin areas.
Quick Tip: Goosebumps = arrector pili muscle action.
Nails
Definition: Keratin plates from germinal matrix.
Importance: Protects fingertips and aids precision.
Function: Enhances fine motor skills.
Location: Ends of fingers and toes.
Quick Tip: Cuticle protects nail root from infection.
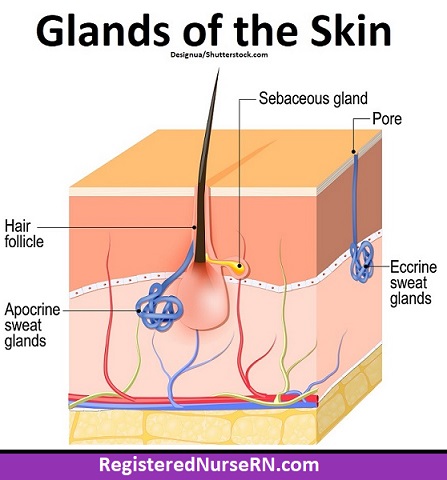
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Definition: Sweat glands that regulate temperature.
Importance: Prevents overheating.
Function: Secrete sweat directly to skin surface.
Location: All over body.
Quick Tip: Active during exercise or heat.
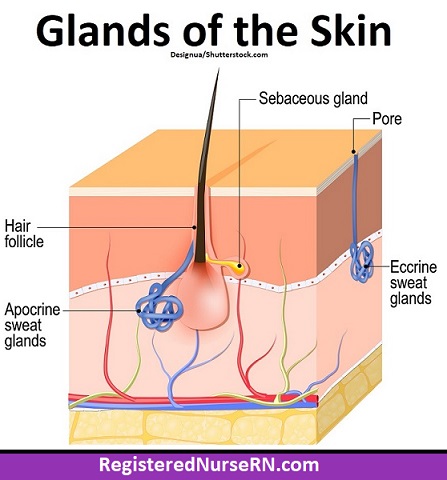
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Definition: Stress-related sweat glands.
Importance: May release pheromones.
Function: Secrete sweat through hair follicles.
Location: Armpits and groin.
Quick Tip: Start working at puberty.
Sebaceous Glands
Definition: Oil glands that secrete sebum.
Importance: Lubricates and protects skin and hair.
Function: Moisturizes and prevents drying.
Location: Near hair follicles.
Quick Tip: Overactive glands = acne risk.
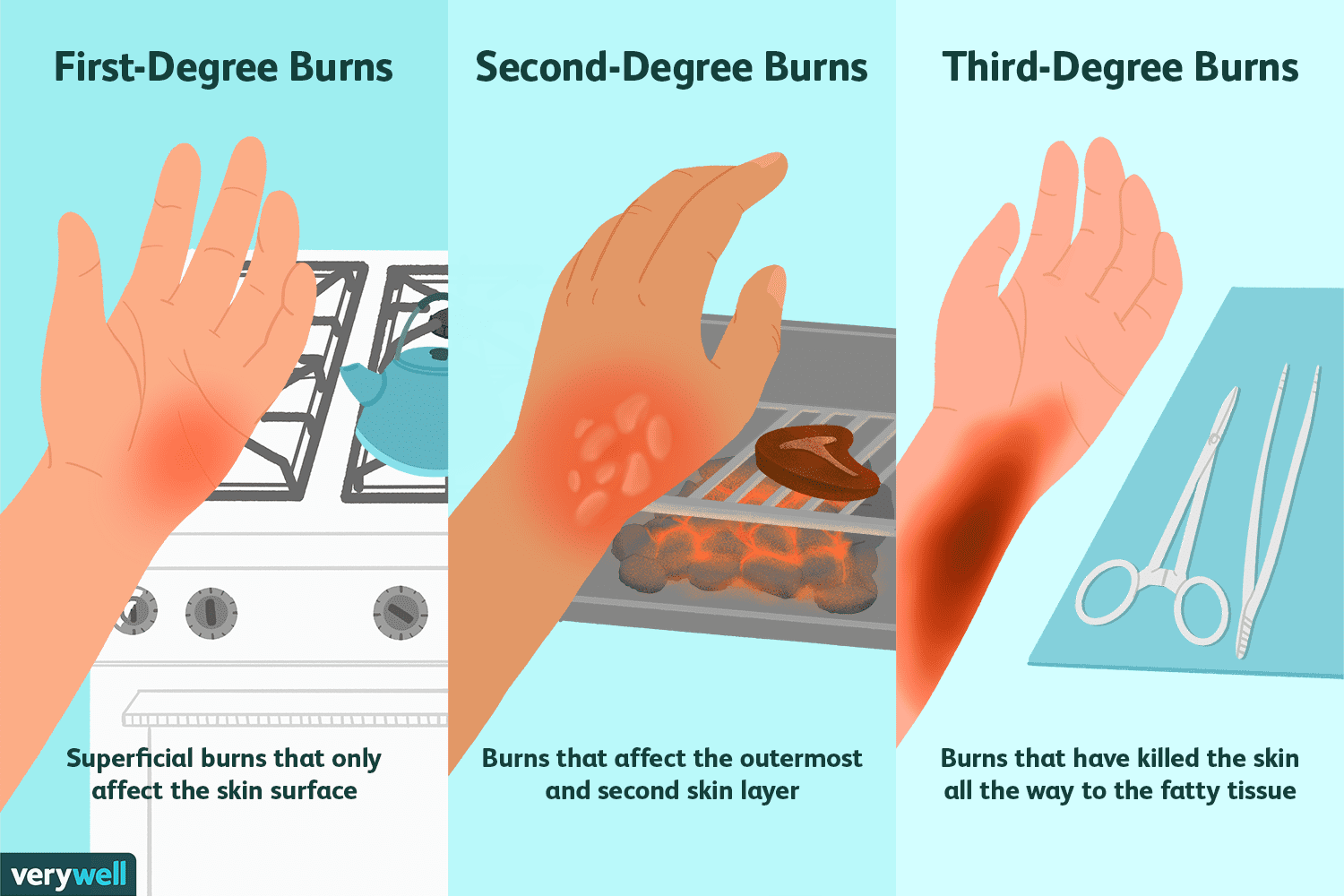
First Degree Burn
Definition: A mild burn affecting only the outer layer of skin (epidermis).
Symptoms: Redness, pain, and slight swelling—no blisters.
Location: Can happen anywhere on the skin, often from sunburn or brief contact with heat.
Importance: Usually heals in a few days without scarring; still needs care to prevent infection.
Quick Tip: Cool the area with water (not ice), keep it clean, and moisturize gently.
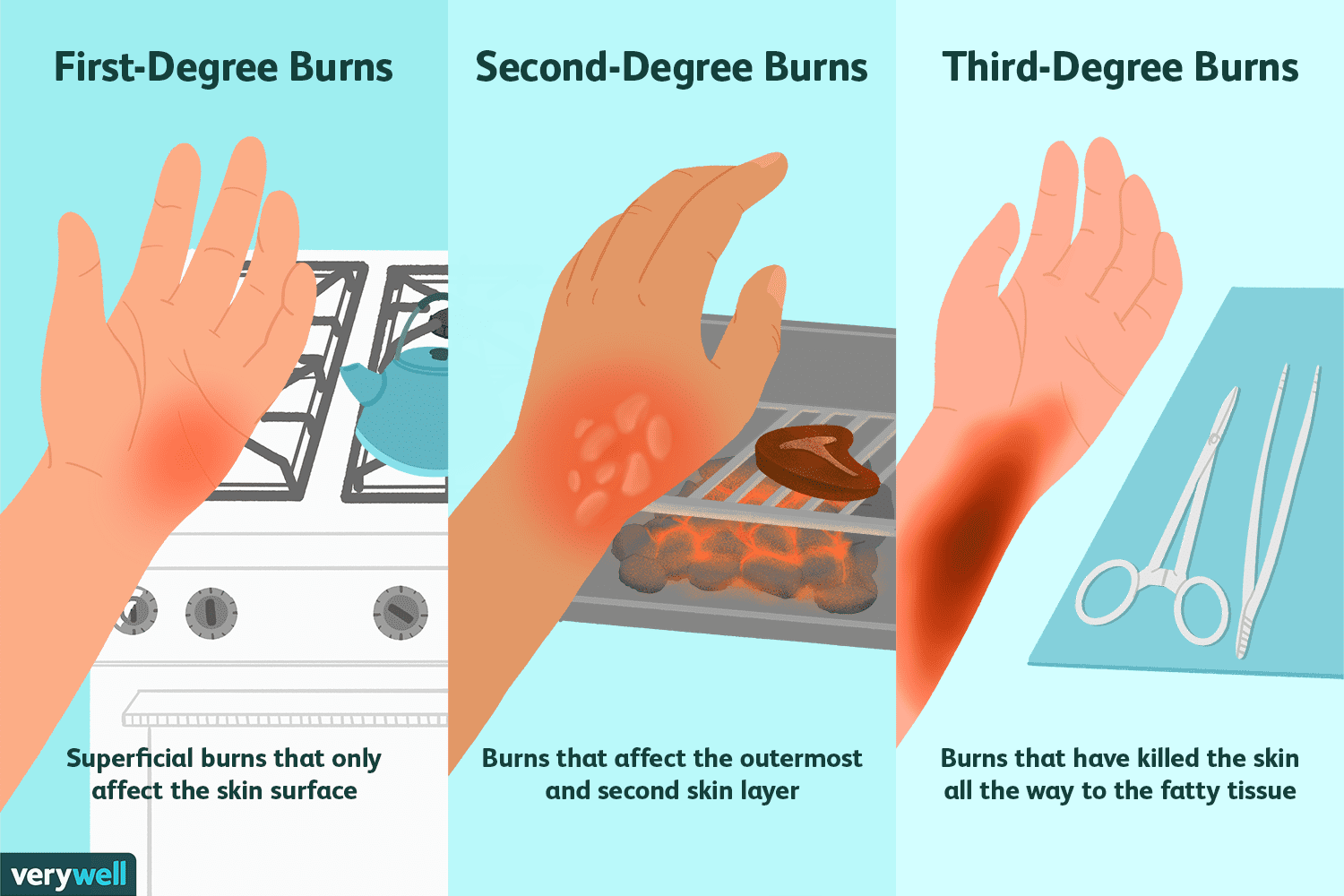
Second Degree Burn
Definition: A burn that affects both the epidermis and part of the dermis.
Symptoms: Redness, pain, swelling, and blisters.
Location: Can occur anywhere on the skin from hot liquids, flames, or chemicals.
Importance: More serious than first-degree; may scar and needs proper care to heal.
Quick Tip: Cool gently with water, cover with a clean cloth—don’t pop blisters
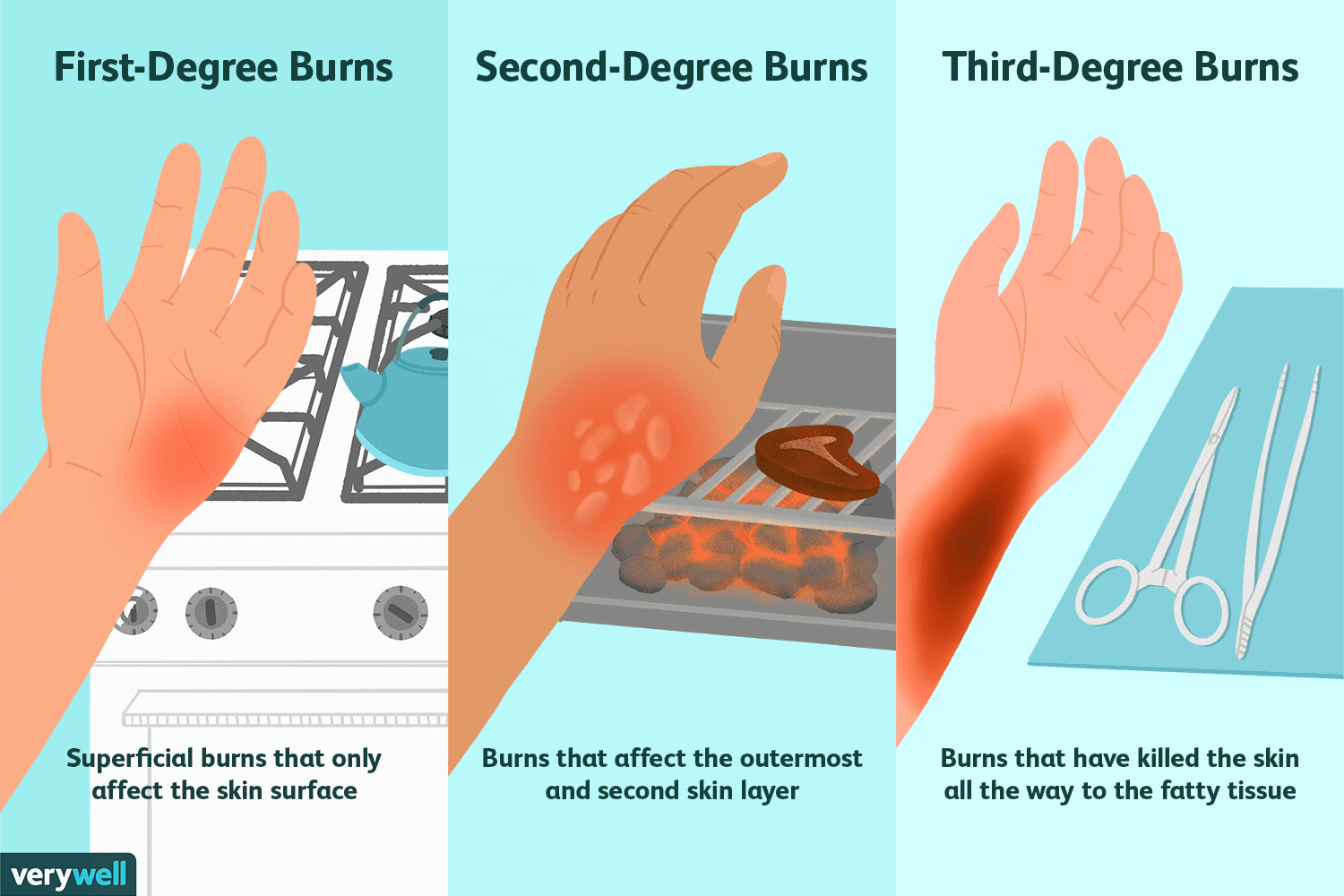
Third Degree Burn
Definition: A severe burn that damages all layers of skin—epidermis, dermis, and sometimes deeper tissues.
Symptoms: Skin may look white, black, or leathery; no pain in the area due to nerve damage.
Location: Can affect any body part exposed to intense heat, chemicals, or electricity.
Importance: Requires urgent medical care; healing is slow and often needs skin grafts.
Quick Tip: Never treat this at home—call emergency services immediately.
Fourth Degree Burn
Definition: A burn that goes through all skin layers and into muscle, bone, or deeper tissues.
Symptoms: Charred skin, exposed tissue, no pain due to complete nerve destruction.
Location: Often from prolonged exposure to fire, electricity, or chemicals.
Importance: Life-threatening; requires emergency care, surgery, and often amputation or grafting.
Quick Tip: This is a medical emergency—call 911 immediately and avoid touching or treating the area
Scar
Definition: A mark left on the skin after healing from a wound or injury.
Function: Protects the repaired area with collagen, but lacks full strength and flexibility.
Location: Can form anywhere the skin or tissue was damaged.
Importance: Shows where healing occurred; may affect appearance or movement depending on depth.
Quick Tip: Keep healing skin moisturized and protected from sun to reduce scarring.
Immune System
Definition: Your body’s defense network against germs and disease.
Function: Detects, attacks, and remembers harmful invaders.
Location: Found in blood, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and more.
Importance: Keeps you healthy and heals damage.
Quick Tip: Sleep, eat well, and manage stress to stay strong.
First line of defense
Definition: Physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes.
Importance: Prevents pathogen entry.
Function: Blocks invaders before they enter.
Location: Body surfaces.
Quick Tip: Washing hands strengthens this line.
Second line of defense
Function: Responds quickly to pathogens that breach physical barriers, using internal, non-specific immune mechanisms.
Importance:
Destroys invaders before they spread
Activates inflammation and fever
Bridges to adaptive immunity
Location & Components:
Bloodstream
Phagocytes (neutrophils, macrophages): engulf and digest microbes
Natural Killer cells: destroy infected or abnormal cells
Inflammation: increases blood flow and immune cell access
Fever: raises body temperature to slow pathogens
Complement system: tags and bursts microbes
Interferons: warn nearby cells of viral threats
Quick Tip: “Second line = internal strike team.” Fast, fierce, and non-specific — like emergency responders inside the body.
Third Line of Defense
Function: Targets specific pathogens using learned immune responses.
Importance:
Builds long-term immunity
Remembers past invaders
Activates B cells (antibodies) and T cells (cell-mediated defense)
Location & Components:
B cells: produce antibodies
T cells: kill infected cells and regulate response
Found in lymph nodes, spleen, and blood
Quick Tip: “Third line = smart sniper squad.” Precise, powerful, and remembers the enemy.
What does Dermis and Connective tissue have in common?
Vascular
Dermis made of clumped collagen (part of dense irregular CT)
Have extracellular matrix
What does Epidermis and Epithelial Tissue have in common?
Avascualar
Lacks packed cells
Lack extracellular matrix
Both are surface covering
Can Epidermis regenerate?
Yes!
The epidermis renews itself using basal stem cells in the bottom layer.
New cells rise, harden with keratin, and shed—completing a cycle in 4–6 weeks.
Minor injuries heal without scarring since it has no blood vessels.
Can Dermis regenerate?
Yes! the dermis can regenerate, but not as completely as the epidermis.
It heals through fibroblasts, which produce collagen and rebuild tissue.
However, deep damage often leads to scarring, since the dermis doesn’t fully restore its original structure.
Its blood vessels help deliver nutrients and immune cells to support healing.
Temperature Homeostasis via Dermal Blood Supply
Vasodilation:
Blood vessels widen when you're hot.
More blood flows near the skin surface → heat is released → body cools down.
Vasoconstriction:
Blood vessels narrow when you're cold.
Less blood reaches the surface → heat is conserved → body stays warm.
Quick Tip: Think “dilate to dump heat, constrict to conserve.”
White blood cells
Definition: Immune cells that fight infection and disease.
Types:
Neutrophils – fast responders to bacteria
Lymphocytes – include B and T cells for targeted defense
Monocytes – clean up debris and become macrophages
Eosinophils – fight parasites and trigger allergies
Basophils – release histamine during allergic reactions
Location: Found in blood, lymph, and tissues.
Quick Tip: Think of WBCs as your body’s defense squad—each with a special role.
Self Tolerance
Definition: The immune system’s ability to ignore your own cells while attacking foreign invaders.
Why It Matters: Prevents autoimmune diseases—where the body mistakenly attacks itself.
How It Works:
During development, immune cells are trained to avoid reacting to self-antigens.
B and T cells that strongly recognize self are deleted or silenced.
Failure of Tolerance: Leads to conditions like Type 1 diabetes, lupus, or multiple sclerosis.
🧠 Quick Tip: Think of self-tolerance as your immune system’s “do not attack home base” rule.

Lanugo (Hair)
Function: Helps hold vernix caseosa (a waxy coating) on the skin for protection in the womb.
Location: Covers the entire fetal body, especially shoulders, back, and face.
Aids in skin protection and moisture balance
Keeps baby warm before fat develops
May signal nutritional issues if seen in adults (e.g., anorexia)
Quick Tip: Think of lanugo as “nature’s fuzzy blanket” for babies before birth
Before birth hair

Vellus (Hair)
Function: Provides light insulation and sensation; helps regulate body temperature subtly.
Location: Covers most of the body—face, arms, chest, back—except palms, soles, lips, and some genital areas.
Importance:
Replaces lanugo after birth
Protects skin gently without being visible
Can convert to terminal hair during puberty (e.g., on legs or face)
Quick Tip: Think of vellus as your “invisible armor”—soft, fine, and quietly protective.
Peach fuzz —- after birth hair
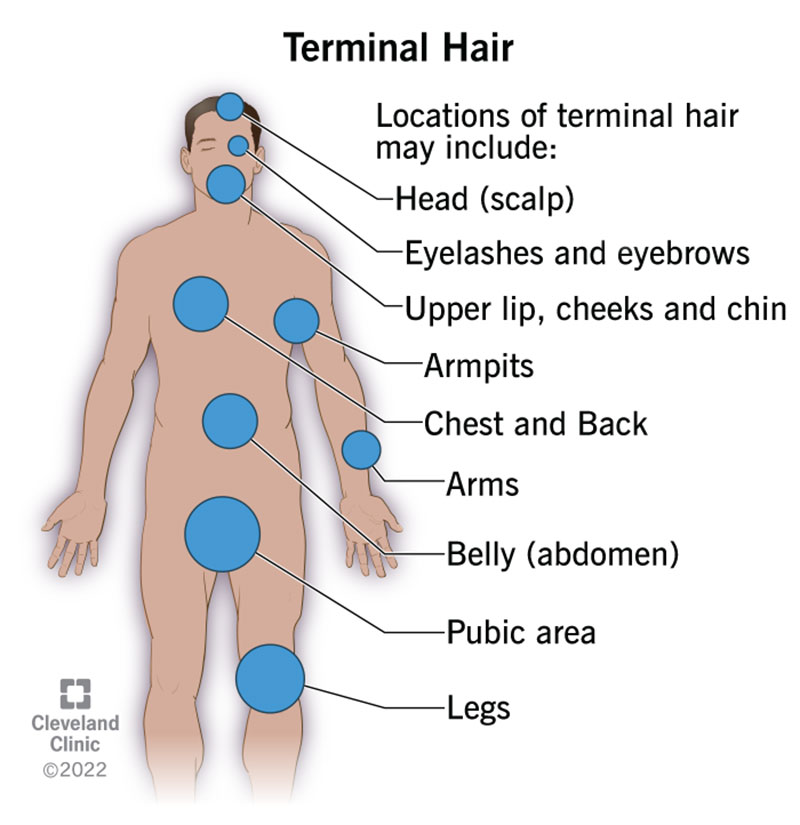
Terminal (Hair)
Function: Offers protection, sensation, and plays a role in social and sexual signaling.
Location: Found on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and after puberty—armpits, pubic area, beard, chest, legs.
Importance:
Shields sensitive areas (e.g., lashes protect eyes)
Helps with temperature regulation (e.g., scalp hair)
Responds to hormones like androgens during puberty
Quick Tip: Think of terminal hair as your “grown-up strands”—thicker, darker, and hormone-driven.
After puberty hair — found on axillary areas
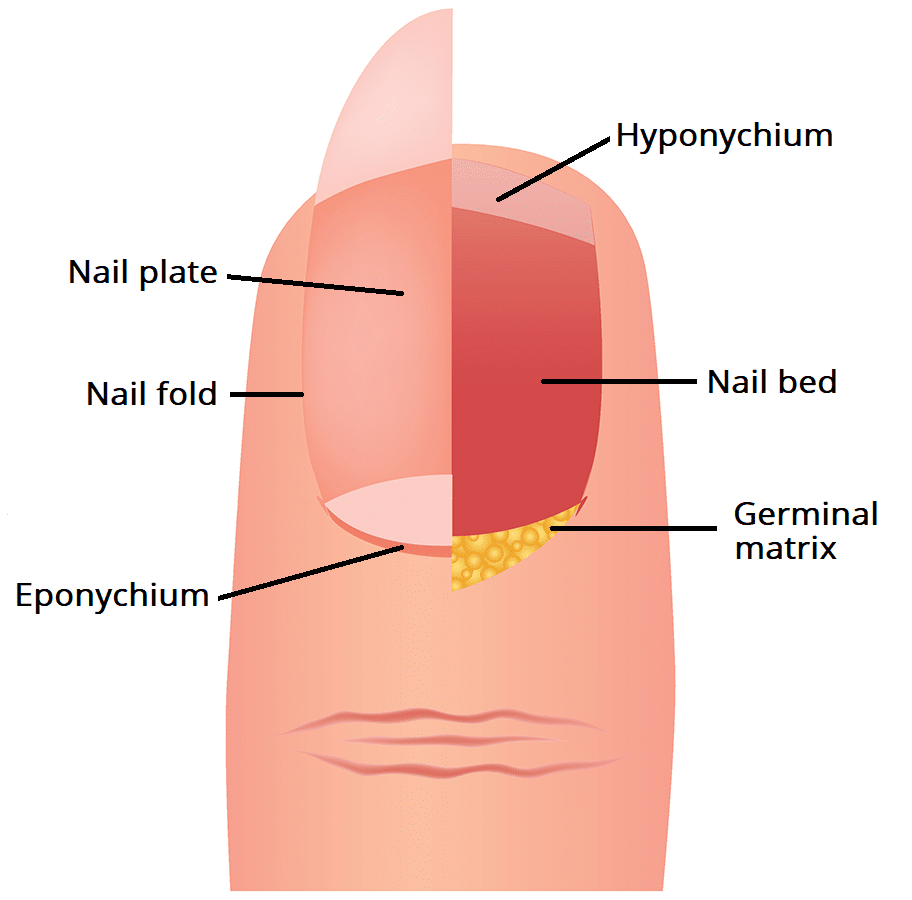
Eponychim (Nail)
Function: Shields the nail matrix (where new nail cells form) from bacteria and injury.
Location: Found at the base of the nail, overlapping the nail plate—often confused with the cuticle.
Importance:
Prevents infection
Supports healthy nail growth
Acts as a barrier between skin and nail
Quick Tip: Think of the eponychium as your nail’s “security guard”—protecting the growth zone.
Above Nail
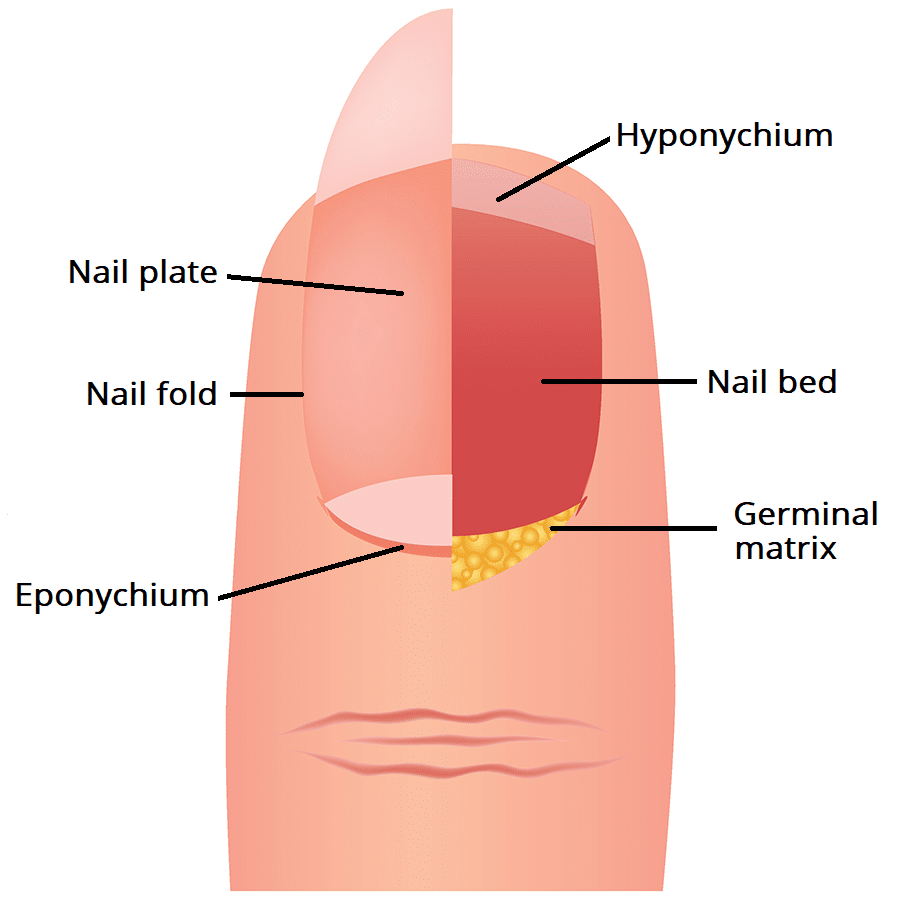
Hyponychium
Function: Acts as a barrier to protect the nail bed from dirt, bacteria, and infection.
Location: Found under the free edge of the nail—where the nail separates from the fingertip.
Importance:
Seals the space beneath the nail
Supports nail hygiene and defense
Helps prevent pathogens from entering the nail bed
Quick Tip: Think of the hyponychium as your nail’s “undercover guard”—quietly keeping invaders out from below.
Under nail
Rule of nine
Body divided into 11 areas (9%) each
11(9) = 99%
- Except the perineum area
T cells
Function:
Helper T cells signal other immune cells.
Killer T cells destroy infected or abnormal cells.
Regulatory T cells prevent autoimmunity.
Memory T cells remember past invaders.
Importance:
Key players in adaptive immunity
Fight infections, cancer, and prevent self-attack
“Detectives”
Location:
Made in bone marrow, mature in the thymus
Found in blood, lymph nodes, and tissues
Quick Tip: Think of T cells as your “immune system’s special ops”—smart, targeted, and trained for defense.
B cells
Function:
Detect invaders and produce antibodies to neutralize them
Some become memory B cells for faster future defense
Importance:
Key players in adaptive immunity
Help fight bacteria, viruses, and toxins
Form the basis of vaccine protection
“Cops”
Location:
Made in bone marrow
Found in blood, lymph nodes, and spleen
Quick Tip: Think of B cells as your “immune system’s pharmacists”—dispensing custom antibodies on demand.
MHC
Function: Displays antigen fragments on cell surfaces to help T cells recognize threats.
Importance:
Essential for immune response
Helps distinguish self vs. non-self
Crucial in organ transplant compatibility
Location: Found on the surface of most body cells (especially immune cells).
Quick Tip: Think of MHC as your “immune ID badge”—showing T cells what’s going on inside each cell.
MHC I
Function: Shows internal cell problems (like viruses or cancer) to killer T cells.
Importance: Helps the immune system find and destroy sick cells.
Location: Found on almost all body cells (except red blood cells).
Quick Tip: MHC I = “Hey T cells, something’s wrong inside!”
MHC II
Function: Shows external invaders (like bacteria) to helper T cells (CD4⁺).
Importance: Helps start the immune response by activating other immune cells.
Location: Found on immune cells like macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells.
Quick Tip: MHC II = “Look what I found outside—let’s fight it!”
MHC III
Function: Doesn’t present antigens like MHC I or II. Instead, it helps by producing immune-related proteins like complement proteins and cytokines.
Importance:
Supports inflammation
Helps destroy pathogens
Aids communication between immune cells
Location: Genes for MHC III are found in the same region as MHC I and II on chromosome 6.
Quick Tip: MHC III = “immune system’s backstage crew”—not flashy, but essential for the show.
Non-self
Function: The immune system detects non-self antigens—proteins from viruses, bacteria, or other outsiders—and attacks them.
Importance:
Keeps the body safe from infections
Prevents disease by recognizing what doesn’t belong
Helps avoid autoimmune reactions (when it works correctly)
Example: Allergyns, Medicine, Transplanted Tissue, and pathogens
Location: Non-self antigens come from outside the body—on pathogens, allergens, or transplanted tissue.
Quick Tip: Non-self = “Not me? Not welcome!” It’s how your immune system knows what to fight.
True or false? Specific antibodies bind only to specific antigens
True — Antibodies are highly specific proteins that recognize and bind to unique antigens using a lock-and-key fit. This precise match occurs at the antibody’s variable region, which is tailored to the antigen’s epitope.
🧠 Quick Tip: Think of antibodies as custom puzzle pieces — they only fit one antigen shape!
True or false? Pathogens are very sensitive
Partially True. Some pathogens are sensitive to environmental changes (like heat, pH, or UV light), while others are highly resilient. For example:
Enveloped viruses (like influenza) are sensitive to drying, heat, and detergents.
Bacterial spores (like Clostridium difficile) are extremely resistant to harsh conditions.
Fungi and protozoa vary — some thrive in tough environments.
🧠 Quick Tip: Enveloped = fragile (think of a soap bubble) Spore-forming = tough (like a seed in winter)
True or false? The immune system is more aggressive toward antigens that are less similar to human proteins
True — The immune system recognizes non-self antigens — especially those structurally different from human proteins — as threats. The greater the difference, the stronger the immune response tends to be.
Self-like antigens may trigger tolerance or weak responses.
Highly foreign antigens (like bacterial toxins or viral proteins) provoke robust reactions.
🧠 Quick Tip: More foreign = more firepower. Think of it like a security system: the more unfamiliar the intruder, the louder the alarm.
Inflammatory response
Function: Reacts to injury or infection by sending immune cells to the area.
Importance:
Stops the spread of harmful agents
Starts healing
Activates immune defenses
Location: Happens wherever there’s damage—skin, organs, tissues.
Classic Signs:
Redness
Heat
Swelling
Pain
Loss of function
Quick Tip: Inflammation = “Help is on the way!”—your body’s emergency alert system.
Body’s first response
Fever
Function: Raises body temperature to fight infection and make it harder for viruses and bacteria to survive.
Importance:
Activates immune cells like T cells
Boosts metabolism and speeds up immune response
Helps clear infections faster
Location: Fever affects the whole body, triggered by the brain’s hypothalamus in response to infection.
Quick Tip: Fever = “heat alert!” Your body’s way of turning up the thermostat to kick out invaders.
Non Specific immunity
Function: Defends against any invader, not just specific ones. It’s fast and general.
Importance:
Stops infections early
Doesn’t need prior exposure
Works the same way every time
Location: Found in skin, mucous membranes, stomach acid, fever, inflammation, and immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils.
Quick Tip: Non-specific immunity = “universal bouncer”—keeps out trouble no matter who it is.
Specific immunity
Function: Fights specific invaders using tailored responses—like antibodies or killer T cells.
Importance:
Learns and remembers pathogens
Provides long-term protection
Basis for vaccines
Location: Involves B cells and T cells found in blood, lymph nodes, and tissues.
Quick Tip: Specific immunity = “custom defense plan”—smart, precise, and remembers past battles.
Naive B cell
Function: A B cell that hasn’t met its matching antigen yet—it’s ready, but not activated.
Importance:
Waits in lymph nodes and spleen
Once it meets its specific antigen, it activates, divides, and becomes:
A plasma cell (makes antibodies)
Or a memory B cell (for long-term defense)
Location: Found in secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes, spleen, and tonsils.
Quick Tip: Naive B cell = “rookie immune scout”—trained, equipped, just waiting for its first mission.
Antibodies
Function: Bind to specific antigens (foreign invaders) like viruses or bacteria to neutralize or tag them for destruction.
Importance:
Key part of adaptive immunity
Help fight infections
Used in vaccines and diagnostic tests
“Handcuffs”
Location: Made by plasma B cells, found in blood, lymph, and secretions (like saliva and tears).
Quick Tip: Antibodies = “targeted missiles”—each one built to lock onto a specific invader.
Macrophages
Function:
Swallow and digest pathogens, dead cells, and debris
Show pieces of invaders to T cells (antigen presentation)
Release signals to start inflammation
Importance:
First responders in non-specific immunity
Help activate specific immunity
Clean up and repair tissue
Location: Found in tissues all over the body—especially lungs, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
Quick Tip: Macrophages = “immune vacuum cleaners”—they eat, alert, and clean up the mess.
Cell Mediated Immunity
Function: Uses T cells (not antibodies) to find and destroy infected or abnormal cells.
Importance:
Kills virus-infected and cancerous cells
Activates other immune cells
Crucial for organ transplant rejection and intracellular infections
Location: Happens in tissues and lymph nodes, wherever infected cells are found.
Quick Tip: Cell-mediated immunity = “T cells take the lead”—no antibodies, just direct action.
Active Immunity (Specific Immune response)
Function: Your body makes its own antibodies after exposure to a pathogen or vaccine.
Importance:
Builds long-term protection
Creates memory cells for faster future defense
Basis of vaccination
Location: Happens in your immune system—especially B cells and T cells.
Quick Tip: Active immunity = “I fought it, I remember it!”
Passive immunity (Specific immune reponse)
Function: You receive ready-made antibodies from another source—your body doesn’t make them.
Importance:
Gives immediate protection
Useful in emergencies or for newborns
Doesn’t create memory cells (short-term only)
Location: Antibodies come from mother’s milk, placenta, or injections (like antivenom or immunoglobulin shots).
Quick Tip: Passive immunity = “I didn’t make it, but it protects me!”
Vasolidation
Function: Widening of blood vessels due to relaxation of smooth muscle in vessel walls.
Importance:
Increases blood flow to tissues
Helps regulate body temperature
Delivers immune cells to sites of infection or injury
Reduces blood pressure
Location: Occurs in arterioles and capillaries, especially near inflamed or heated tissues.
Quick Tip to Remember: “Dilation = wider = more delivery.” Imagine turning a narrow hallway into a wide tunnel — easier for traffic (blood) to flow through!
Widening of blood cells
Sudoriferous Glands
Function: Produce and secrete sweat to help regulate body temperature and excrete waste.
Importance:
Cool the body through evaporation
Aid in thermoregulation
Help eliminate small amounts of metabolic waste
Maintain skin hydration and pH
Location: Found all over the skin, especially on the palms, soles, forehead, and armpits. Two types:
Eccrine glands (most common, all over the body)
Apocrine glands (in armpits, groin — activate during stress/emotion)
Quick Tip to Remember: “Sudor = sweat.” Think: Sudoriferous = sweat factories working to cool you down!
Artifical Active Immunity
Function: Trains your immune system to make its own antibodies by exposing it to a harmless form of a pathogen (like a vaccine).
Importance: Builds long-term protection by forming memory cells that respond faster to future infections.
Location: Involves B cells, T cells, and lymphoid tissues like lymph nodes and spleen.
Quick Tip: “Fake germ, real defense.” Vaccines = practice battle for your immune army.
Active Adaptive Immunity
Function: Enables the body to recognize, respond to, and remember specific pathogens by producing its own antibodies and memory cells.
Importance:
Provides long-term protection
Learns and adapts to new threats
Forms the basis of immunological memory (e.g., after infection or vaccination)
Location: Involves B cells (antibody production) and T cells (cell-mediated defense), mainly in lymphoid tissues like lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus.
Quick Tip to Remember: “Active = your body fights. Adaptive = it learns.” Like a smart army that trains, fights, and remembers the enemy.
Innate Immunity
Function: Provides immediate, non-specific defense against pathogens.
Importance:
Acts as the body’s first line of defense
Responds quickly to infections
Triggers and supports adaptive immunity
Location: Found throughout the body — includes skin, mucous membranes, phagocytes, natural killer cells, and inflammatory molecules.
Quick Tip to Remember: “Innate = instant.” Like a security guard that reacts fast but doesn’t ask questions.
Vitamin D
Function: Helps absorb calcium and phosphorus for strong bones; also supports immune and brain health.
Importance:
Prevents rickets and osteoporosis
Regulates mood and cognitive function
Supports immune defense and reduces inflammation
Location: Synthesized in the skin via sunlight; also found in fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified foods, and supplements.
Quick Tip to Remember: “Sunshine vitamin = strong bones + sharp brain.”
Systemic Inflammation
Function: Body-wide immune response to infection, injury, or chronic stress.
Importance:
Fights infections
Can damage tissues if prolonged
Linked to chronic diseases (diabetes or heart disease)
Location: Affects blood, organs, and immune cells; tracked by markers like CRP and IL-6.
Quick Tip: “Systemic = everywhere. Inflammation = fire.” Like a full-body alarm — helpful short-term, harmful if stuck on.
A fetus receives immune protection from the mother through ____ immunity
Passive Adaptive — The fetus doesn’t make its own antibodies — it receives them
Function: Provides immediate protection by receiving ready-made antibodies from another source.
Importance:
Offers fast, short-term defense
Useful when immediate immunity is needed (e.g., after exposure to toxins or viruses)
Location: Antibodies circulate in the bloodstream; no activation of the body’s own B or T cells.
Quick Tip: “Passive = borrowed. Adaptive = specific.” Like borrowing someone else’s shield — strong but temporary.
_____ immunity occurs when exposure to pathogen prompts the building of memory within immune system
Specific (Adaptive) Immunity
Function: Targets and remembers specific pathogens using tailored immune responses.
Importance:
Provides long-term protection
Builds memory after infection or vaccination
Learns and adapts to new threats
Location: Involves B cells (antibodies) and T cells (cell-mediated defense) in lymph nodes, spleen, and blood.
Quick Tip: “Specific = smart + selective.”
Which immunity is short lasting?
Passive Immunity — involves receiving antibodies from another source (e.g., mother to fetus via IgG, or through antibody injections).
Since the body doesn’t produce its own memory cells, the protection fades within weeks to months.
🔬 Examples:
Maternal antibodies passed to a newborn
Antiserum injections for snake bites or rabies
🧠 Mnemonic: "Passive = Pre-made, Passing Protection"
The germinal matrix is an area of..
developing fetal brain that is highly cellular and vascularized, serving as a major site of neurogenesis — the production of neurons and glial cells.
🧠 Key facts:
Located near the lateral ventricles in the subventricular zone
Most active between 8 and 28 weeks gestation
Cells migrate from this area to form the cerebral cortex
Extremely fragile — especially in preterm infants, where it’s prone to hemorrhage (germinal matrix hemorrhage)
High miotic activity
🧠 Mnemonic: "Germinal = Growing Brain Matrix"
Which layer of epidermis do cells divide by mitosis to replace cells lost from outermost surface of body?
stratum basale (also called the basal layer) ✅
🧬 This is the deepest layer of the epidermis, where mitosis actively occurs to produce new keratinocytes. These cells then migrate upward through the layers, eventually replacing those lost from the stratum corneum, the outermost layer.
📚 Key facts:
Stratum basale contains stem cells and melanocytes
It’s a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells
Essential for skin regeneration and repair
🧠 Mnemonic: "Basale Builds the Barrier"
T and B cells are examples of..
lymphocytes, which are part of the adaptive immune system 🧠🛡
🔬 Here's the breakdown:
T cells: Mature in the thymus; involved in cell-mediated immunity (e.g., helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells)
B cells: Mature in the bone marrow; responsible for producing antibodies (humoral immunity)
🧠 Mnemonic: "T for Thymus, B for Bone marrow"
Scars form due to..
fibroblasts creating a collagen weave to repair damaged tissue 🧵🧬
🔬 Here’s how it works:
After injury, the body initiates wound healing, which includes:
Inflammation: Immune cells clear debris and pathogens
Proliferation: Fibroblasts migrate to the site and produce collagen
Remodeling: Collagen forms a dense, organized matrix — the scar
🧠 Mnemonic: "Fibroblasts Fix with Fibers"
Scars lack the original tissue’s structure (like glands or hair follicles), which is why they look and feel different.
Fingerprint arise from the structure of the…
dermal papillae located in the papillary layer of the dermis 🌀
🔬 Here's how it works:
Dermal papillae are ridged projections of the dermis that push into the epidermis.
These ridges form the epidermal ridges visible on the surface of the skin — what we recognize as fingerprints.
The pattern is genetically determined and formed during fetal development, remaining unchanged throughout life.
🧠 Mnemonic: "Papillae Push Patterns"
Antigens
Function: Act as molecular markers that trigger an immune response. They’re recognized as “foreign” by the immune system.
Importance:
Help the body identify and fight pathogens
Stimulate antibody production
Used in vaccines and diagnostic tests
Play a role in transplant compatibility and autoimmune diseases
Location: Found on the surface of viruses, bacteria, parasites, allergens, tumor cells, and even normal body cells (e.g., blood group antigens, HLAs).
Quick Tip to Remember: “Antigen = anti-body-gen-erator.” Think: a name tag that says “I’m not from here” — and your immune system reacts.
Melanocytes
Function: Produce melanin, the pigment that gives color to skin, hair, and eyes, and protects against UV radiation.
Importance:
Shields DNA from UV damage
Regulates pigmentation
Plays a role in immune defense by releasing cytokines and presenting antigens
Location: Found in the stratum basale of the epidermis, hair follicles, eyes, inner ear, and meninges.
Quick Tip to Remember: “Melanocyte = melanin maker.” Think: pigment-producing sentinels guarding your skin from the sun.
Vaccine
Function: Trains your immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens by exposing it to a harmless version of the germ (e.g., weakened, killed, or fragment).
Importance:
Prevents serious diseases before they start
Builds long-term immunity through memory cells
Protects vulnerable populations via herd immunity
Reduces risk of complications and death from infections
Location: Administered via injection, oral drops, or nasal spray; immune response occurs in lymphoid tissues, involving B cells, T cells, and antigen-presenting cells.
Quick Tip to Remember: “Vaccine = practice battle.”
Neutrophils
Function: First responders of the immune system — they engulf, digest, and destroy invading microbes.
Importance:
Most abundant white blood cell (55–70%)
Key players in inflammation, infection control, and tissue repair
Use phagocytosis, degranulation, and NETs (DNA traps) to kill pathogens
Location: Made in bone marrow, circulate in blood, and migrate to tissues during infection
Quick Tip to Remember: “Neutrophil = neutralizing ninja.” Fast, fierce, and disposable — they fight hard and die young (lifespan 24 hrs)