Vas week 6: Content review
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
When encountering a stent or graft, what photos do we take?
inflow
prox edge or attachment
mid
dist edge or attachment
outflow
if your ABI is less than _____ it suggests multi level disease
0.5
if your beyond a stenosis, what happens to the pressure distally?
decreases
if your brachial pressures are greater than 20, we should sample the _____ artery to look at flow direction and rule out subclavian steal
vertebral
a change in an ABI or a WBI of more than what is significant?
0.15
characteristic waveform for an AVF
Hyperemic
a _____ type of waveform indicates a proximal occlusion
Tardus parvus or post stenotic
what’s the normal velocity ratio in artery’s
less than 2.0
how to calculate velocity ratio
highest psv at narrowing / proximal segment before narrowing
The external iliac artery, after crossing the inguinal ligament becomes the _____ artery
CFA
The arms should be within ____ mmHg of eachother
20
What’s the pressure gradient between the cuffs in the legs thats allowed
30 or less mmHg
3 cuff will ____ to brachial
4 cuff will be _____ to brachial
equal
30 higher
45 yo guy with digital ischemia and digital necrosis with history of smoking. what is diagnosis
Buergers disease
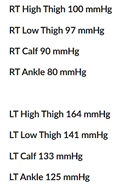
Consider pressures. where is disease?
Right inflow since entire left leg is low starting from top
pt has pain in arm in certain positions, what is diagnosis
TOS
Pt has bypass graft two days ago coming in ER with S/o leg pain for 4 hours, what is diagnosis?
mechanical failure (because this is so soon after the bypass graft)
pt has history of right lower fem pop bypass graft 3 years ago. they now have new intermediate claudication. ABI is .71 on right and .91 on left. is there disease?
yes on the right since ABI is less than .9
velocity measurements at the right leg at the distal anastomosis at the graft are 336cm/s with a velocity ratio of >2.0. what is likely diagnosis
right fem pop bypass graft distal anastomosis stenosis
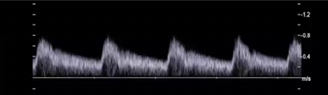
Considering waveform, is this artery feeding a high or low resistant vascular bed?
why?
which type of anatomical structure would require an artery providing this type of flow?
low resistant
because the end diastole is 30-40 of psv and has constant forward flow
An organ
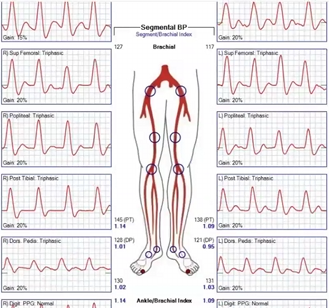
Pt presents with hx of CAD,HTN,DM x 22 years of smoking x 40 years. you obtain these waveforms and ABI info
1.are the results of study normal?
2.is ABI reliable? why or why not?
yes because they are over .9
no because pt has DM
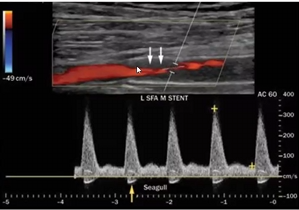
Pt is s/p stent placement x 3 years. pt ABI decreased from previous visit by .15 indicating a hemodynamically significant stenosis.
consider ultrasound image obtained
what is contributing to the narrowing in stent?
is this prox or distal sten edge area?
is this ultrasound finding causing the decrease in ABI when compared to previous vist?
progression of atherosclerosis
proximal
yes it is since it is a narrowing
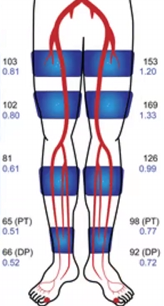
Considering exam results for both legs, where is location of disease?
is this a 4 cuff or 3 cuff method
identify two areas of suspicious for hemodynamically significant disease
right inflow
this is 4 cuff method
right inflow and diseae between 2nd and 3rd cuff on the left leg so illiac
patient s/p insitu fem-pop bypass graft x 3 days. arterial duplex exam ordered to determine baseline velocities
1.what was used for graft material?
2.Which vessel is proximal anastomosis? distal?
the pts own vein
prox is femoral artery. distal is popliteal artery
what are examples of arterial grafts?
Aorto-iliac (aorta to unilateral or bilateral iliacs)
Aorto-Fem (aorta to unilateral or bilateral femoral arteries)
Ax-Fem (axillary artery to femoral)
Fem-Fem (femoral artery to femoral artery)
Fem-Pop (femoral artery to popliteal artery)
Fem-Tib (Femoral artery to tibial artery)
what are synthetic bypass grafts made of?
PTFE, Dacron
What is it called when a graft is a pts own vein?
Autogenous/ autologous vein
What does in situ mean?
Vein used for bypass in its original anatomic position and its usually the GSV
if a graft fails less than 30 days then what happened?
Technical failure (Retained valve, problem at anastomotic site)
Restenosis 1 month to 2 years, where did it occur?
Occurs at valve sites and prox and distal anastomosis
what is an abnormal velocity ratio?
>2.0
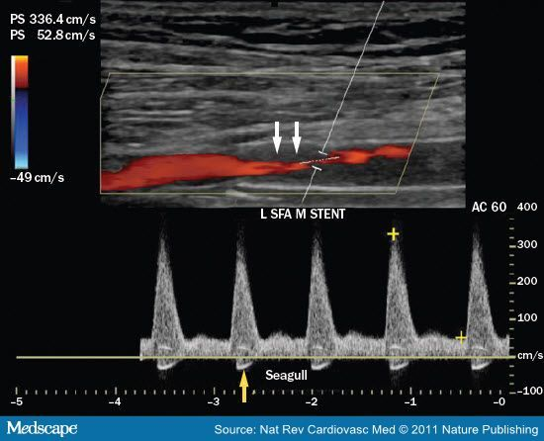
Patient s/p angioplasty with stent x 4 years with reintervention x 2
Patient presents with symptoms of LT calf pain after walking 2 blocks.
ABI LT = .6 and ABI RT = .9
This is your image SFA stent.
Consider velocities
1.What additional information is necessary to calculate the inflow velocity ratio?
2.Is this PSV abnormal?
3.Does this finding explain patient symptoms?
4.Does this finding explain results of ABI?
5.What about angle? How would you improve?
1.Proximal PSV
2. No because anything over 180 is suspicious. So it is high
3.Yes because abi on left is abnormal and
4.Yes because there is a stenosis in the stent
5.The angle is fine and the angle is fine since its with the direction of flow since the thrombus changed where walls are
Patient s/p carotid artery stent x 3 weeks
f/u ultrasound ordered and you take this image
1.What is possible diagnosis?
2.What system adjustments will you perform to optimize image?
3.How will you prove possible diagnosis?
4.What is reason for diagnosis considering timeline of procedure?
1.Mechanical error cause by occlusion
2.Lower the scale and increase color gain to see if theres flow
3.Use PW to see if theres any flow velocities
4.Mechanical complication due to somthing
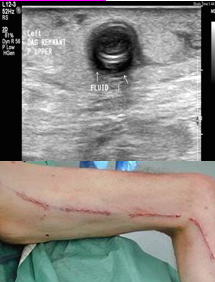
Pt s/p bypass graft (Fem-Tib) LLE x 2 weeks
c/o pain, redness LLE and fever
Your patient leg to right and you obtain this image.
1.What is finding?
2.Does this finding possibly explain symptoms?
3.Where is distal anastomosis?
1.Periographed fluid
2.Yes because infection
3.Tibial artery
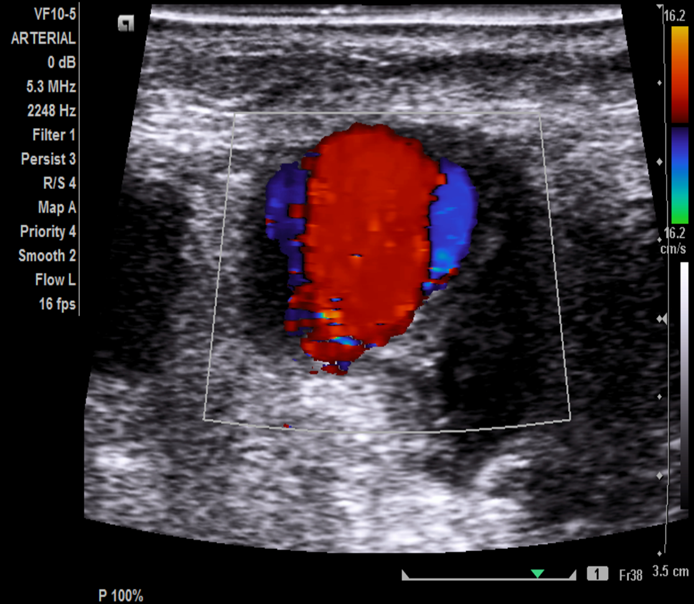
Pt s/p RLE Fem-Pop graft x 4 years
Palpable, pulsatile mass area of proximal anastomosis.
You take this image in your arterial duplex imaging exam.
1.Where is proximal anastomosis and therefore palpable mass?
2.What possible findings are associated with aging grafts?
3.What is this likely finding in image?
4.What other steps will you take to document this finding?
1.CFA, above
2.Pseudoaneurysm at the anastomotic site
3.Ap width and length
4.Throw color on and PW to see if there’s flow
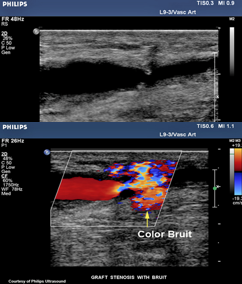
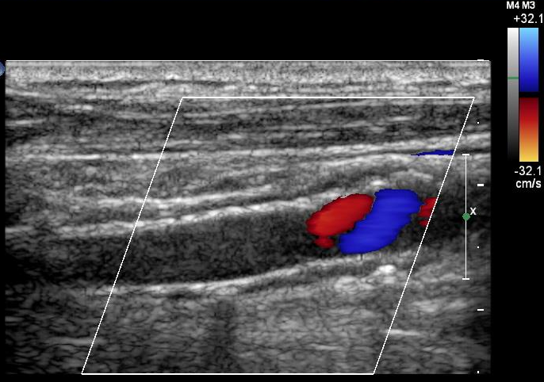
Pt s/p in-situ bypass graft RLE
STAT ultrasound exam ordered with order indication as ‘bruit’
You take your machine portable to post-op recovery room to perform exam. You take these images.
1.Considering type of graft, what is possible finding?
2.What is color image information indicating?
3.Is color diagnostic?
4.What will your spectral Doppler most likely indicate?
5.Do these images explain clinical indication for exam?
1.Since its an insitu possible finding is valves
2.Aliasing from fast speeds
3.No because there is no velocities info
4.Increased velocities resulting in hemodynamically stenosis
5.Yes, it does because we found what's causing the bruit
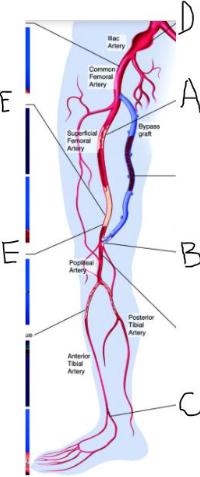
Your patient has significant peripheral arterial disease and treatment! Label the structures and pathology identified by letters.
What is the name of the bypass graft?
Include laterality.
1.A=right mid SFA stenosis
B=right fem pop distal anastomosis stenosis
C=Right DPA occlusion
D=Right Common illiac aneurysm
E=right distal SFA occlusion
2. right fem pop
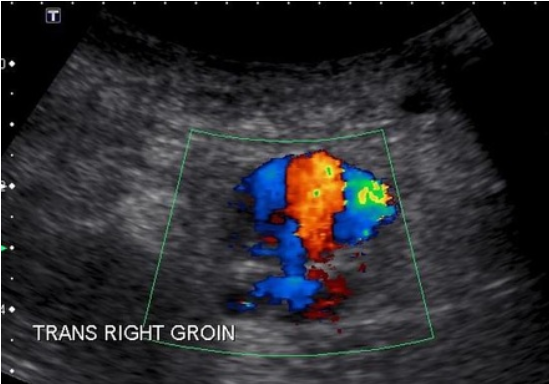
Pt is s/p cardiac catherization RT groin x 2 days. Patient presents with pain, palpable pulsatile mass RT groin. Duplex arterial ultrasound ordered to evaluate area of pain. Consider this image taken in area of pain.
1.What is most likely diagnosis?
2.What is important in patient history supporting diagnosis?
3.It is possible to have another vascular finding with this patient history and diagnosis. What is it?
4.Why is sonographer using abdominal curved probed?
1. pseudoaneurysm
2. pt had recent right groin vascular access
3. yes, a hematoma
4. Increased penetration
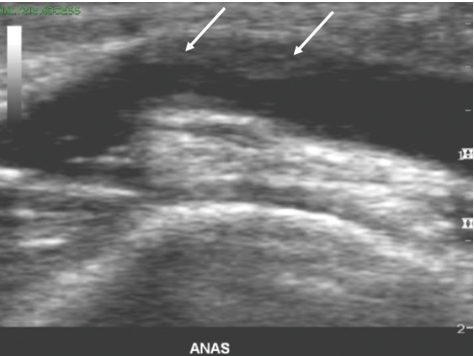
Patient is s/p LE bypass graft x 3 years. Patient has not had previous ultrasound exam for 2 years.
You obtain this image and the white arrows most likely indicate which of the of following?
progression of artherosclerosis
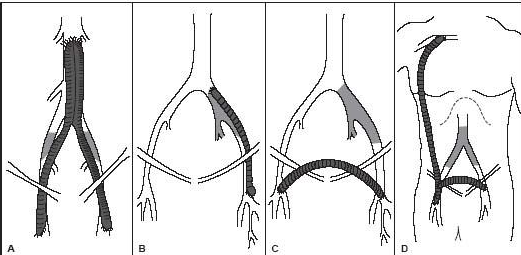
Recall that the inguinal canal is the point at which the iliac artery becomes the common femoral.
Name the bypass grafts.
A. aorto bi femoral bypass graft
B. left ilio fem bypass
C. right to left fem fem bypass graft
D. Right axillo bi fem bypass graft or right axillo fem bypass graft with right to left bypass graft
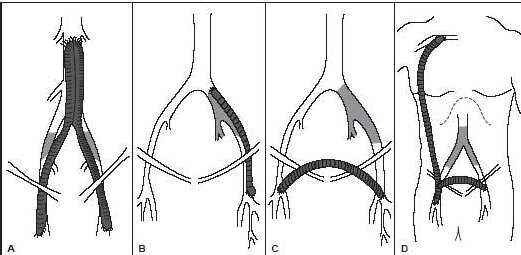
What is the proximal anastomosis for graft type A?
Aorta
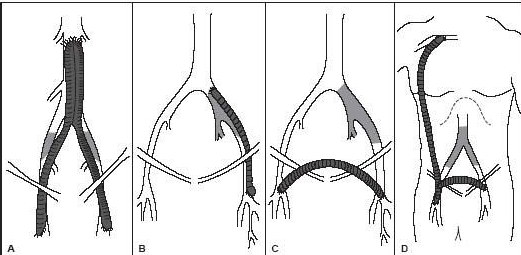
What is the proximal anastomosis for graft type D?
Axillary
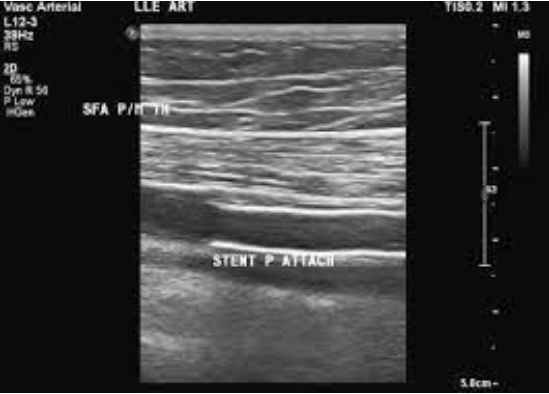
Patient presents for f/u ultrasound exam. She is s/p stent placement x 3 weeks.
Describe your imaging protocol.
Mid stent
color doppler
velocities proximal and distal stent edge
PW doppler and psv
grayscale assessment
proximal to and distal to stent edge
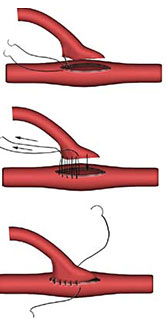
What type of anastomosis is this?
end to side
Patient in the ER with cold left leg. Patient has history of vascular disease with revascularization however he is a poor historian and cannot provide valuable surgical information. Ultrasound is ordered STAT.
What are your next steps to prepare for patient?
Look at leg for proximal and distal linear incisions
How do we typically treat pseudoaneurysm (PA)?
thrombin injection
What is usually the cause of pseudoaneurysm and arteriovenous fistula in LE?
vascular access
All the following are symptoms for PA except:
coldness
Which of the following is not a risk factor for arterial disease?
history of venous disease
When trauma occurs to all three layers of the arterial wall resulting in a pulsating hematoma, this is known as __________.
pseudoaneurysm
The typical waveform associated with the neck of a pseudoaneurysm is:
to and fro
Bypass grafts can be located between any two vessels and are named for the:
two arteries they connect
Which of the following is an example of graft failure due to technical error?
retained valve cusp
Which technical failure, in a stent, is more common after angioplasty?
occlusion
A moderately significant stenosis is indicated in the body of a graft when velocities are:
>180 cm/s and Vr >2.0
Graft entrapment typically occurs at the:
popliteal
Immediate post-operative evaluation of a prosthetic graft may not be possible due to __________ within the graft walls.
air
All of the following are used to treat lower extremity vascular disease EXCEPT:
endarterectomy
At which location is it easiest to visualize the stent?
proximal portion
Which of the following makes it difficult for ultrasound to evaluate presence and patency of stents?
atherosclerotic plaque and calcific shadowing
Which statement best describes term 'inflow' when assessing both stents and grafts?
the flow just proximal to stent and used as a reference for stent/graft patency
Autologous refers to using patient's vein for bypass graft-such as saphenous vein.
true
Considering terminology, we use _______________ to describe proximal and distal stent and ________________ for to describe proximal/distal location in bypass grafts.
Attachments; anastomosis
The bypass graft and autologous graft wall have the same sonographic appearance.
false
It can be difficult to visualize chronically occluded artery when assessing bypass graft.
true
When struggling to visualize chronically occluded artery, what can you use as a landmark?
adjacent deep vein
In the lower extremity, where is the proximal anastomosis usually located?
groin