3. Adrenal Glands
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
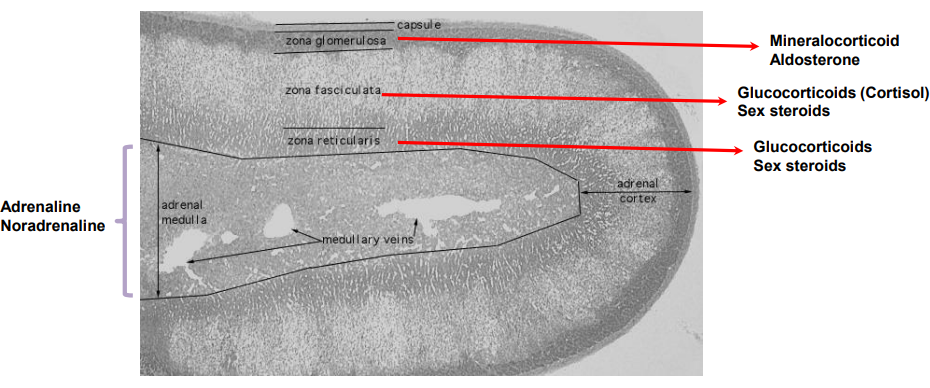
What are the three layers of the adrenal cortex and what do they secrete?
Zona glomerulosa: Secretes mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone)
Zona fasciculata: Secretes glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol) and sex steroids
Zona reticularis: Secretes sex steroids and glucocorticoids
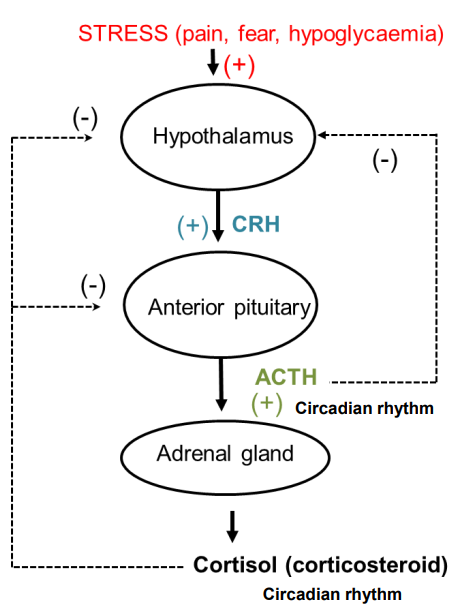
How is the release of cortisol controlled?
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates the release of ACTH from the anterior pituitary.
ACTH stimulates the adrenal gland to secrete cortisol.
Negative feedback: High cortisol levels decrease ACTH and CRH secretion, reducing cortisol production.
Cortisol follows a circadian rhythm:
Low levels at night
Peak around 8:00 AM
Decreases throughout the day.
Stress (e.g., pain, fear, hypoglycemia) stimulates the release of CRH, ACTH, and cortisol to help cope with stress.
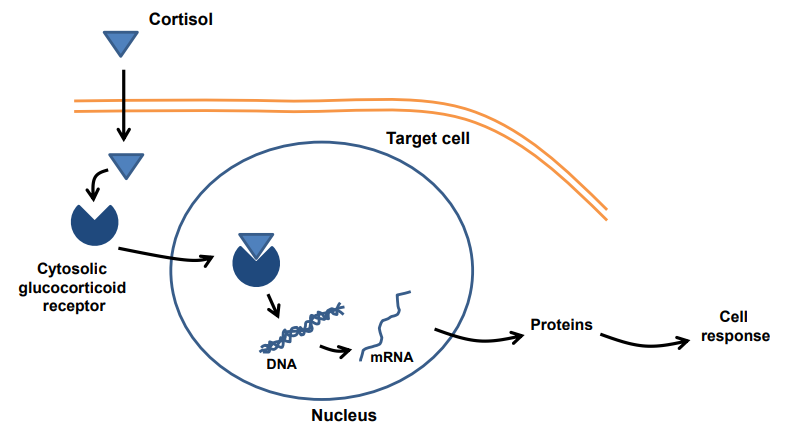
What is the mechanism of action of cortisol (a glucocorticoid)?
Cortisol diffuses through the cell membrane
Binds to cytosolic glucocorticoid receptors
The cortisol–receptor complex enters the nucleus
Binds to DNA and alters gene transcription
Leads to protein synthesis → causes a cell response
What are the metabolic actions of glucocorticoids?
Carbohydrate metabolism:
↑ Liver glucose formation
↑ Liver glycogen synthesis & storage
↓ Insulin action on glucose uptake (muscle & fat)
Protein metabolism:
↓ Amino acid uptake & protein synthesis (peripheral tissues)
↑ Protein breakdown (muscle, skin, bone)
Fat metabolism:
↑ Fat breakdown (adipose tissue)
↓ Fat synthesis
What are the anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids?
In high doses, they inhibit tissue inflammatory processes
Used to treat chronic inflammatory conditions
Examples: prednisolone, betamethasone, dexamethasone
What are the anti-allergic effects of glucocorticoids?
In high doses, inhibit histamine synthesis & release from mast cells
Used to treat severe asthma & anaphylactic shock
Examples: beclomethasone, budesonide
What are the immunosuppressive actions of glucocorticoids?
Affect T-lymphocytes at therapeutic doses
Used to treat autoimmune diseases
Prevent tissue rejection after transplants
Why must glucocorticoid treatment not be stopped suddenly?
Sudden withdrawal can cause adrenal crisis
Long-term steroid use suppresses adrenal gland function
Patients need gradual dose reduction unless advised otherwise
Patients should carry a steroid treatment card or bracelet
Alerts healthcare providers in emergencies (e.g. car crash)
Ensures they receive necessary steroids during stress

What are the causes, features & treatment of glucocorticoid hyposecretion?
Primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison’s disease):
Cause: adrenal gland dysfunction
↓ cortisol, ↑ ACTH
Features: muscle weakness, postural hypotension, dehydration, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, ↑ skin pigmentation (due to ACTH acting like MSH)
Secondary adrenocortical insufficiency:
Cause: pituitary dysfunction
↓ cortisol, ↓ ACTH
Treatment:
Hydrocortisone (glucocorticoid)
Fludrocortisone (mineralocorticoid)
What are the causes, features & hormone levels in glucocorticoid hypersecretion (Cushing’s syndrome/disease)?
Causes:
Cushing’s disease → pituitary adenoma
Cushing’s syndrome → ectopic ACTH-secreting tumour
Clinical features:
Muscle weakness & wasting (thin limbs)
Back pain (osteoporosis)
Easy bruising, purple striae
Fat redistribution (e.g. moon face, buffalo hump)
Female virilization (hair growth, acne, amenorrhoea)
Hyperglycaemia, polyuria, polydipsia → diabetes tendency
Psychological disturbances
Hormone levels:
↑ plasma cortisol (no diurnal variation)
↓ plasma ACTH
What is the difference between Cushing's Syndrome & Cushing's Disease?
Cushing’s Syndrome → General term for excess cortisol, from any cause
Cushing’s Disease → Specific cause of syndrome: pituitary tumour ↑ACTH
All Cushing’s Disease is Cushing’s Syndrome, but not vice versa
What is the treatment for glucocorticoid hypersecretion (Cushing's syndrome)?
First line treatment:
Trans-sphenoidal surgery + corticosteroid replacement therapy.
Drug therapy:
Inhibition of adrenal steroidogenesis:
Metyrapone: 11β-hydroxylase inhibitor.
Ketoconazole: Antifungal, P450 enzyme inhibitor, glucocorticoid receptor antagonist.
Mitotane: 11β− and 18−hydroxylase inhibitor.
Inhibition of ACTH synthesis and secretion:
Pasireotide (Signifor): Somatostatin analogue.
Inhibition of ACTH secretion from pituitary adenoma:
Cabergoline: Dopamine D2 receptor agonist.
Inhibition of cortisol receptors:
Mifepristone: Progesterone and glucocorticoid receptor antagonist.
What controls the release of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone?
Regulated by the renal renin-angiotensin system
Stimulated by a large ↓ in plasma [Na⁺] or a small ↑ in plasma [K⁺]
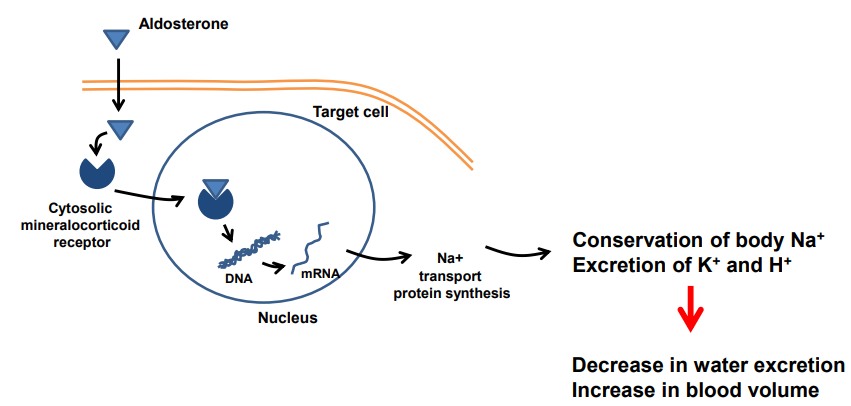
How does aldosterone exert its effects in the body?
Aldosterone crosses the membrane & binds to cytosolic mineralocorticoid receptors
The complex enters the nucleus & binds DNA
This ↑ synthesis of sodium transport proteins
Results in:
↑ Na⁺ reabsorption (conservation) &↑ K⁺ & H⁺ excretion
Which leads to ↓ water excretion & ↑ blood volume
What are the causes, symptoms & treatment of mineralocorticoid (aldosterone) hyposecretion?
Causes: Renal disease due to diabetes mellitus or AIDS
Symptoms:
↑ Na⁺/H₂O excretion
↑ plasma K⁺
Hypotension
Treatment: Replacement therapy
What are the causes, symptoms & treatment of mineralocorticoid (aldosterone) hypersecretion (Conn’s syndrome)?
Causes:
Adrenal hyperplasia (adrenal gland enlargement)
Adenoma in zona glomerulosa
Symptoms:
Hypertension (↑ Na⁺ & H₂O retention)
↓ plasma K⁺
Alkalosis
Muscle weakness, fatigue
Cardiac dysrhythmias
↓ plasma renin
Treatment:
Surgery
Spironolactone (aldosterone receptor antagonist) 4 weeks before surgery
What is secondary aldosteronism and how is it treated?
Caused by ↑ renin release = ↑ angiotensin II = ↑ aldosterone
Triggers: poor renal perfusion, malignant hypertension, renal tumour, diuretics, CHF, hepatic failure
Treatment: manage underlying cause + spironolactone (aldosterone antagonist)