CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Definition of Carboxylic Acids
Organic compounds containing a carboxyl group (-COOH), characterized by a carbonyl (C=O) and hydroxyl (-OH) group on the same carbon.
Naming Open-Chain Acids
Replace the "-e" in the alkane name with "-oic acid" (e.g., methanoic acid).
Naming Cyclic Acids
Use the suffix "-carboxylic acid" for acids attached to rings (e.g., benzenecarboxylic acid).
Biological Importance
Includes fatty acids, mevalonic acid (precursor to steroids), and essential acids like EPA and DHA.
Physical Properties: Boiling Point
Higher boiling points than alcohols due to hydrogen-bonded dimers.
Physical Properties: Solubility
- Lower molecular weight acids are water-soluble.
- Solubility decreases with increasing molecular weight.
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
Stronger acids than alcohols and phenols due to resonance-stabilized carboxylate ions.
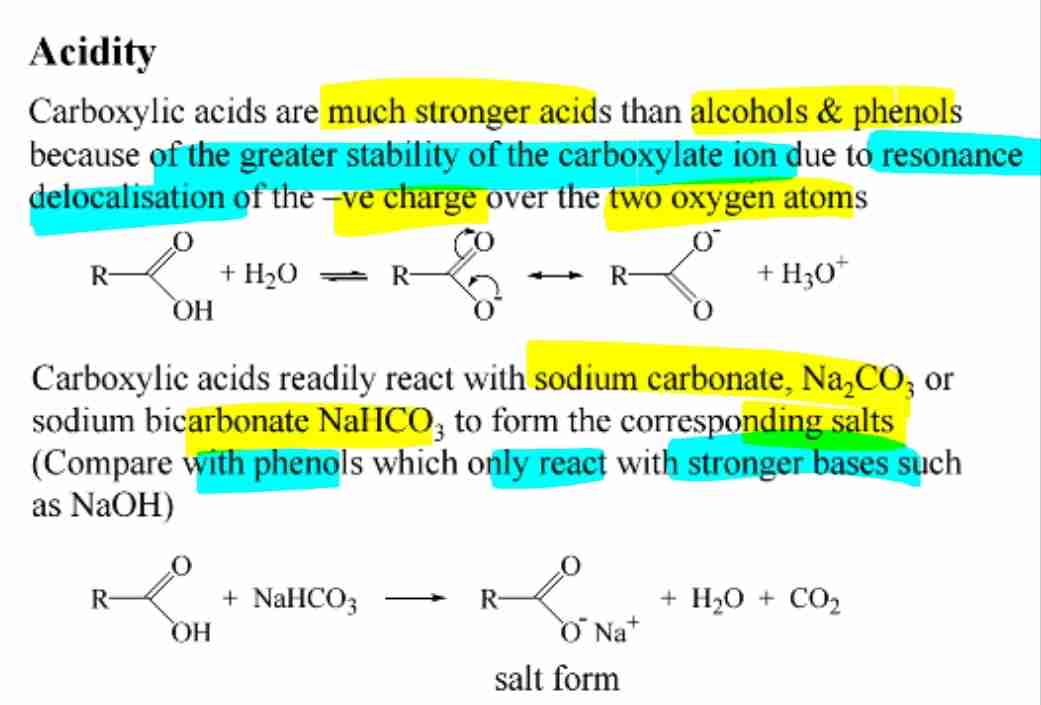
Reaction with Bases
React with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) or bicarbonate (NaHCO3) to release CO2 and form salts.
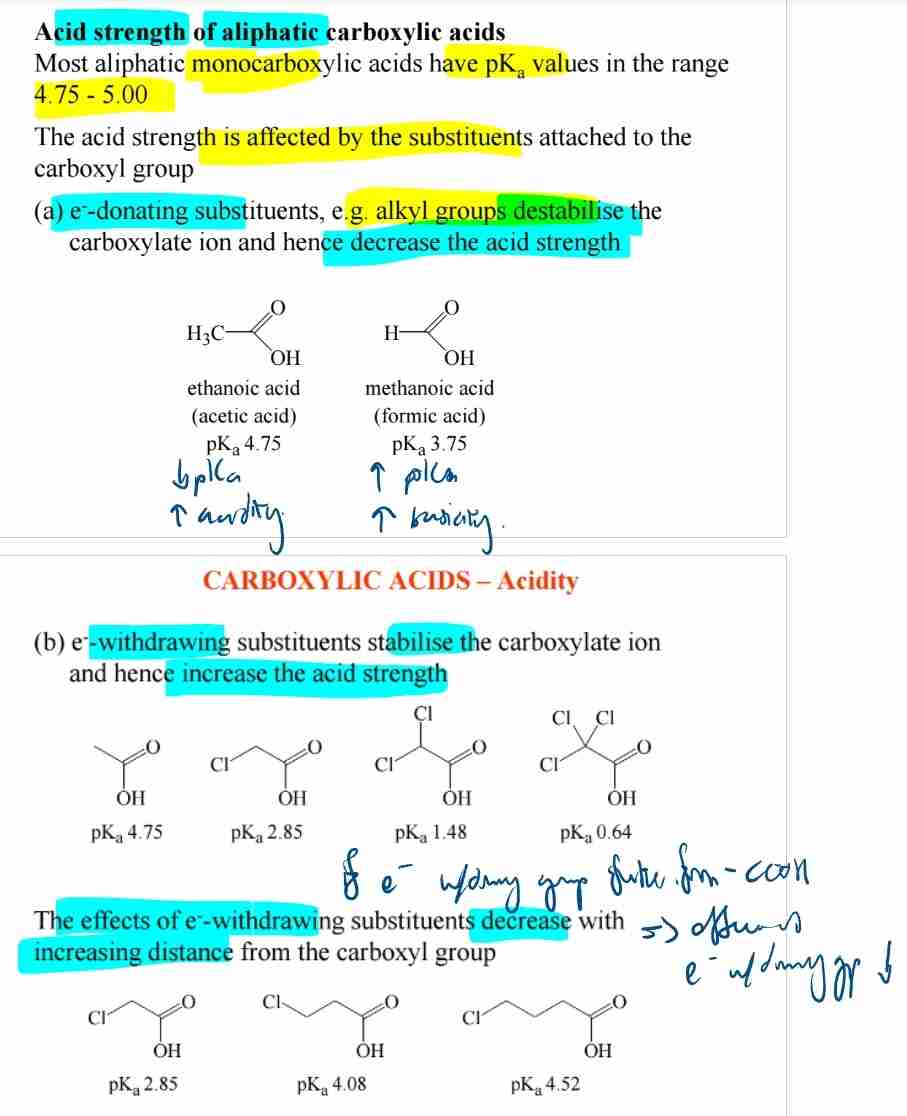
Effect of Substituents on Acidity
- Electron-donating groups decrease acidity.
- Electron-withdrawing groups increase acidity.
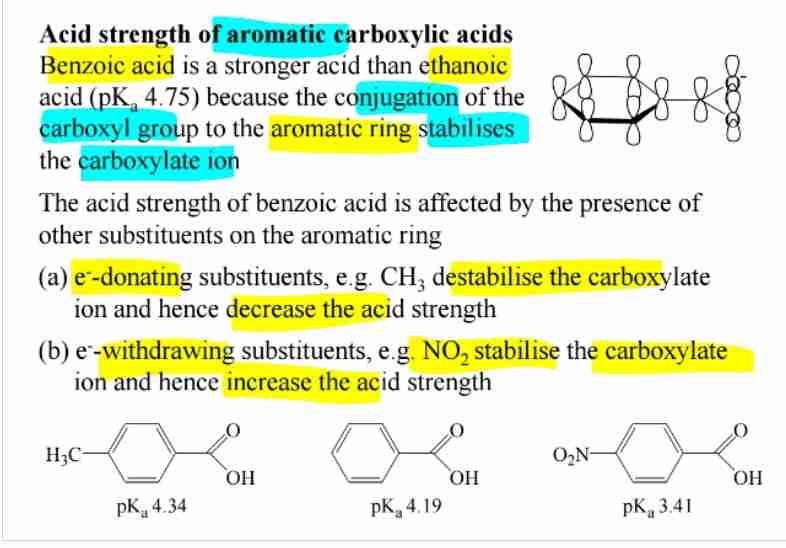
Aromatic Carboxylic Acids
Benzoic acid is more acidic than aliphatic acids due to conjugation with the aromatic ring.
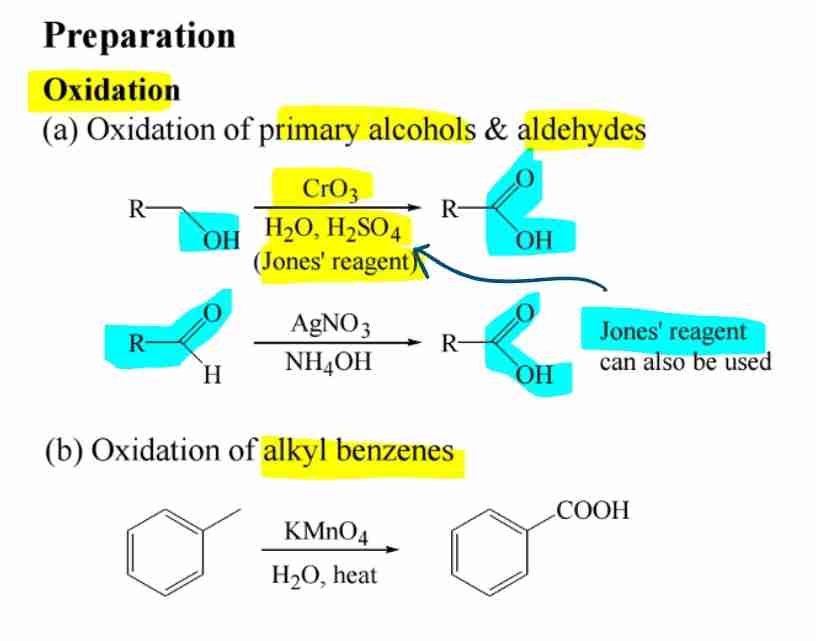
Preparation by Oxidation
- Primary alcohols and aldehydes oxidize to carboxylic acids.
- Alkyl benzenes oxidize with KMnO4.
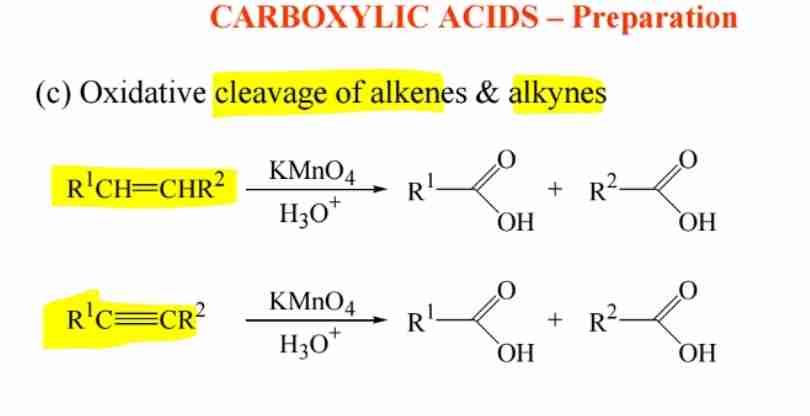
Preparation by Alkyne and Alkene Cleavage
Oxidative cleavage with KMnO4 produces carboxylic acids.
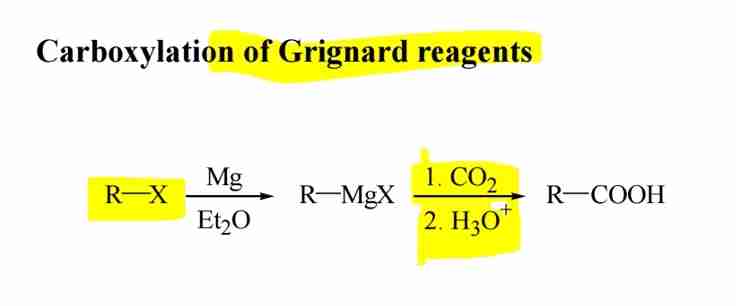
Grignard Reaction
Reaction of Grignard reagents with CO2 followed by acidification forms carboxylic acids.
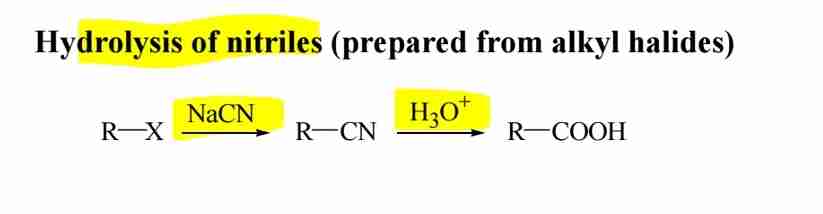
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
Nitriles hydrolyze in acidic or basic conditions to form carboxylic acids.
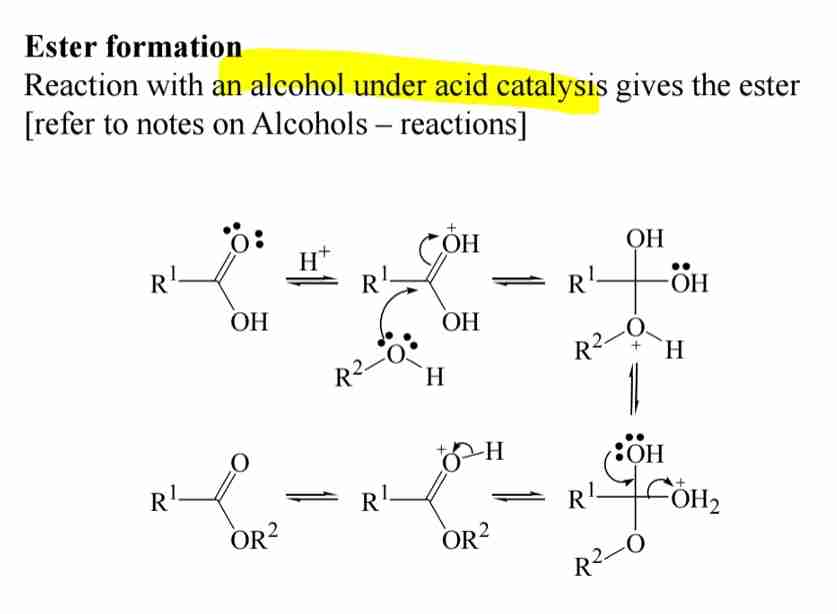
Nucleophilic Substitution: Ester Formation
Reaction with alcohols under acid catalysis forms esters.
Acid Chlorides
Reaction with SOCl2 or PCl5 converts acids into acid chlorides.
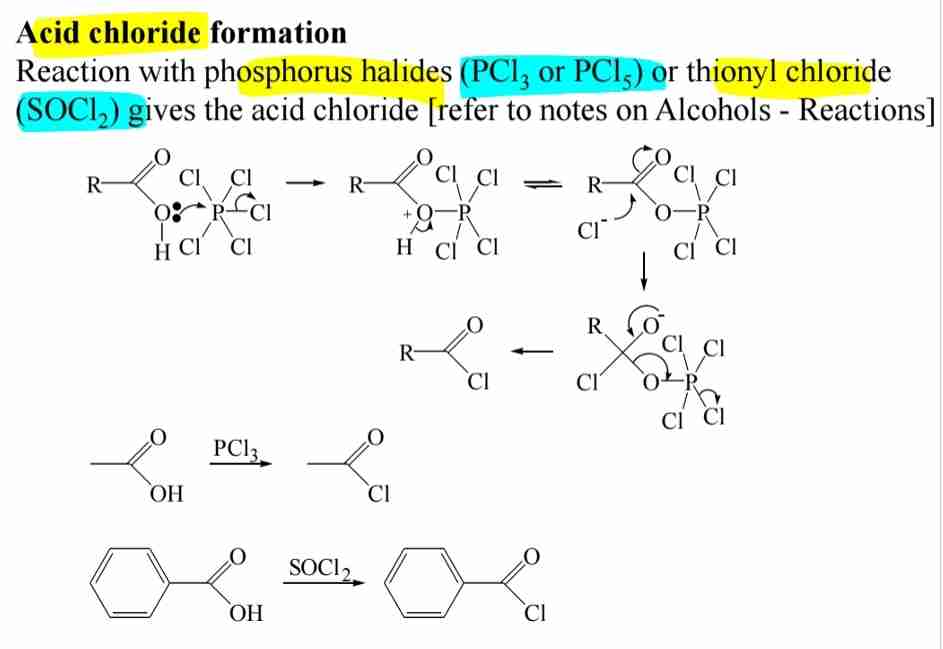
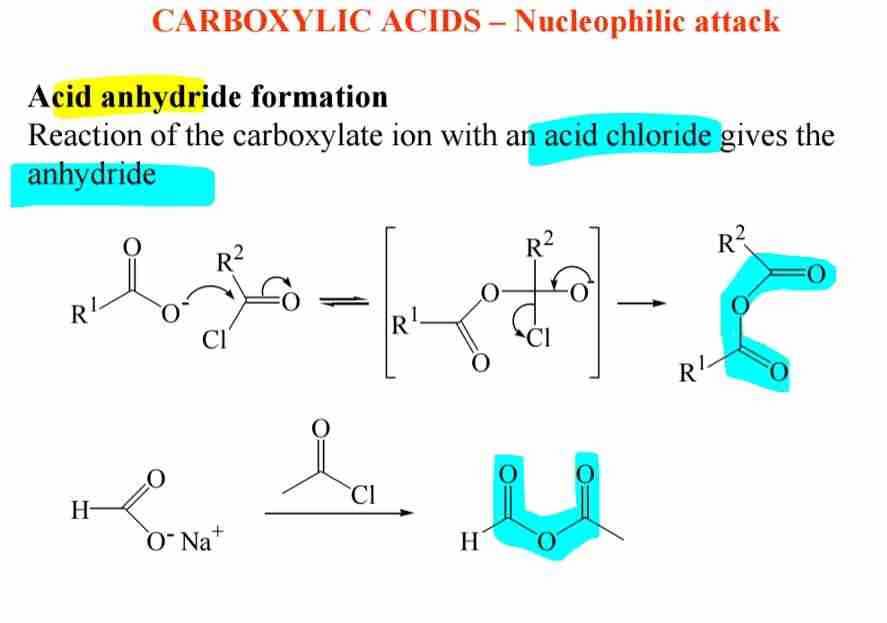
Acid Anhydrides
Formed by reacting carboxylic acids with acid chlorides in the presence of a base.
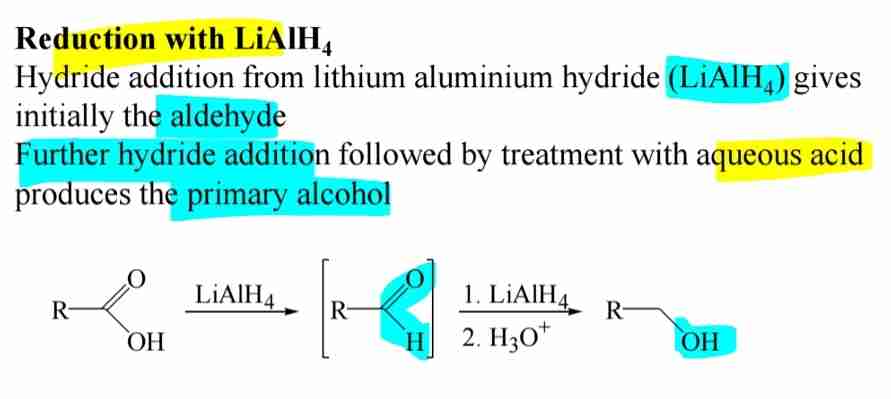
Reduction to Alcohols
Reduced by lithium aluminium hydride LiAlH4 to form primary alcohols.
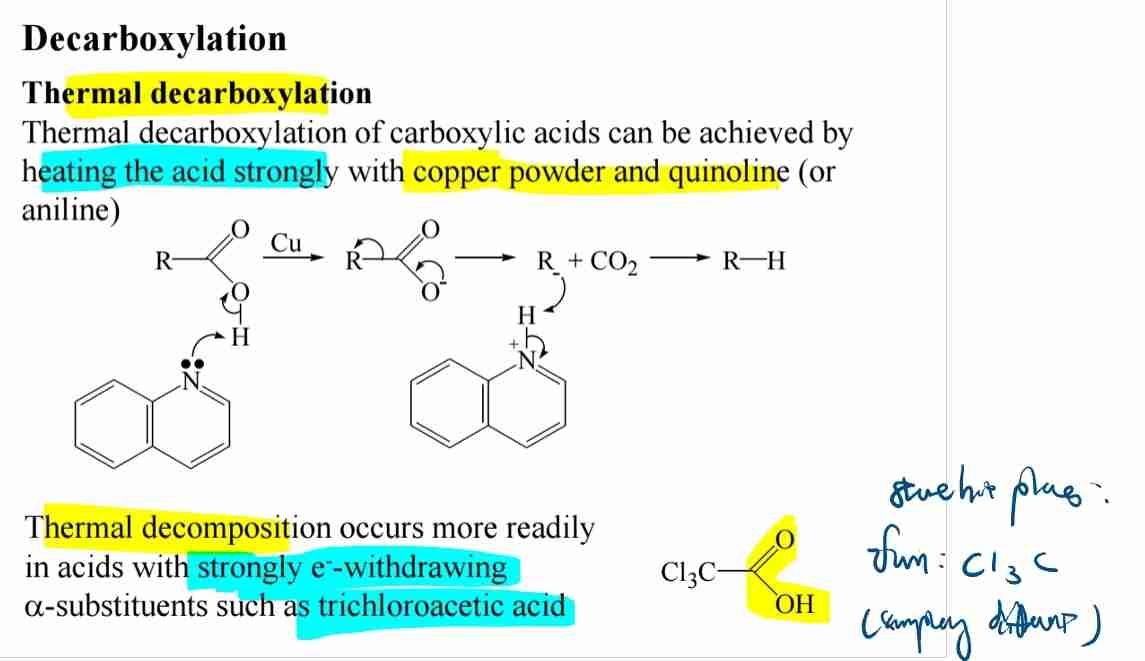
Decarboxylation of carboxylic acids
Thermal decarboxylation releases CO2, especially with electron-withdrawing groups.
Phase 1 Metabolism: β-Oxidation
Fatty acids are metabolized into acetyl-CoA through β-oxidation.
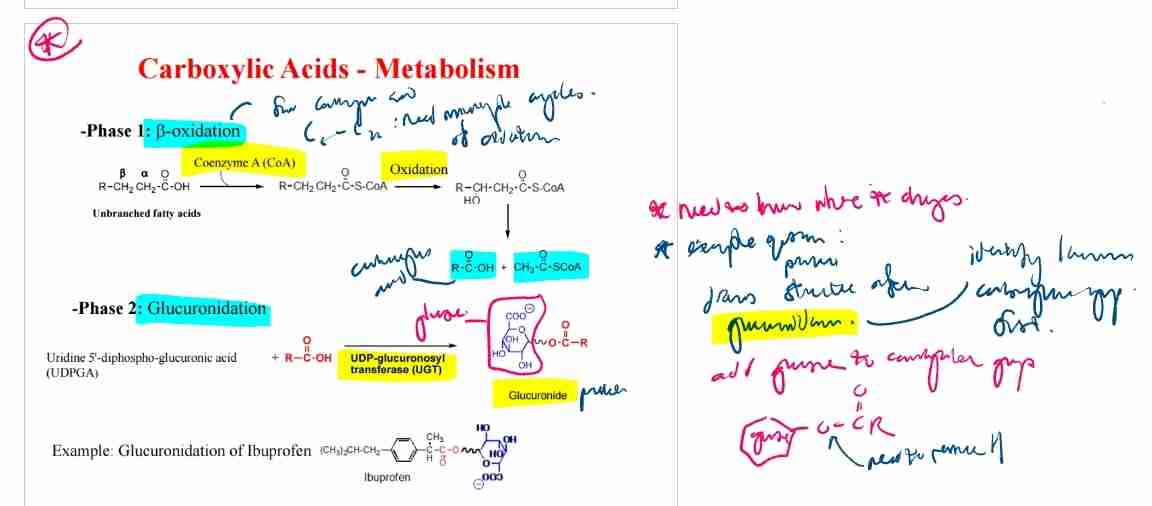
Phase 2 Metabolism: Glucuronidation
Conjugation with glucuronic acid increases solubility for excretion (e.g., ibuprofen).
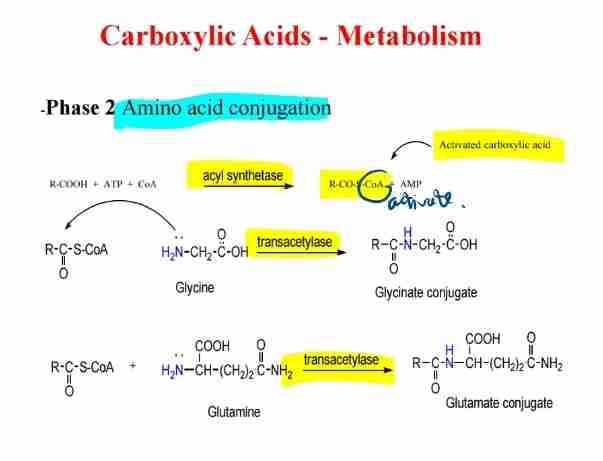
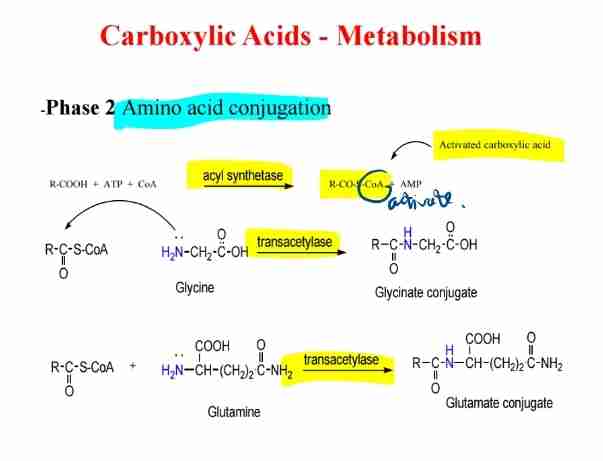
Amino Acid Conjugation
Amino acids (e.g., glycine, glutamine) form conjugates with activated carboxylic acids.
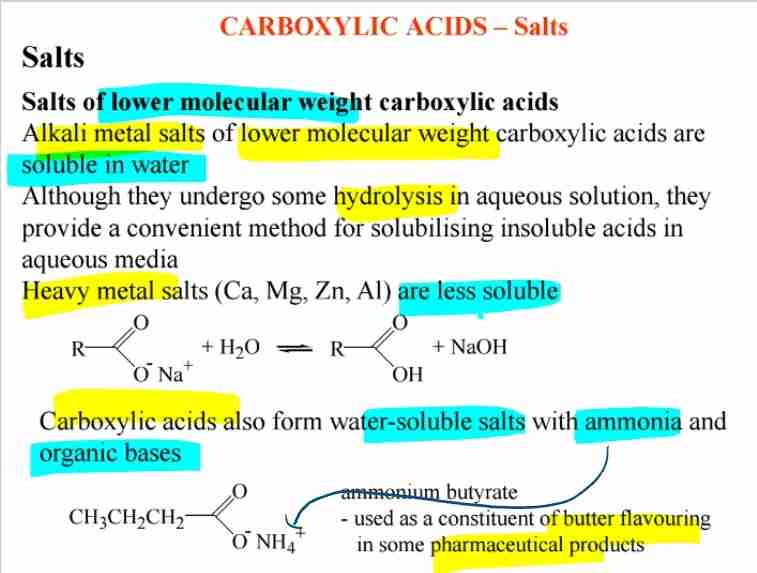
Salts of Carboxylic Acids
- Alkali metal salts are water-soluble.
- Heavy metal salts are less soluble.
Soaps & Saponification
Sodium or potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids form soaps, which act as emulsifying agents.

Applications of Carboxylic Acids
- Pharmaceutical excipients (e.g., benzoic acid as a preservative).
- Precursors in ester and polymer synthesis.