Toxicology of antimicrobial drug
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what is the danger of UV light
UV light damages DNA, protein, lipids and cells
Acute exposure leads to sunburn via an inflammatory response in the skin
Chronic exposure can lead to skin cancer via DNA damage
phototoxicity enhances sunburn → some medicines can increase this due to a molecule being activated by sunlight
how does sun tan and burn occur
the UV light from the sun stimulates your skin to produce melanin
this is the natural defence against sunlight → makes your skin darker
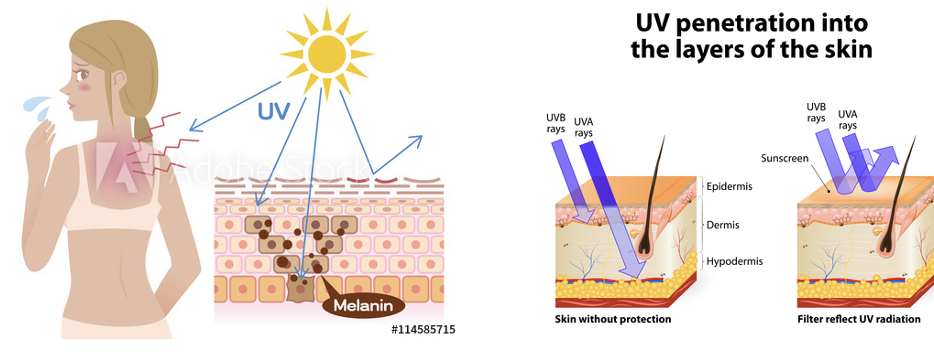
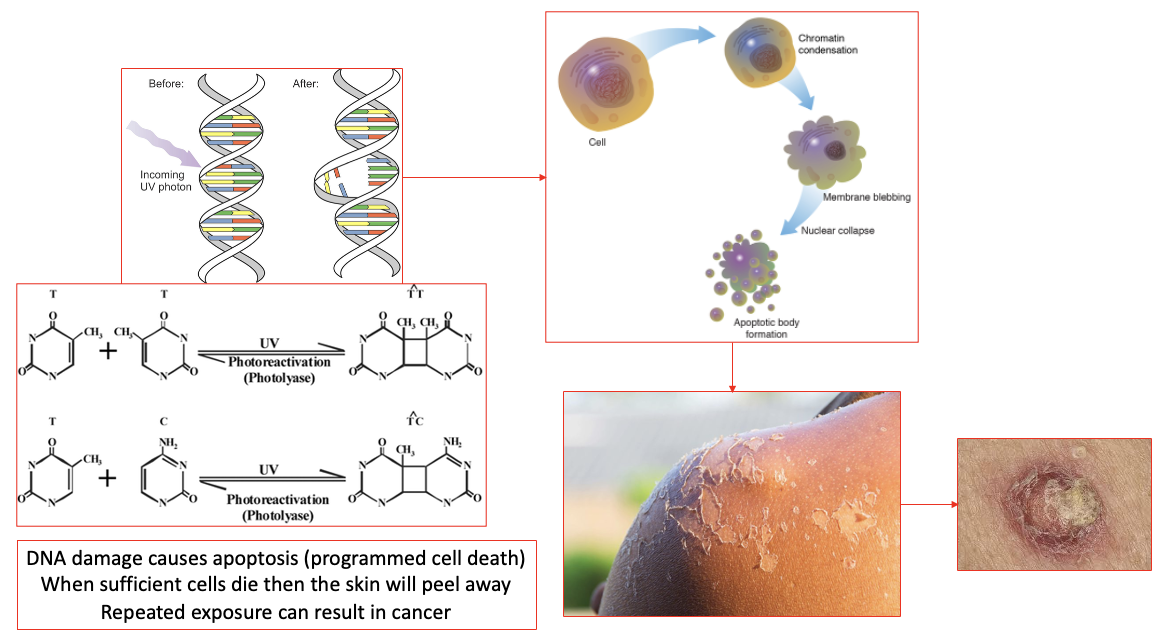
how does sun damage occur
UV light breaks the bonds between DNA bases (left side)→ bases reform in different ways → rings form a tricyclic structure (right side)
when we’re young, we are good at repairing this DNA damage
body responds to this DNA damage by apoptosis (programmed cell death)
when sufficient cells die, the skin will peel away
repeated exposure makes it harder to repair → cancer
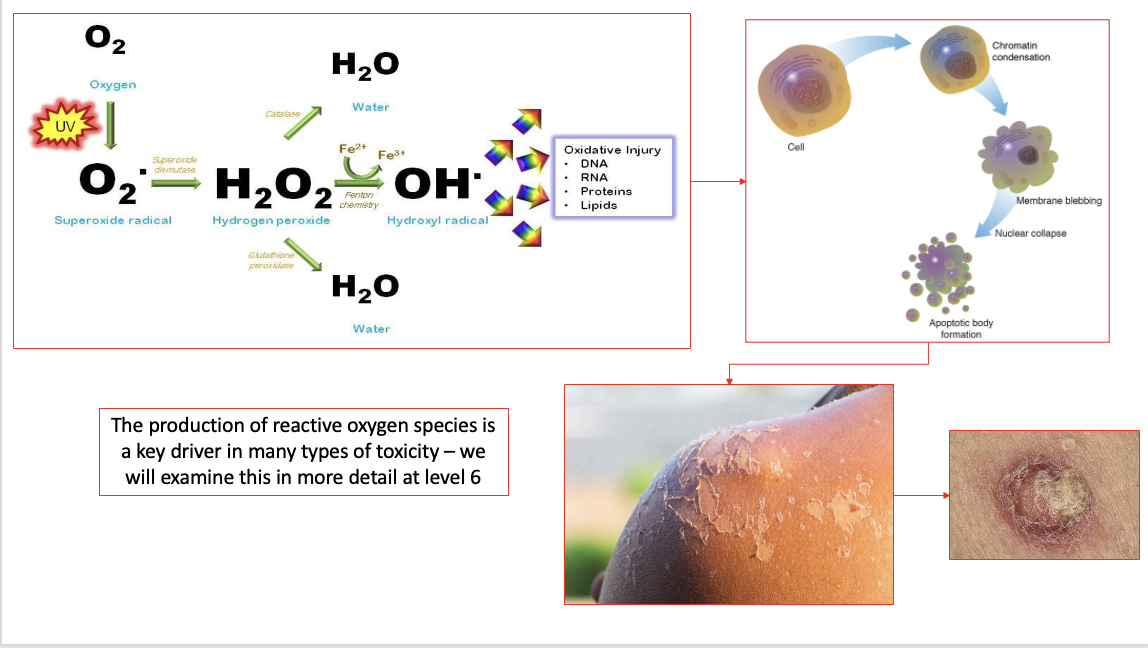
how does the production of reactive oxygen species cause toxicity
UV light exposure to oxygen → superoxide radical → hydrogen peroxide → free hydroxyl radical
hydroxyl radical has an unpaired electron, which is really toxic in a cellular environment → oxidative stress as it wants its electron paired → reacts with our DNA, RNA, proteins and lipids in an uncontrolled fashion
body responds by telling cells to die by apoptosis → damage to skin
how do tetracycline antibiotics cause phototoxicity
by redox cycling and toxicity
chemicals that undergo redox reactions are known as redox cyclers → tetracycline
tetracycline produces superoxide, O2- → excess superoxide, O2- leads to oxidative stress → apoptosis → skin phototoxicity
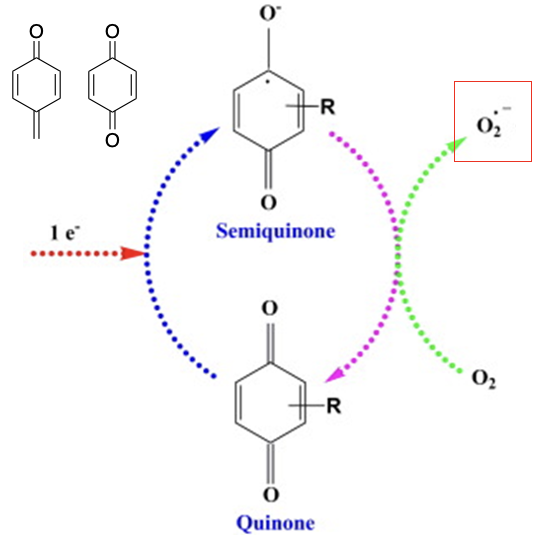
what is quinone redox cycling and how does this lead to toxicity
Drugs that contain a quinone moiety can be reduced to a semi-quinone
semi-quinone can then be re-oxidised to the quinone (oxygen is reduced)
this second process releases superoxide (electron is released)
molecule has an unpaired electron, which is toxic in the cellular environment
wants to pair by reacting with DNA, proteins and lipids
cells die by apoptosis
Other quinone-type species can behave in a similar way
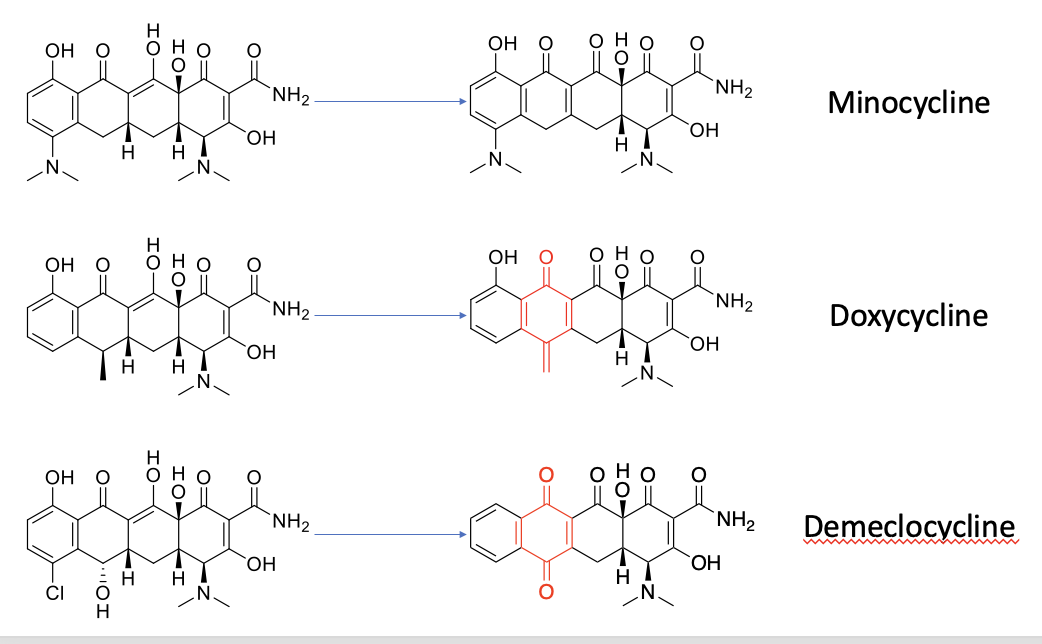
why does phototoxicity increase in these tetracyclines
minocycline doesn’t contain the quinone moiety when it gets oxidised
doxycycline and demeclocycline contain the quinone moiety → can go through redox cycling and cause toxicity
doxycycline contains one quinone-like carbonyl group
demeclocycline contains two quinone-like carbonyl groups → better redox cycler
superoxide, O2- produced → excess superoxide, O2- leads to oxidative stress → apoptosis → skin phototoxicity
do you think phototoxicity or photoallergy is more of a concern
Phototoxicity
as it is generally related to the dose and UV exposure.
It is more widespread as it does not rely on the immune system for a response.
It also enhances the risk from sunburn
What types of patients are more at risk from phototoxicity?
fair skin, freckles etc
Patients who use sunbeds
elderly
those who work outside