Biological Bases of Behavior
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
phrenology
study of bumps on the skull. wasn’t valid but brought awareness to the idea of localization of function
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
biological psychologists
study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes
dendrite fibers
a neuron’s bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. (DENDRA GOT A BUSH)
Axon
the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
myelin sheath
a fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hop from one node to the next.
if degenerates: multiple sclerosis: communication to muscles slow.
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
resting potential
inside the axon, it is - and outside is +
refractory period
period of time after a neuron fires to recharge
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse.
all or none response
a neuron’s reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not firing even if the level of stimulation is increased greatly. more neurons may fire, and more often, but not the speed or strength.
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
reuptake
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that deals with learning and memory. IT IS AT EVERY JUNCTION BETWEEN MOTOR NEURONS
endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure. ex. runner’s high
agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
antagonist
molecules that bind to a receptor cite and blocks a response. similar enough to the natural neurotransmitter to occupy its receptor site and block its effect
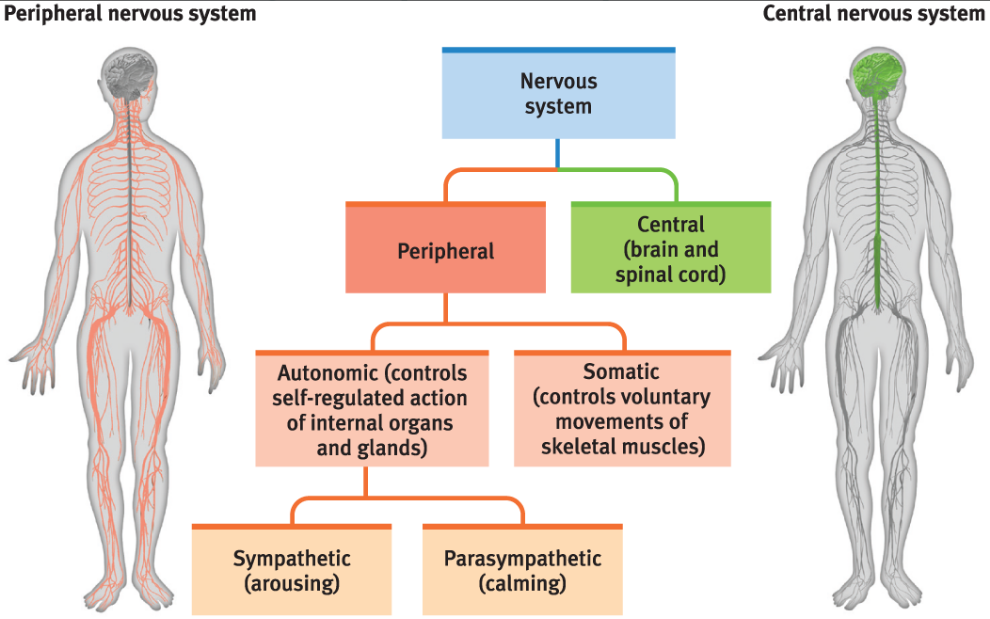
nervous system
the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems.
central nervous system
includes the brain and spinal cord. is the body’s decision maker. it is a two-way information highways connecting the peripheral nervous system and the brain
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
nerves
bundled axons that form neural “cables” connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs.
sensory neurons
carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles. (Also called the skeletal nervous system.) VOLUNTARY
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations.
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy.
endocrine system
it is a slower chemical communication system; glands that secrete HORMONES into the bloodstream
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress
pituitary gland
TOP DOG Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands. (releases growth hormone and oxytocin (birth). (brain → pituitary → other glands → hormones → body and brain)
lesion
tissue destruction. A brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue.
electroencephalogram (EEG)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
CT (computed tomography) scan
a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure. (Also called CAT scan.)
PET (positron emission tomography) scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task. (PETS ARE SO SWEETTTT)
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. MRI scans show brain anatomy.
fMRI (functional MRI)
a technique for revealing bloodflow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRI scans show brain function as well as its structure. this is all while a person looks or imagines something.
brainstem
reticular formation, pons, and medulla
oldest part of the brain. beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions. this is where the nerves on each side of the brain cross to the other side of the body.
medulla
base of the brainstem, controls heartbeat and breathing
pons
brainstem, coordinates movements
reticular formation
brain stem, neuron network that extends from the spinal cord to the thalamus. filters incoming stimuli and relays important info to other brain areas. if severed coma, if stimulated, wide awake
thalamus
above the brainstem, sensory control area. receives sensory info from all senses EXCEPT SMELL and routes it to higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, touching. receives some of the higher brain’s replies, which it then directs to the medulla and cerebellum.
cerebellum
rear of the brainstem. nonverbal learning and memory. judges time, modulate emotions, and discriminate sounds and textures. coordinates voluntary movement w/pons.
malfunc: difficulty walking, balance, etc. movements would be jerky
limbic system
hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives
amygdala
limbic system. two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion. if removed, one will become mellow and no longer ill tempered.
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
reward deficiency syndrome
crave whatever provides that missing pleasure or relieves negative feelings
hippocampus
limbic system, processes conscious memories (HUNGRY HIPPO FOR MEMORY)
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information-processing center.
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they may also play a role in learning and thinking. (more complex animal brains → proportions of glia to neurons increases)
frontal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments.
parietal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position.
occipital lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields.
temporal lobes
auditory cortex
portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. (UNCLE YUSUF HAS A TEMPER)
motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
somatosensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. more sensitive a body region is, the larger the somatosensory cortex area devoted to it is.
association areas
cerebral cortex
are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. CANNOT BE MAPPED. ARE NOT DORMANT, they interpret, intergrate, and act on sensory info and link it w/ stored memories.
prefrontal cortex
forward part of frontal lobe. judgement, planning, and processing new memories
Broca’s area
speaking
Wernicke’s area
understanding
plasticity
the brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience.
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain’s two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them.
right hemisphere
can not say what they had seen, but could identify it. left hand may almost be independent. makes inferences. modulate speech and orchestrate our sense of self
left hemisphere
could say what they saw. speech
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment.
cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language).
dual processing
the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks.
blindsight
you pretend you can’t see it but you can see it. you just don’t consciously know that you can.
molecular genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes
heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied.