bio paper 2 final final
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
How was disease spread between trees so quickly?
short distance between trees
low genetic diversity/ lack of resistance
climate favoured spread of vector
spores carried by wind
(i) Explain why mitosis, and not meiosis, is used for asexual reproduction in plants.
produces genetically identical , cells / organisms ✓ maintains , chromosome / diploid , number (between generations) ✓
how is dna replication and PCR different?
PCR only on short sequences, whereas DNA replication whole chromosome possible
primers required for PCR
cycles of heating and cooling required in PCR
benefits of coppicing re biodiversity
provides variety of habitats
provides variety of light levels
shorter plants get more light as tree grows
roots remain so no soil erosion
maintains soil quality
prevents succession
lifespan of tree extended
can continue indefinitely
how can inserting new gene into chromosome affect functioning of other genes in chromosome
frameshift → altered base triplets
gene could be inserted in middle of functioning gene, disabling it
adjacent genes cld be switched off
why preserve organisms that have not undergone artificial selection? & gene banks
source of potentially useful alleles
useful in changing population e.g. source of replacement if population were in danger
increase genetic variation & gene pool
Why use clones of plant?
increase validity
control variable
no genetic variation

modern med developed from traditional remedies
many plants produce molecules with medical benefits
many such plants yet to be discovered

b) Suggest an advantage to a non-infected cell of having this process.
b) incorrect RNA destroyed so wrong proteins not made


infections
irritation
coughing
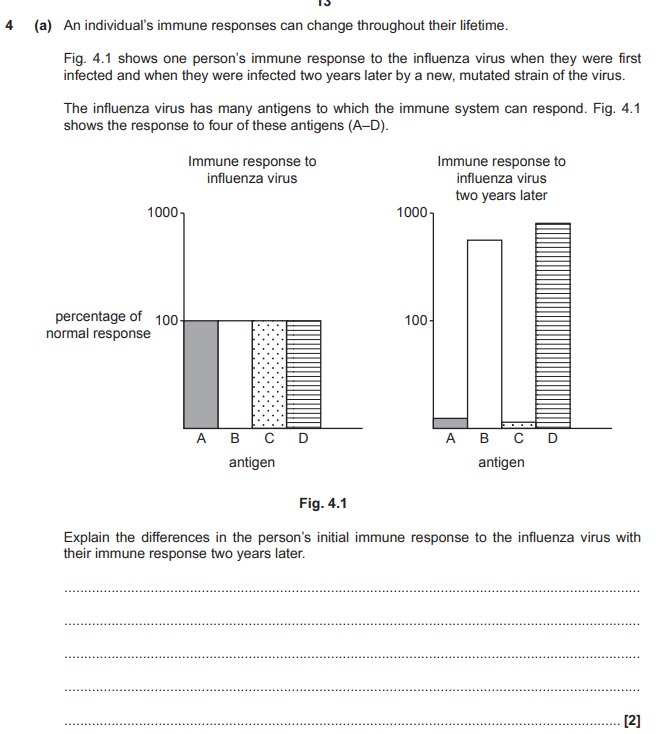
* The specific immune response involves B and T lymphocytes. There is variation in specific immune responses between individual animals. Variation between immune responses can be influenced by genes and the environment. Using examples, explain how both genes and environment can cause animals to vary in their specific immune responses.
inherit genes that code for diff immune cells
different alleles code for diff versions of immune cells
alleles code for different variable regions

Explain how the following activities could have contributed to increased habitat diversity.
Constructed dams
Felled trees
Built lodges
1) slow moving water for aquatic species
2) opened up tree canopy to let light to ground level
3) provide sheltered habitat for insects
woodland vs farmland

A group of students were studying invertebrate biodiversity in two areas of local woodland, Area A and Area B. They used pitfall traps to sample the two areas. i. Explain how a pitfall trap can be set up and used to sample invertebrate biodiversity.


last step: divide by 10 for ten fold, then divide by 100 to convert


suggest how allele b inhibits the expression of allele A
allele B codes for transcription factor
transcription factor binds to promotor region on allele A
preventing genes that allele A codes for from being transcribed


Cyanide inhibits carriers in electron transport chain. Why more CO2 produced with yeast cells in pyruvate only than yeast cells with pyruvate and cyanide? (3)
when cyanide absent, pyruvate fully respire to produce CO2
when cyanide present, pyruvate does not enter mitochondrial matrix
anaerobic respiration
incomplete breakdown of pyruvate
some CO2 produced in pyruvate’s breakdown to ethanol
Explain why CO2 produced when mitochondria incubated with pyruvate, but not when incubated with glucose. (3)
pyruvate is end product of glycolysis
pyruvate can enter mitochondria
glucose cannot
decarboxylation
in Krebs cycle and link reaction to produce CO2
no carriers for glucose in mitochondrial
membranes
Cyanide inhibits carriers in ETC. Why can ethanol production still occur in presence of cyanide? (3)
pyruvate→ ethanal in cytoplasm
ethanol→ ethanol
does not involve ETC/ oxidative phosphorylation
enzymes in cytoplasm not inhibited
State where the FADH and NADH molecules are reoxidised and what happens to the H atoms. (4)
1 inner mitochondrial membrane/cristae;
2 ref to (NADH) dehydrogenase;
3 hydrogen split into protons and electrons;
4 ref to, electron carriers/ETC/cytochromes;
5 energy released from electrons;
6 ref to protons pumped across membrane;
7 protons accumulate in intermembrane space;
8 proton gradient/pH gradient/H+ gradient;
9 protons pass through ATP synthase
10 ref. to oxygen (final) hydrogen/electron acceptor;
11 formation of water;
The liver is responsible for producing enzymes which detoxify alcohol by breaking it down into smaller units. This breakdown by enzymes uses NAD. This means that other reactions that use NAD are less likely to take place. The build up of fats in the liver is one of the first signs of liver damage due to excessive alcohol intake.
Explain why the build up of fats occurs in the liver of an individual who consumes large amounts of alcohol.
fats/fatty acids, not respired;
oxidation (of fatty acids) requires NAD;
NAD used in breakdown of alcohol;
NAD is, limiting/in short supply/AW;
fats formed from fatty acids plus glycerol;
AVP; e.g. further detail of alcohol/fat metabolism
After chasing prey, a cheetah breathes rapidly (pants) for half an hour before it can run again.
Explain why panting is necessary.
heat loss
1 body/blood, temperature rises;
2 may affect/denature, enzymes/proteins;
3 panting cools body;
4 ref. evaporative cooling;
fate of lactate
5 (high) lactate concentration needs to be reduced;
6 due to anaerobic respiration;
7 panting provides extra oxygen/ref. oxygen debt;
8 lactate oxidized to pyruvate;
respiratory gases
9 myoglobin would be reoxygenated;
10haemoglobin would be reoxygenated;
11ATP/CP, resynthesised in muscle tissue;
12removal of extra carbon dioxide;
Suggest how the low body mass of the birds in spring may be related to enhancing the birds’ survival during the moulting period, when the feathers are lost and regrown.
flying, easier/uses less energy
can, escape predators/find food, (by flying);
food used for feather growth;
therefore, fat stores used/less food stored
high body mass and low metabolic rate. why?
E1 less food used;
E2 (for) less respiration/lower BMR/lower body temperature;
E3 more food stored;
E4 as fat;
E5 (food store/fat) for, migration/flight;
There are a number of organic molecules in cells whose role is to transfer hydrogen atoms from one compound to another. Examples include NAD, FAD and NADP.
NAD, FAD and NADP are important molecules in plant cells. Describe, in detail, the role of these molecules within a palisade mesophyll cell.
NAD / FAD, involved in respiration
dehydrogenation ;
2 molecules of NAD (reduced) in glycolysis ;
link reaction producing 1 molecule of NAD (reduced)
Krebs cycle produces 3 NAD (reduced) (per turn of cycle) ;
detail of any one step in respiration where NAD (reduced) is produced ;
Krebs cycle produces 1 FAD (reduced) (per turn of cycle) ;
carriers / transfers, hydrogen to, inner mitochondrial membrane / ETC ;
AVP ; e.g. hydrogen split into electrons and protons at ETC
mitochondrial shuttle (bringing NAD reduced from glycolysis into matrix) ;
NADP involved in photosynthesis ;
produced in non-cyclic (photo)phosphorylation
hydrogen comes from, water / photolysis
Calvin cycle / light independent stage ;
GP to TP step ;
AVP ; e.g. NADP involved in transporting hydrogen from grana to stroma
Explain why, under aerobic conditions, lipids have a greater energy value per unit mass than carbohydrates or proteins.
Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production
requires H
to form reduced NAD/ FAD form
lipids have highest proportion of H compared to carbs/ proteins
more acetyl coenzyme A/ turns of Krebs cycle
In this situation, the energy released by oxidation of food materials is converted into heat instead of being used to form ATP. One such compound is dinitrophenol, People working in these factories were exposed to high levels of dinitrophenol.
Suggest and explain why these people became very thin regardless of how much they ate.
dinitrophenol in body ;
ETC still functioning ;
less ATP formed in respiration ;
food not enough to meet metabolic demands of body / AW ;
had to respire, body tissues / food stores ;
AVP ; e.g. heat production increasing metabolic rate
Aerobic respiration may be summarised by the following equation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Although carbon dioxide and water are products of aerobic respiration, the equation is an over-simplification of the process.
State and explain one way in which this equation is an over-simplification.
glucose isn’t only substrate
e.g. fats also respired
ATP used in glycolysis
ATP produced in substrate-level/ oxidative phosphorylation
not only 1 step, e.g. Krebs cycle and link reaction also happens
A scientist used a respirometer to investigate the rate of respiration and photosynthesis of maize in different light intensities. • The scientist placed ten maize seedlings in a respirometer and kept it in the dark for three hours. • The respirometer contained soda-lime to remove any CO2 produced by the seedlings. • The scientist placed ten maize seedlings in a separate respirometer without soda-lime and placed it in different light intensities for three hours at a time.
Suggest why soda-lime was not placed in the respirometer with the seedlings grown in the light.
CO2 prevents photosynthesis
CO2 is limiting factor
(light should be only limiting factor)
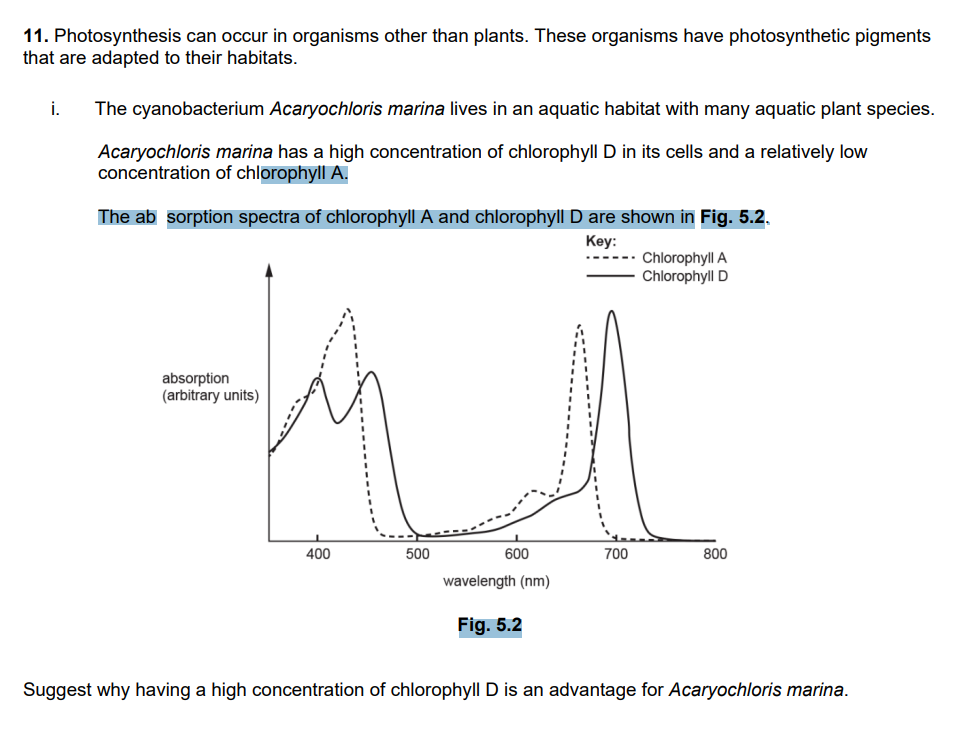

Chromista are photosynthetic protoctists that live in water. Chromista are different from other photosynthetic organisms because they contain the pigment chlorophyll c. Chlorophyll c is not found in plants. The wavelengths of light absorbed by chlorophyll c are different from those wavelengths absorbed by chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Suggest why Chromista need pigments that are different from those of other photosynthetic organisms.
chromista have to absorb shorter wavelengths
some wavelenghts don’t reach depths/ them
Hold the TLC plate carefully by the edges and avoid damaging the surface of the plate. Why
(so that) movement of spots not affected (by damage) OR (so that) plates are not contaminated (by fingerprints / oils from skin) ✓
Make sure the TLC plate does not touch the sides of the jar anywhere else. why?
condensation / liquid / solvent , on walls of jar may affect movement of spots
Step 1: Extraction of pigments • Take 0.5 g of fresh spinach and add 1 g of sand. • Grind the mixture until it becomes a fine, light green powder. • Transfer the powder to a test tube and add 2 cm3 of propanone. • Stir for about 1 minute then allow to stand for another minute. • Transfer the dark green upper layer with a pipette to a clean test tube and seal with film when not in use.
Why must you work quickly?
prevent/reduce degradation of pigments
(since exposed to light)
reduce/ prevent evaporation of solvent/ propanone
The Hill reaction is a model system used to study the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis. It uses a blue dye, DCPIP, which is colourless when reduced. DCPIP is reduced in the Hill reaction. Suggest and explain the function of DCPIP in the Hill reaction.
replaces NADP (usual electron acceptor)
acts as final electron acceptor
allows photolysis to continue (since even when no more NADP left, dcpip can accept electrons from photolysis )
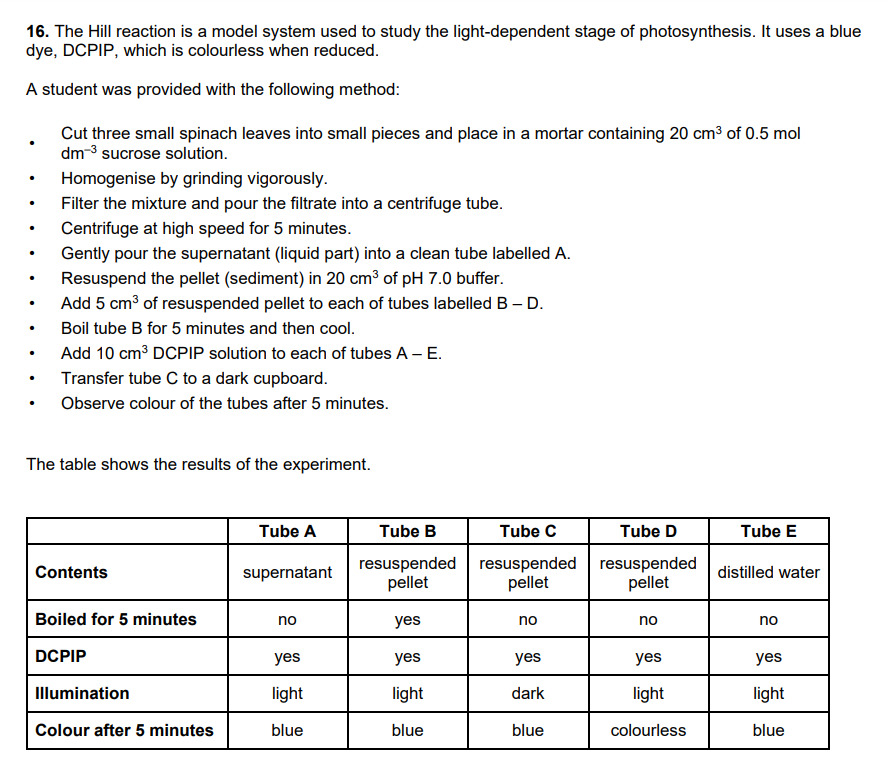
Using the results shown in the table, explain what can be concluded from each tube, or pair of tubes, about the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis.: A, B, C and D, E
2) The student knew that it was important to use sucrose solution when homogenising the leaves. Explain why it was important that the pellet was suspended in buffer solution and why it did not contain sucrose.
2)
maintains optimum pH for enzymes
no need to prevent damage to chloroplasts
/ damage to chloroplasts increases access of DCPIP to (reaction) components
why are synapses between neurones important?
ensure action potentials move in 1 direction
1 neurone can receive impulses from or transmit impulses to many neurones
summation
filters out low level stimuli & ensures that only stimulation that is strong enough is passed on
prevents continuous stimulation of neurones (since neurotransmitter removed from synapse)

C


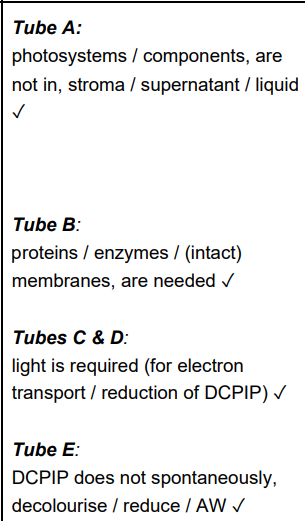
why are fruit flies used for research into genes controlling body plan
why are mice chosen for investigations into genes controlling body plan
cheap/ rapid reproduction rate OR body plan is well understood
more than 1 species needed to demonstrate conservation of base sequence
similar to humans
how do synapses allow transmission in 1 direction only?
receptors for neurotransmitter only on post-synaptic neurone
ACh broken down at post-synaptic neurone
only pre-synaptic neurone releases neurotransmitter
only pre-synaptic neurone has calcium ion channels
qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq
remember, cannot refer to refractory period as this not a feature of synapses
how is genetic diversity in a population measured?
genetic polymorphism
proportion of mutated alleles
proportion of heterozygotes
why cannot support idea that species B shows greater polymorphism than A, despite B having higher calculated polymorphism value (0.4 and 0.35)?
same gene loci may not have been sampled
no statistical test performed
similar polymorphism values
no indication of sample size
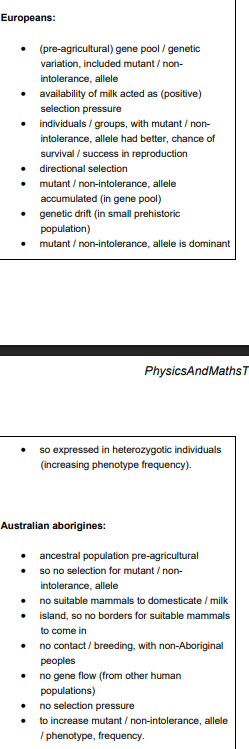
It is thought that the modern cheetah population has low genetic diversity because the population, relatively recently, experienced a genetic bottleneck. Explain why a genetic bottleneck can lead to low genetic diversity.
alleles lost
modern pop descended from few survivors
Suggest how the interdisciplinary field of bioinformatics may be useful in determining whether a newly-sequenced allele causes a genetic disease.
computational analysis allows rapid comparison of sequences w/ newly sequenced allele
data on protein structures and amino acid sequences
data on base sequence of normal allele and alternatives
Explain how the high occurrence of this disease in West Highland Terriers could have been a result of artificial selection.
inbreeding ,reducing genetic diversity
allele for the disease linked to desirable trait so inherited tgt