AP Psychology- Unit 3 (Development and Learning)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
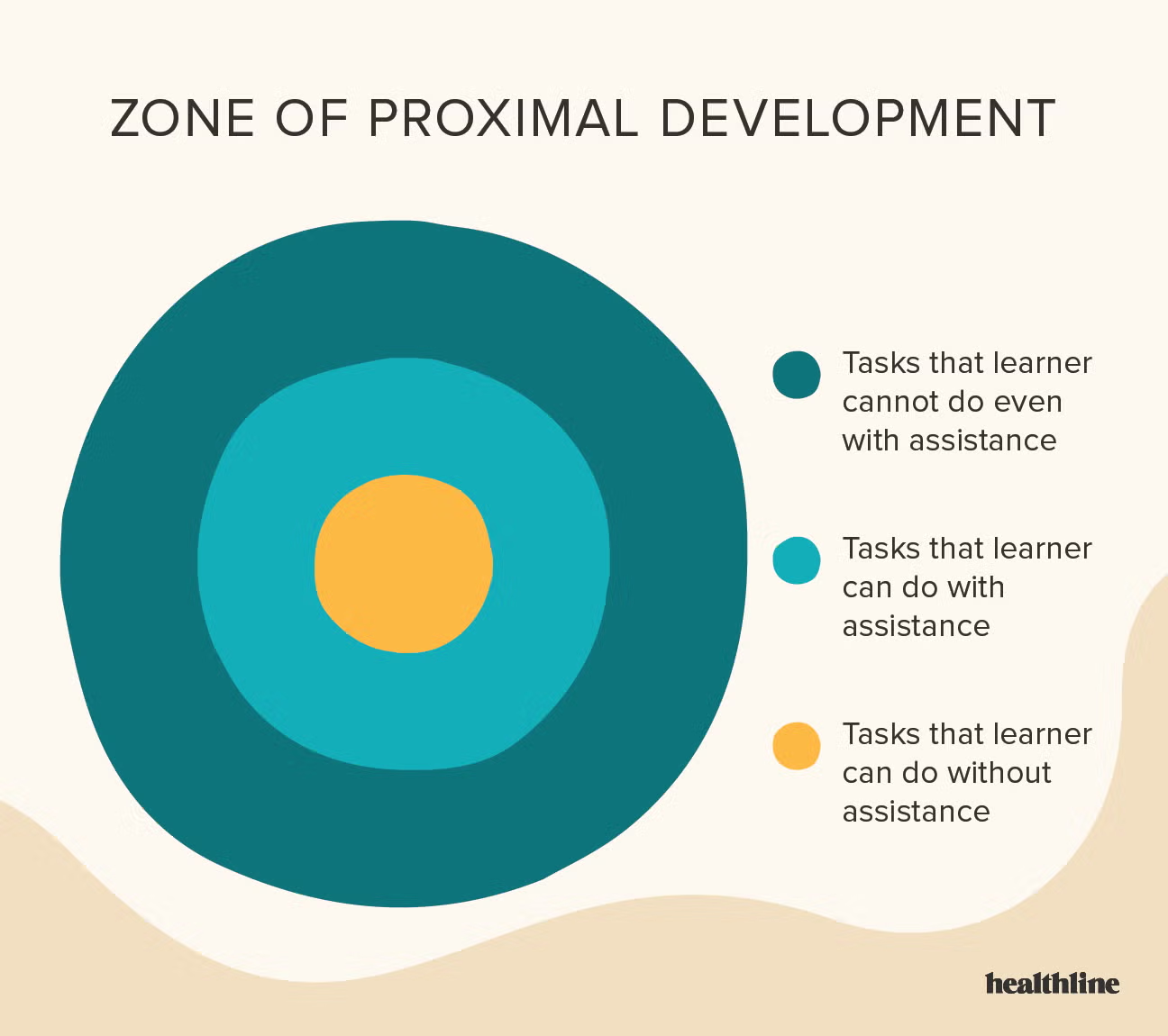
Zone of Proximal Development
range of tasks that a learner can perform with the guidance of a more knowledgeable peer, but not yet independently
(Lev Vygotsky)
Morphemes
smallest meaningful unit of language
basic element that conveys meaning withing a word
ex: prefix/suffix
Scaffolding
(as it pertains to Vygotsky)
temporary support provided by a more knowledgeable person to a learner until they can complete the task on their own
Gross-Motor Skills
skills that depend on development of the large muscles
ex: jumping, running, throwing
Autonomy
independence that includes personal responsibility and decision making
Growth
physical changes in size, such as gains in height and weight and an increase in physical strength and coordination
Development
gradual increase in skills and abilities that occurs over a lifetime and encompasses physical, cognitive, and social changes
Developmental Delay
lag in a particular aspect of development (in a child)
Sensorimotor
1st stage of Jean Piaget’s development theory
birth - 2 years
infants learn about their senses
develop object permanence
Preoperational
2nd stage of Jean Piaget’s development theory
between 2-7
begin using symbols and language
struggle with concrete logic and understanding others' viewpoints.
Concrete Operational
3rd stage of Jean Piaget’s development theory
between 7-11
can perform logical operations on concrete, tangible objects
understand conservation
struggle with abstract concepts
Formal Operational
4th (final) stage of Jean Piaget’s development theory
around 11-12
think abstractly, logically, and systematically
can solve complex problems using abstract reasoning and logical deduction
Jean Piaget’s Development Stages
Sensorimotor
Preoperational
Concrete Operational
Formal Operational
Identity Moratorium
an individual is actively exploring different options and identities without making a firm commitment to any one path
often seen in adolescence, where individuals try various roles and beliefs before settling on a stable identity
Identity Achievement
an individual has explored various options and made a commitment to their values, beliefs, and goals
Identity Diffusion
where a person lacks a strong sense of self and isn’t actively working to develop one
Identity Foreclosure
an individual commits to an identity without exploring other options
accepting values or roles handed down by others, such as, parents or peers
Classical Conditioning
theory that behaviors can be associated with responses through repeated pairings of stimuli, leading to learned reactions.
Fine-Motor Skills
skill that depends on the development of small muscles
ex: coloring, drawing, writing, cutting with scissors
Operant Conditioning
tendency of people to repeat behaviors that have a positive result and avoid those that lead to negative consequences
this learning process involves reinforcement and punishment to shape behavior
Vicarious Conditioning
learning through observing other people’s responses to an environmental stimulus that is most noticeable to the observer
Social Learning Theory
learning that takes place through an observational process that emphasizes the importance of social influences and modeling in acquiring new behaviors
Continuous Development
theory that says development is a gradual, continuous process with no distinct stages
Primary Sex Characteristics
biological features directly involved in reproduction
ex: ovaries/testes
sex organs themselves
Secondary Sex Characteristics
physical traits not directly related to reproduction
ex: facial hair/breast development
Menarche
female’s first menstrual period, signaling the onset of puberty and the fertility potential
key transition from childhood to adolescence
Spermache
the first time a male experiences ejaculation
male equivalent of menarche
Mental Symbols
internal cognitive representations, like images, words, or concepts
allow individuals to process and understand information about the world around them
Theory of Mind
cognitive ability to understand that other people have their own thoughts, beliefs, desires, and intentions
Critical Periods
organism is most sensitive to environmental influences/stimuli
could result in irreversible changes to the brain
Sensitive Periods
offers a broader window for experience to shape neural activity
Discontinuous Development
theory that says development occurs in a series of distinct stages and that each stage involves qualitative differences in behavior and thinking.
Crystallized Intelligence
ability to use previously learned knowledge and experience to solve problems
“book smarts”
Teratogens
substances that damage the process of fetal development (tobacco and alcohol)
Fluid Intelligence
ability to solve new problems and reason abstractedly in novel situations
capacity to think flexibly and logically without relying heavily on previously learned knowledge
“street smarts”
Ecological Systems Theory
framework that explains how a person’s development is influenced by various interconnected environmental systems
Ecological Systems
Microsystem (immediate family and friends)
Mesosystem (interactions between family and friends)
Exosystem (wider societal influences)
Macrosystem (cultural values)
Chronosystem (time-related factors)
Object Permanence
understanding that an object continues to exist even when it cannot be seen or directly perceived
developed by Jean Piaget
is fundamental in cognitive development during the Sensorimotor stage
Phonemes
smallest unit of sound in a spoken language
ex: “p” sound in “pat” or “b” sound in “bat”
Semantics
the study of meaning in language, focusing on how words, phrases, and sentences convey meaning and how context affects interpretation
Reinforcement Schedules
rules that control the delivery of reinforcement
fixed interval
variable interval
fixed ratio
variable ratio
Secondary Reinforcers
a stimulus that reinforces a behavior after it has been associated with a primary reinforcer
Primary Reinforcers
a stimulus that leads to some type of natural or automatic response
unconditioned stimulus
Reinforcements
Positive Reinforcement: gives something they like (candy/praise)
Positive Punishment: gives something they don’t like (chores)
Negative Reinforcement: takes away something they don’t like (lessen homework)
Negative Punishment: takes away something they do like (take away phone)
Counterconditioning
conditioning an undesirable response or behavior with a more desirable one
ex: fear of public speaking → feeling rewarded after public speaking
Classical Conditioning
learning through association
people/animals repeatedly exposed to 2+ stimuli and learn to associate the two
they learn to exhibit a new learned response when in the presence of the stimuli
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
potentially traumatic events that occur before a child reaches 18
Abuse (physical + mental)
Neglect (physical + mental)
Household Dysfunction (mental illness, substance abuse)
Social Clock
culturally preferred timing of significant life events like marriage, parenthood, and retirement
Temperament
an individual’s characteristic level of emotional excitability or intensity
foundational aspect of personality that influences how a person reacts to stimuli and situations
Attachment Styles
Secure
Insecure:
Avoidant
Anxious
Disorganized
Behaviorism
theory based on the belief that an individual’s behavior is determined by forces in the environment that are beyond their control
Asynchronous
development rates uneven in physical, emotional (SEL), and cognitive development
Associative Learning
a learning principle that states that ideas and experiences reinforce each other and can be mentally linked to one another
Biological Preparedness
the idea that people and animals are inherently inclined to form associations between certain stimuli and responses
Behavioral Perspective
explains behavior through conditioning
ex: classical conditioning/operant conditioning
Taste Aversion
a learned response to eating spoiled or toxic food or a food you associate with illness
ex: not liking tacos after throwing them up
Parenting Styles
Authoritarian: high expectations but low emotional support
Authoritative: high expectations and emotional support
Permissive: low expectations but high emotional support
Neglectful Permissive: low expectations and low emotional support
Syntax
set of rules that govern how words are combined to for grammatically correct sentences within a language
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory Stages
Trust vs Mistrust (infant)
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt (toddler)
Initiative vs Guilt (pre-schooler)
Industry vs Inferiority (school-age)
Identity vs Role Confusion (adolescent)
Intimacy vs Isolation (young adult)
Generativity vs Stagnation (middle age)
Ego Integrity vs Despair (older adult)