International economics - chp.8
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Why do governments sometimes apply a tariff on imported goods?
Government use tariffs to protect local industries from cheaper foreign goods. Tariffs make import more expensive, so people buy more local products.
Tarrif, quotas or export subsidides(financial support for local exportets) are some of trade policy tools governemnt respons with to protect domestic industries
Why does the world trade organization try to reduce the use of tariffs
The WTO wants fair trade. It ensures that tariffs are not misused and encourages countries to trade freely, which helps all economies grow.
When was the World Trade Organization (WTO) established?
1995
What agreement existed before the WTO?
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), created in 1947.
What was the main purpose of GATT and the WTO?
To promote free and fair trade by reducing tariffs and removing trade barriers.
Key rules of GATT
Same tarrif for all members
Tariffs allowed for unfair trade(dumping)
No import quotas allowed
Declare export subsidies -governements must report or declare if they have given financial support to domestic firms so that they can export cheaply
Temporary tarrifs allowed
Security exception- tarrif for national security
Regional trade agreements
What is the “Same tariff for all members” rule?
Countries must apply the same tariff to all WTO members, no special treatment.
Rule 2- tarrif allowed for unfair trade - “dumping”?
Dumping means selling goods abroad below domestic price or cost.
Countries can respond with anti-dumping tariffs to protect their markets.
Are import quotas allowed under GATT?
Generally no, strict import limits are prohibited — with a few exceptions.
What must countries do about export subsidies?
Countries must report if they give financial help (subsidies) to industries or companies for exports. They should also discuss plans to reduce or remove such subsidies.
Rule 5 - temporary tarriffs allowed?
Countries may raise tariffs for a short time if domestic industries are harmed by sudden import increases.
This is called the “safeguard provision” or “escape clause”.
Rule 6 - security exception
Countries are allowed to impose tariffs if they believe it's necessary for national security.This is called a "security exception".
Rule 7 - What are the two main types of RTAs?
GAAT allows groups of countries to make their own trade deals. There are two types
Free-Trade Area: Internal trade barriers removed for countries that sign the free-trade agreement. This is for instancem EU - EFTA (EEA area). US, Canada, Mexico in NAFTA. However each country keeps its own external tariffs toward non-members
Customs Union: Internal barriers removed and all members adopt a common external tariff towards non-members
Why do countriess use tarrifs if they cause losses?
They protect domestic produsers from foreign competition
Producers gains are big and concentrated, consumer losses are small and spread out. So industries fight strongly for protection, while consumers barely notice.
Protected industries have strong political influence.
If the quantity of imports is restricted by a quota, how is the different from using a tariff?
A tariff is a tax on imported goods – money paid to the government.
A quota is a limit on how much can be imported – no tax, just a set number.
Both raise prices, but only tariffs give money to the government. With quotas, the importer or seller gains that benefit instead.
Differance between perfect and imperfect competition
Perfect competition: Many firms, same product, no price control → price takers.
Imperfect competition: Fewer firms, different or unique products, some price control → price makers. Under imperfect competition we find monopol
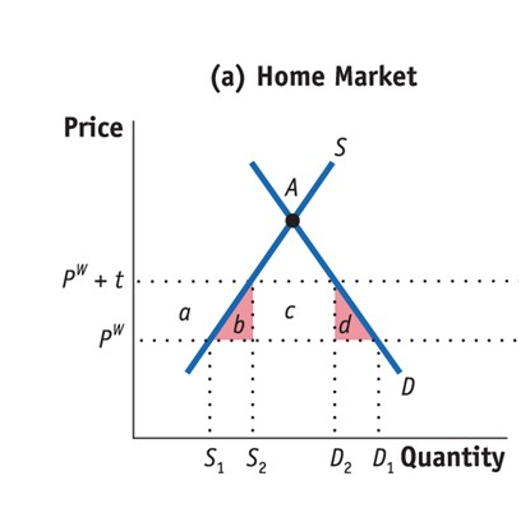
Explain deadweight loss here
B-triangel: production loss
The tariff makes producers produce more at higher costs(pw+t) instead of importing cheaper goods at the world price(pw).
D-traingel: consumption loss
The D-triangle shows the loss in consumer welfare because higher prices from the tariff reduce demand and satisfaction.
Differance between consumer and producer surplus
Consumer surplus: extra benefit that consumers get when they pay less than what they were willing to pay
Producer surplus: extra income producers get when they sell at a higher price than their miminal acceptable price(mc/supply curve)
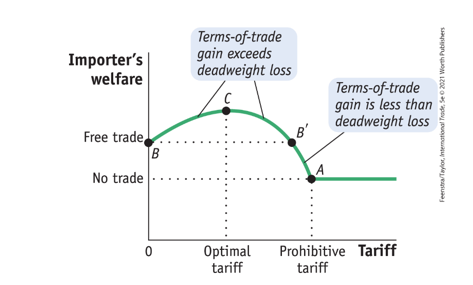
Optimal tarrif for large country
Ex* = elasiticty of foreign export supply
Inelastic export supply:
Foreign sellers cannot easily sell elsewhere.
They stay even if you raise tariffs.
→ Optimal tariff is high.
Elastic export supply:
Foreign sellers can easily sell elsewhere.
They leave if you raise tariffs.
→ Optimal tariff is low.
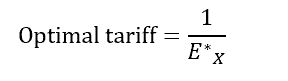
What does zero sum game mean
Zero-sum game means:
👉 One side’s gain = the other side’s loss.
👉 Total = 0 (no net change for the world).
How quotas can be given out?
Auction
Give to home firms
Rent seeking
Voluntary export restraint(VER)
Auction
The government sells import licenses to the hgihest bidders. Those who buy the licenses can import the limited quanitity.
The government earns money from selling them — that’s how it collects the quota rent indirectly.
While, the firm earns the extra profit(quota rent), by buying cheap aborad and selling expensive at home. Thanks to limited imports.
Giving the quota to home firms
The Home importers get the licenses for free.
They buy at world price (Pᵂ) and sell at higher domestic price (P₂).
They keep the quota rent (c) as profit.
Welfare loss: (b + d) — same as a tariff, since the rent stays inside the country.
Rent seeking
Firms waste money or effort trying to get licenses. By:
Bribing officials
Lobbying the government(firms try to influence government decision), or
Producing extra goods just to qualify, but this creates waste of resouces. They do this because government can give licenses based on past output to society.
That wasted money means the quota rent (c) is not real profit anymore — it’s lost.
“Voluntary” export restraint"
A Voluntary Export Restraint (VER) is when the exporting country agrees to limit how much it sells to the importing country.
Because exports are limited, the price in the importing country rises (from Pᵂ to P₂).
That higher price creates profit (area c) — but this time, the foreign exporters keep it.
Formula quota rent
The extra profit(per unit) that importers earn when the domestic price is higher than the world price because of an import quota. Who gets it depends rentseeking, auction, voluntary og just goes to home country,
QUOTA RENT FORMULA:
(P domestic under quota– P world) * Q import
Differance between boarder price and domestic price
Border price = the price foreign exporters receive. It is the price at the border, before the tariff is added.
Domestic price = the price the home consumers pay
Formula:
Domestic price = Boarder price + tarrif
Boarder price = domestic price - tarriff
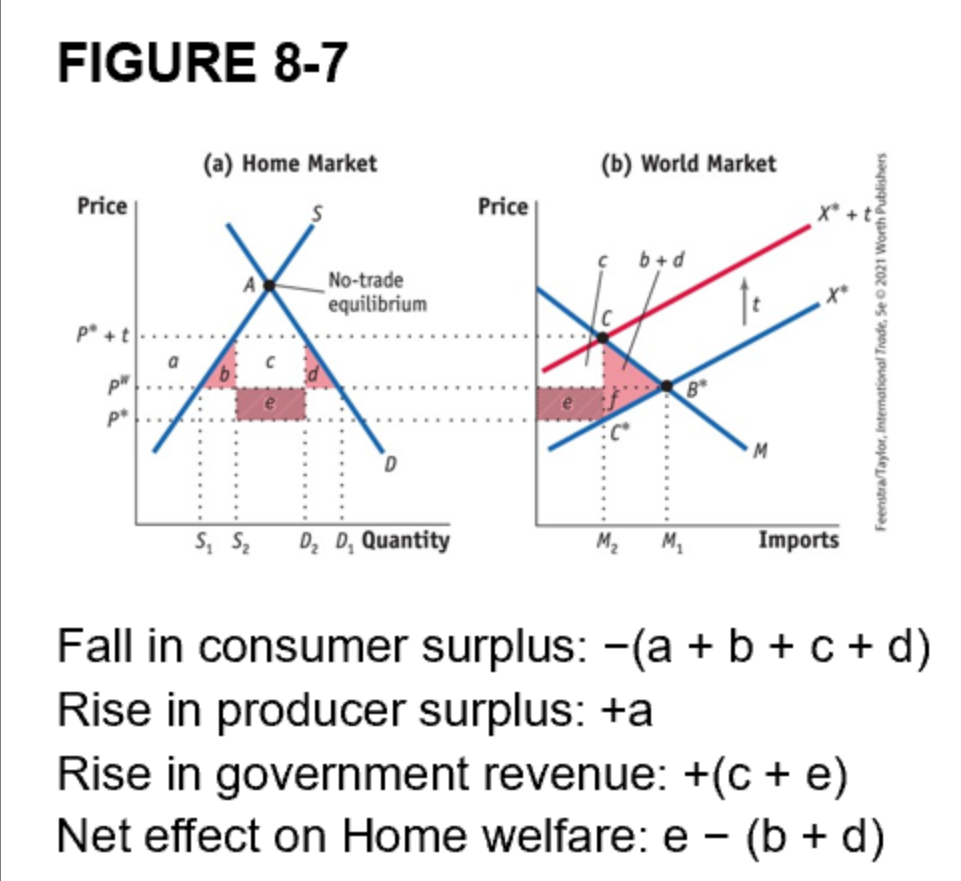
What are the benefits for a large country that imposes tarrif
The tariff helps the large Home country by making foreign sellers accept a lower price, and that’s the terms-of-trade improvement shown in Figure 8-7.
What is an import quota
Fixed limit on how much of a product can be imported.
Example: A country might allow only 10,000 cars from abroad per year — no more, no matter the price.