E1/2: Heart Sounds & EKG's
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
what occurs during systole?
ventricular contraction
what valves are OPEN during systole?
semilunar
aortic and pulmonary
what valves are CLOSED during systole?
AV
bicuspid and tricuspid
what occurs during diastole?
ventricular relaxation
what valves are OPEN during diastole?
AV
bicuspid and tricuspid
what valves are CLOSED during diastole?
semilunar
aortic and pulmonic
what is heart valve stenosis?
narrowing of the diameter of valve
what does a heat valve stenosis sound like?
louder, harsher, longer
what is heart valve regurgitation?
something block valve from fully closing
causing a backward movement of blood
what does a heart valve regurgitation sound like?
softer, longer
what heart sounds are normal?
S1 and S2
what sounds do S1 and S2 make?
S1: Lub
S2: Dub
when is S3 normal?
children, pregnancy, high level athletes
when do you hear S3?
early diastole
Lub Dub Dub
Is S4 heart sound ever normal?
no, always abnormal
what does S4 heart sound like? why does it occur?
Ta Lub Dub
decreased compliance of ventricles
How is a normal heart sound described?
short and soft
how is a stenotic heart sound described?
loud, long, harsh
When does a stenotic heart sound occur?
Sound is created when the valve is OPEN
If a pulmonic valve has stenosis, when will you hear the sound?
S1 / Systole
Semilunar valves are open
If a bicuspid valve has stenosis, when will you hear the sound?
S2 / Diastole
AV valves are open
how is a regurgitation heart sound described?
soft and longer
when does a regurgitation heart sound occur?
when the valves are closed
how is a ductus arteriosus heart sound decribed?
continuous through S1 and S2
Heart Sound Example:
a louder, longer first heart sound is present, then followed by a short, soft second sound. what condition is present
S1: abnormal → stenosis → SL Open
S2: normal
Aortic or pulmonic stenosis present
Heart Sound Example:
A short and soft first heart sound is present, then followed by a longer, softer heart sound. What condition is present
S1: Normal
S2: Abnormal → Regurgitation → SL Closed
Aortic or pulmonic regurgitation
Heart Sound Example:
A longer, softer first heart sound is present, then followed by a short and soft second heart sound. What condition is present?
S1: Abnormal → regurgitation → AV closed
S2: Normal
Bicuspid or tricuspid regurgitation
what rate does the SA node keep the heart pumping at?
60-100 bpm
what rate will the AV node keep the heart pumping at if the SA node is damaged?
40-60 bpm
what rate will the heart pump at if the SA and AV nodes are damages and via what mechanism?
<40 bpm
ventricular pacemaker rate AKA Hail Mary
Give an example of a mechanism that could “knock out” or inhibit the SA node from firing?
dilation or stretching of the right atrium
SA node is a nerve, and nerves do not like to be stretched or compressed!
an electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) assess what?
the electrical conductivity of the heart
what is a limitation to an ECG or EKG?
it only assess what is going on in the moment the test is ran, it does not predict future events
What is happening during the P wave
Atrial depolarization (contraction)
what occurs during the PR segment
slows down to get last of atrial blood into ventricle
allows for more ventricular filling and stretch for optimal contraction
what occurs during the PR interval?
combination of P wave and PR segment
“atrial kick” occurs
increased ventricular filling
how does the “atrial kick” during the PR interval affect ventricular output?
increased it by 20%
allowing for maximal filling and pre-stretch to ventricle for optimal contraction
what occurs during the QRS complex?
systole → ventricular depolarization (contraction)
Atrial repolarization
why cannot you not see atrial repolarization on a ECG or EKG?
it is hidden in the QRS complex due to the significant electrical activity caused by ventricular depolarization
What occurs during the ST segment?
happening after ventricular depolarization but before repolarization
relaxation?
what occurs during the T wave
Ventricular repolarization
What occurs during the QT interval?
total time ventricles are electrically active between depolarization and repolarization
what is the time duration for a small square on a EKG paper?
0.04 seconds
what is the time duration for a big square on a EKG paper?
0.20 seconds
how long is a normal time duration for a PR interval
0.12 - 0.2 seconds
within one big box
how long is a normal time duration for a QRS complex?
0.08 - 0.10 seconds
2-3 small boxes
what is the normal time duration for a QT interval?
less than 0.45 seconds
less than 2 big boxes
What is the R-R interval
Space between “R” point to “R” point
R point = peak of QRS complex
What does R-R interval Assess?
Heart Rhythm and Rate using EKG strip
how do you assess R-R interval using a note card?
Ensure even spacing between R points
When assessing R-R interval, what is considered regular?
may very 2-3 small boxes
breathing during test will cause slight variation
When assessing R-R interval, what is considered irregular?
more than 3 small boxes is consdiered irregular heart rate
Describe how to calculate heart rate using the 6 second strip method
Count R points and multiply by 10 for estimated HR
Can you assume all strips are 6 seconds?
NO BAD BAD BAD
it must specifically say 6 second strip
what is the “counting backwards” method to estimate HR?
Count number of big boxes in R-R interval then count backward using assigned numerical order for each box
what is the “counting backward” numerical order you have to follow exactly?
300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50
describe the counting large boxes method for HR estimation
Count how many big boxes are in an R-R interval
then divide 300 by number of big boxes
describe the counting small boxes method for HR estimation
count how many small boxes are in a R-R interval
then divid 1500 by number of small boxes
when analyzing a EKG strip, what are the main/big categories you check?
P waves
QRS complexs
T wave
PR interval
R-R interval
when anazlying a EKG strip’s P waves, what are you looking for?
Present
symmetrical
upright
single p wave before every QRS complex
when analyzing a EKG strip’s QRS complexes, what are you looking for?
present
time duration: 0.08 - 0.10 (<2.5 small boxes)
when analyzing a EKG strip’s T wave, what are you looking for?
Present
symmetrical
upright
when analyzing a EKG strip’s PR interval, what are you looking for?
interval time duration: 0.12 - 0.20 (3-5 small boxes)
when analyzing a EKG strip’s R-R interval, what are you looking for?
if its regular or irregular
determine using note card
If the QRS complex is more than 2.5 small boxes, what does that potentially mean?
bundle branch block
what is a normal rhythem called?
Sinus Rhythm
What is a rhythm called that has less than 60 bpm?
Sinus Bradycardia
what is a rhythem called that has more than 100 bpm?
sinus tachycardia
Define Ectopic Focus
a singular area of tissue in the heart that will randomly fire outside of normal conduction system
its trying to preserve contraction
Define Ectopic Foci
Multiple area’s of tissue in the heart that will randomly fire outside of normal conduction system
its trying to preserve contraction
When you see Multiple P-waves before QRS complexes, what rhythm is it?
Artrial Flutter
looks like saw blade
Ectopic Focus or Foci: Atrial Flutter
Ectopic Focus
When you see no P-waves before a QRS complex, what rhythm is it?
Atrial fibrillation
chicken scratch
Ectopic Focus or Foci: Atrial Fibrillaiton
Ectopic Foci
what did Dr Himes call atrial fibrillation that caused a frenzy?
irregularly irregular rate
What are patients at a higher risk for during Atrial Fibrillations?
blood clots due to the muscles “quaking”
When you see inconsistent QRS complex durations, what rhythm is that?
Pre-mature Ventricular Contractions (PVC’s)
wide and bizarre QRS complexes
>0.10 time duration
What causes PVC’s?
irritation coming from outside the conduction system
what is the result of a PVC?
lower cardiac output
When are PVC’s no concerning? when are they concerning?
Not concerning: Occasional, not consistent
Concerning: the more they occur, the more concerning, decrease in CO every time they occur
what can cause an occasional PVC?
Caffeine
What are PVC’s called when they look the same on a EKG strip?
Unifocal PVC
What is it called when you have PVC’s, but they all look different?
Multifocal PVC
What is it called when every other beat is a PVC?
Bigeminy
What is trigeminy rhythm?
normal QRS, normal QRS, PVC, repeat
What does it mean when you see a upside down QRS complex?
heart damage
bad bad bad
What can cause Ventricular Tachycardia?
3-4 PVCs in a row that all look the same
unifocal PVCs
Ectopic Focus or Foci: Ventricular tachycardia?
Ectopic foci ventricles
what makes Torsades de pointes different from tachycardia?
undulating waveform from 1 big box to 3 big boxes
amplitude of waveforms are all inconsistent
what does Ventricular fibrillation look like
inconsistent QRS complex, shape and form
what does ventricular fibrillation lead to?
asystole or flat line
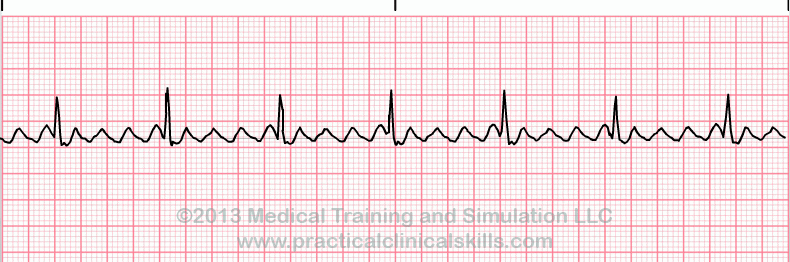
what is this heart rhythm?
Atrial Flutter
mutiple P waves
saw blade
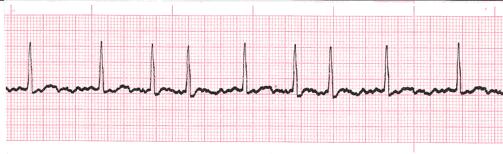
what is this heart rhythm?
Atrial Fibrillation
no P waves
chicken scratch
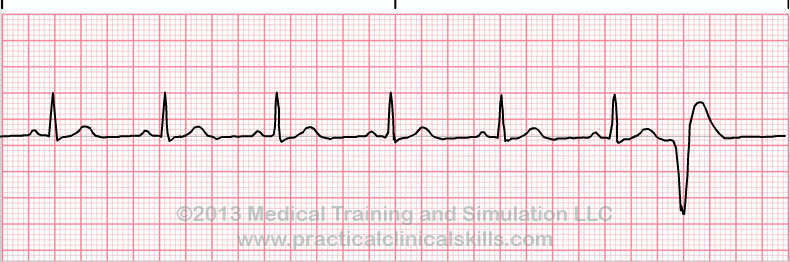
what is this heart rhythm?
pre-mature ventricular contraction PVC
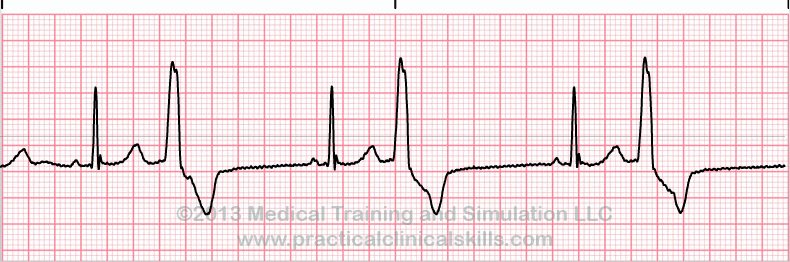
what is this heart rhythm?
Pre-mature ventricular contraction - Bigeminy
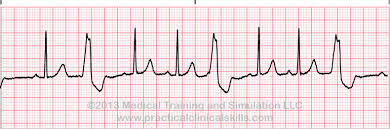
what is this heart rhythm?
pre mature ventricular contraction - Trigeminy
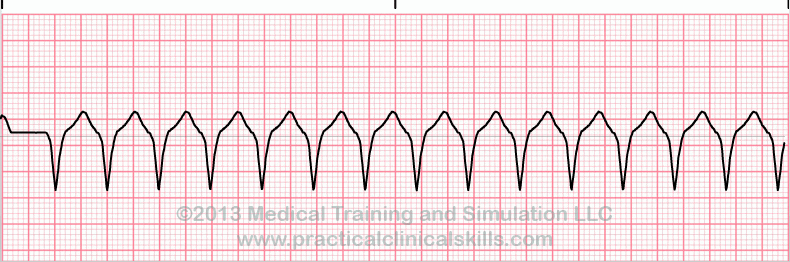
what is this heart rhythm?
ventricular tachycardia
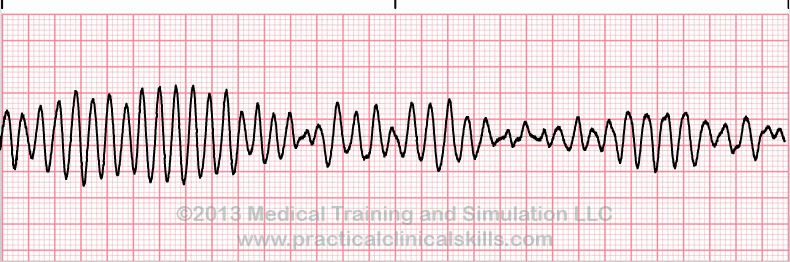
what is this heart rhythm?
Ventricular tachycardia
Torsades de pointes
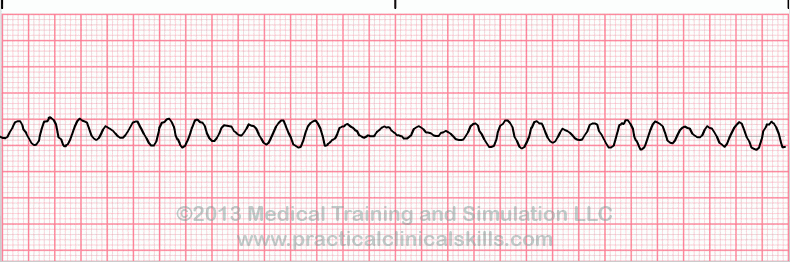
What is this heart rhythm?
Ventricular fibrillation
what is a junctional rhythm?
SA node not working