Chapter 6: Skeletal System
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
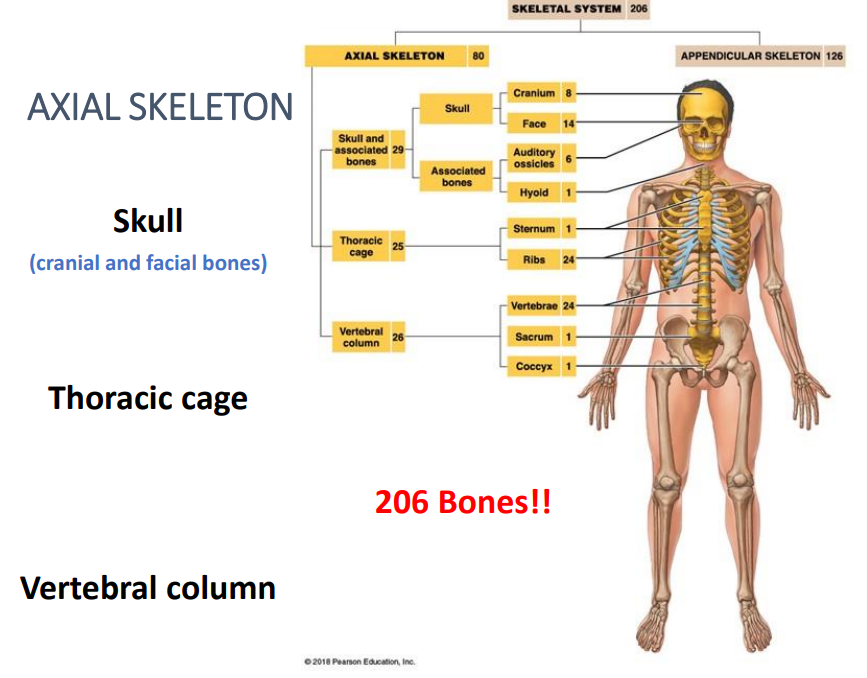
Axial Division
The bones of the skull, thorax, and vertebral column.
Axial Skeletons consist of ..
206 Bones!!
Skull (cranial and facial bones)
Thoracic cage
Vertebral column
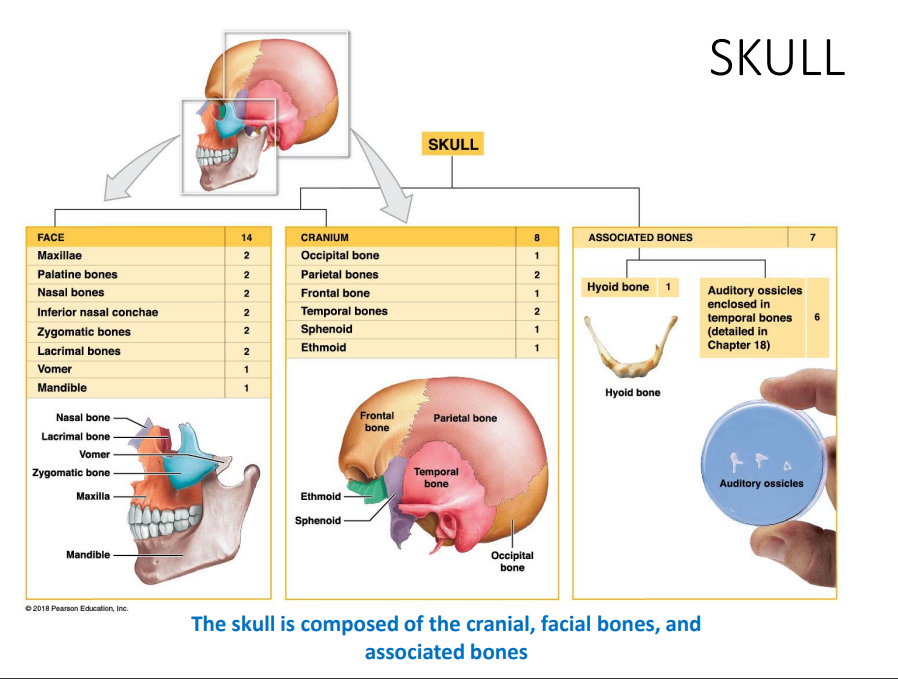
Skull is composed of…
cranial,
facial bones
associated bones
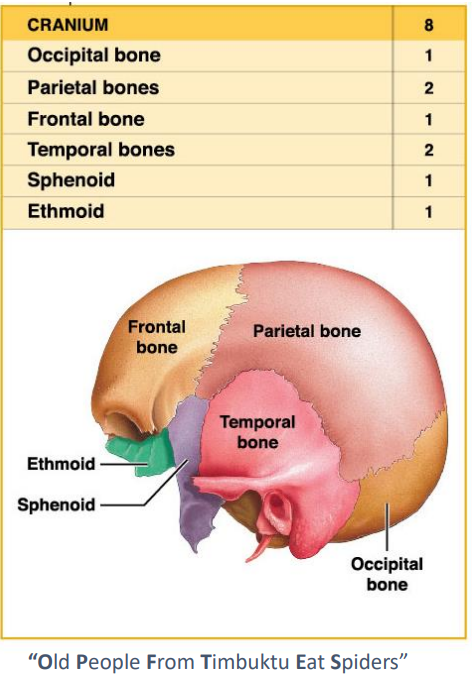
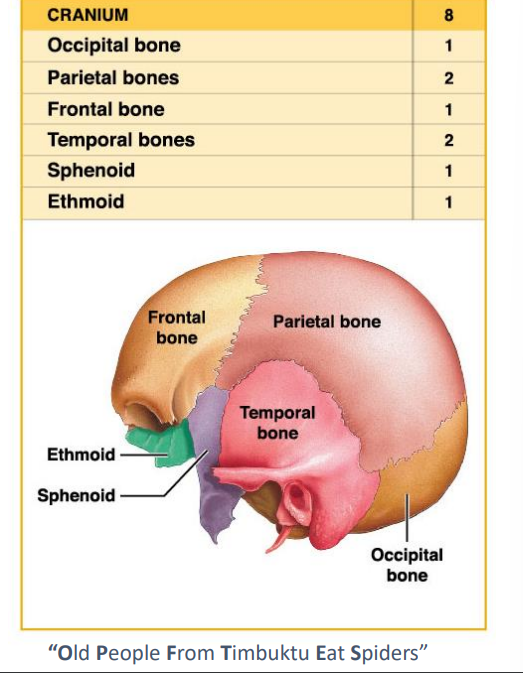
What is the Cranium compose of what bones?
Occipital
Parietal 2
Frontal
Temporal 2
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Cranial Bones encloses…
The cranial cavity-Fluid filled chamber that supports the brain.
Cranium provides an extensive area for muscle attachment
Movement of eyes, jaw and head.
What does the Cranium provide?
Extensive area for muscle attachment and movement of eyes, jaw and head.
What are Sutures?
Dense fibrous connective tissue joints between flat bones of the skull.
Fission of bone
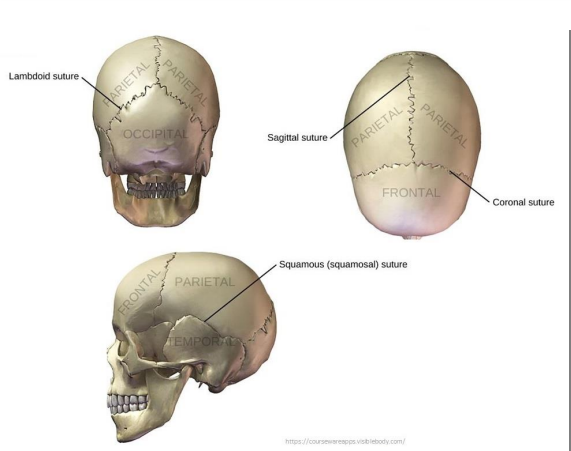
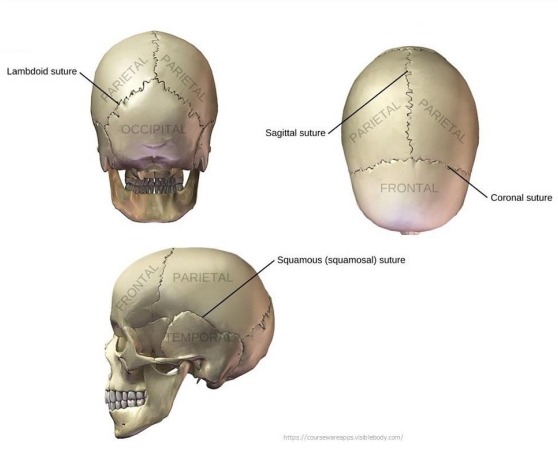
What are the 5 Sutures in the skull?
Lambdoid - occipital and parietal bones
Sagittal - between parietal bones
Coronal - Frontal to parietal bones
Squamous - Boundary between parietal and temporal
Frontonasal - Boundary between the nasal bone and the frontal bone
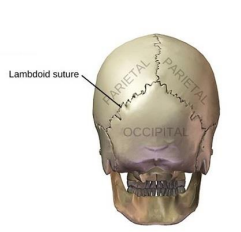
What does the lambdoid connect?
Occipital and parietal bones
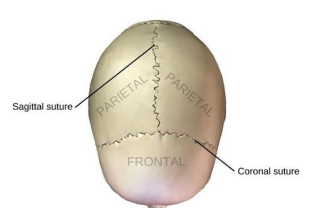
What does the sagittal suture connect?
Between parietal bones
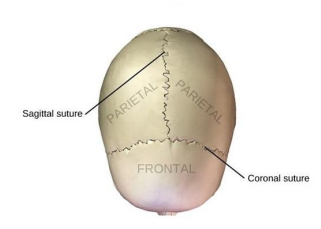
What does the Coronal suture connect?
Frontal to parietal bones
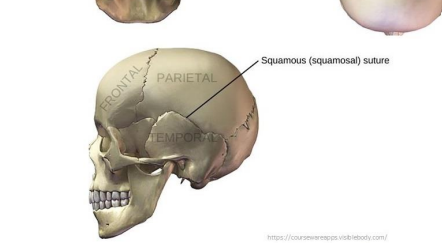
What does the Squamous suture connect?
Boundary between parietal and temporal
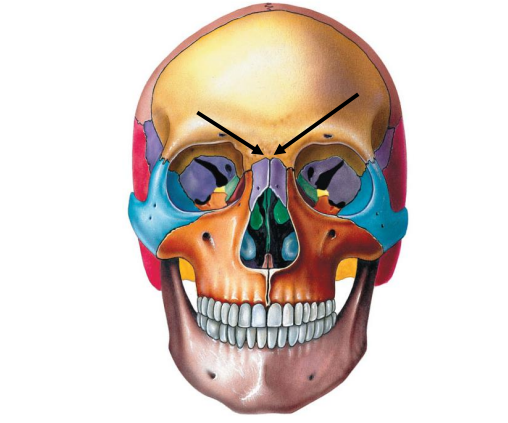
Where is the Frontonasal Suture located?
Boundary between the nasal bone and the frontal bone.
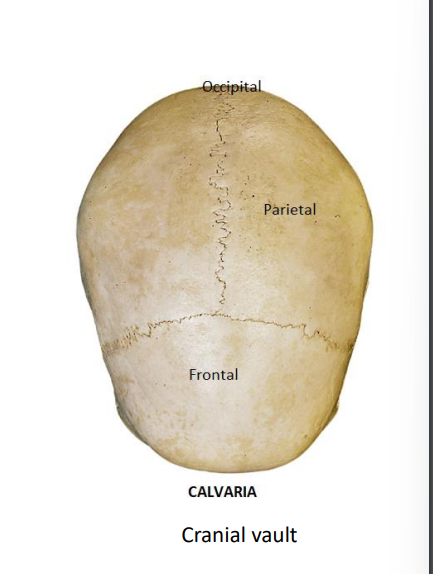
What is the calvaria/Cranial vault? What 3 bones does it consist of?
Cranial space that encases and protects the brain together with the base of the skull
Occipital
Parietal
Frontal
Occipital bone (1) - part of Posterior, lateral and inferior surface of the cranium
Hypoglossal Canal
Foramen magnum
Occipital condyle
Occipital bone
Superior nuchal line
External occipital protuberance
Inferior nuchal line External occipital crest
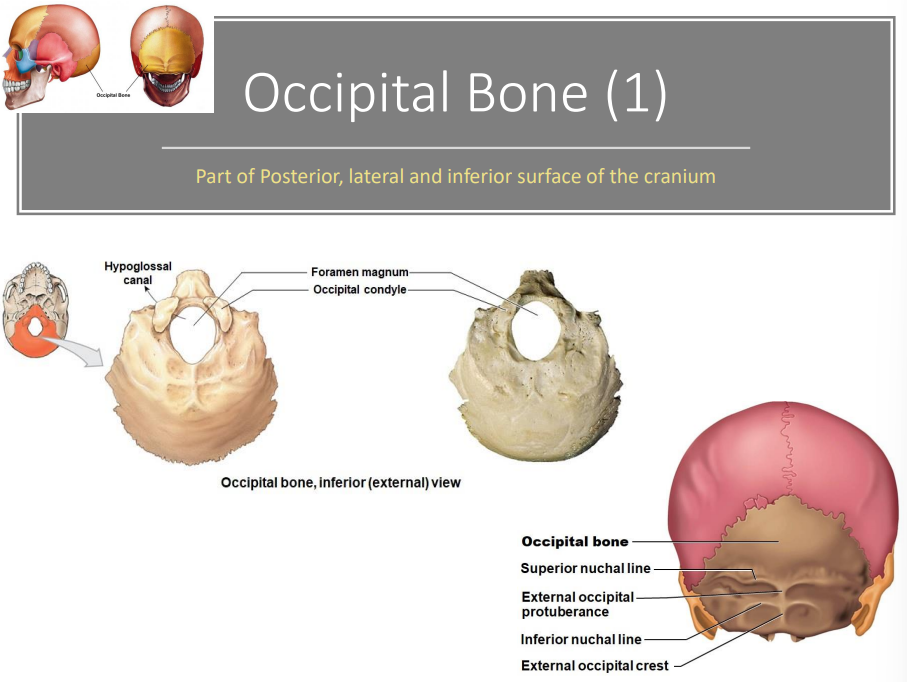
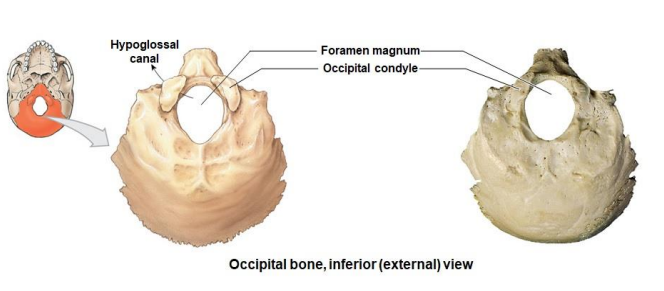
What are the 3 markings of the inferior view of the occipital bone? location?
Hypoglossal Canal
Foramen magnum
Occipital condyle
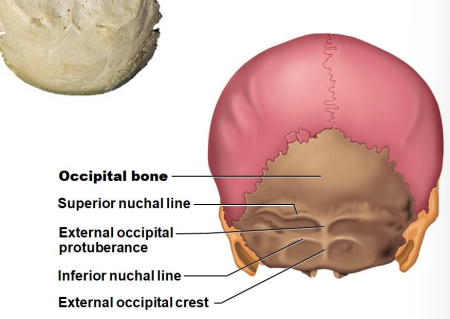
What are the 2 lines and 2 protuberances of the superior view of the occipital bone? location?
Superior nuchal line
External occipital protuberance
Inferior nuchal line
External occipital crest
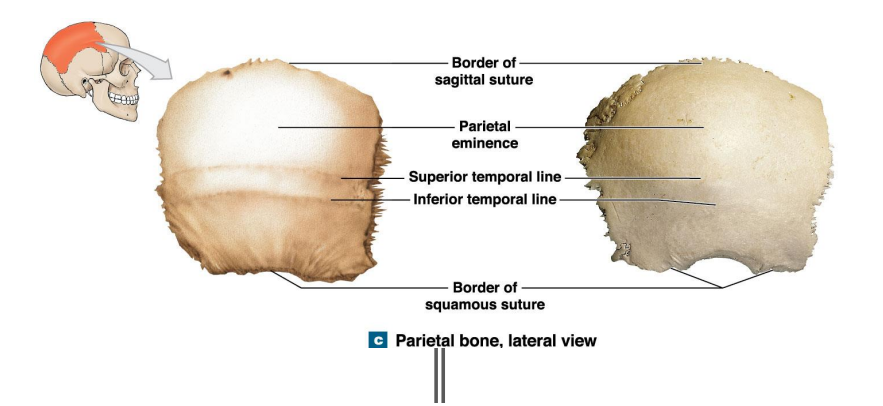
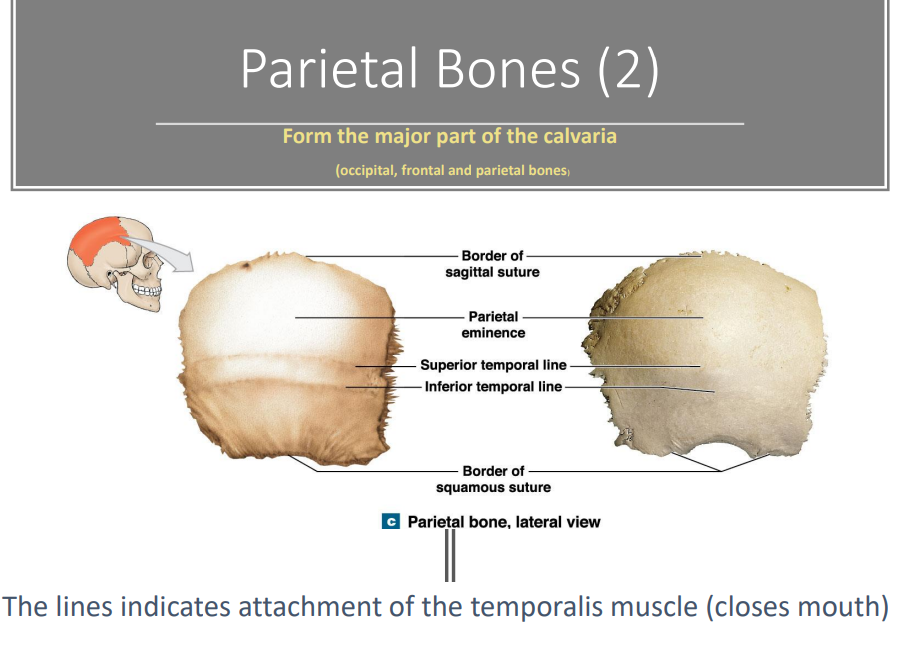
Parietal Bones overview. - form the major part of the calveria
What do the lines indicate?
Attachment of the temporalis muscles (closes mouth)
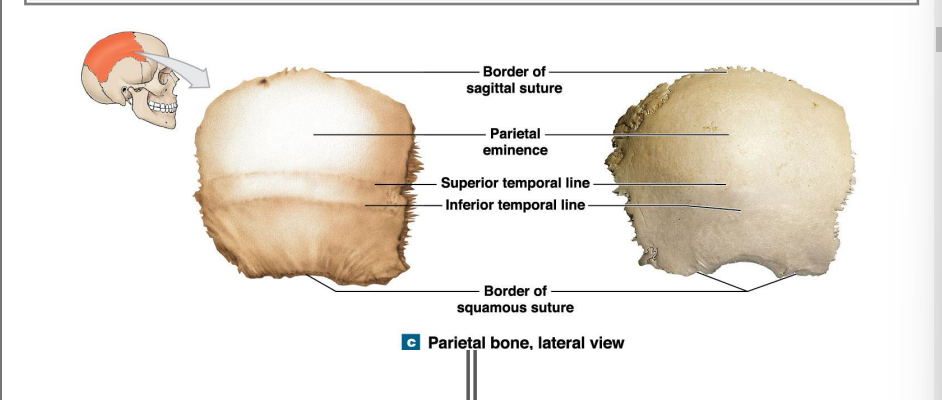
Where are the 2 lines, 2 borders, and markings of the parietal bone?
Border of sagittal suture
Parietal eminence
Superior temporal line
Inferior temporal line
Border of squamous suture
Where are the Anterior surface, lateral surface, and frontal part the frontal bone? (7)
Anterior view
Squamous Part
Frontal (metopic) suture
Superior temporal line
Supercillary Arch
Supra-orbital margin
Supra-orbital notch
Supra-orbital formen
What is the Anterior surface, Lateral surface, frontal part of the Frontal bone
Anterior surface: the squamous part.
Lateral surface: anterior continuous of the superior temporalis lines.
Frontal part: supraorbital margins
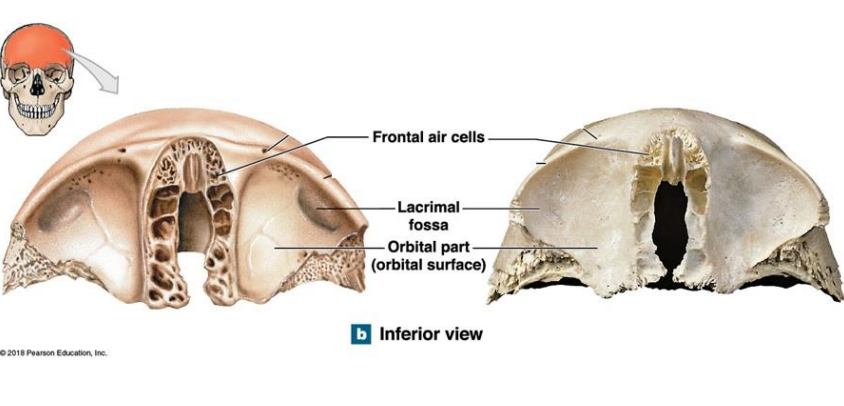
What is the Inferior view (orbital part) of the Frontal bone compose of?
What does the orbital surface of the Frontal bone form?
Frontal air cells
Lacrimal fossa - form lacrimal gland
Orbital part (orbital surface) - forms the roof of each orbit
Inferior surface - forms opening for blood vessels
Frontal Bone internal surface (posterior view) What are the 5 components? Location?
What is the purpose of the Frontal Bone?
Conforms the shape of the anterior potion of the brain
Margin of coronal suture
Squamous part
Frontal crest
Orbital part
Notch for ethmoid
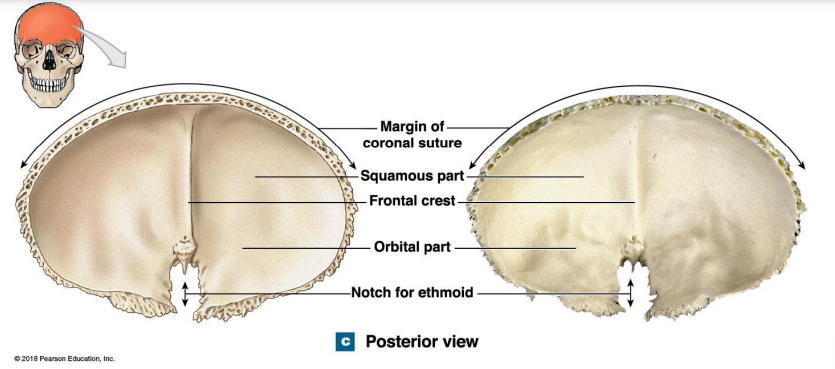
What does the frontal crest function?
Attachment of membranes that protect the brain
Temporal Articulate with? (5)
• Zygomatic
• Parietal
• Occipital
• Sphenoid
• Mandible
The inferior of the parietal bone function? (5)
Form an attachment area to muscles for jaw and head movement.
Form the articulation with the mandible
Form part of the lateral and inferior walls of the cranium
Form the zygomatic arches of the cheek
Protect organs of the internal ear
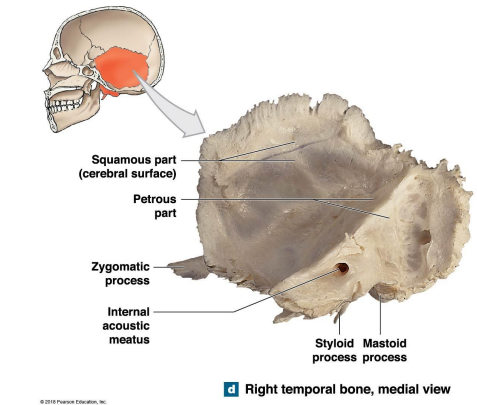
What are the three parts of the Temporal bones?
Squamous
Tympanic
Petrous - dominates medial surface of the temporal bone
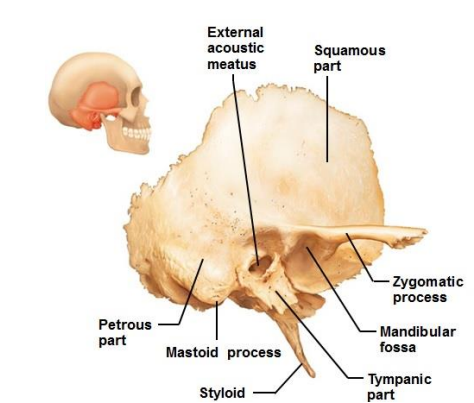
What are the 7 components of the petrous part of the temporal bones?
Mastoid process
Mandibular fossa
Styloid process
Stylomastoid
Carotid Canal
External acoustic meatus
Internal acoustic meatus
What are the Mastoid process and mandibular fossa location? What are their functions?
Mastoid process - Attachment site for muscles that rotate the head
Mandibular fossa - Depression → Mendible
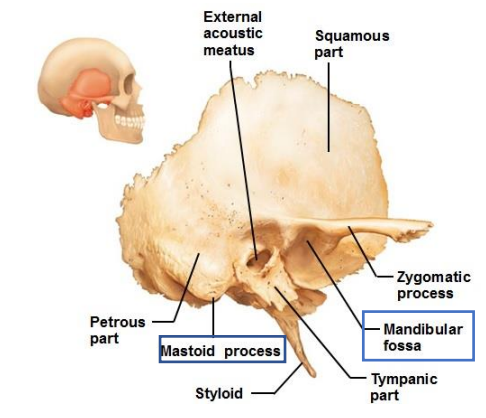
Where are the styloid process and stylomastoid foramen located? What are their functions?
Styloid process - Ligament that support the hyoid (muscles: tongue, pharynx, and larynx)
Stylomastoid foramen _ facial nerve
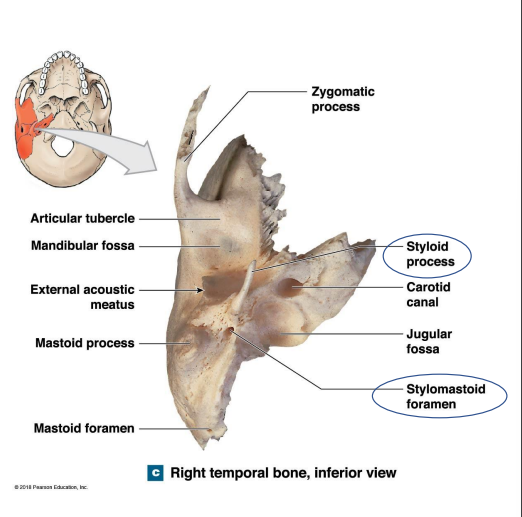
What are the location of the External acoustic meatus and Carotid canal of the petrous part of the temporal bone? What are the functions of each?
Carotid canal - Carotid artery (supplies blood to the brain)
External acoustic meatus - Passageway that ends at the eardrum (tympanic membrane)
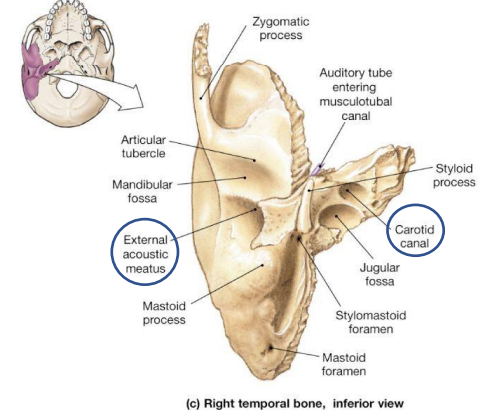
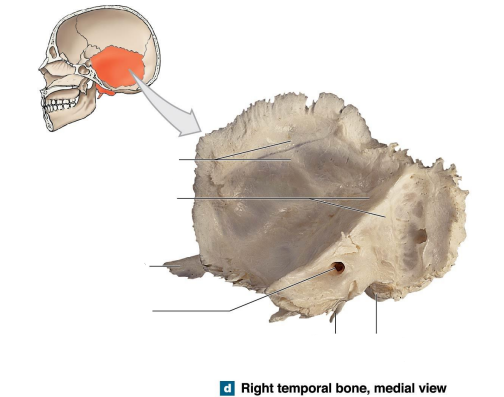
What is the location of the internal acoustic meatus, petrous part of the temporal bone? What is the function?
Internal acoustic meatus - carries blood vessels and nerves - internal ear
The Sphenoid unites all the … and … bones? and also articulates with them.
Cranial and Facial bones
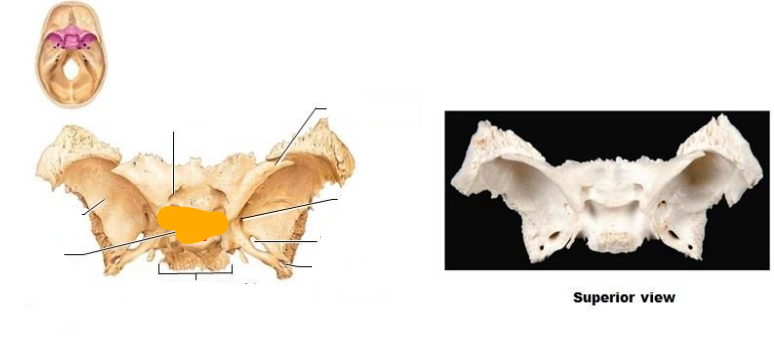
What is the sphenoid composed of? Superior view (9)?
Superior view:
Optic canal
Greater wing
Sella turcica
Hypophysial fossa
Body of sphenoid
Lesser wing
Foramen rotundum
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
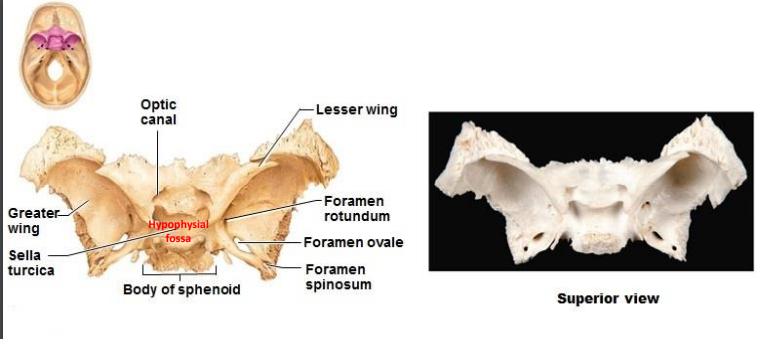
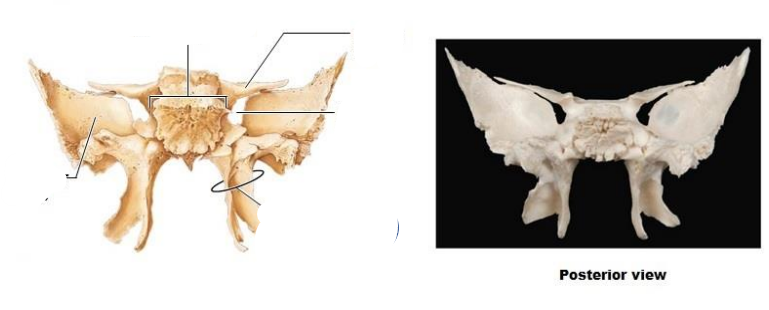
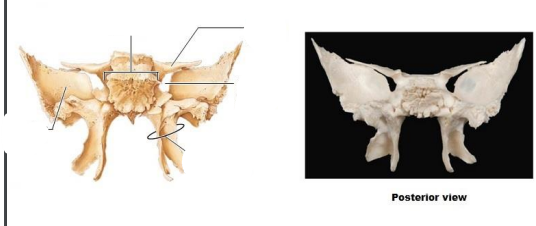
What is the sphenoid composed of? Posterior view (5)?
Greater wing
Lesser wing
Body of sphenoid
Superior orbital fissure
Pterygoid process
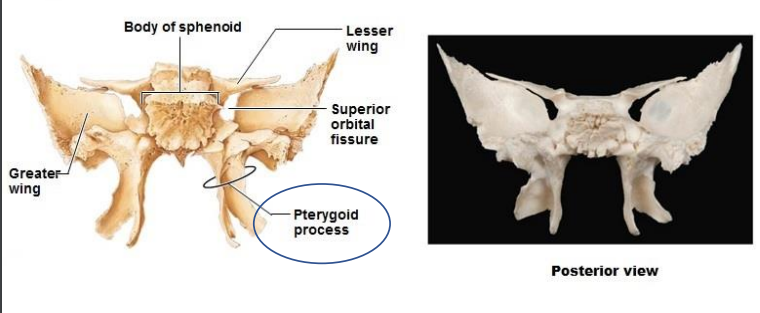
The Sphenoid is composed of what process? Function? (temporal bone)
Pterygoid processes - attachment site for muscles that move lower jaw and soft palate.
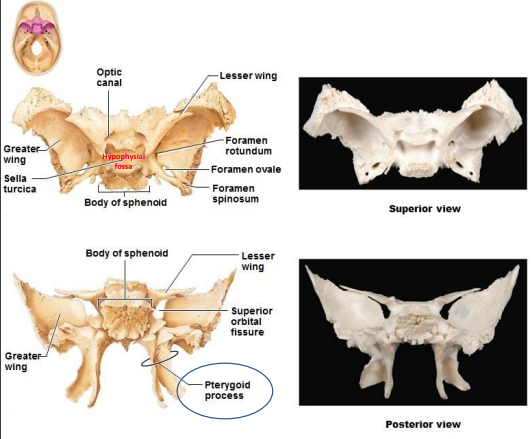
What is the Foramina and Sella turcica of the sphenoid of the temporal bone? functions
Foramina: Blood vessels and cranial nerves to orbits, face and jaw.
Sella turcica encloses Hypophysial fossa. Pituitary gland
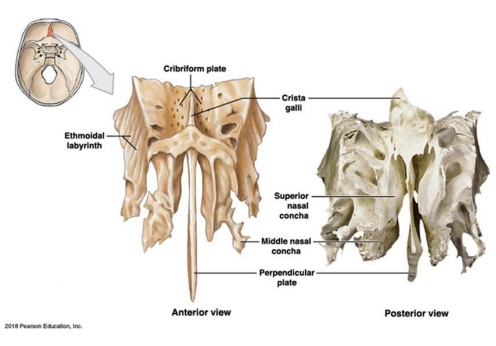
What are the Three parts of the Ethmoid? (temporal bone)
Cribriform plate
Ethmoidal labyrinth
Perpendicular plate (olfactory receptors)
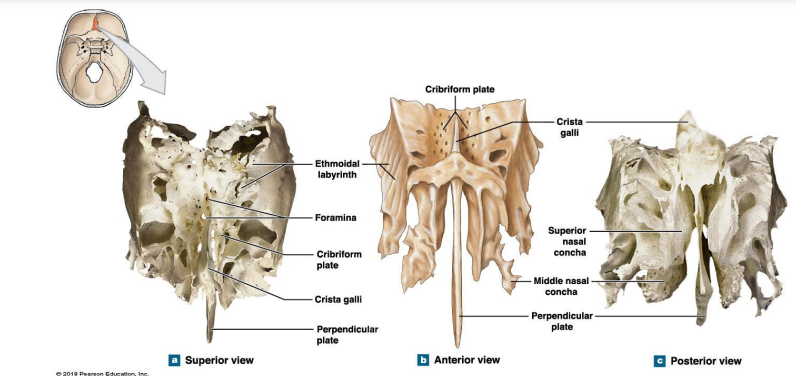
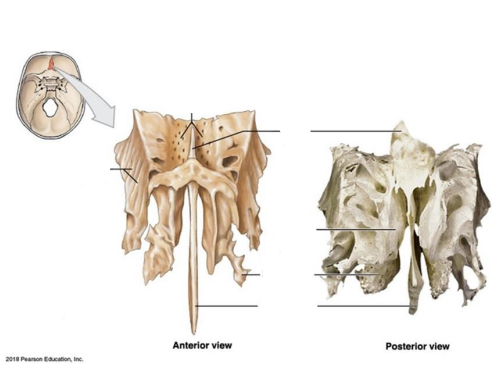
Where is the Cribriform plate, Ethmoidal labyrinth, Perpendicular plate located? what are their functions?
Extra - Where is the:
Crista galli
Superior nasal concha
Middle nasal concha
Cribriform plate: Foramina →olfactory nerves Separated by Crista Galli.
Ethmoidal labyrinth: Superior and middle nasal conchae.
Perpendicular plate: Thin plate of bone that form part of the nasal septum
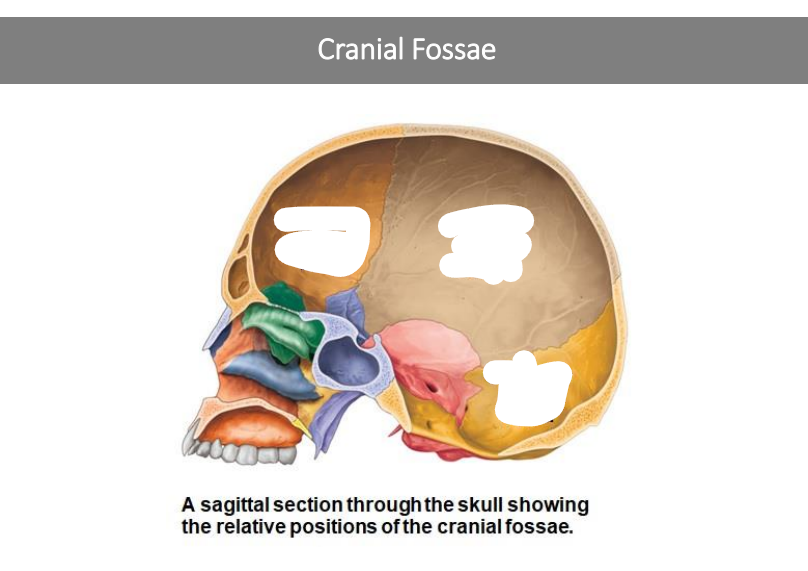
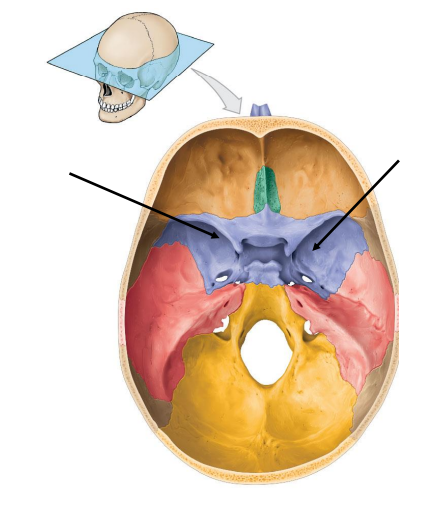
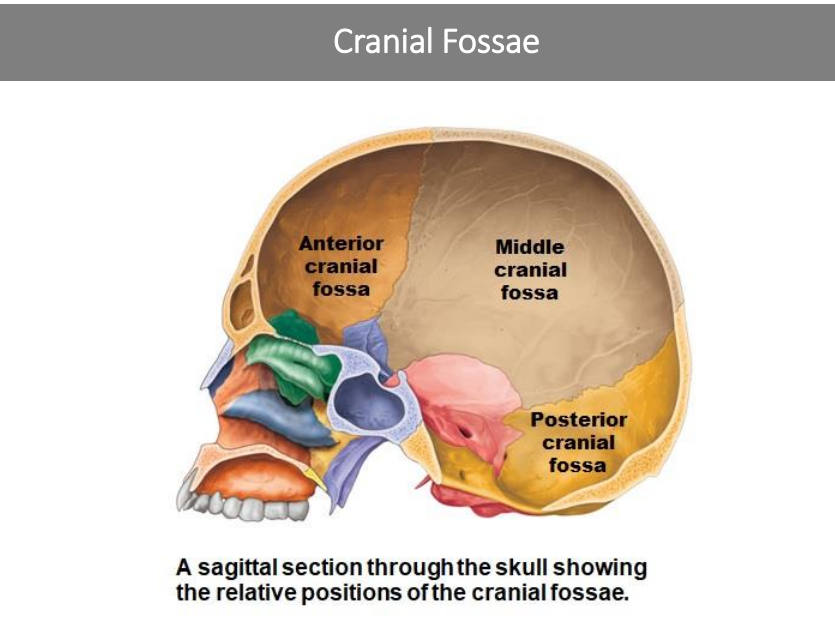
Cranial Fossae is composed of three sections. What are they?
Anterior cranial fossa
Middle Cranial fossa
Posterior Cranial fossa
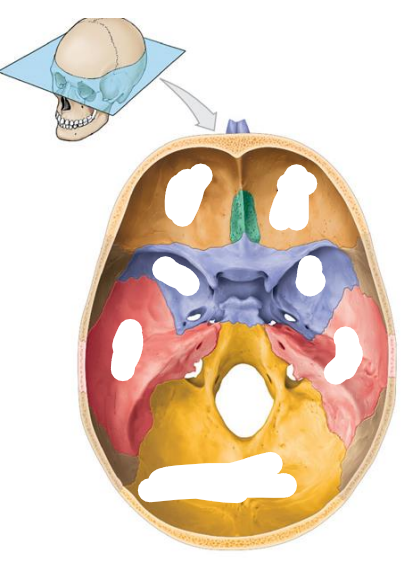
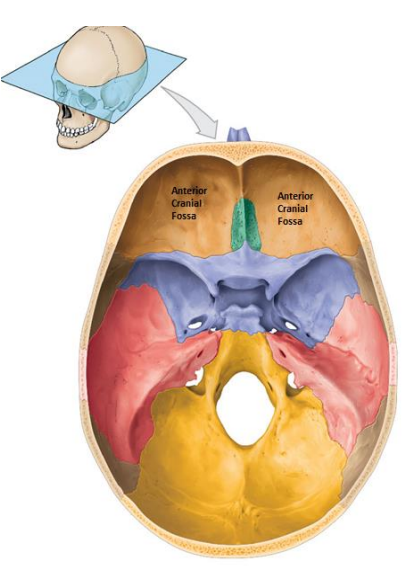
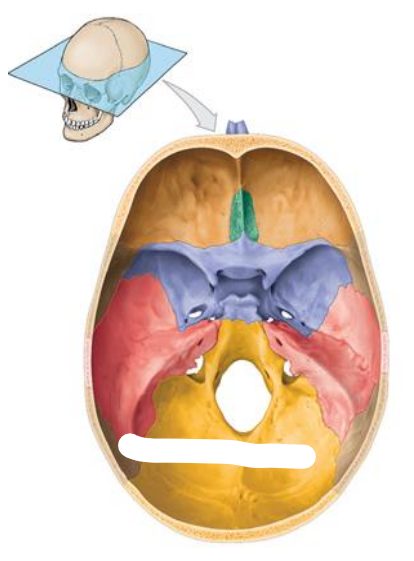
Location of the Anterior cranial fossa? What bones do they compose of? (3) What organs do they contain?
Bones:
Frontal bone
Ethmoid
Lesser wing of the sphenoid
Contains:
Frontal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
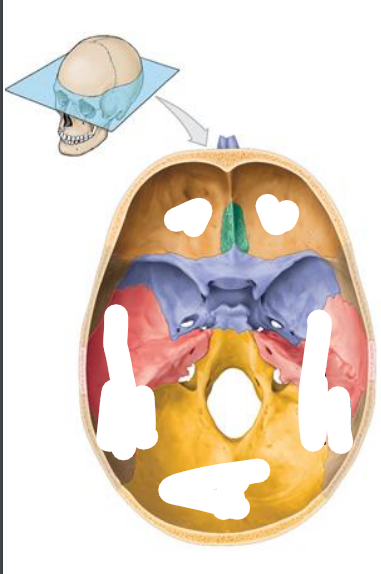
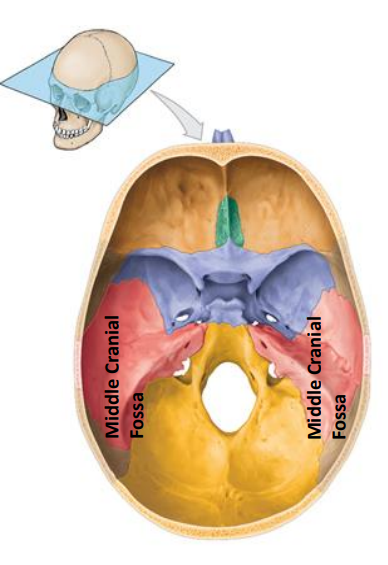
Location of the Middle cranial fossa? What bones do they compose of? (3) What organs do they contain?
Extends of the posterior nasal apertures to the petrous part of the temporal bones
Sphenoid
Temporal
Parietal bones
Contains:
Temporal lobe, diencephalon, brain stem
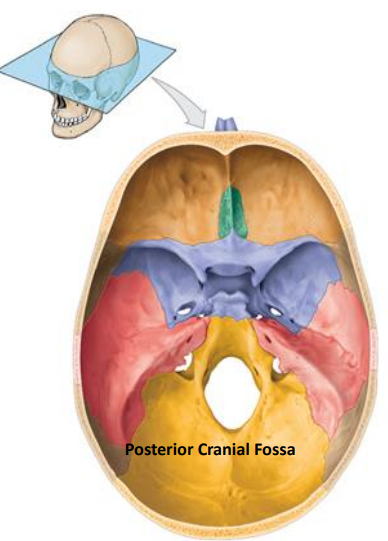
Location of the Posterior cranial fossa? What bones do they compose of? (3) What organs do they contain?
Extends from the petrous parts of the temporal bones to the posterior skull surface
Occipital
Part of Temporal
Part of Parietal
Contains
Occipital lobes
Cerebellum
Brain stem (pon and medulla)
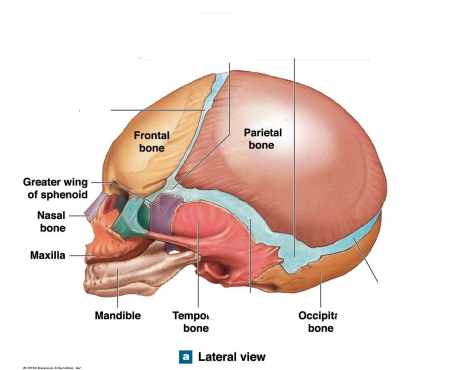
Skull of Infants, Children and Adults
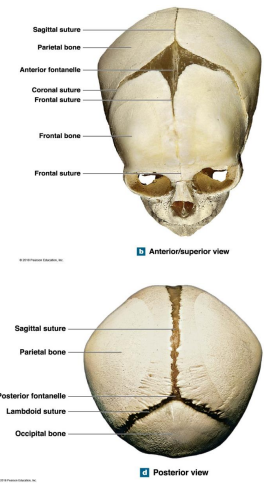
At birth areas of …. connect that cranial bone
The fibrous regions are called?
Connective tissue
Fontanelles
Before age 5, there is … of the cranium
Significant growth
After age 5, growth… and the cranial sutures…
growth stops and cranial sutures develop
Fontanelles allow?
Cranial expansion, and distortion at birth
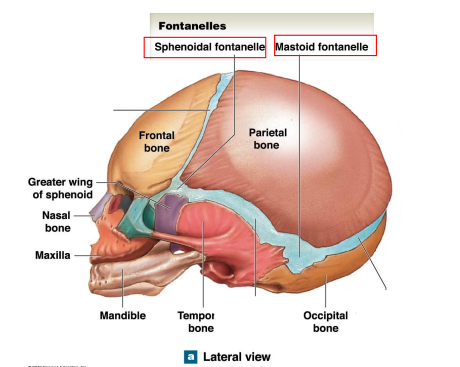
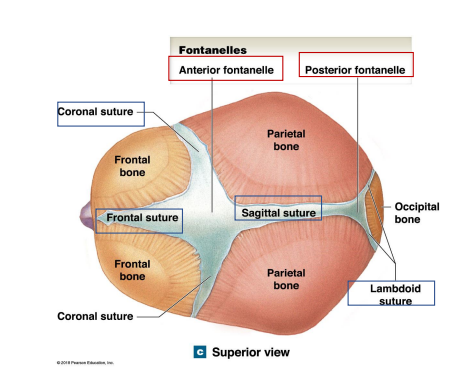
What are the 4 Fontanelles in children?
Anterior Fontanelle
Posterior Fontanelle
Sphenoidal Fontanelles
Mastoids Fontanelles
Locations the anterior fontanelle and posterior fontanelle? What are their junctions?
Anterior Fontanelle Junction: Frontal/coronal/sagittal sutures
Posterior Fontanelle Junction: Lambdoid/sagittal sutures
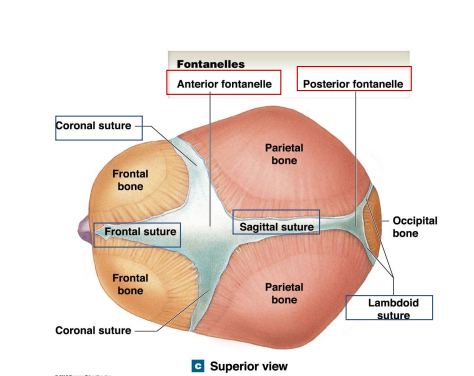
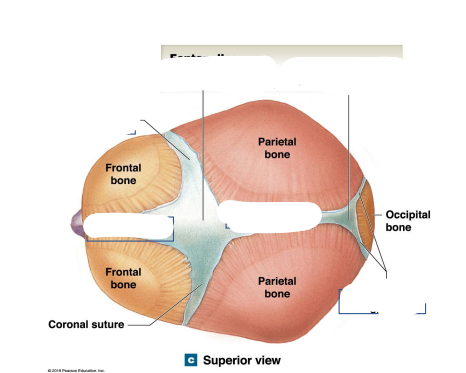
Locations the Sphenoidal fontanelle and Mastoid fontanelle? What are their junctions?
Sphenoidal Fontanelles Junction: Squamous/coronal sutures
Mastoid Fontanelles Junction: Lambdoid/squamous sutures
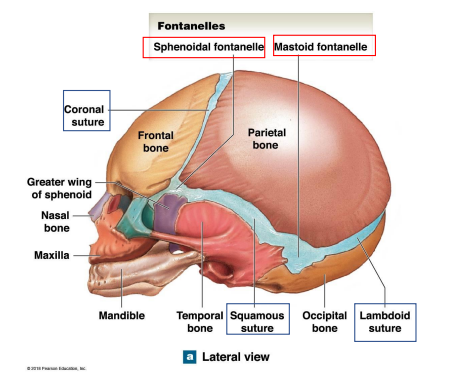
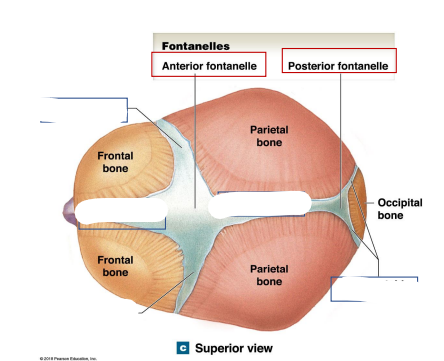
Where are the Coronal, frontal, sagittal, lambdoid sutures of the skull of infants?
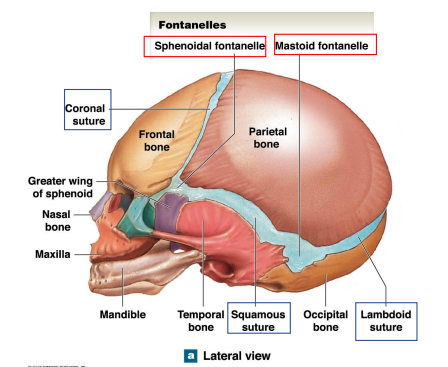
Where are the Coronal, squamous, lambdoid sutures of the skull of infants?