bio 20 ch6 - digestive system
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
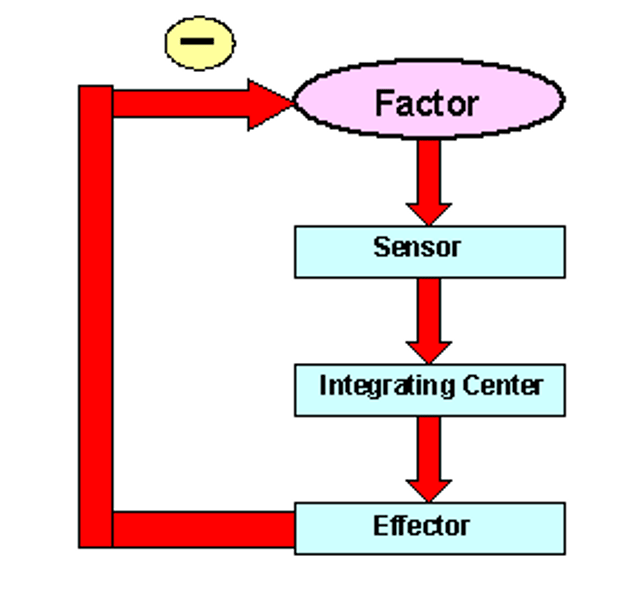
Negative Feedback
mechanism by which the body keeps a variable stable, maintaining homeostasis
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state
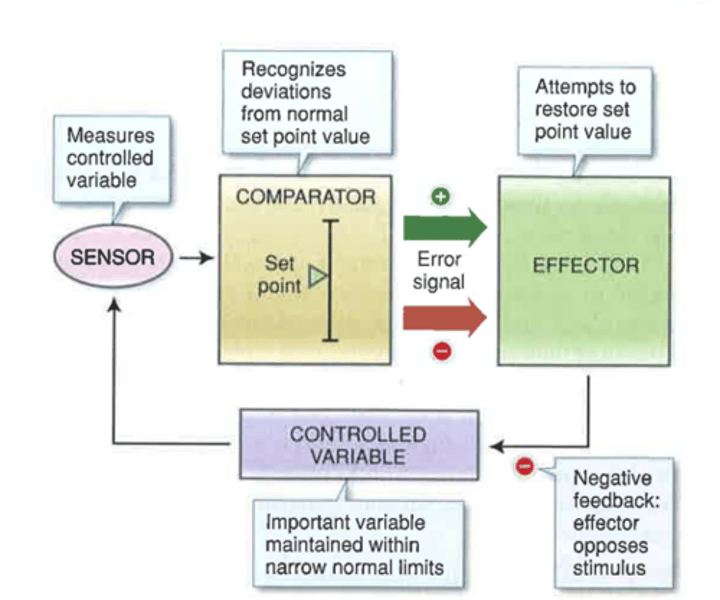
3 Components of Negative Feedback & Homeostasis
1) Sensor - detects change in internal environment
2) Effector - brings condition back to normal
3) Control center - activates effector based on sensory info
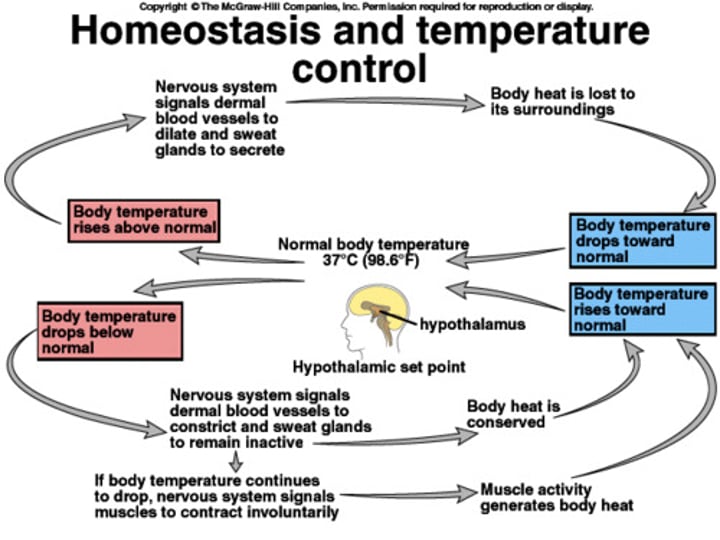
For example, if your body temperature is too high, a negative feedback loop will act to bring it back down towards the set point, or target value.
Working Out & Sweating...
Working out --> Excessive Heat production --> Sensor --> Control center (brain) --> Effector (dilated blood vessels, increase sweat) --> Heat released --> Cool down--> Back to sensor
The cycle repeats
Macromolecules
Foods can be grouped into 4 major macromolecules:
Macromolecules - large, complex organic molecules
1) Carbohydrates
2) Lipids
3) Proteins
4) Nucleic Acid

How are macromolecules assembled/disassembled?
2 processes:
1) Dehydration synthesis
2) Hydrolysis
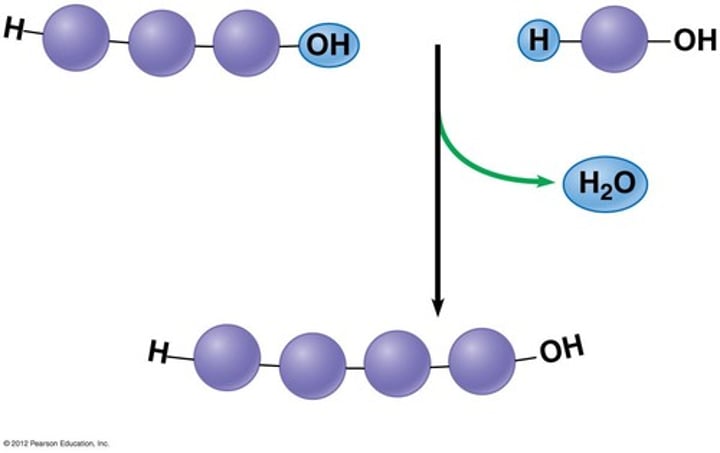
Dehydration Synthesis (pg207)
chemical reaction that BUILDS macromolecules
-2 smaller molecules are joined together by removing an H₂O (water) molecule
-Requires enzymes to speed up reaction
-"Anabolic" reaction (smaller --> larger)
A + B --> AB + H₂O
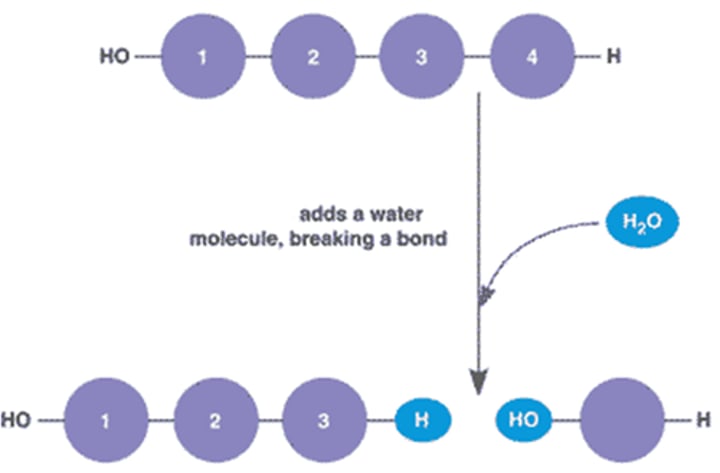
Hydrolysis (pg207)
-Large macromolecules BROKEN into smaller units by adding H₂O (water) molecules
-Requires enzymes
-"Catabolic" reaction (larger --> smaller)
AB + H₂O --> A + B
Carbohydrates
-Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (C:H:O) in a 1:2:1 ratio
-Produced by photosynthesis
-Main function: Energy storage
Two types:
1) Simple sugars
- a) monosaccharides
- b) disaccharides
2) Polysaccharides
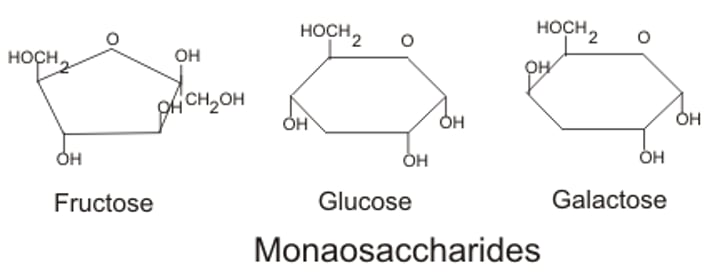
Monosaccharides
-Simple sugars (mono = 1)
-glucose, fructose, galactose - all C₆H₁₂O₆
-Can have 3-7 C's i.e. trioses (3 C) or pentoses (5 C) - ribose, deoxyribose
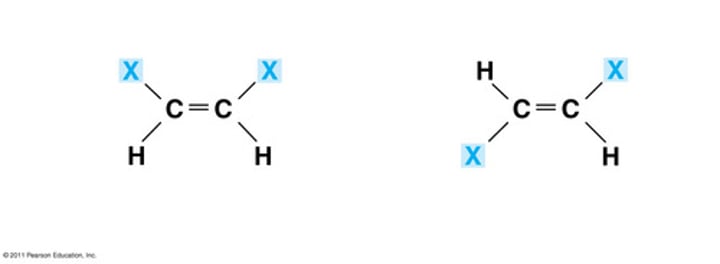
Isomers
same molecular formula, different structures, so different chemical properties
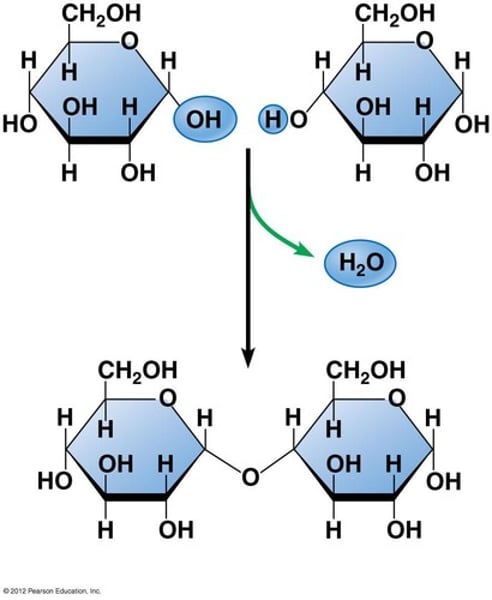
Disaccharides
-2 monosaccharides joined together by dehydration synthesis
3 important ones:
Malt sugar - 1) glucose + glucose --> maltose + H₂o
Table sugar - 2) glucose + fructose --> sucrose + H₂o
Milk sugar - 3) glucose + galactose --> lactose + H₂o
C₆H₁₂O₆ + C₆H₁₂O₆ --> C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ + H₂o
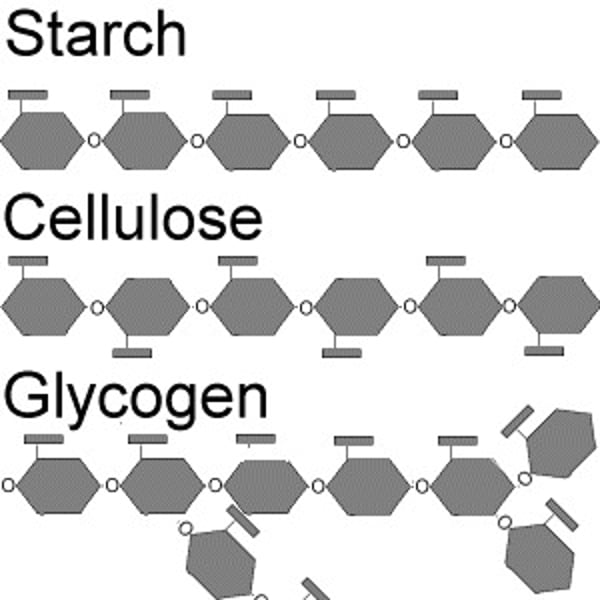
Polysaccharides
-many simple sugars combine. Ex. glycogen, starch, cellulose
a) Glycogen - storage form of carbs in ANIMALS
- in liver and muscle cells
- ~700 glucoses, branched
b) Starch - storage form of carbs in PLANTS
- 2 forms - amylose, amylopectin
- ~1100 glucoses
c) Cellulose - in plants
- insoluble "fibre," in plant cell walls
- ~3000 glucoses. We cannot digest it, lack enzymes
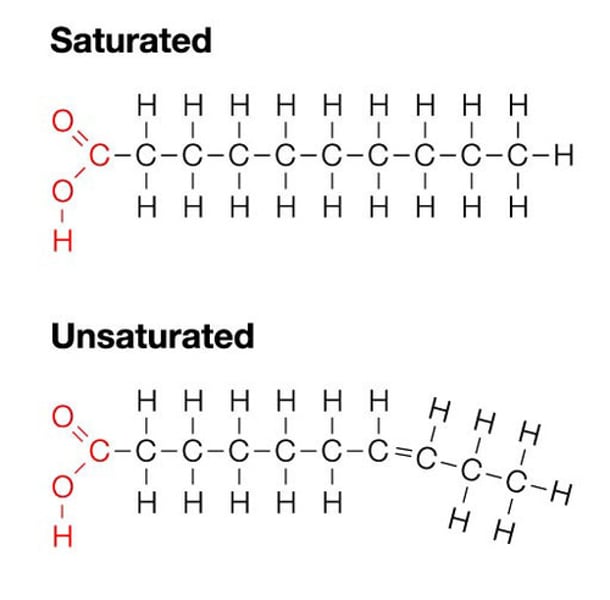
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
C-H-O compounds
- Have higher energy bonds than carbs
- Non polar --> equal sharing of electrons
Functions: membrane structure (phospholipids), insulation, energy storage after carbs, some hormones (steroids)
Lipids structure
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids = triglyceride (dehydration synthesis)
Fatty acids can be:
Saturated = only single C-C bonds, maximum amount of H's making it very stable
Unsaturated = has double (C=C) or triple bonds (C=C), easier to break down
Proteins
- C, H, O & N, S
- Produced by ribosomes
- Most abundant organic molecule
- Functions : structural - membrane, hormones, enzymes, muscle components
- Energy is NOT a main function
Protein structure
-Structure: made of chains of Amino Acids
-There are 20 amino acids
> 9 essential (must eat them)
> 11 non-essential (body produces)
-"Peptide bond" joins amino acids
-"Polypeptide" = proteins
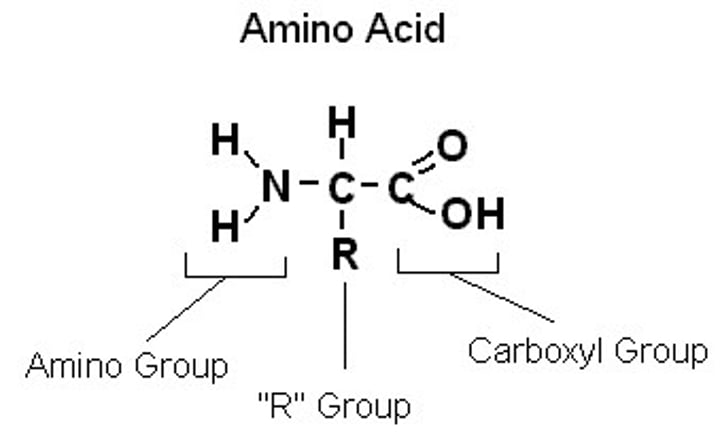
What makes one amino acid differ from another?
Amino acids differ from each other with respect to their side chains, which are referred to as R groups.
The R group for each of the amino acids will differ in structure, electrical charge, and polarity.
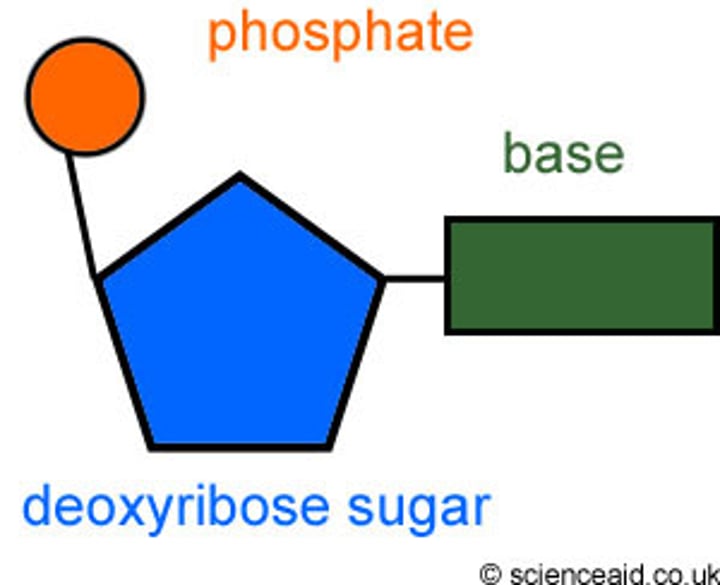
Nucleic Acids
-Mixtures of 4 nucleotides --> nitrogenous base, 5-C sugar and a phosphate group
-Form DNA and RNA
-Function: provides the instructions for protein synthesis, cell function/activity
Benedict's solution
tests for "reducing sugars" = monosaccharides & some disaccharides
blue ------> cloudy green, yellow, orange, red
(-) (+)

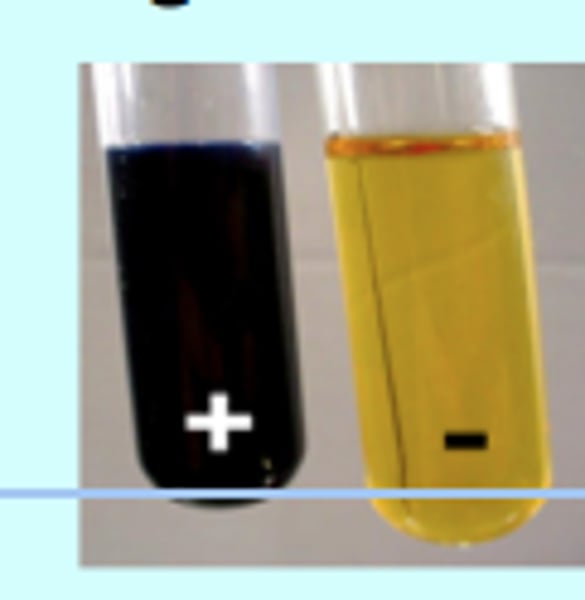
Iodine
tests for starch
yellow -----> blue/black
(-) (+)

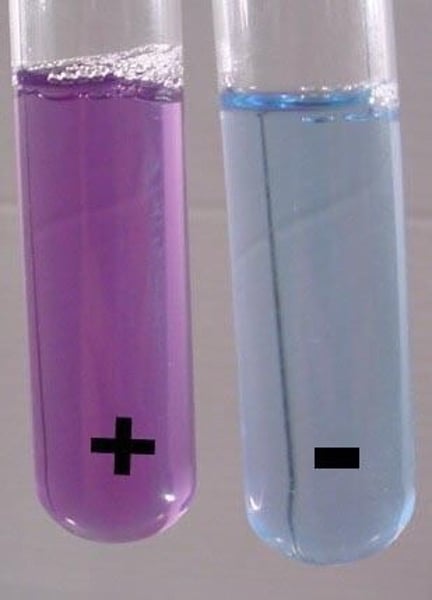
Biuret
tests for proteins, binds to peptide bonds
Blue ------> purple
(-) (+)

Sudan IV
tests for lipids
insoluble black powder ----> dissolves to make red
(-) (+)
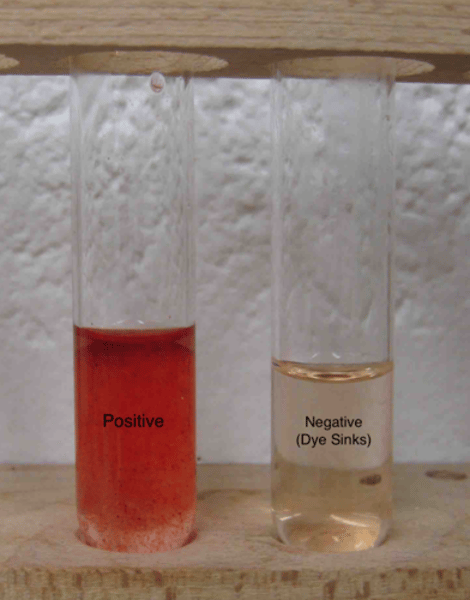

Translucence test
tests for lipids
no grease spot ----> grease spot
(-) (+)
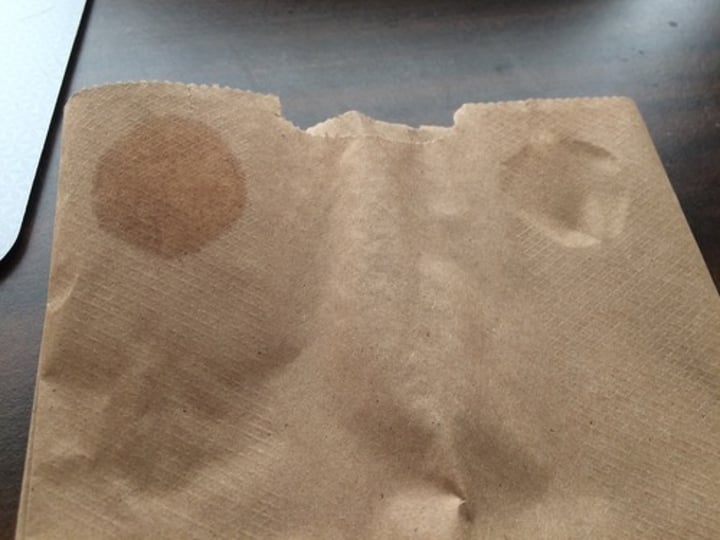

Summary
Dehydration Synthesis:
3 fatty acids + glycerol ---> triglyceride + H₂o
AA + AA ----> polypeptide + H₂o
glucose + fructose ----> sucrose + H₂o
Hydrolysis:
lipid + H₂o ---> 3 fatty acids + glycerol
protein + H₂o ----> AAs
sucrose + H₂o ----> glucose + fructose
Other substances
Vitamins - help chemical reactions in body
- only a small amount required
- our body can make a few
Can be:
Fat soluble - stored in fat tissue, too much can be toxic, Ex. Vit A, D, E, K
Water soluble - dissolve in water, not stored in body (washed out), Ex. Vit C and B Complex

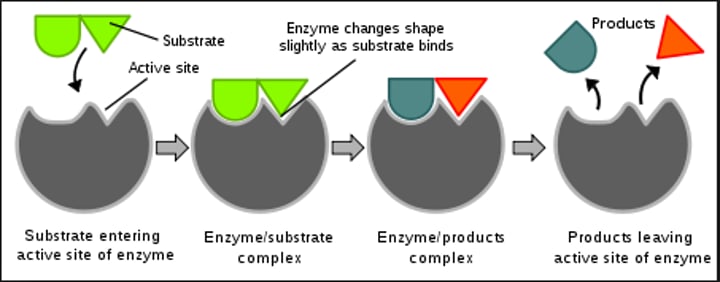
Enzymes
-Protein catalysts (speed up reaction)
-Lowers the activation energy (energy needed for reaction to occur), reactions occur faster
-Have specific "substrates" = molecules on which an enzyme works i.e. lactose --> lactose
-Have an active site on which substrate attaches
-Are reusable!! (do NOT get consumed)
-May be assisted by coenzymes (metals, vitamins) to help build substrates OR cofactors (organic materials from inorganic minerals)
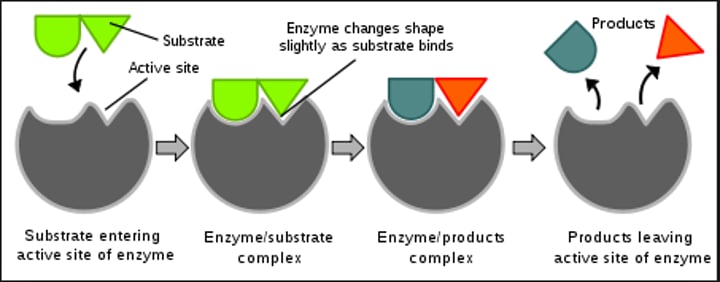
Substrate
-the reactants
-only the correct substrate will fit on the active site
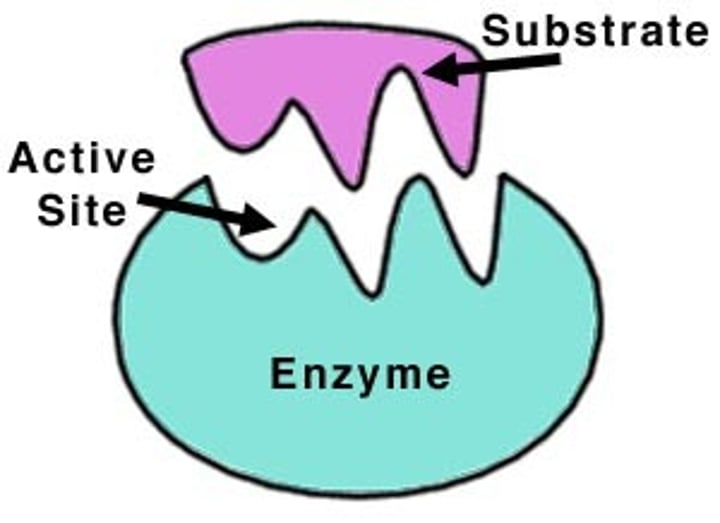
Active Site
-Site of highest surface area
-reaction occurs here
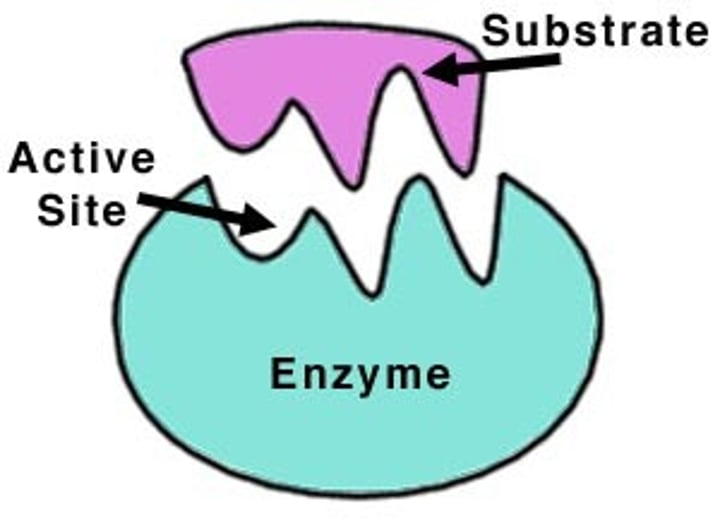
Enzyme
-the reactants achieve a lower activation energy as a result of the enzyme
-the enzyme is restored to its previous form after the reaction is complete
Factors that affect Reaction Rate
1) Temperature
2) pH
3) Substrate concentration
4) Competitive inhibitors
5) Non-competitive inhibitors
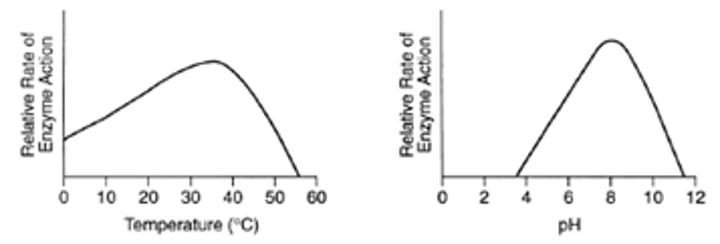
Temperature & pH
-have optimums --> high temps and extreme pH causes denaturation/coagulation
Substrate Concentration
-reactions occur faster with more substrate until max speed and concentration is reached
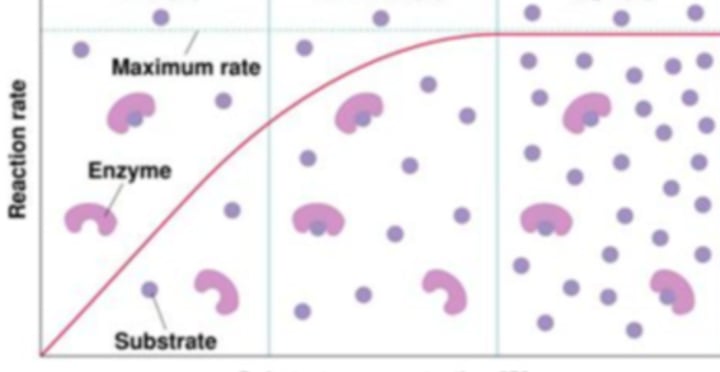
Competitive inhibitors
-molecules compete with substrate for active sites on enzyme, prevents substrate from attaching
*competes/interferes with substrate
e.g. - poisons, penicillin, cyanide

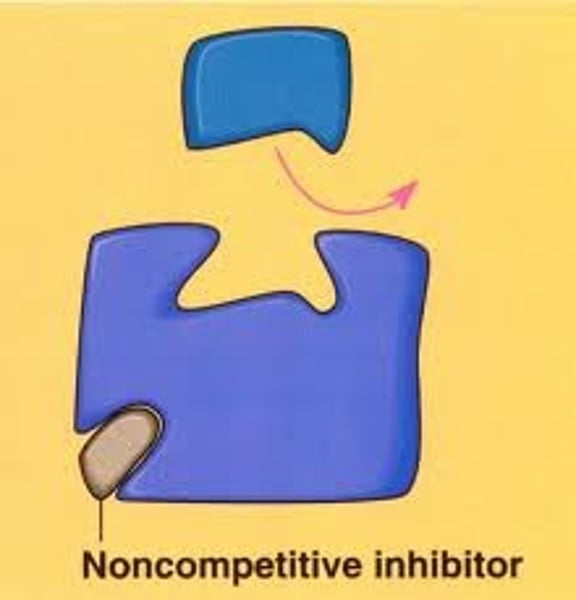
Non-competitive inhibitors
-inhibitor does NOT attach on active site, but somewhere else called the "allosteric site", changing the shape of the enzyme... preventing the enzyme from working with substrate!
An inhibitor binds to a secondary site on the enzyme. This changes the shape of the active site and and prevents the substrate from binding
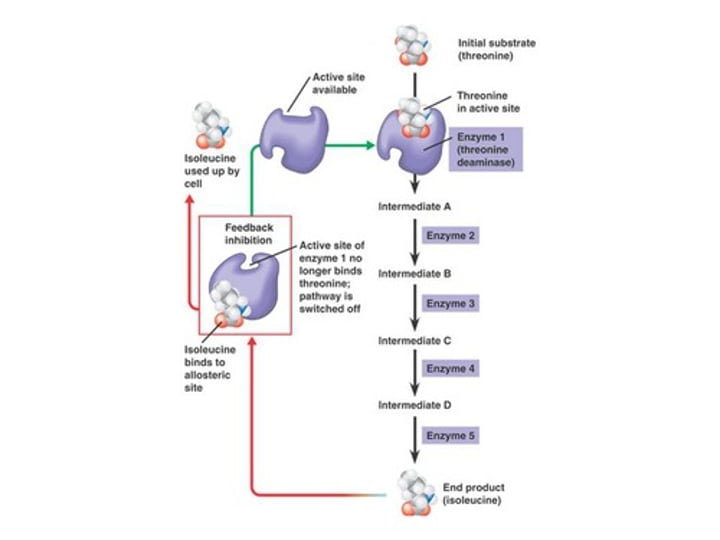
In biological systems, the competitive inhibitor is often the...
end product of the enzymatic reaction. As more end product is created and binds to the active site, enzyme activity is inhibited. That's a negative feedback loop!
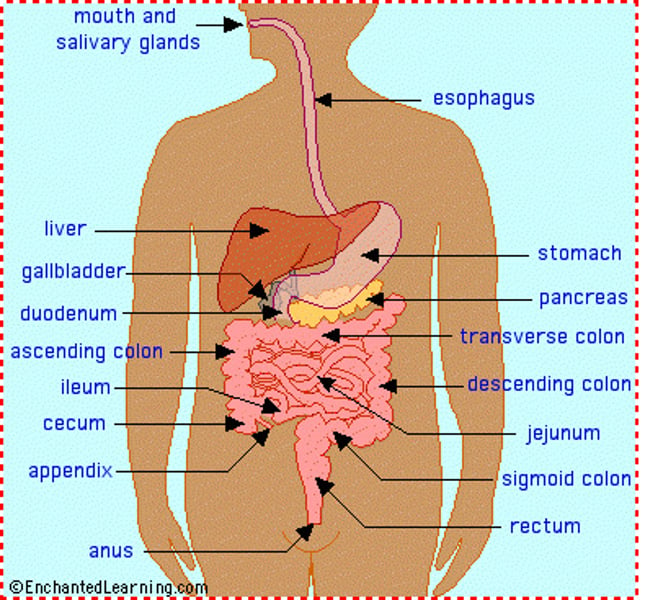
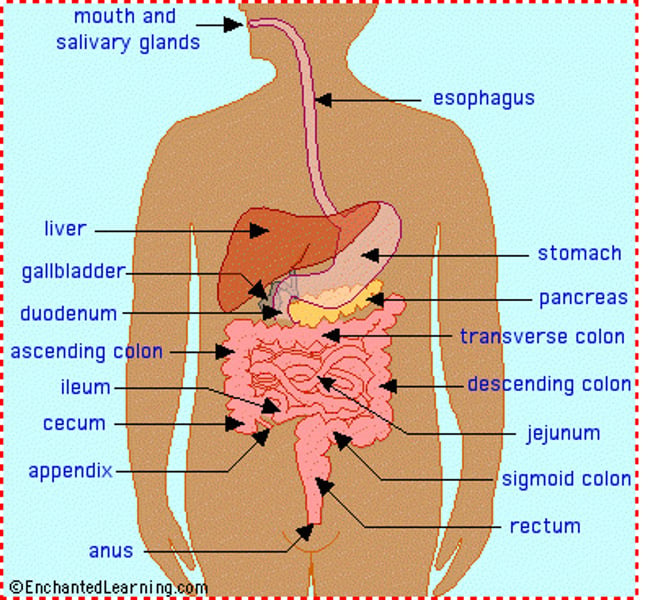
The Digestive System
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells. A series of hollow organs joined in long twisting tube from the mouth to anus.
Ingestion
Intake of food
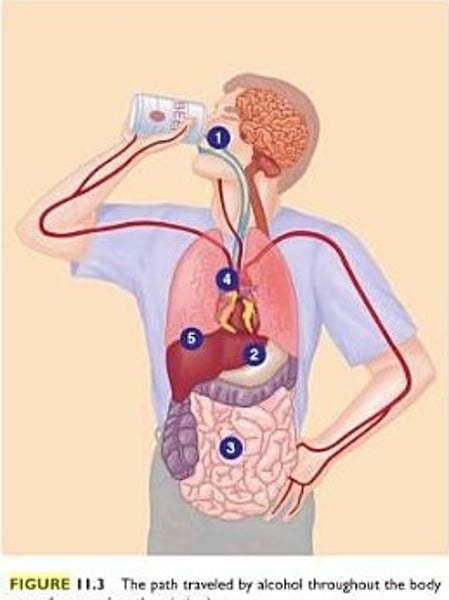
Digestion
Breakdown of food substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used
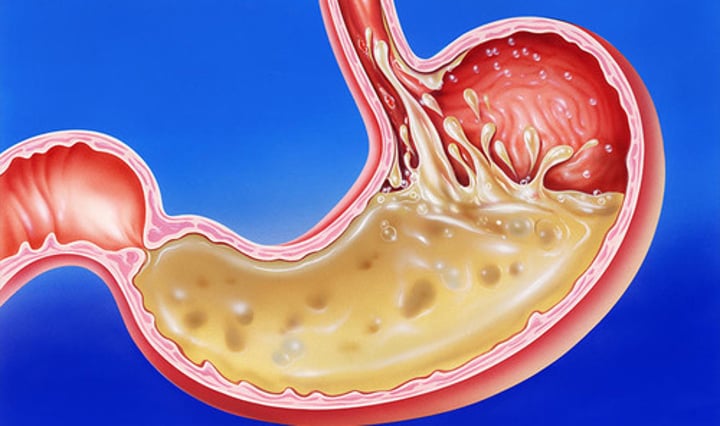
2 ways of Digestion
1) Physical breakdown - ex. teeth
2) Chemical breakdown - ex. saliva
Egestion
removal of undigested waste

Mouth & Esophagus
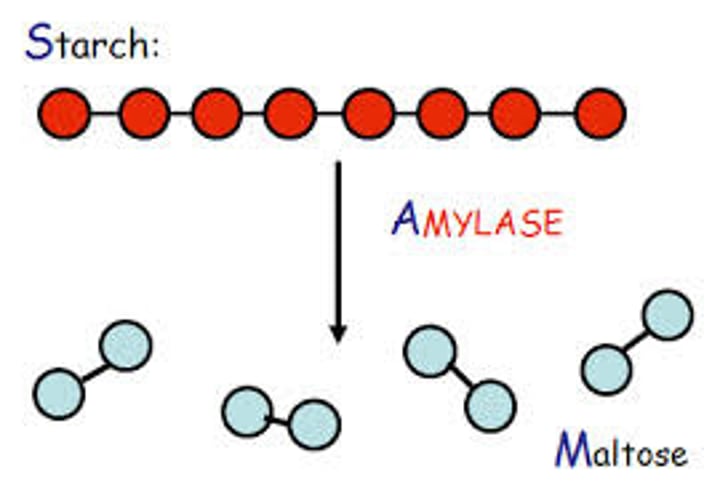
first step in digestion, with mechanical breakdown and breakdown of carbs with alpha-amylase
pH in mouth is
7
Tongue
-mechanical (physical) digestion
-Contains taste buds
-Mixes food into a bolus
Teeth
-mechanical (physical) digestion
-Creates greater surface area for enzymatic reactions
Salivary glands
-Chemical digestion
-produces saliva (~1L/day)
-Moistens food
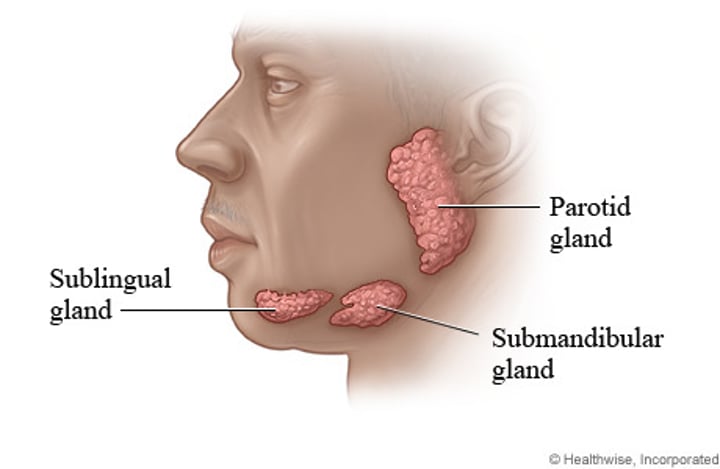
Salivary amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch into disaccharides
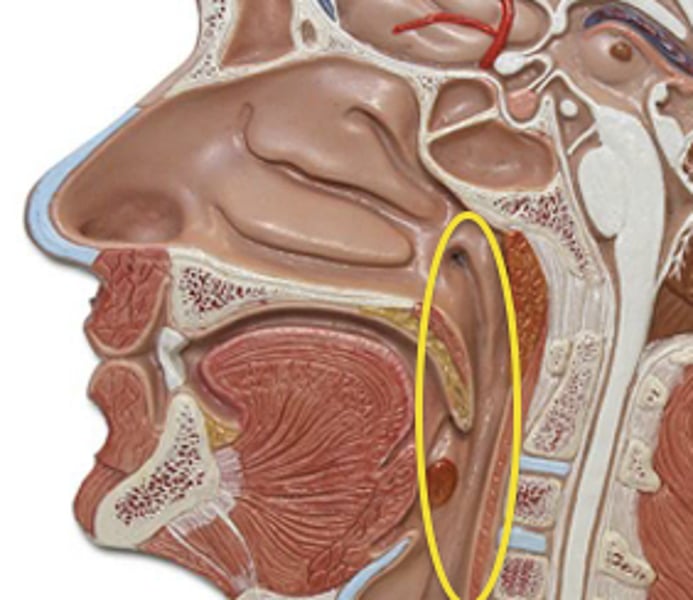
Pharynx
-where nasal and oral cavities meet
-last place where digestion is voluntarily
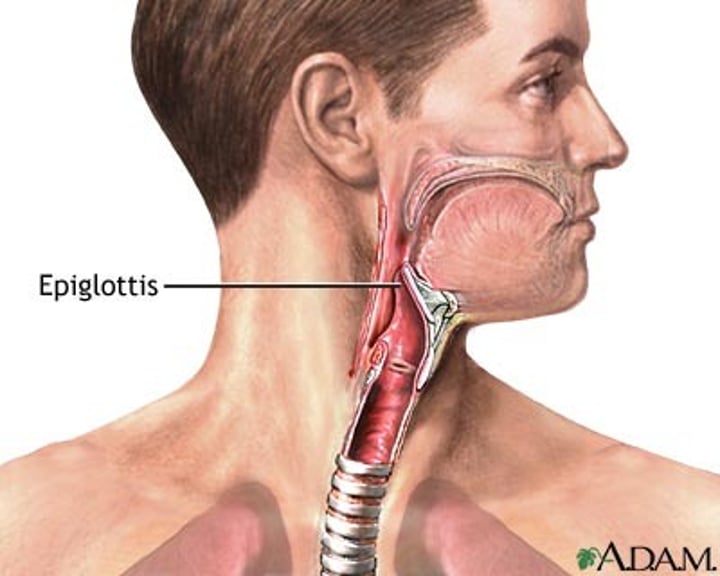
Epiglottis
-a flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Uvula
-covers the sinuses
-pH around 7
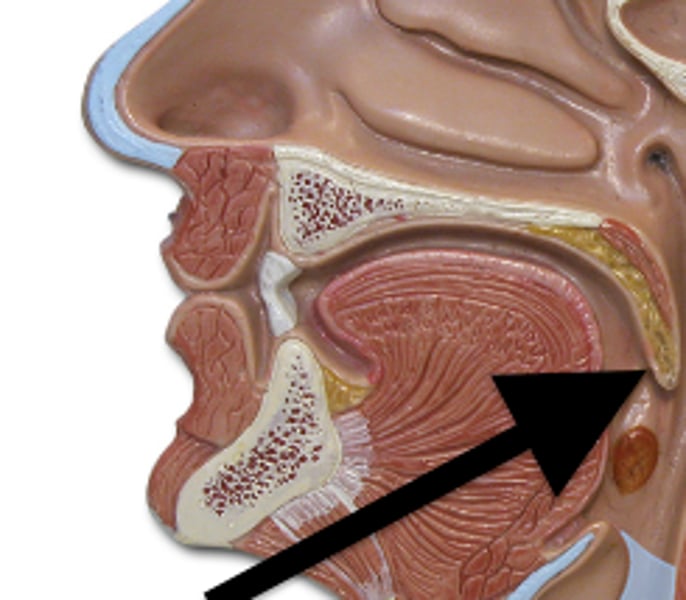
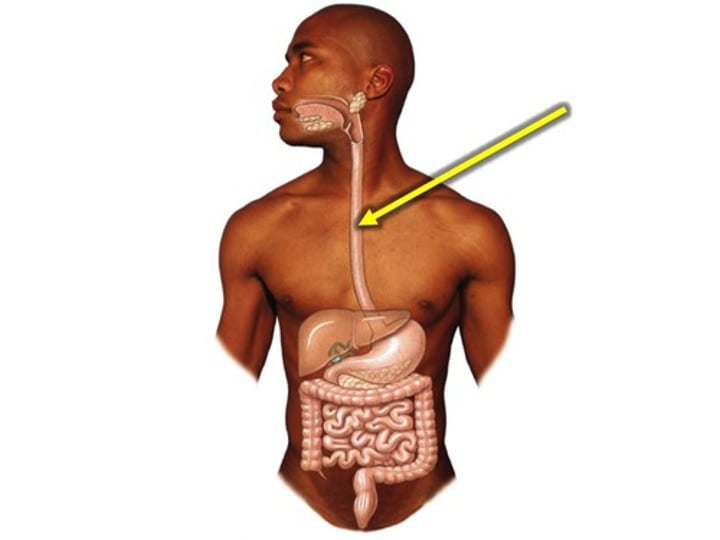
Esophagus
-A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
-pushes the bolus (food) towards the stomach using peristalsis
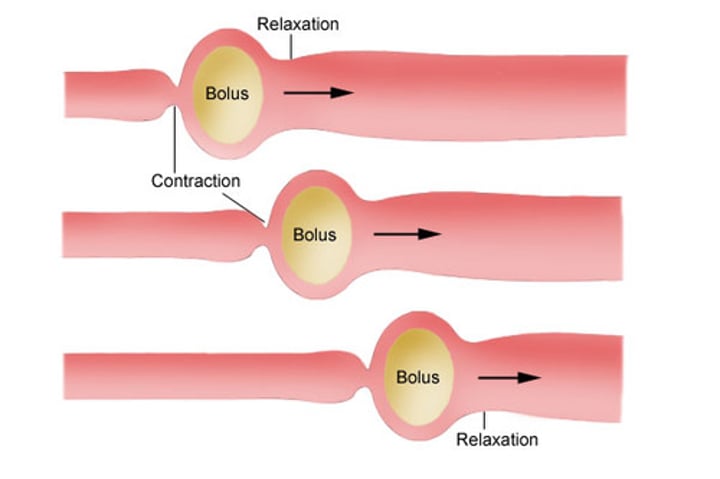
Peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
Sphincters
Control the passage of material with smooth circular muscle
Muscles arranged in circles that are able to decrease the diameter of tubes. Examples are found within the rectum, bladder, and blood vessels.
Esophageal Sphincter
a controlled opening to the stomach from the esophagus
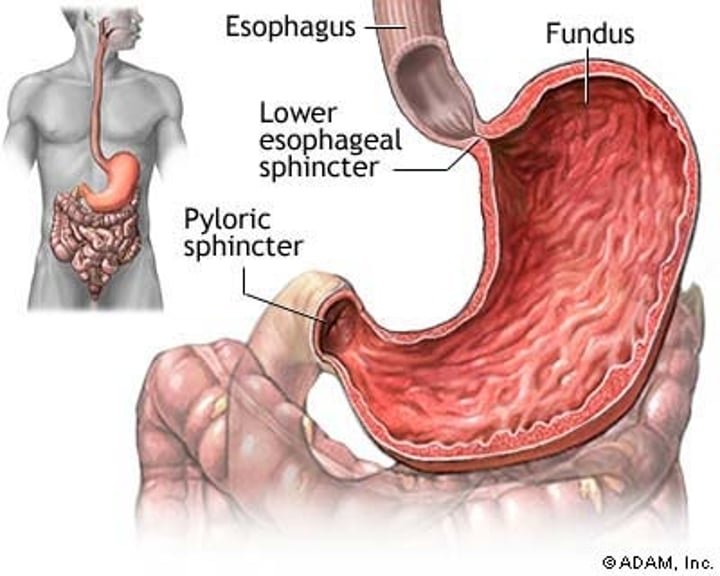
Pyloric Sphincter
a controlled opening to the small intestine from the stomach
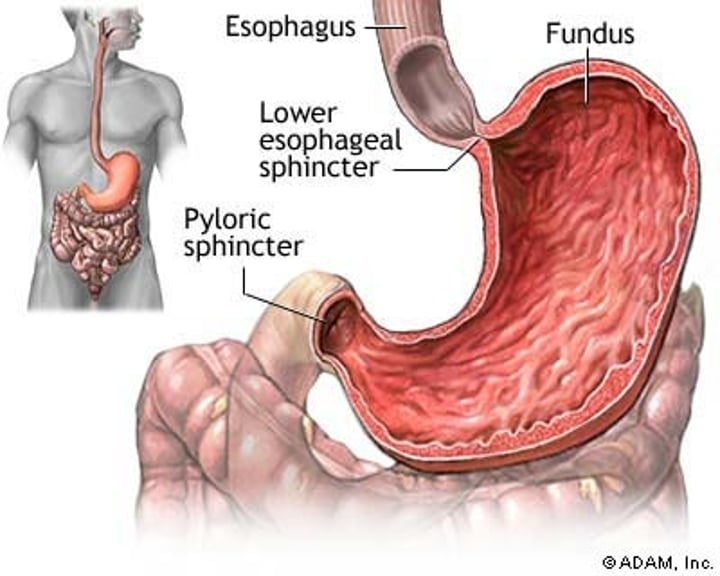
Stomach
-A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat.
-Mechanical digestion - churns food
-Chemical digestion - releases enzymes
-Has rugae
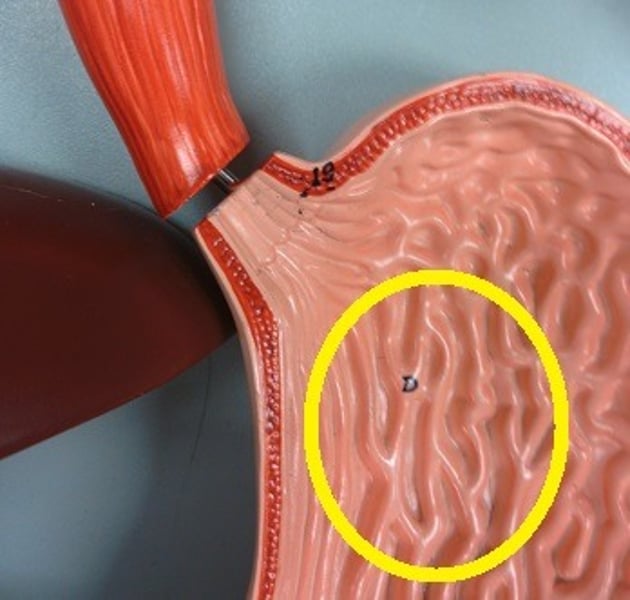
Rugae
folds on inner stomach lining that increase surface area for reactions
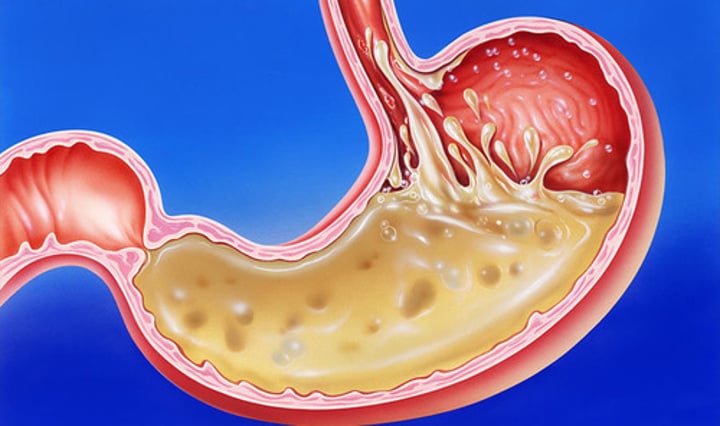
Gastric juices
-Consists of H₂O, mucus, salt, enzymes, and hydrochloric acid.
-pH 1-3 (very acidic)! Helps kill bacteria, soften food
Enzymes & Hormones of gastric juices
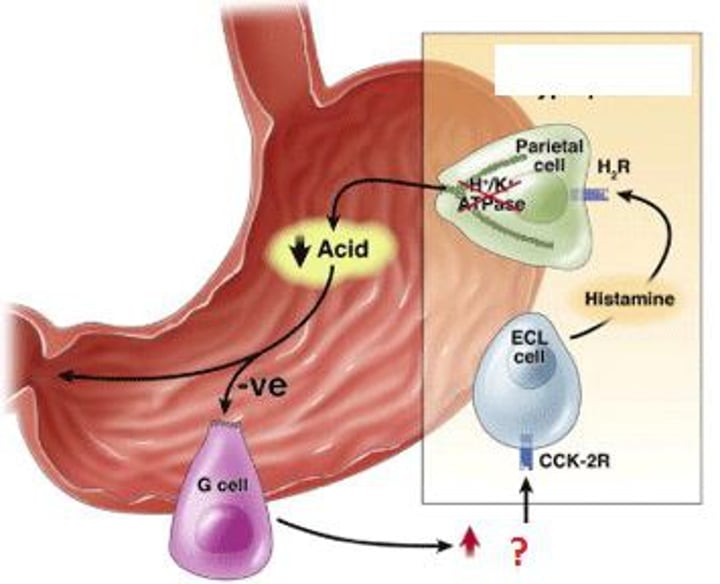
Enzyme: Pepsinogen (inactive) --> Pepsin (active by HCl)
Hormone: Gastrin
Enzyme: Rennin
Pepsinogen/pepsin
-Enzyme
Pepsinogen (inactive) --> Pepsin (active) - becomes activated when in contact with HCl (hydrochloric acid). Breaks down proteins into polypeptides.
Gastrin
-Hormone
-hormone secreted in the stomach that stimulates secretion of HCl and increases gastric motility
-increases acid production. Stimulated by food production
Rennin
Coagulates milk protein. Can slow milk digestion so infants can get maximum nutrients

Small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
The substance produced from stomach, now called chyme, is pushed through via peristalsis.
Duodenum
First 25-30cm of the small intestine, where majority of digestion takes place. Enzyme secretions from the pancreas and liver travel through ducts to here.
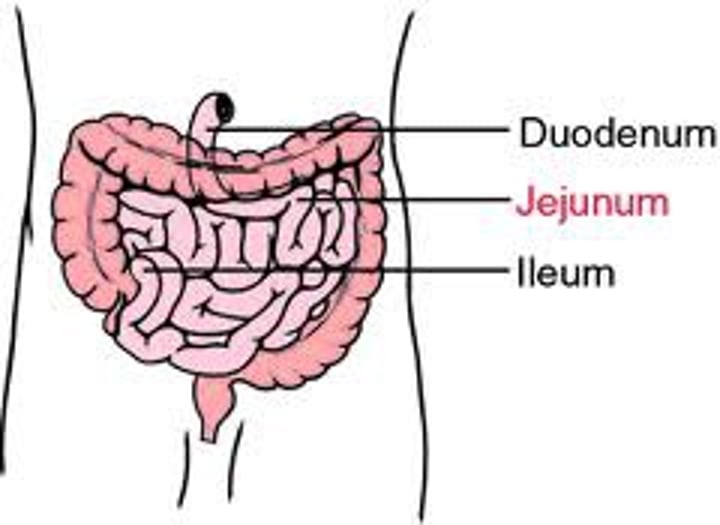
Jejunum
Second part of the small intestine. ~2.5m, responsible for the absorption of nutrients.
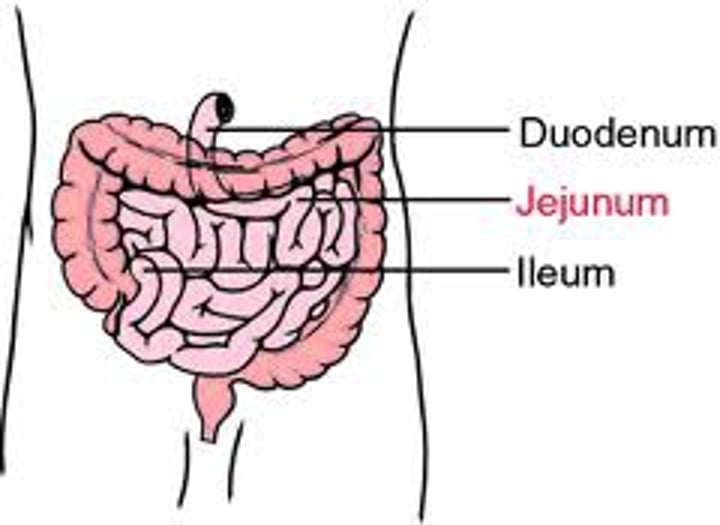
Ileum
The third (last) and longest portion of the small intestine. ~4m. Also responsible for absorption of nutrients.
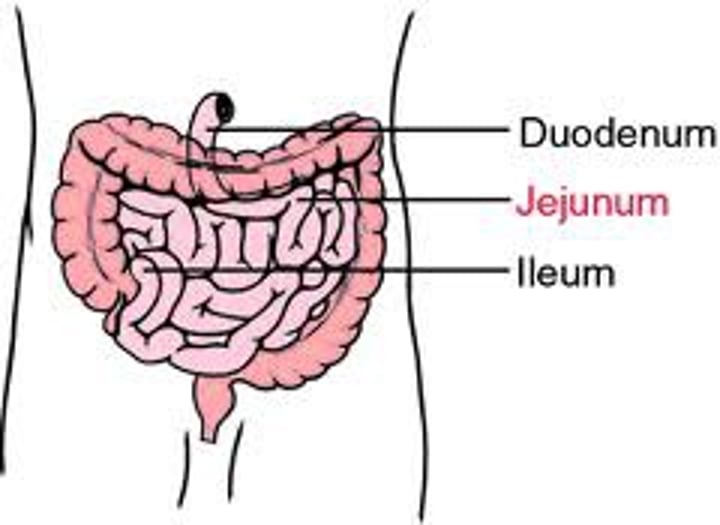
Duodenum completes ___________
digestion of food molecules. Enzymes include: Carbohydrases - (disaccharides) - maltase, sucrase, lactase.
Enterokinase - activates trypsinogen into trypsin.
Peptidase (erepsin) - turns peptides into smaller peptides and amino acids
Accessory organs
Organs that are not in the digestive tract, but secrete materials into tract.
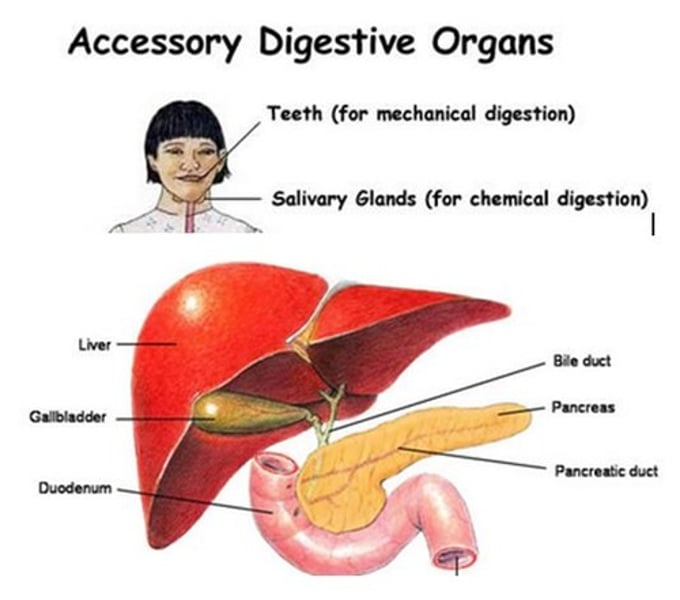
Liver
makes bile salts
Bile
A substance produced by the liver that breaks up fat particles. (physical digestion)
Also stores excess glucose as glycogen & detoxifies blood (alcohol, medication)
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood
-Releases bicarbonate (base in duodenum) which deactivates pepsin back into pepsinogen.
-Releases enzymes into duodenum - peptidase, amylase, lipase. Trypsinogen (inactive) --> Trypsin (active). Activated by enterokinases. Trypsin digests partially digested proteins.
Absorption
Digested nutrients absorbed in the rest of the small intestine.
Villi
increase surface area of small intestine for more absorption
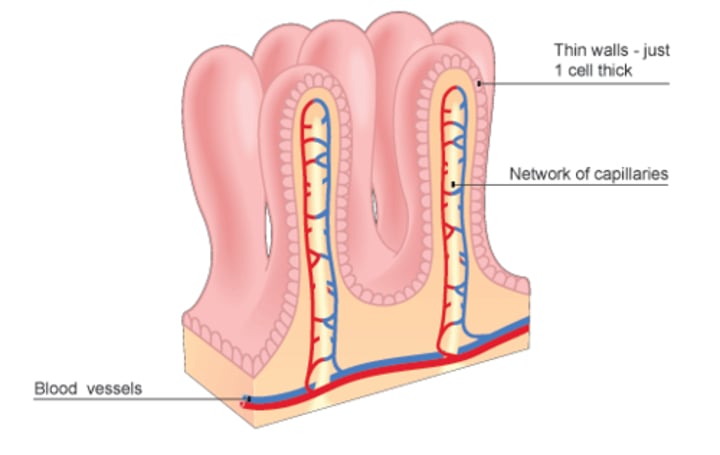
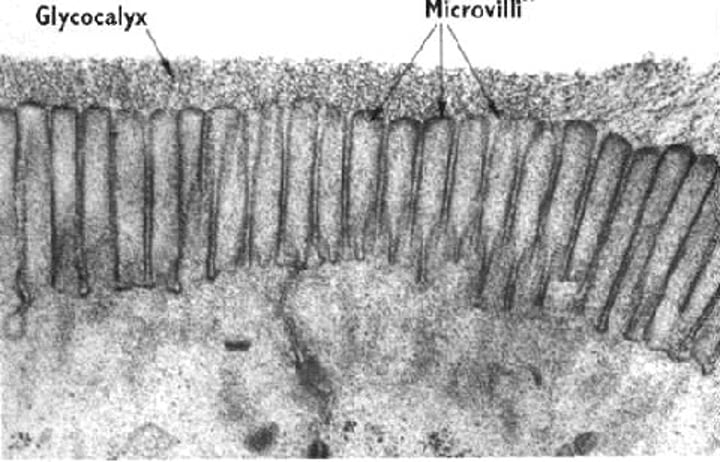
Microvilli
~130 billion per sq. inch in the small intestine
Blood capillaries
absorption through ACTIVE transport of amino acids and monosaccharides
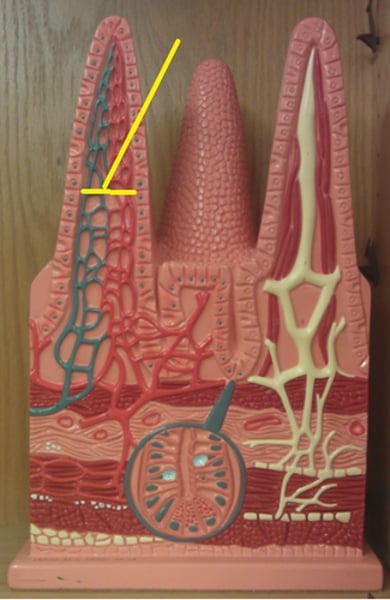
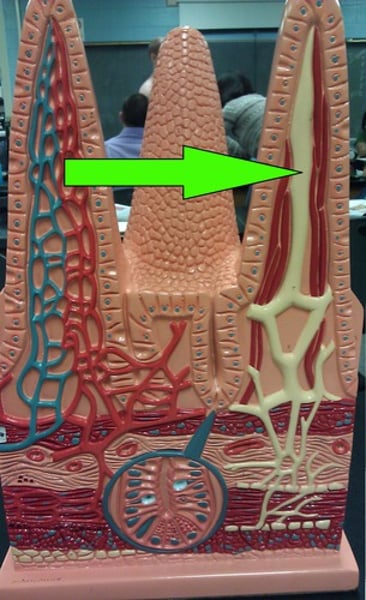
Lacteals
absorption through PASSIVE transport of fatty acids and glycerols
Large intestine (colon)
reabsorption of water and salts (minerals). Has bacteria to produce B-12 and K vitamins.
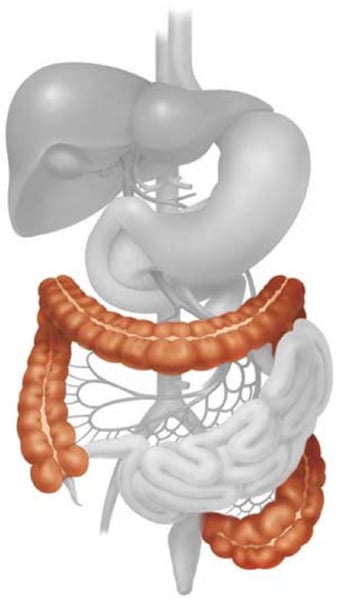
Rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
Storage of feces. If full, can trigger a reflex
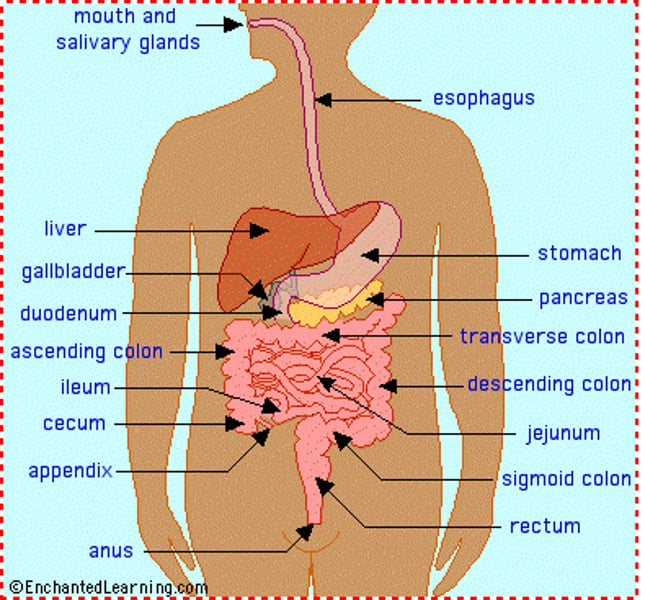
Anus
A muscular opening at the end of the rectum through which waste material is eliminated from the body
sphincter where waste is released from body