BIOL251 Final Exam Review
1/359
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
anatomy
study of structure
physiology
study of how body parts function
level of structural organization
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal
11 systems of the human body
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive
integumentary components
skin, hair, nails
integumentary functions
protection, body temperature regulation, insulation
skeletal components
bones, joints, cartilage
skeletal functions
structure, support, body movements
muscular components
skeletal muscle tissue
muscular functions
movements, produces heat, maintains posture
nervous components
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory organs (eyes and ears)
nervous functions
action potentials, regulates body activities, detects changes in internal and external
endocrine components
hormone producing glands (pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituary gland, ovaries, etc.)
endocrine functions
releasing hormones (chemical messengers)
cardiovascular components
blood, heart, blood vessels
cardiovascular functions
pumping blood, helps regulate temperature and water content of body fluids
lymphatic components
lymphatic fluid, vessels, spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, and tonsils
lymphatic functions
returns proteins and fluids to the blood, carries lipids
respiratory components
lungs, trachea, bronchial tubes, pharynx, and larynx
respiratory functions
transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air
digestive components
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, anus
digestive functions
achieves physical and chemical breakdown of food, absorbs nutrients
urinary components
kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
urinary functions
produces, stores, and eliminates urine
reproductive components
gonads, uterine tubes, mammary glands, etc.
reproductive functions
gonads produce gametes to help form a new organism, mammary glands produce milk, etc.
life processes in humans
metabolism, responsiveness, movement, growth, differentiation, reproduction
homeostasis
a condition of equilibrium, or balance, in the body's internal environment
fluid in homeostasis
extracellular fluid
components of a feedback loop
stimulus, receptor, control center, effector, response
negative feedback loop
a feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving (example: change in blood pressure)
positive feedback loop
a feedback loop in which change in a system is amplified (example: pregnancy)
tissue
a group of cells that usually have a common embryonic origin in an embryo and function together to carry out specialized activities
4 basic types of tissue
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
cell junctions
cells that are held together in a variety of ways; point of contact between cells
tight junctions
adjacent plasma membranes with intercellular space between; stands of transmembrane proteins on the sides
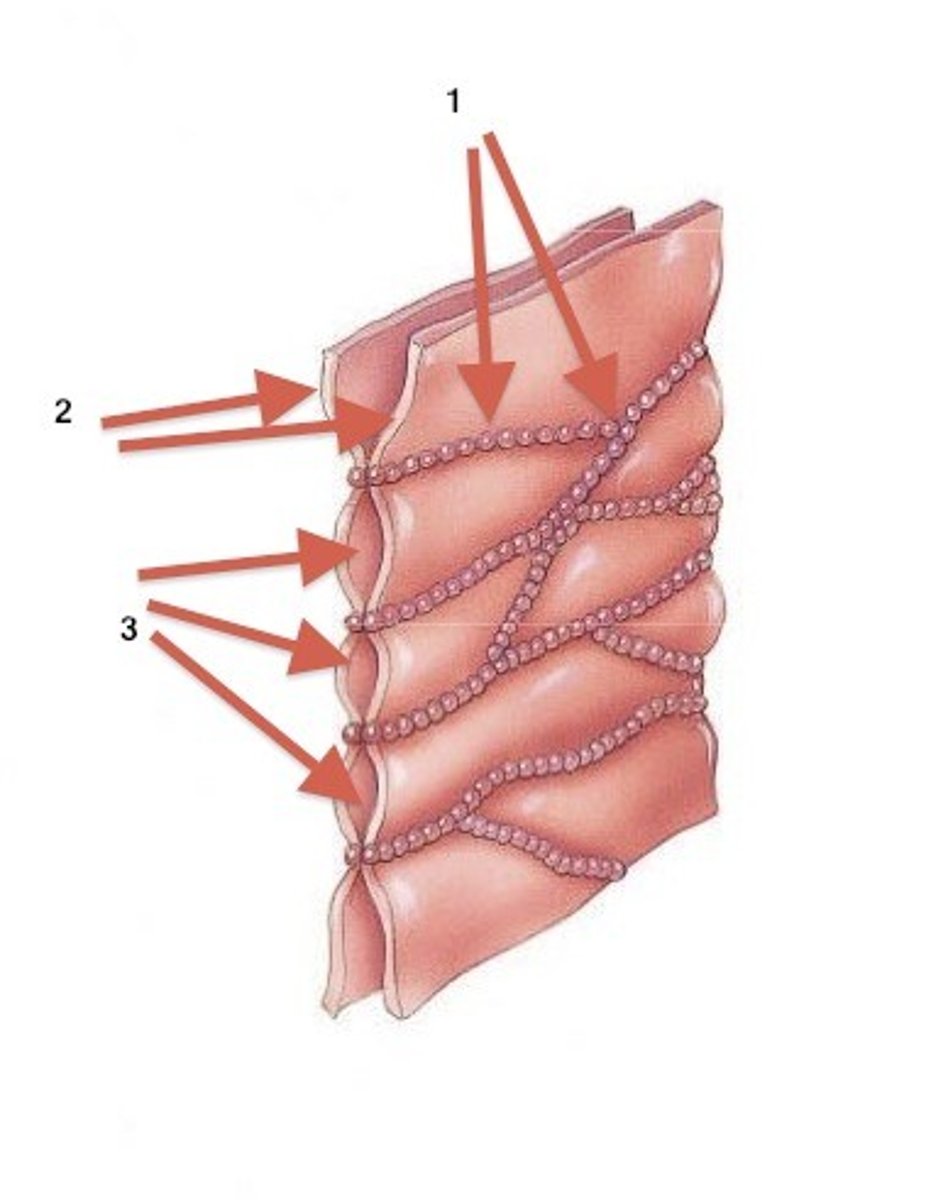
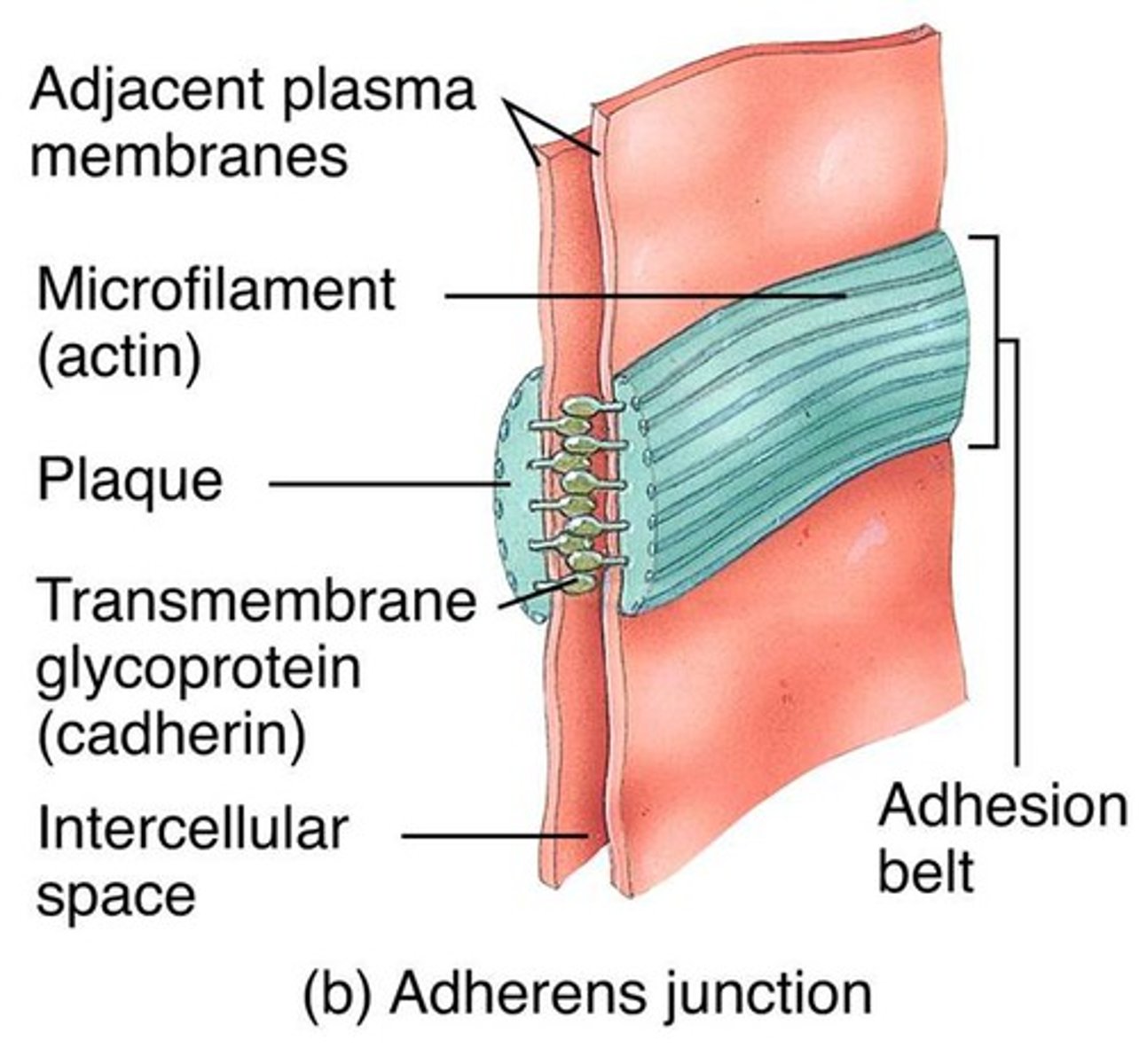
adherens junctions
adjacent plasma membranes with microfilament (actin) along the middle with plaque in between
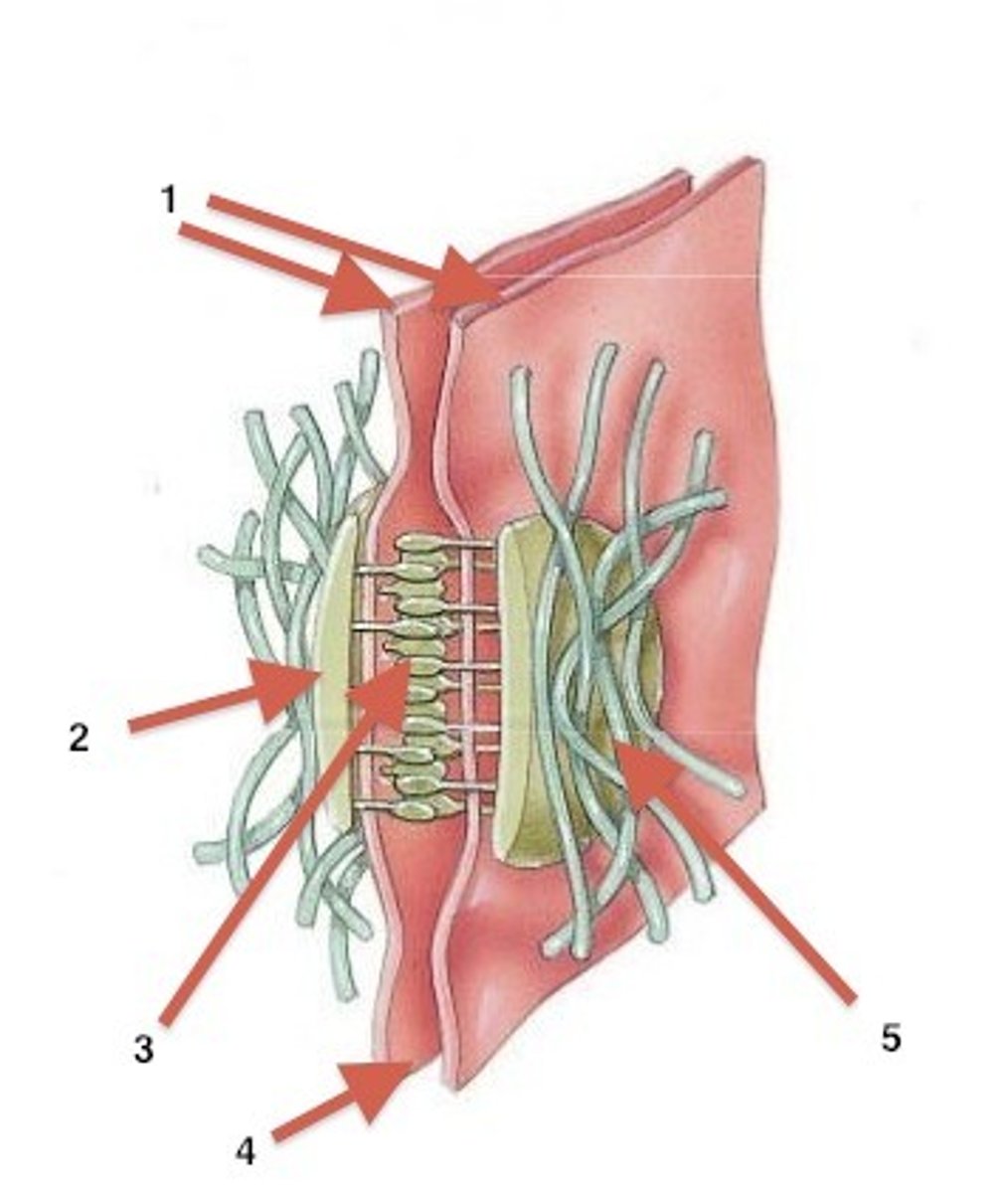
desmosomes
adjacent plasma membranes with plaque in the middle and keratin on the sides (crazy looking)
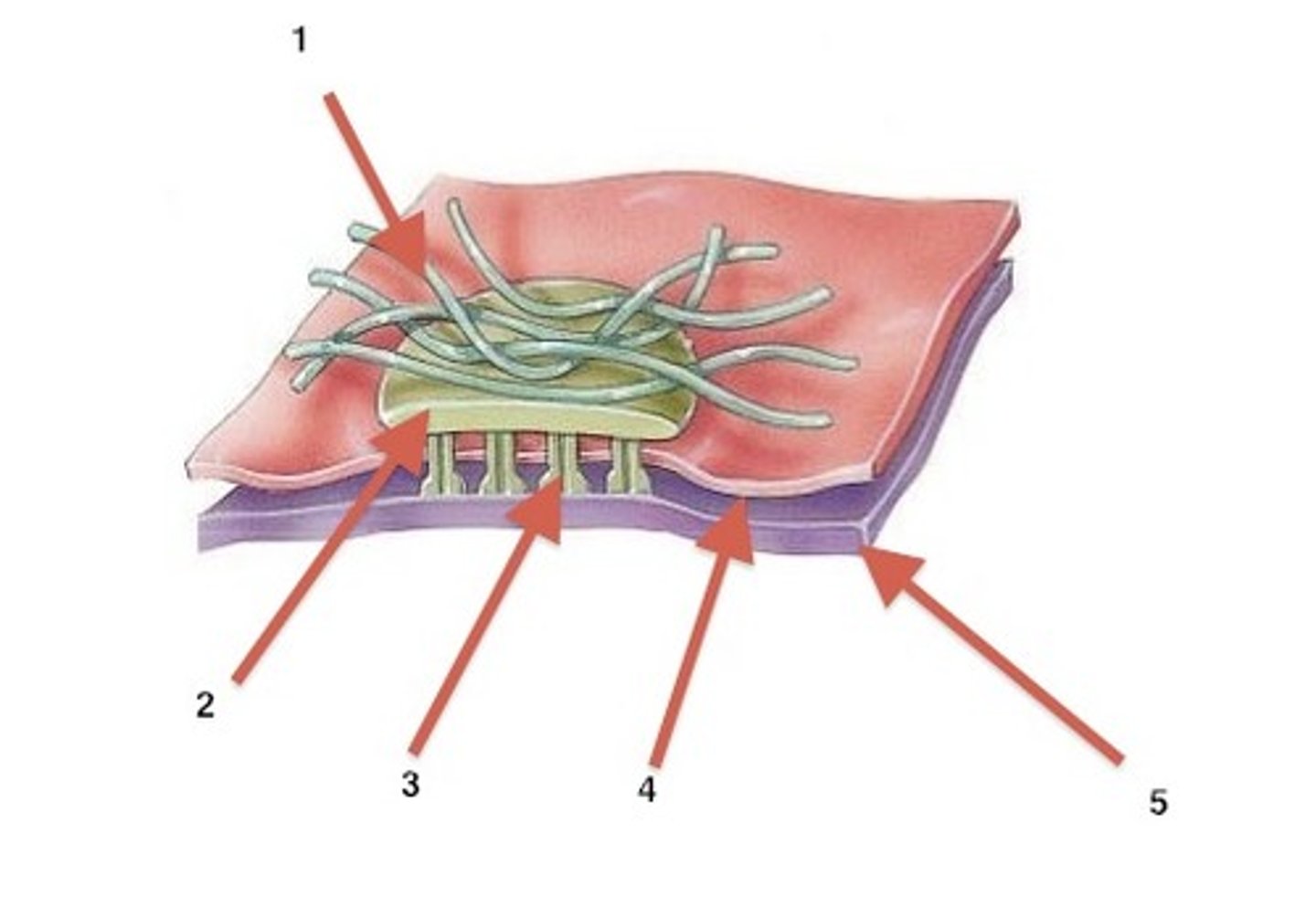
hemidesmosomes
attach epithelial cells to the basement membrane with keratin on the top
gap junctions
adjacent plasma membranes with connexons and gaps between
epithelial tissue
cells arranged in sheets and are densely packed, many cell junctions present, attaches to basement membrane, avascular with nerve supply, mitosis occurs frequently
epithelial cell diagram
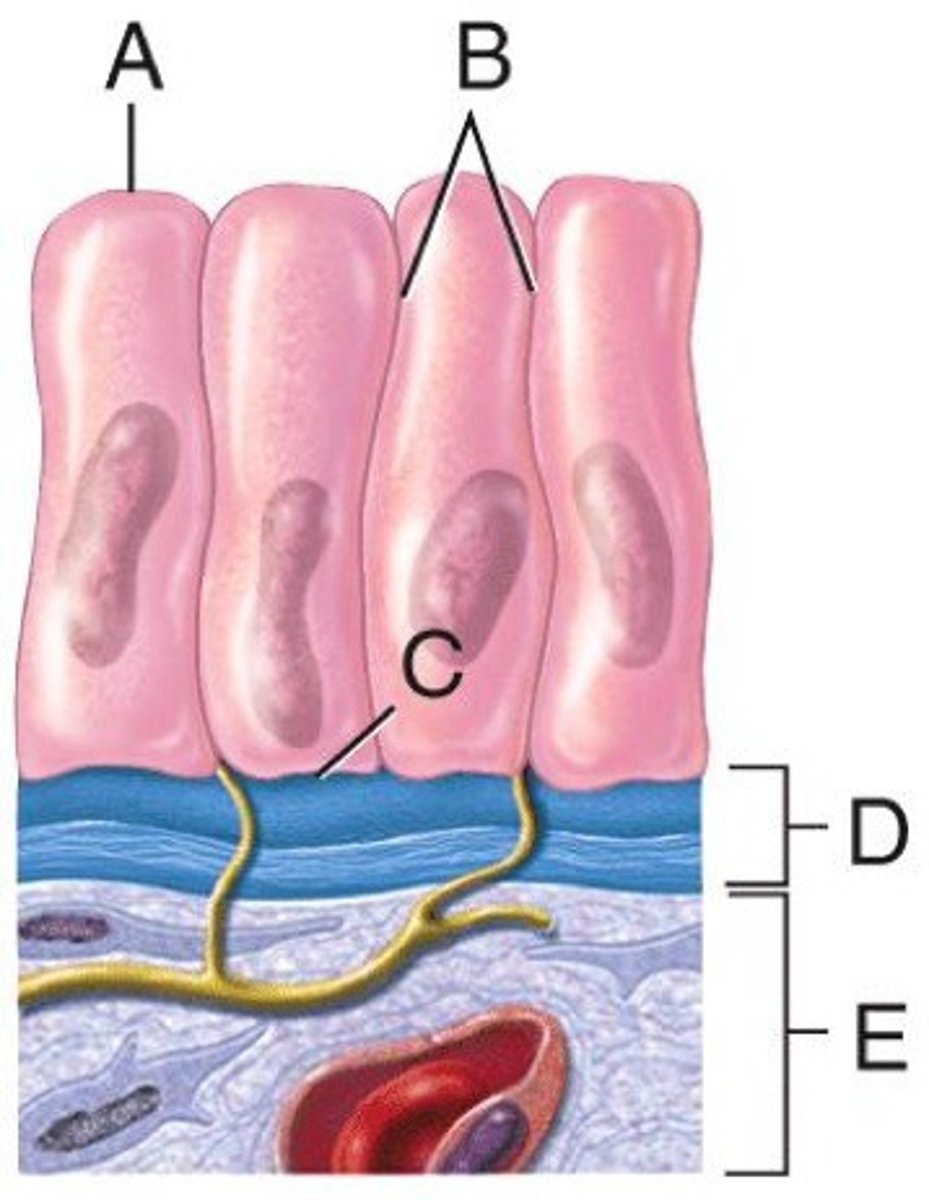
classifications of epithelial tissue
simple, pseudostratified, stratified, squamous, cuboidal, columnar
gland
a single cell or a mass of epithelial cells adapted for secretion
endocrine and exocrine glands
glandular epithelium can have these two gland types
endocrine glands
glands that enter interstitial fluid and then diffuse the bloodstream without flowing through the duct; found in the pituitary gland, pineal gland, etc.; regulate metabolic and physiological activities
exocrine glands
glands that secrete onto the surface of covering and lining epithelium, such as the skin; sweat, oil, and cerumen glands; produce substances such as sweat to lower body temperature
structural classification of glandular epithelium
unicellular and multicellular
unicellular
single cells (example: goblet cells)
multicellular
composed of many cells that form a distinctive microscopic structure (sweat glands)
connective tissue
tissue that consists of cells and extracellular matrix; no free surfaces; highly vascularized with nerve supply (exceptions include tendons and cartilage)
extracellualr matrix (ECM)
located between the spaces of connective tissue cells; composed of fibers and ground substance
connective tissue fibers
collagen, elastic, reticular
classifications of connective tissue
loose, dense, cartilage, bone, blood
membranes
flat sheets of pliable tissue that cover or line a part of the body
2 types of membranes
epithelial and synovial
types of epithelial membrane
mucous, serous, cutaneous
integumentary system components
skin, hair, oil and sweat glands, nails and sensory receptors
integumentary system functions
helps the body maintain its temperature, production of vitamin D, provides sensory information, helps maintain homeostasis
2 major layers in skin
epidermis and dermis
hypodermis
located deep to the dermis but not a layer of skin; composed of areolar and adipose tissue (aka subQ)
integumentary system diagram
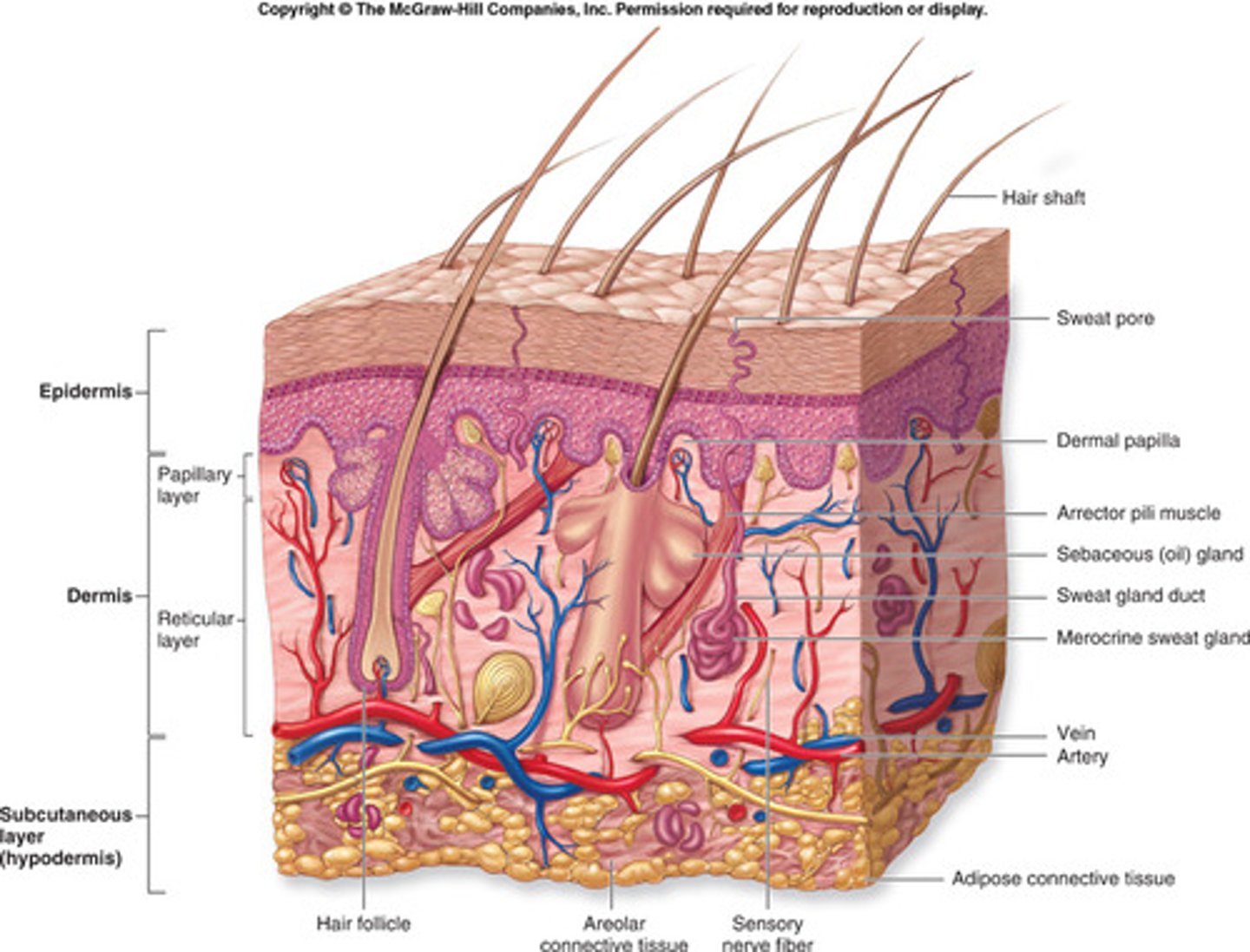
4 cell types in epidermis
keratinocytes, melanocytes, langerhans cells (intraepidermal macrophages) , merkel cells (tactile epithelial)
types of skin in the epidermis
thin (hairy) skin and thick (hairless) skin
thin (hairy) skin
type of skin that covers all body regions EXCEPT the palms, palmar surfaces of digits, and soles
thick (hairless) skin
type of skin that covers the palms, palmar surfaces of digits, and soles
five layers of the epidermis (superficial to deep)
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale (CLGSB)
stratum lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin
epidermis diagram
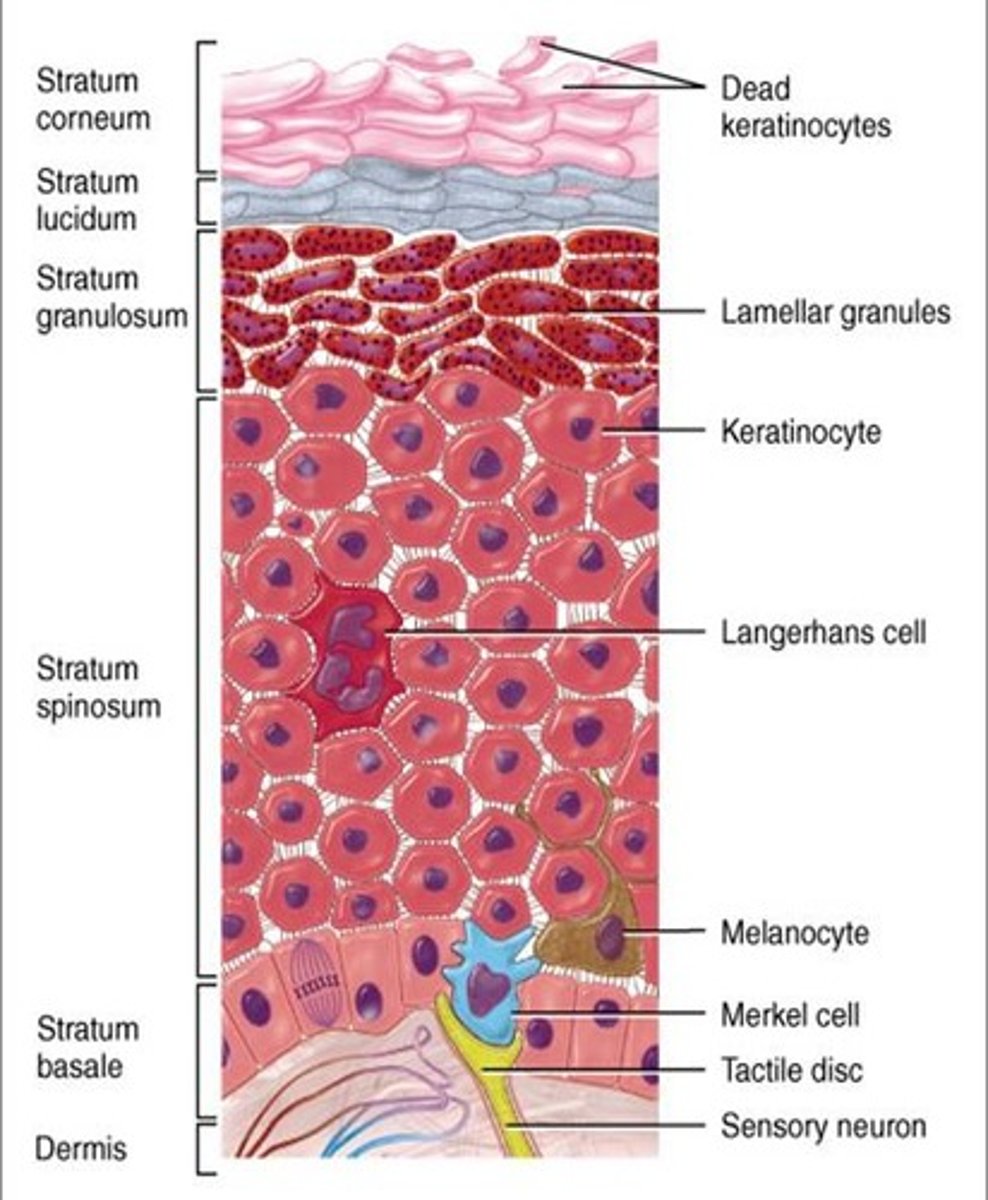
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis, composed of single row of cuboidal or columnar keratinocytes; melanocytes and tactile epithelial cells scattered
stratum spinosum
8-10 layers of keratinocytes with bundles of keratin intermediate filaments
stratum granulosum
3-5 layers of flattened keratinocytes, organelles are beginning to regenerate
stratum corneum
3-50 or more layers of dead, flat keratinocytes that contain mostly keratin
dermis
layer of skin composed of connective containing collagen and elastic fibers
papillary region
superficial portion of dermis; consists of areolar CT with thin collagen and fine elastic fibers
reticular region
deeper portion of dermis; consists of dense irregular CT with bundles of thick collagen and some coarse elastic fibers
melanin
pigment in the skin produced by melanocytes in the stratum basale
pheomelanin
yellow-red pigment
eumelanin
brown-black pigment
hemoglobin
red pigment in the red blood cells
carotene
a yellow/orange pigment stored in the stratum corneum and adipose tissue
albinism
congenital disorder characterized by the complete or partial absence of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes due to a defect involving the production of melanin
vitiligo
chronic disorder that causes depigmentation patches in the skin
hair
composed of dead, keratinized epidermal cells; genetic and hormonal influences determine the thickness and distribution
parts of hair
the shaft, follicle, root
shaft
hair above the surface of the skin
follicle
hair below the level of the skin
root
hair that penetrates into the dermis (through the epithelial root sheath and dermal root sheath)
4 types of skin glands
sebaceous glands, eccrine sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and ceruminous glands
sebaceous (oil) glands
gland found in lips, penis, labia minora, and tarsal glands; located in dermis; mostly connected to hair follicles; secretes sebum; prevents hair from drying out; relatively inactive until puberty
eccrine sweat glands
throughout skin of the body, especially on thick skin; mostly in deep dermis and terminates on surface of epidermis; perspiration; active soon after birth
apocrine sweat glands (SMELLY)
found on axillary, groin, bearded regions of face; mostly in deep dermis and upper subQ; terminates through hair follicles; secretes perspiration; stimulated during emotional stress and sexual excitement; active after puberty
ceruminous glands
found in the external auditory canal; subQ layer; secretes ear wax; stops foreign bodies and insects from getting into ear canal; active soon after birth
functions of the skin
thermoregulation, blood reservoir, protection, cutaneous sensations, excretion and absorption, synthesis of Vitamin D
thermoregulation
sweat; blood flow to dermis (vasodilation and vasoconstriction)
blood reservoir
up to 5% of body's blood volume
protection of the skin
keratin, lipids, sebum, acidic sweat, melanin, macrophages
cutaneous sensations
tactile, thermal, pain
tactile sensations
touch, pressure, vibration, itch, tickle
synthesis of Vitamin D
UV rays activate precursor molecule allowing Vitamin D to be made; aids the absorption of calcium from foods in the GI tract