ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE
types of adaptive immunity
cell-mediated immunity
humoral immunity
characteristics of adaptive immunity (4)
specific
acquired/ learned
requires lymphocytes therefore has a memory
quicker response on second encounter
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
types of adaptive immunity
cell-mediated immunity
humoral immunity
characteristics of adaptive immunity (4)
specific
acquired/ learned
requires lymphocytes therefore has a memory
quicker response on second encounter
what is adaptive immunity made up of (2)
cells: T cells - generally target intracellular microbes
soluble factors/ humoral: B cells - generally targets extracellular microbes
why do we need adaptive immunity (3)
microbes can evade innate immunity
intracellular viruses and bacteria ‘hide’ from innate immunity
need ‘memory’ to specific antigens so response is faster, become sick less often, more likely to survive
the adaptive players
MALT = Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue
T cells mature in thymus
B cells mature in bone marrow
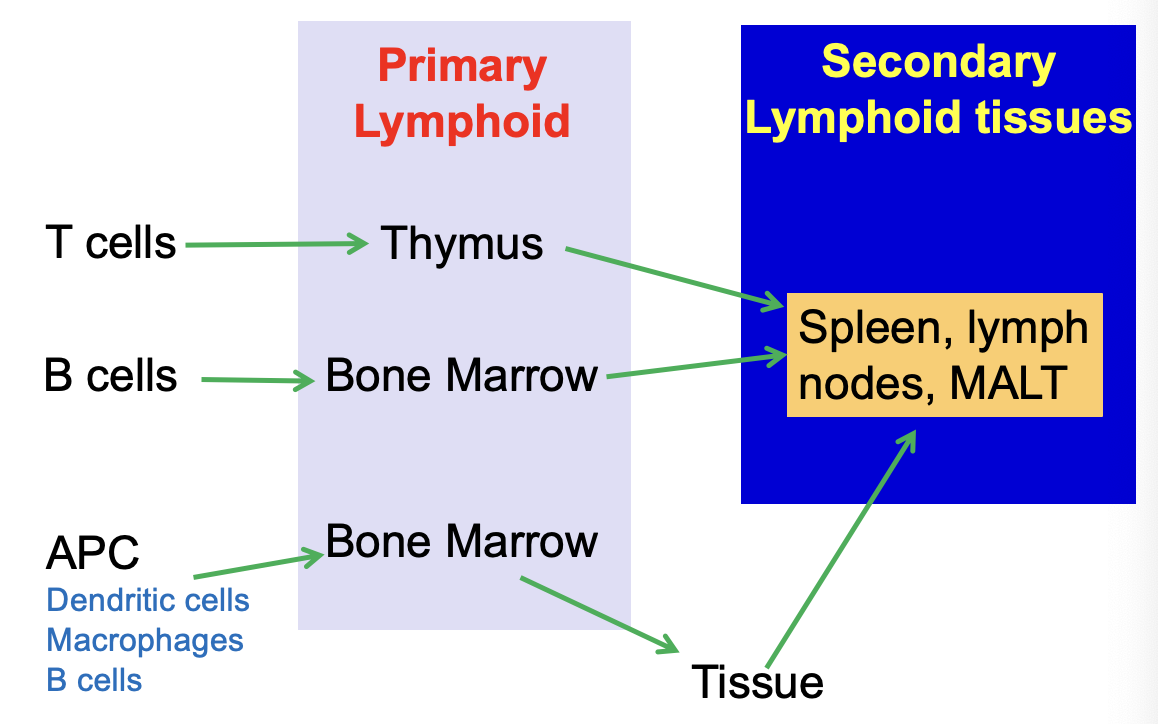
lymphoid tissues of the body
cell-mediated immunity
interplay between:
infected cells
OR
APC (macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells)
AND
T cells
what does cell-mediated immunity require (4)
intimate cell to cell contact:
to directly recognise and kill infected cells
to control antibody responses via contact w B cells
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) - everyone has different MHC
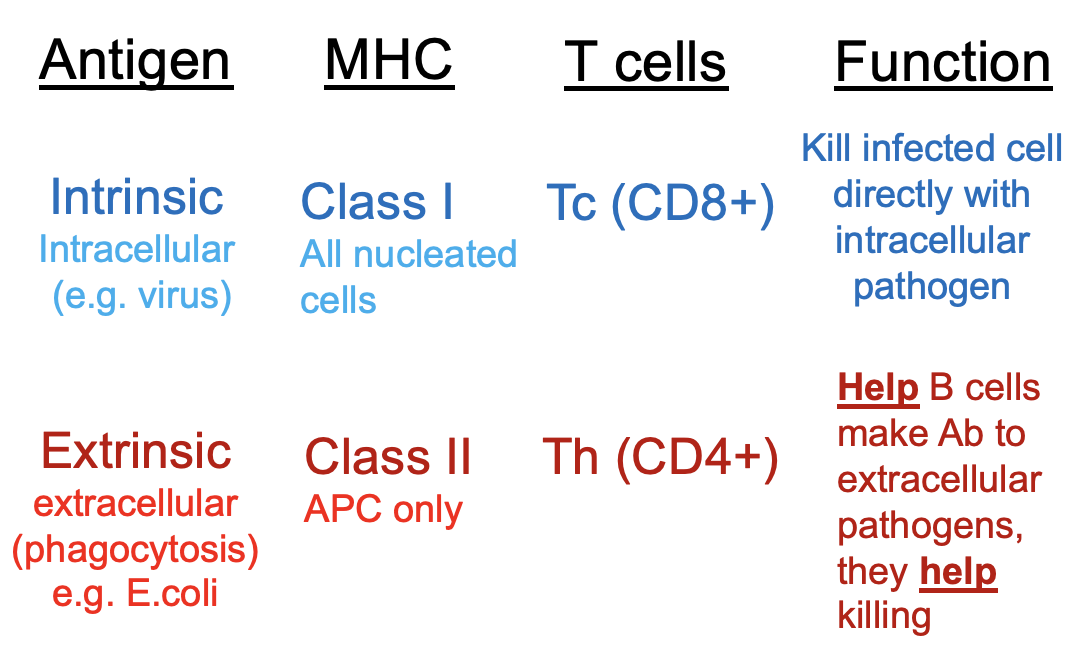
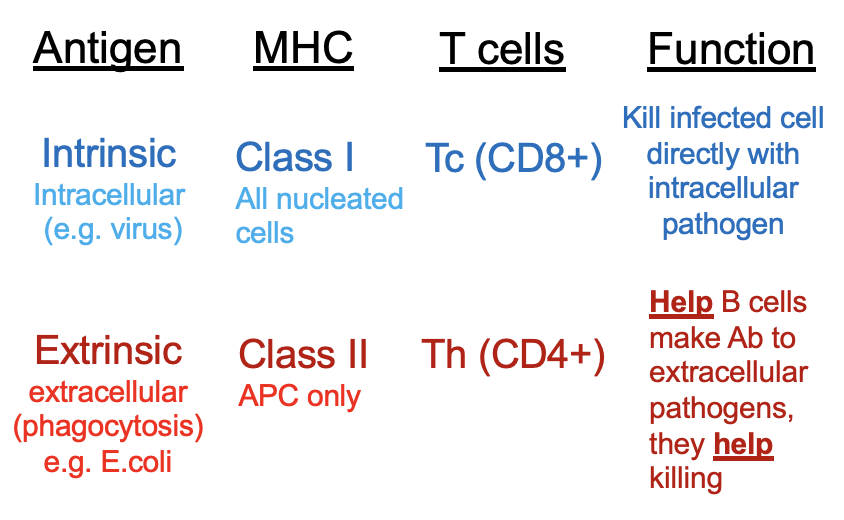
intrinsic/ endogenous/ intracellular antigens
extrinsic/ exogenous/ extracellular antigens
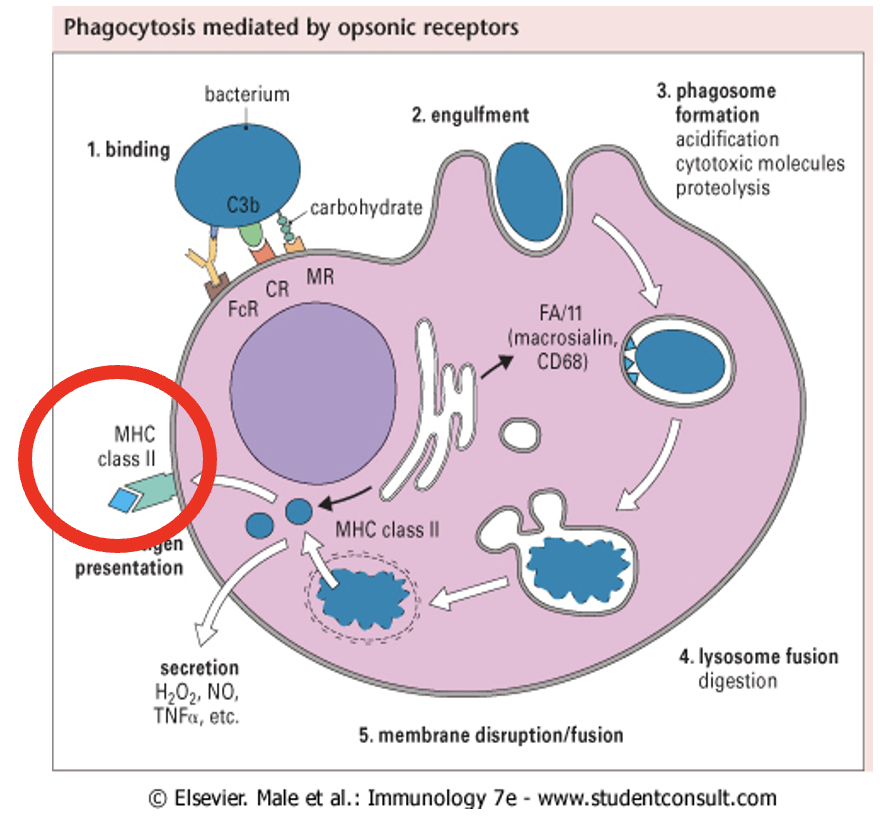
antigen presentation: dendritic cells and macrophages
dendritic cells:
phagocytose a non-self organism
migrate to lymph nodes and present Ag to T cells
macrophages:
phagocytose a non-self organism
present Ag at site of infection
T cells: before and after activation
before activation: naive T cell
after activation: activated T cell
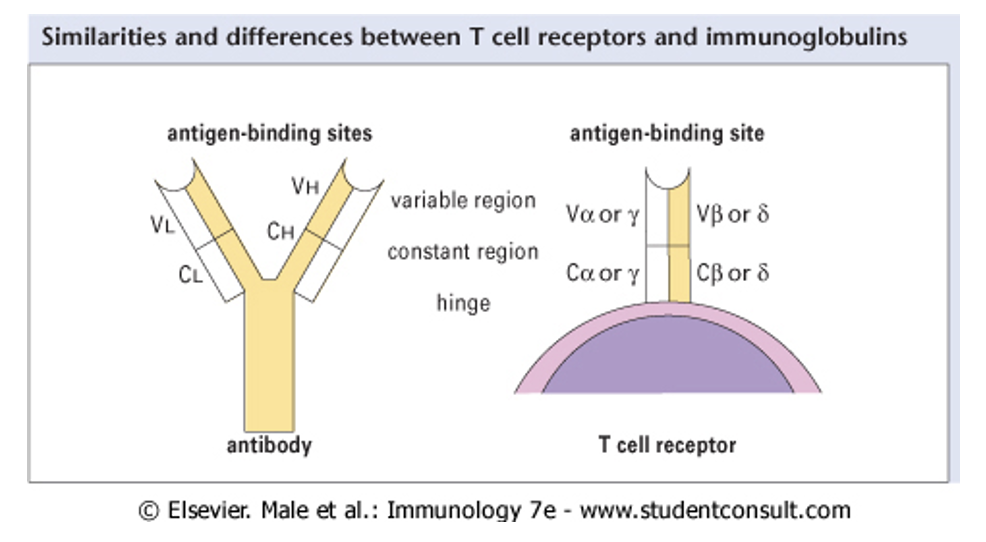
T Cell Receptor (TCR) structure
structure is similar to F Igs
made up of two polypeptide chains (heterodimer)
T cells: T cells that recognise self
T cells that recognise self are killed in the foetal thymus as they mature during development
i.e. T cell selection
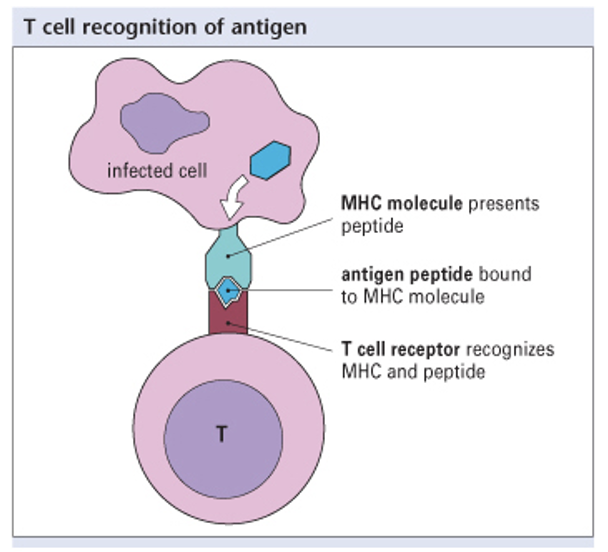
T cells: what do they respond to?
do NOT respond to soluble antigens, only to antigens presented by MHC
T cell receptor (TCR) recognises foreign antigens only when in associated w MHC
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
MHC display peptides from self or non-self proteins
in humans MHC molecules (glycoproteins) are coded for by Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) genes
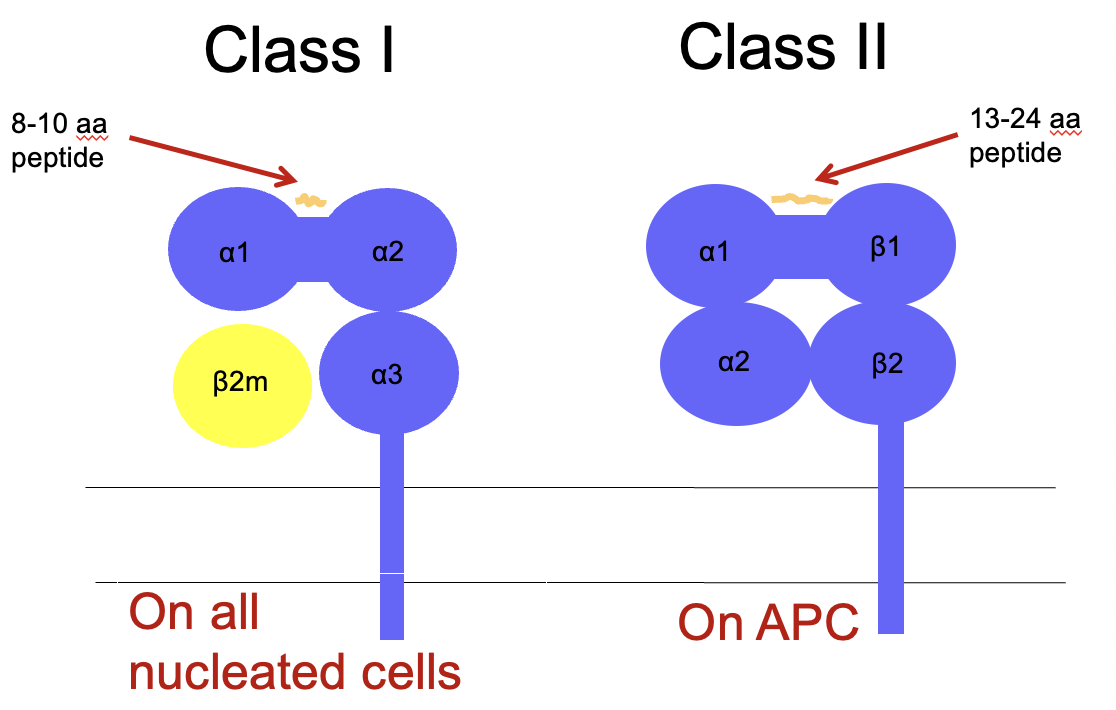
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC): classes
MHC I - encoded by HLA (A, B, C genes)
glycoproteins on ALL nucleated cells (not erythrocytes) will express MHC class I
MHC II - encoded by HLA (DP, DQ, DR genes)
glycoproteins ONLY on APC will express MHC class II
MHC III genes encode complement proteins
MHC class I and II structure
class I: display peptides w 8-10 aa
class I: a heavy chain (alpha 1, 2, 3 domains) and a light chain (beta m)
class II: display peptides w 13-24 aa
class II: alpha polypeptide chain and beta polypeptide chain
what is the link between innate and adaptive immunity
antigen presentation via MHC
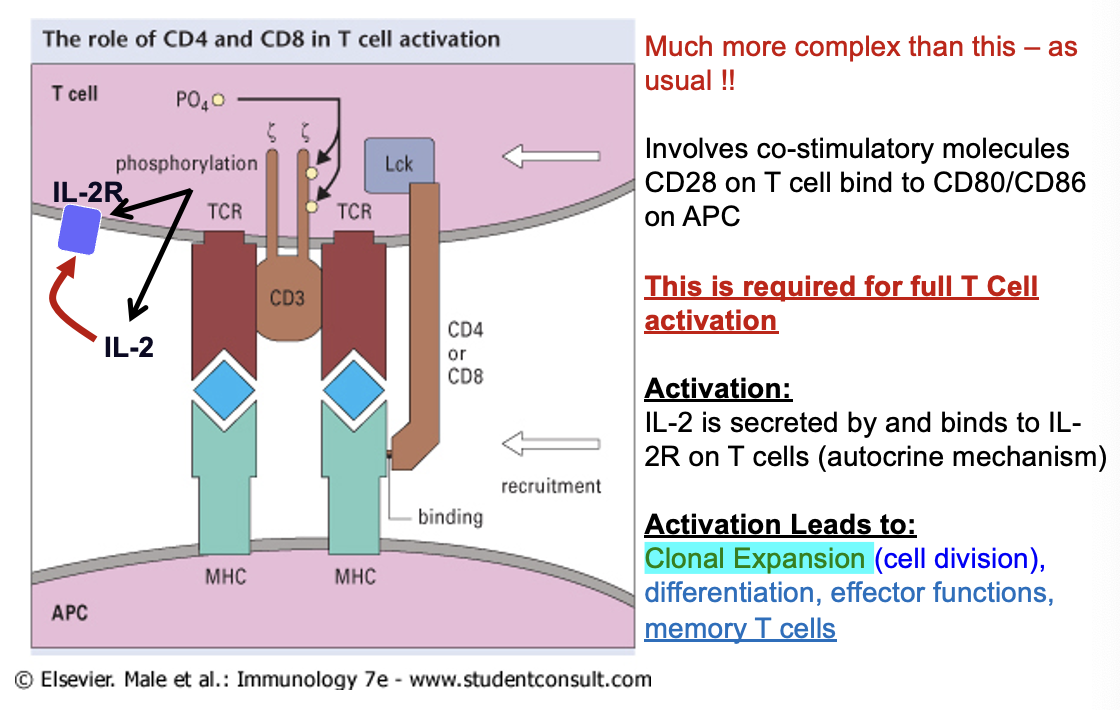
T cell Ag recognition and activation process (5)
T cell receptor (TCR) recognises antigen displayed by MHC
co-stimulatory molecules CD28 on T cell must bind to CD80/ CD86 on APC
IL-2 secreted by T cell and binds to IL-2R on T cell (autocrine mechanism)
causes T cell to undergo clonal expansion (cell division)
also causes T cells to differentiate into effector T cells (Tc, Th, Treg) and memory T cells
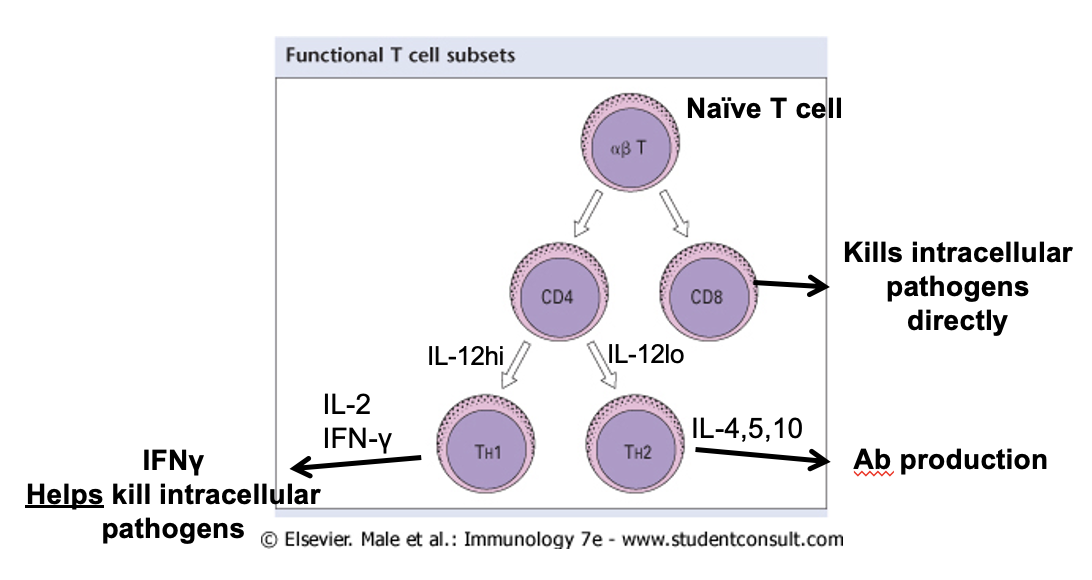
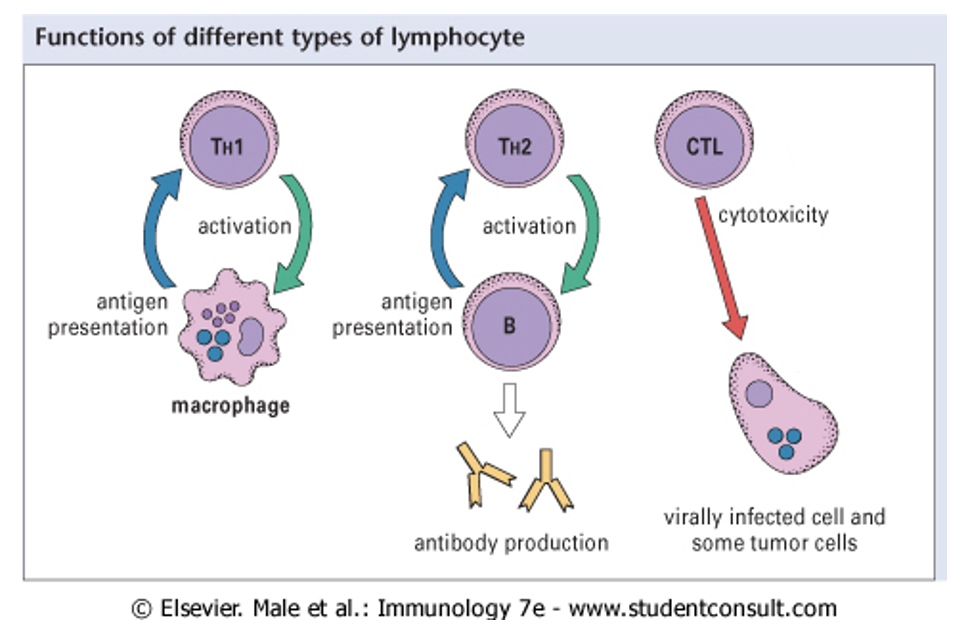
functional T cells differentiate into?
IL-12 high levels = Th1 pathway
IL-2 low levels = Th2 pathway (helps B cells make antibodies)
cytotoxic T cell (CD8) activation (6)
APC presents INTRINSIC antigen on MHC class I which binds to naive CD8 T cell
naive CD8 T cell is activated and differentiates into cytotoxic effector T cell (CTL)
CTL releases perforins and granulysin - kills infected cell directly w intracellular pathogen
perforins: form pores in cholesterol-containing cell membranes, initiates cell death via direct lysis and apoptosis
granulysin: damages cholesterol-poor cell membranes
CTL secretes IFNγ which activates macrophages
CTL secretes cytokines which attract more immune cells
memory CD8 T cells are formed
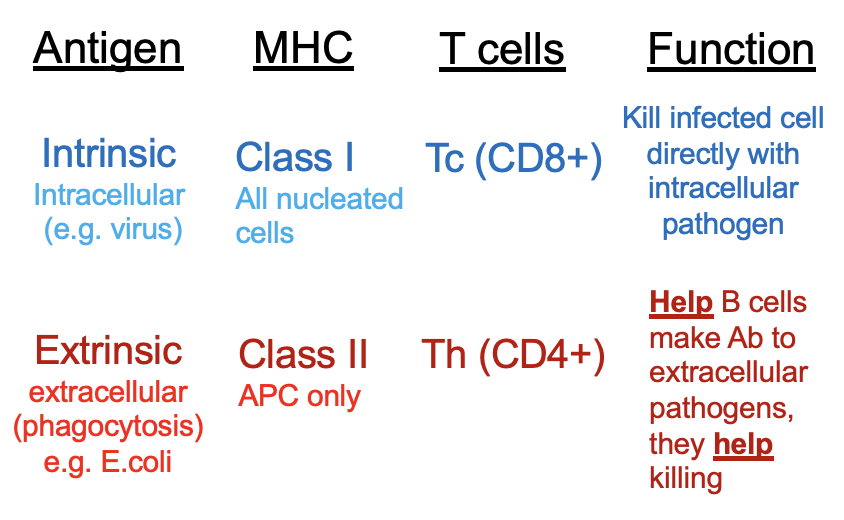
T helper cell (Th1) (CD4) activation (7)
phagocytosis of pathogen occurs
APC presents EXTRINSIC antigen via MHC class II to a naive CD4 T cell
APC secretes IL-12 which activate naive CD4 T cells to differentiate into Th1 cells
activated CD4 Th1 cells proliferate (clonal expansion)
Th1 recognises Ag on infected cells with MHC class II via TCR
Th1 secretes IFNγ which stops virus spread and increases macrophage activity
memory T cells are formed
B cells
B cells express membrane bound Ig (IgM or IgD monomer)
each B cell can only make one Ab that will only bind to one epitope on one antigen
humoral adaptive immunity: B cell activation (5)
B cells bind to appropriate Ag and become activated
activated B cells go to lymph nodes where they proliferate via clonal expansion and differentiate into plasma cells
plasma cells secrete Ab of same specificity - generally IgM which layer turn into IgG WITH THE SAME Ag SPECIFICITY
some B cells form memory B cells that last for many years
re-stimulation of memory B cells leads to a very quick secondary response
B cells: B cells that recognise self
B cells that recognise self are killed in the bone marrow during foetal development i.e. B cell selection
we are born w > 109 immature B cells
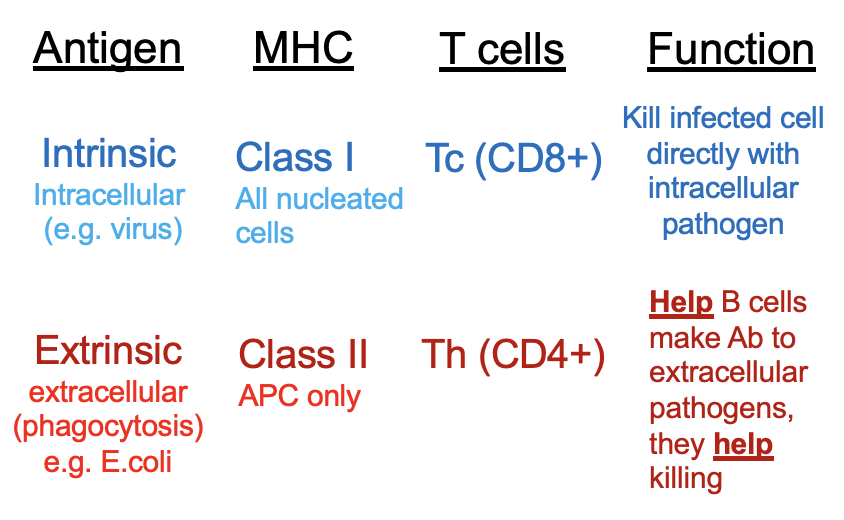
B cells: antigen presentation (MHC class II)
B cells present EXTRINSIC Ag to T cells via MHC II (only on APC)
—
mIgM or MIgD (Abs) binds Ag
phagocytosis occurs and the peptide is displayed on B cell surface with MHC II
T cell receptor of naive Th1 (CD4) binds to MHC II/ peptide surface
several other co-stimulatory molecules required
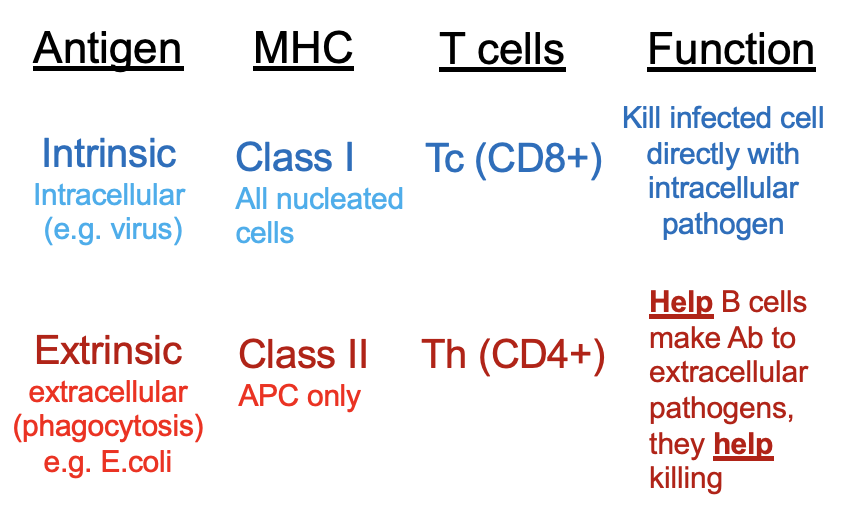
how T cells help B cells (7)
pathogen taken up by APC (macrophage/ dendritic cell) and presented with MHC class II
naive CD4 T cells bind to EXTRINSIC antigen on APC
these turn into primed Th2 cells
Th2 cells bind to B cells presenting the same antigen via MHC class II
Th2 cell secretes cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13)
these cause B cell clonal expansion (division)
B cells differentiate into plasma cells (AFC) and memory B cells (Bm)
actions of antibodies (4)
binds to microbes and prevent them from binding to and entering cells
neutralise toxin/ enzymes by binding to the active site
opsonisation - increases phagocytosis
activate complement
LINK BETWEEN INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
adaptive immunity summary diagram
switching OFF the immune response
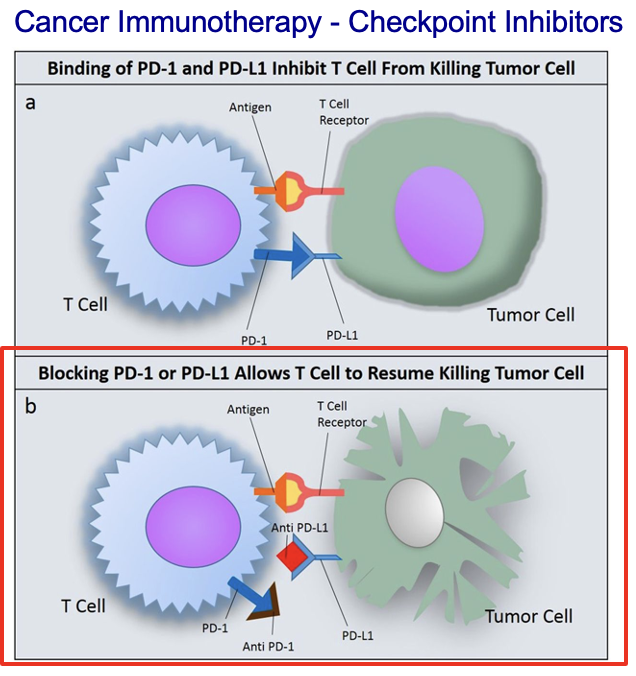
when T cells need to be stopped PD-1 will be expressed on cell surface
when PD-1 encounters and binds to PD-L1 receptor (on APC and other lymphocytes) it tells the T cell to turn ‘off’, inhibiting it from killing other cells
how do some tumour cells avoid being killed by T cells
some tumour cells have PD-L1 on its surface which help it evade being killed by T cells
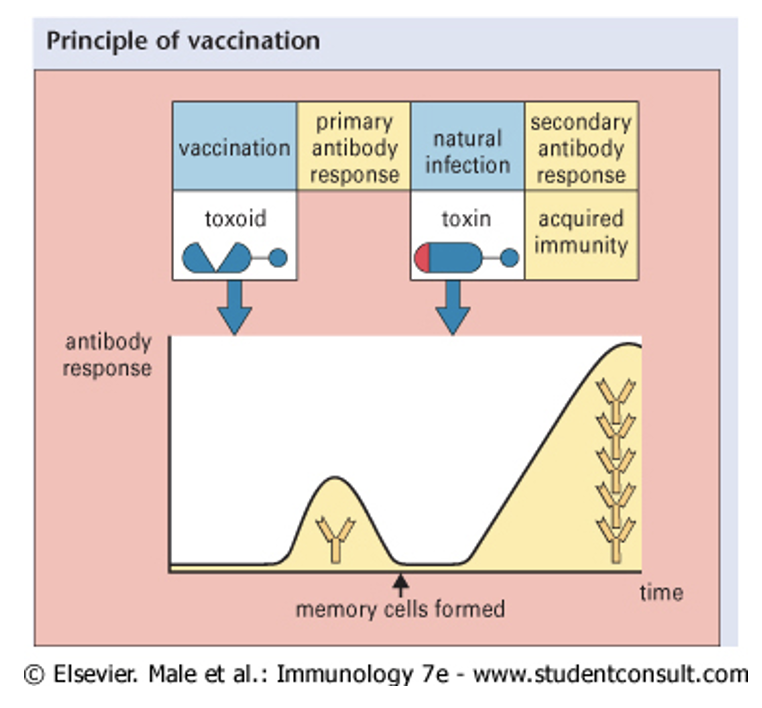
vaccination: tetanus vaccine (example)
tetanus toxoid from Clostridium tetani causes muscle contractions/ spasms - interference w neurons
can cause lock jaw
vaccine: treat purified toxoid in lab w formalin which removes toxicity but maintains epitopes
primary immune response still occurs meaning secondary will be faster
vaccination: principle and diagram