basics of pharmacology
1/273
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
274 Terms
drugs are substances that alter biological activity in a
person to promote healing, cure disease, control or slow progress of disease, decrease risk of complications, etc.

pharmacokinetics: processing of
drugs by the body
pharmacokinetics: processing of drugs by the body: human cytochrome P450 (CYP)
play important role in metabolism

pharmacokinetics: processing of drugs by the body: research shows that drug-metabolizing enzyme activity
impacts patient response to medication

pharmacokinetics: processing of drugs by the body: absorption, bioavailability,
distribution, metabolism, and execration
pharmacodynamics: effects of drugs on body,
either favorably or unfavorably

pharmacodynamics: effects of drugs on body, either favorably or unfavorably, receptor binding,
post-receptor effects, and chemical interactions

pharmacotherapeutics: use of
drugs in treatment of disease

drug discounts are partnered with surescripts to allow
clinicians access to drug discount information
evolution of medications: treatment based on
little scientific knowledge in early history
evolution of medications: treatment based on little scientific knowledge in early history, such as
Opium, morphine or cocaine was main ingredient
evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906:
evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906: formulary, if you have a medication not on the list you
have to bring the medication to the hospital and they will properly administer it if they can't find one similar on their list
evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906: formulary is specific for every hospital, every one has one,
they can't administer drugs that are not on the list

evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906: formulary lists
every drug, the side effect, ingredients, and when it should be taken
evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906: this introduced the
national formulary *
evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906: 1912 amendment require accurate
labeling of drugs to prevent substitution or mislabeling of ingredients

evolution of medications: food and drug act of 1906: drug mfg’s opposed drug laws but
public outrage resulted in passage

1914 - harrison narcotic act
limits indiscriminate use of addictive drugs
1938 - federal food, drug, and cosmetic act
determines: safety of drugs before marketing; labeling specifications; ensures advertising claims are met
1951 - durham-humphrey amendment
restricts number of prescription that can be refilled
1962 - kefauver-harris amendments
product must be proven safe and effective before it is released for sale
1970 - comprehensive drug abuse prevention and control
improve administration and regulation of manufacturing, distributing and dispensing controlled substances. DEA created
1983 - orphan drug act
offers federal financial incentives to nonprofit and commercial orgs to develop/market drugs to treat rare diseases
1987 - prescription drug marketing act
prohibits reimportation of drugs by anyone other than mnfg
1990 - safe medical devices
users report to mnfg’s and FDA occurrences in which device caused death or illness
1990 - anabolic steroid control act
placed anabolic steroids under ACA
1990 - omnibus budget reconciliation act
pharmacists offer to counsel medicaid and medicare pts about drug information and potential adverse effects for all new and refilled prescriptions
1994 - dietary supplements and health and education act
guidelines established and mnfg liable for claims against products in accordance w/ FDA guidelines
1992 - occupational safety and health act
ensures safety or workers
1996 - health insurance portability and accountability act
EHR standards, unique identifiers, security and electronic signature standards, privacy and confidentiality standards
1997 - FDA modernization act
patients have increased access to experimental drugs and devices
2003 - medicare prescription drug, improvement and modernization act
help seniors by reducing drug costs and help employers offer drug benefits
2005 - combat methamphetamine epidemic act
designed to stop illegal use of methamphetamine and regulated trafficking or drug
HIPAA really started with
portability
drug surveillance: includes the
drug enforcement administration (DEA)
federal controlled substances act (CSA)
FDA
drug surveillance: drug enforcement administration (DEA): physician must
renew registration every 3 years

drug surveillance: drug enforcement administration (DEA): any theft or loss
must be reported
drug surveillance: drug enforcement administration (DEA): regulates and enforces
manufacturing and dispensing of dangerous and potentially abused drugs

federal controlled substances (CSA) part of comprehensive drug abuse prevention and control act of 1970
drug surveillance
drug surveillance is concerned with
prevention and control of abuse of controlled substances
Administered and enforced by DOJ
Unit of DEA

food, drug, and cosmetic act (FDA) looks to fix the rules and regulations by
which drugs are imported, manufactured, distributed and sold in U.S.

state regulate laws more than
the federal
states are the main regulators of
pharmacy practice
state laws differ
from state to state
state laws require minimal qualification for individuals involved with
pharmacy practice (licensing)
state laws: health care providers must use
prescription pads
Must be secured at all times
prescription drug monitoring program (PDMP) allows prescription drug information to be
shared across all pharmacies
Helps with doctor hopping

development process of new drugs: first step is
New compound developed by pharmaceutical company
development process of new drugs: New compound developed by pharmaceutical company →
pre-clinical testing (making sure it's safe)
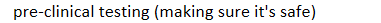
development process of new drugs: New compound developed by pharmaceutical company -> pre-clinical testing (making sure it's safe) ->

investigational new drugs status if approved

development process of new drugs: New compound developed by pharmaceutical company -> pre-clinical testing (making sure it's safe) -> investigational new drugs status if approved ->

clinical trials in humans

development process of new drugs: New compound developed by pharmaceutical company -> pre-clinical testing (making sure it's safe) -> investigational new drugs status if approved -> clinical trials in humans ->

new drug application sent to FDA
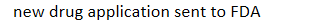
development process of new drugs: New compound developed by pharmaceutical company -> pre-clinical testing (making sure it's safe) -> investigational new drugs status if approved -> clinical trials in humans -> new drug application sent to FDA →

FDA approval of NDA

development process of new drugs: New compound developed by pharmaceutical company -> pre-clinical testing (making sure it's safe) -> investigational new drugs status if approved -> clinical trials in humans -> new drug application sent to FDA -> FDA approval of NDA ->

post-marketing surveillance

1 phases of clinical trials: 10 – 100 healthy volunteers study safe dose range, evaluate side effects & establish final, correct dose for 1 – 1.5 yrs:
Pharmacokinetics are studied

1 phases of clinical trials: 10 – 100 healthy volunteers study safe dose range, evaluate side effects & establish final, correct dose for 1 – 1.5 yrs: “want ads” in
classified section of newspapers
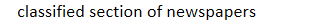
1 phases of clinical trials: 10 – 100 healthy volunteers study safe dose range, evaluate side effects & establish final, correct dose for 1 – 1.5 yrs: informed consent is
mandatory
1 phases of clinical trials: 10-100 healthy volunteers
study safe dose range, evaluate side effects & establish final, correct dose for 1 – 1.5 yrs
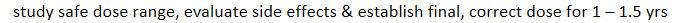
2 phase of clinical trials: given to 50-500 patients who have
disease/condition on experimental basis for ~ 2 yrs

3 phase of clinical trials: administered to several hundred/thousand ill patients in exactly way in which it will be used once it’s on the market for ~ 3 yrs: relative
effectiveness evaluated
3 phase of clinical trials: administered to several hundred/thousand ill patients in exactly way in which it will be used once it’s on the market for ~ 3 yrs: double-blind
studies conducted (placebo)

3 phase of clinical trials: administered to several hundred/thousand ill patients in exactly way in which it will be used once it’s on the market for ~ 3 yrs: ____________ studies
gender issues
3 phase of clinical trials: administered to several hundred/thousand
ill patients in exactly way in which it will be used once it’s on the market for ~ 3 yrs

3 FDA drug classifications
over the counter (OTC)
prescription (legend)
controlled substances
3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): usually
first line of defense
3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): may be same as
prescription ingredients but dosage is much smaller
3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): 1992 OTC Drugs Advisory Committee created to
review drugs & determine which ones are safe/appropriate for OTC use

3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): must meet following criteria - use of drug doesn’t
require patient to have special monitoring or testing
3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): must meet following criteria - low rate of
effects/toxicity and low potential for abuse
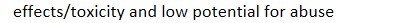
3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): must meet following criteria - patient can easily
easily diagnose/monitor their own condition

3 FDA drug classifications: over the counter (OTC): must meet following criteria - indication for use is
similar to prescription drug
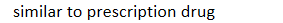
3 FDA drug classifications: prescription (legend): must contain
specific information
3 FDA drug classifications: prescription (legend): there has to be
mandatory information on the label

3 FDA drug classifications: prescription (legend):
Name
When to be taken

3 FDA drug classifications: prescription (legend):
Patient name
What form given
How much are in the container
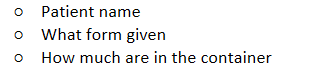
3 FDA drug classifications: prescription (legend):
Is there a refill
Who's the manufacturer
Expiration data

3 FDA drug classifications: controlled substances: drugs with potential for
abuse and dependence
3 FDA drug classifications: controlled substances: C followed by
class I-V
3 FDA drug classifications: controlled substances: manufacturing, storage,
dispensing and disposal are strictly regulated by federal and state laws
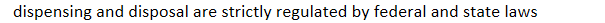
3 FDA drug classifications: controlled substances: must register with
DEA and be issued DEA certificate and number to prescribe/dispense drugs

3 FDA drug classifications: controlled substances: some states also require the
health care provider register with state agency that controls scheduled drugs
half life = T1/2 : short half life =
frequent dosage
If liver/kidney isn’t functioning correctly, higher dosages of meds circulate for longer
half life = T1/2 : standard method of expressing how long it take to
metabolize and excrete 50% of a drug
Major determinant of duration of drug action
half life = T1/2 : major determinant of
duration of drug action

half life = T1/2 : because they are the same for everyone,
it helps determine the dosage, frequency and duration needed for administration

half life = T1/2 : low long it take for the body to get rid of
50% of the drug from the body

half life = T1/2 : basing ____________ on half life
dosing
drug patents: are
trade name registered with US patent office
drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: Last segment Package Code:
id’s package size/type
i.e. NDC# 00185-0144-60
Amiodarone 200 mg – 40 tabs – Eon Lab Manufacturing
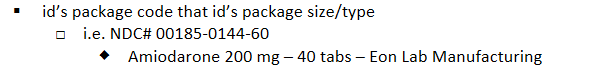
drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: NDC - Next segment Product Code:
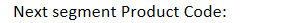
id’s drug’s specific strength/dose
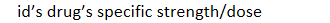
drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: NDC - 1st 3 segment labeler code
id’s drug company
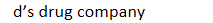
drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: ___________________ are assigned to each drug
national drug codes
drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: after 17 years, any drug company can manufacture
drug under its original generic name or new trade name

drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: protected by
17 year patent
Testing process included in 17 years

drug patents: trade name registered with US patent office: Original drug company has
right to advertise and market

drug withdrawals and recalls: Post-market surveillance performed by
FDA and drug companies

drug withdrawals and recalls: Certain adverse drug effects only
become apparent over time

drug withdrawals and recalls: Healthcare professionals and consumers should report through

MedWatch Adverse Event and Safety Program

drug withdrawals and recalls: MedWatch
monitor what drugs are recalled
