2.2 - Trade Creation & Trade Distortion
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Multilateral liberalisation and X supply curve
With multilateral liberalisation we can summarise RoW with a common export supply curve
pw in the small country case
Regional liberalisation and X supply curve
With regional liberalisation the partner matters as nations differ in efficiencies
More efficient = S at lower p
Less efficient dom producers displaced
Trade Creation
Replacement of less efficient producers by more efficient
Welfare raising
Trade diversion
Efficient producers outside RTA replaced by less efficient inside RTA
Welfare lowering
Discriminatory liberalisation welfare effects
Can lead to ambiguous welfare effects under first best conditions
TC vs TD
CU model - assumptions
1st best conditions
Increasing costs for H producers
Regional / global producers supply at constant cost
H, F and RoW
CU model - TC
RTA forming removes tariff on M for partner
pp < pw
M from partner increase (some dom production replaced) + C increase
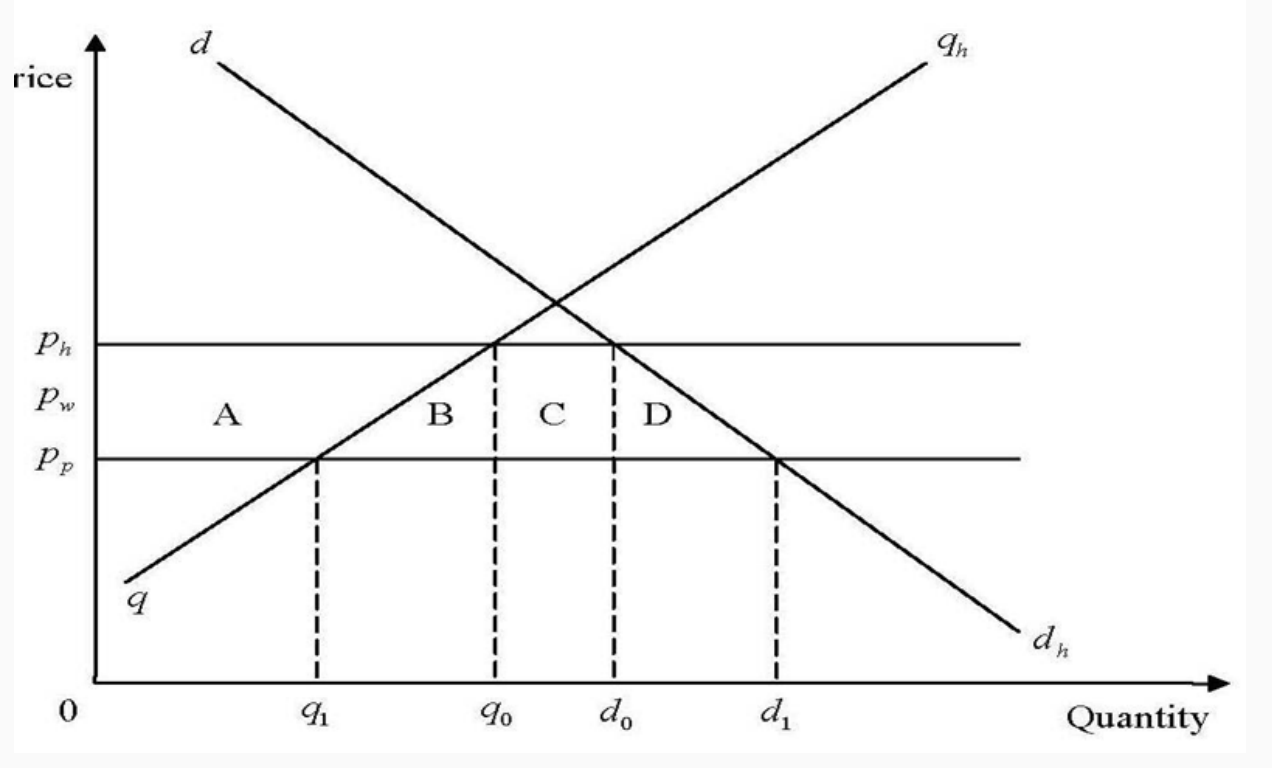
CU model - TD
Discriminatory tariff cut shifts X from RoW → Partner as pp < pw + t
Trade diverted = d0 - q0
TC = q1-q0 + d1-d0
Welfare effects:
CS gain = A+B+C+D
PS loss = -A
Tariff loss = -(C+G)
Net effect = B+D-G
B = TC displacement of inefficient dom producers
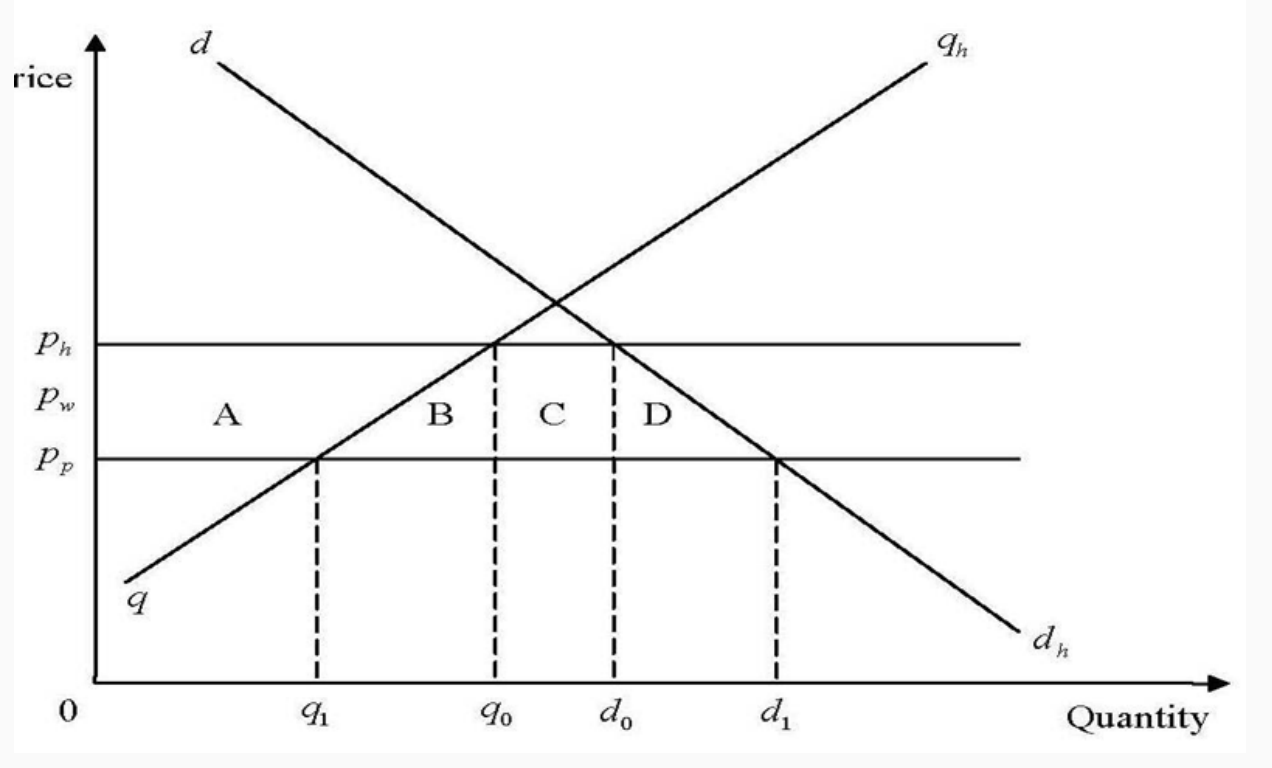
CU model - TC welfare effects
Welfare effects:
CS gain = A+B+C+D
PS loss = -A
Tariff revenue loss = C
Net effect = B+D
Effect same as multilateral liberalisation
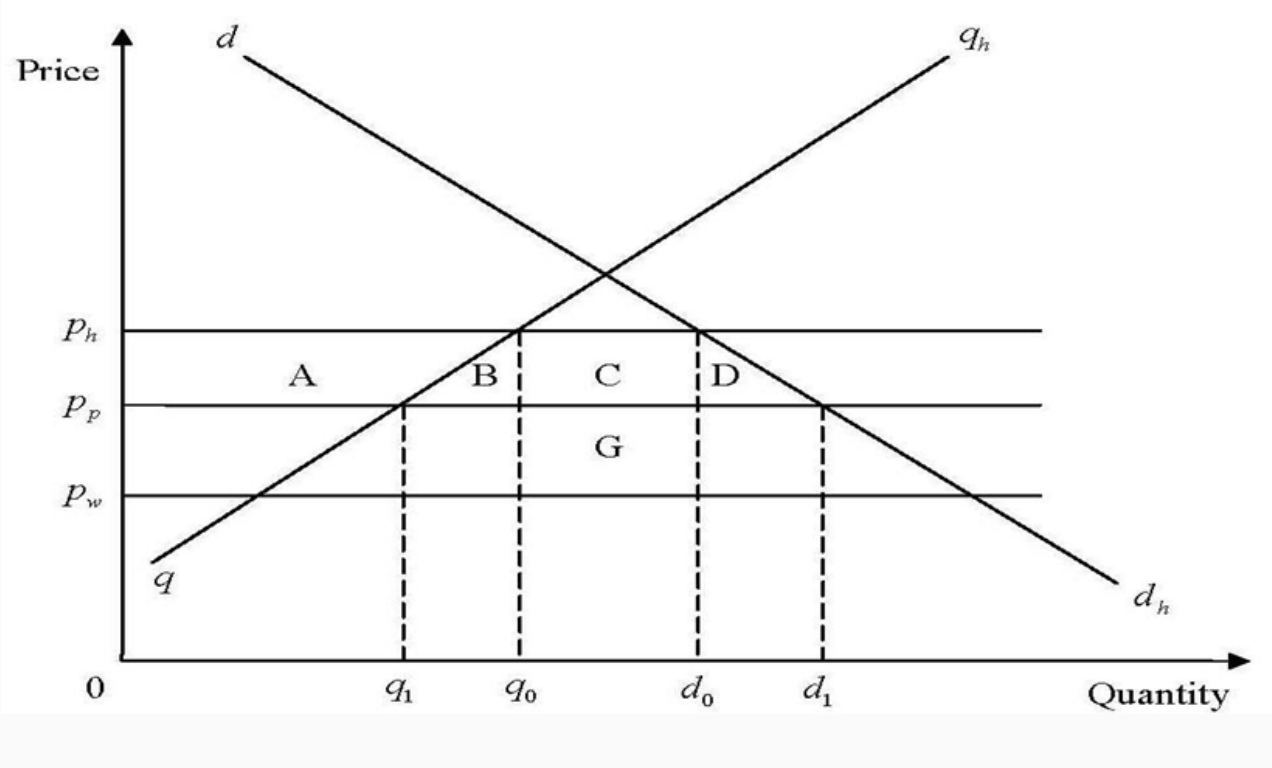
CU model - TD welfare effects
Welfare effects:
CS gain = A+B+C+D
PS loss = -A
Tariff loss = -(C+G)
Net effect = B+D-G
B = TC displacement of inefficient dom producers
D = increased C
E = additional cost of M from less efficient regional partner
Caveats to gains and losses from RTAs
TD is a loss as we assume MC of partner & RoW constant
With decreasing MC the loss may be eliminated
We assume that there is constant cost of X Supply by partner = no PS gains for partner
with increasing costs of X, RTA loses overall in net terms as costs of TD for M < benefits to X nation
When are RTA welfare effects less ambiguous
More likely to be beneficial if:
Regional grouping large - Share of World GDP & no. nations in RTA
more leverage to extract TOT gains from RoW by exploiting market power
Region includes globally efficient producers (competing not complementary producers)
External trade barriers low
Internal trade barriers eliminated
Other positive effects - TOT gains or scale effects