Abdomen
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
AP supine abdomen
KUB (kidneys ureters and bladder)
AP Abdomen 1 view
Acute Abdomen series
2 view abdomen
flat and erect abdomen
PA chest may be included with 2 view abdomen
What soft tissue structures can be visualized on abdomen radiograph?
Muscles
Liver
Kidney
Bladder
What digestive structures can be visualized on abdomen radiograph?
Air filled/fecal filled stomach, small and large intestines
What bones can be visualized on abdomen radiograph?
Spine
Hips
Pelvis
Inferior ribs
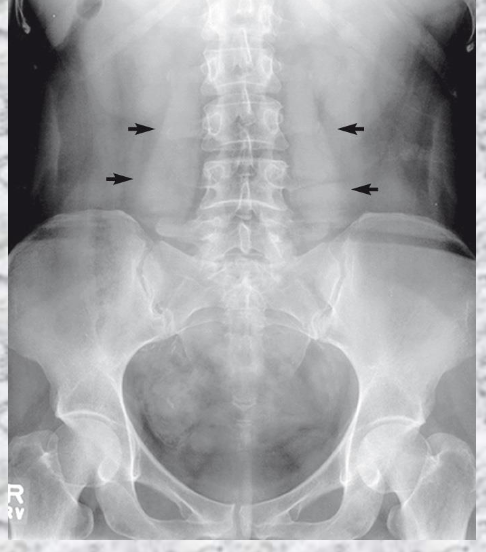
What is seen?
Psoas Muscles
What organ systems are located in the abdominal cavity?
Digestive tract w/ accessory organs
Spleen
Urinary System
Female reproductive
Accessory organs
-Liver
-Gallbadder
-Pancreas
-Spleen
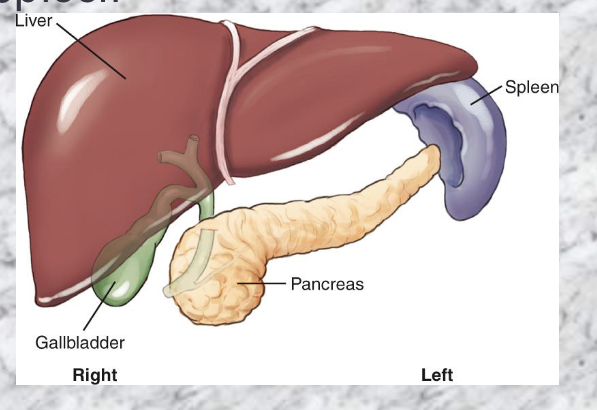
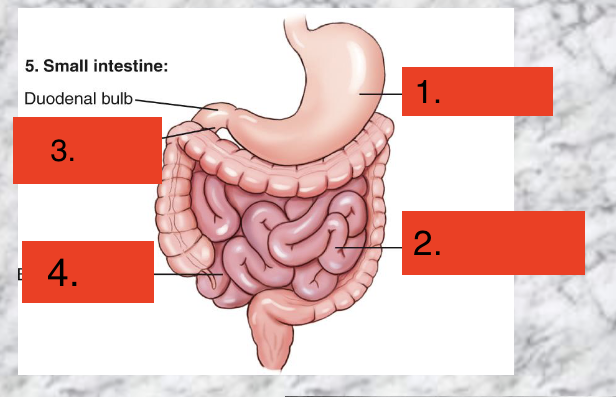
Stomach
Ileum (3/5 of small intestine)
Duodenum (Shortest and Widest)
Jejunum(2/5 of small intestine)
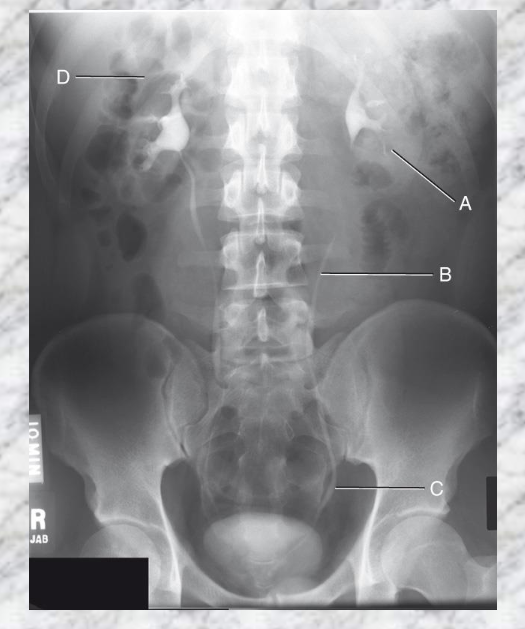
A. Left Kidney
B. Left Ureter
D. Adrenal glands
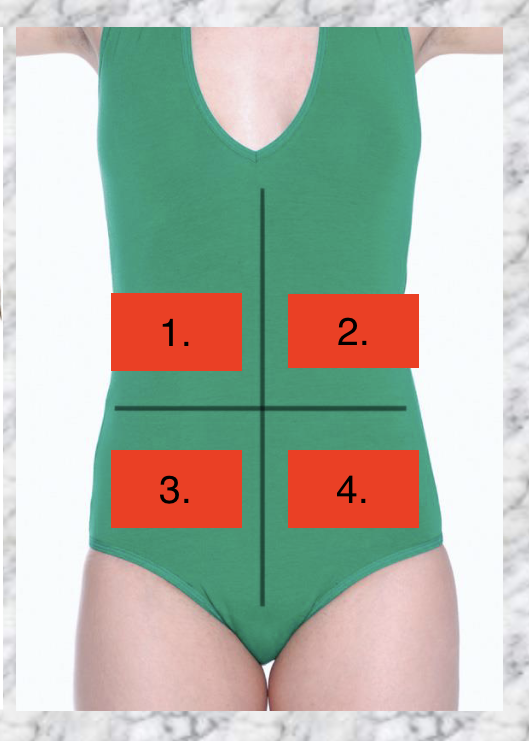

Label the abdominal quadrants
RUQ
LUQ
RLQ
LLQ
What is found in RUQ?
Liver
Gallbldder
What is found in LUQ?
Spleen
Stomach
What is found in RLQ?
Appendix
Ascending colon
What is found in LLQ?
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Retroperitoneal
Retro=backward or behind
Less mobile structures within the abdomen
-Right kidney
-Pancreas
Intraperitoneal
Partially or wholly covered
-Liver
-Gallbladder
Infraperitoneal
Located under or beneath the peritoneum
-Bladder
-reproductive organs
Topographic landmarks for abdomen?
Xiphoid process (T9-T10)
Inferior costal margin (L2-L3)
Iliac crest (L4-L5)
ASIS - 2nd sacral segment
Greater trochanter
Symphysis pubis- coccyx
Ischial tiberosity
AP abdomen/KUB
KVP : 75-85
SID: 40
Expiration breathing
Shortest exposure time
MSP centered to center of table
Central ray at iliac crest
Must include symphysis
-Look at iliac wings/pelvis = rotation
Bladder shot
If symphysis pubis is missed on KUB = need a bladder shot
-CR 2 inches inferior to ASIS
PA Abdomen
Advantage - Natural compression & possible decrease in technique
Prone abdomen utilized for small bowel series
CR at iliac crest
Symphysis pubis is visible
kidneys and lower liver margin are included
Erect AP Abdomen
Why?
Why erect? See air fluid levels
Must include diaphragm by centering 2 inches above iliac crest - See free air
inches to cm?
1 inch = 2.54 cm
Semi Erect AP abdomen
(Sitting on stretcher/bed)
-Tube parallel to floor to elimate distortion of air fluid levels
-May not be able to achieve 40 inch SID
-Center at least 2 inches superior to iliac crest
Left Lateral Decubitus
-air fluid levels
-Left lateral would have fluid in the left side and free air will rise and collect under right hemidiaphram
-Fluid = left side
-Air= right side
-CR 2 inches above iliac crest to include diaphram
Dorsal decubitus - Right or left
Center where?
Why?
-CR 2 inches above iliac crest at midcoronal plane
-Aneurysms or calcified aorta or umbilical hernia
Acute Abdomen series 3 view
3 View: AP supine, AP erect, PA chest
Acute Abdomen series 2 view
2 view: AP supine, AP erect or left lateral decubitus (must include diaphragm)
Pathologic Indications for acute abdomen series
Ileus
Dynamic/mechanical - Adhesions, Intusseption, Crohns, Volvulus
Adynamic/non-mechanical
Ascites
Perforation
Postop (abdominal surgery)
Digestive tract
oral cavity
Pharynx
Esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
Ascites
an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity of the abdomen
Radioopague
increase
ileus
Adynamic/non-mechanical (no power or force) - intestines stop moving normally, no blockage, paralysis
Dynamic/mechanical- physical blockage, bowel is still trying to push
Decrease
Perforation
hole or tear in wall of stomach or intestines
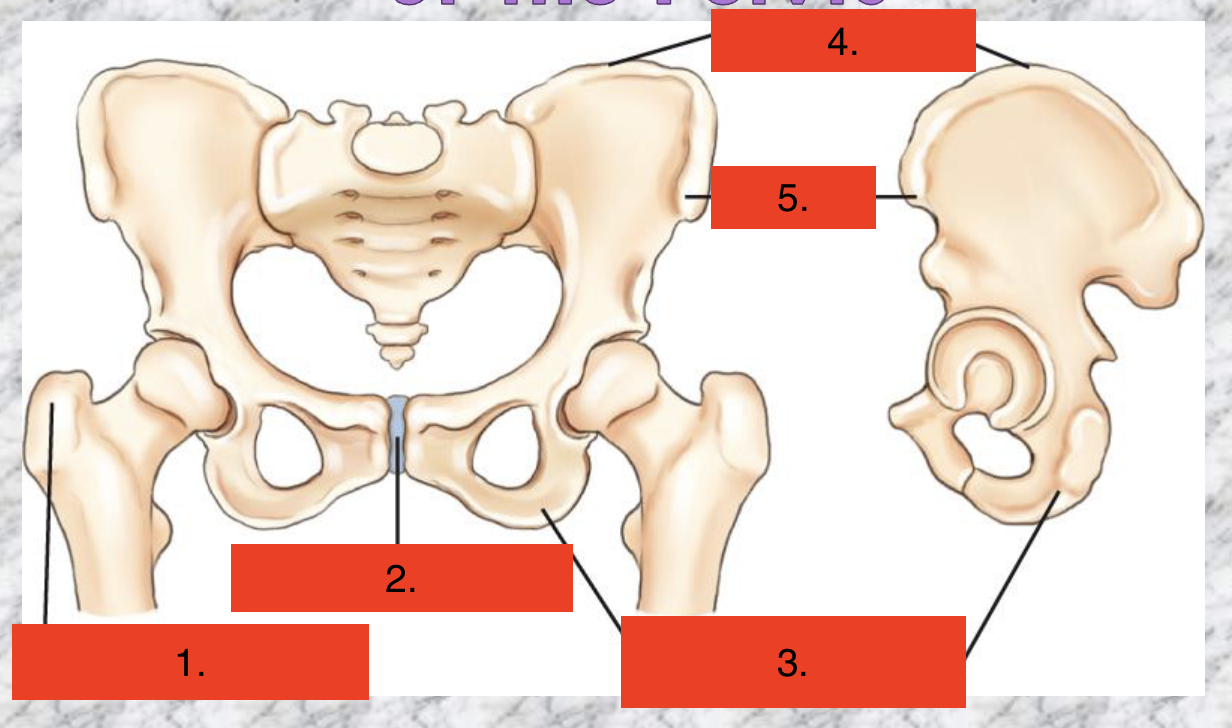
Greater trochanter
Symphysis Pubis
Ischial Tuberosity
Crest of ilium
ASIS