WJEC AS Chemistry (1.4 Bonding)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Ions
Ions are charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons.
Ions form as they are more stable (less energy) as a result forming full shells
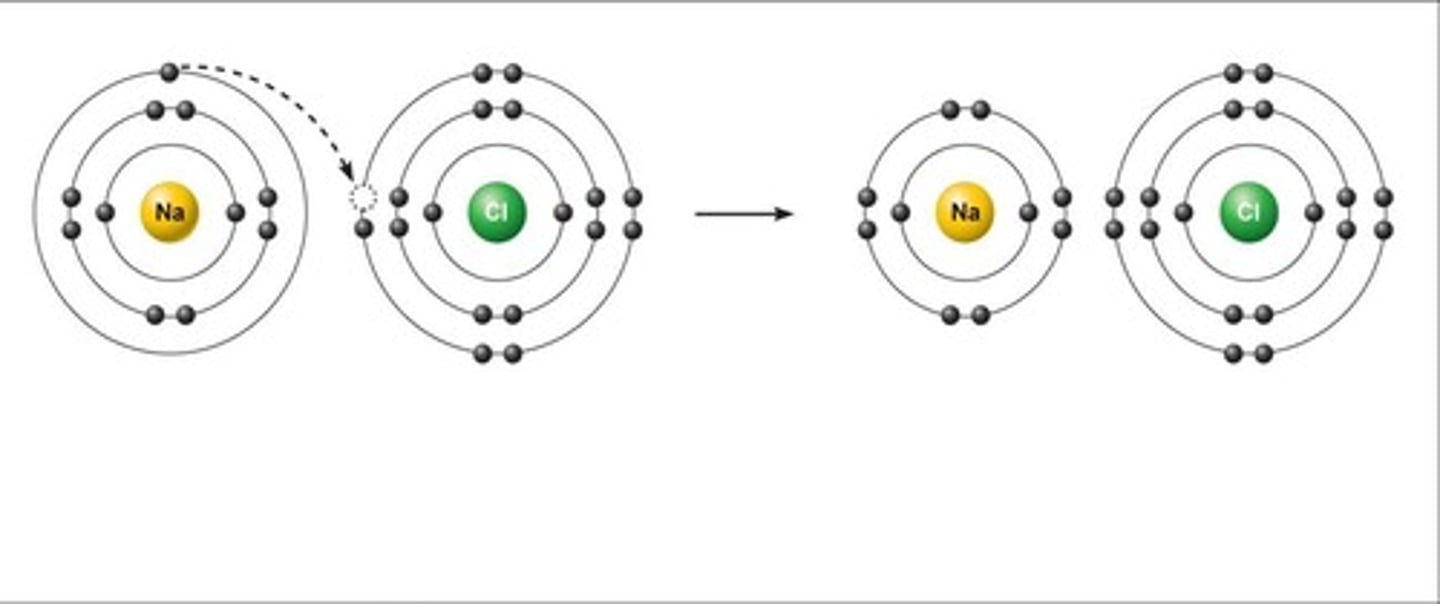
Ionic Bonding
The strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions ( Cation and Anion)
Between a metal and non metal
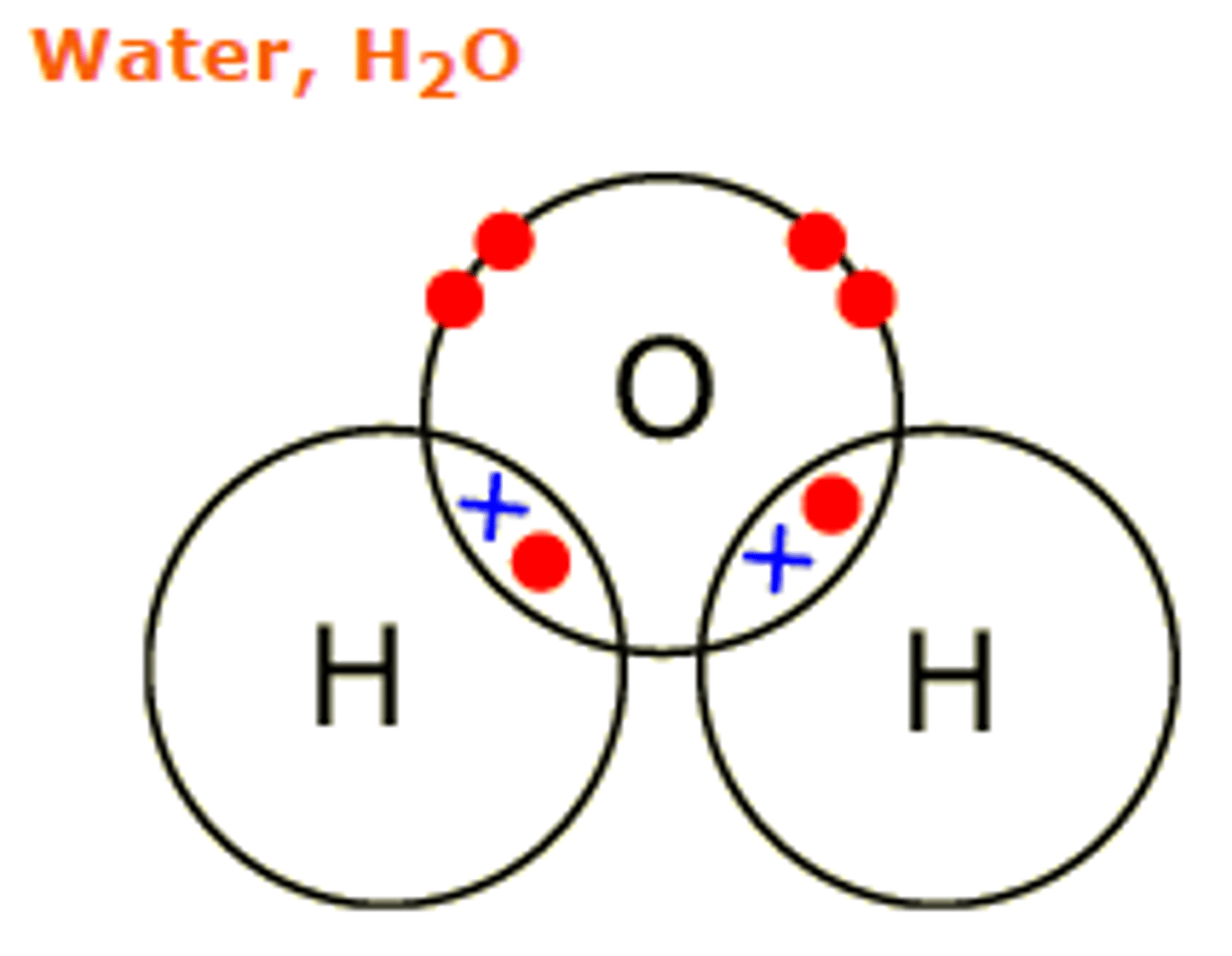
Covalent Bonds
A strong attraction between a shared pars of electrons between two nuclei
Between two non metals
Inside a covalent bond
Electrons are within an orbital, electrons move around this orbitals randomly. The orbital exists between two nuclei.
Coordinate bonds
A covalent bond in which both electrons come from one of the atoms
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract the electron density in a covalent bond towards itself

5 Electronegative atoms
Fluorine, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Bromine, Chlorine
Atomic Radius
Distance from nucleus to outer electrons, Bigger atomic radius the holder to hold
Shielding
The number of full shells in between the nucleus and the outer electron
Effective Nuclear Charge
The amount of protons in the nucleus and they hold on to the outer electrons.
Atomic radius vs Effective nuclear charge
AS atomic radius increase effective nuclear charge decrease. Visa versa
Type of Bonding
0 = Non-polar covalent
>0 <1.7 Polar Covalent
>1.7 Ionic
Intermolecular Bonding
Weak bonding holding the molecules together
Intramolecular Bonding
Strong bonding between atoms in the molecule.
Van der waals
All types of intermolecular force whether dipole or induced dipole. A temporary dipole is formed between the neighbouring molecule.
Movement of electrons on orbital
Electrons move randomly in the orbital and both electrons will eventually move to the same side and make a dipole charge.
Dipole-Dipole
Very strong made when Fluorine, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Bromine, Chlorine are present. They are permanent
Hydrogen bonds
Occurs when Fluorine, Oxygen, Nitrogen are directly bonded.
Bond strength
Covalent
Ionic with covalent characters
Ionic
Hydrogen Bonds
Dipole-Dipole
Van der waals
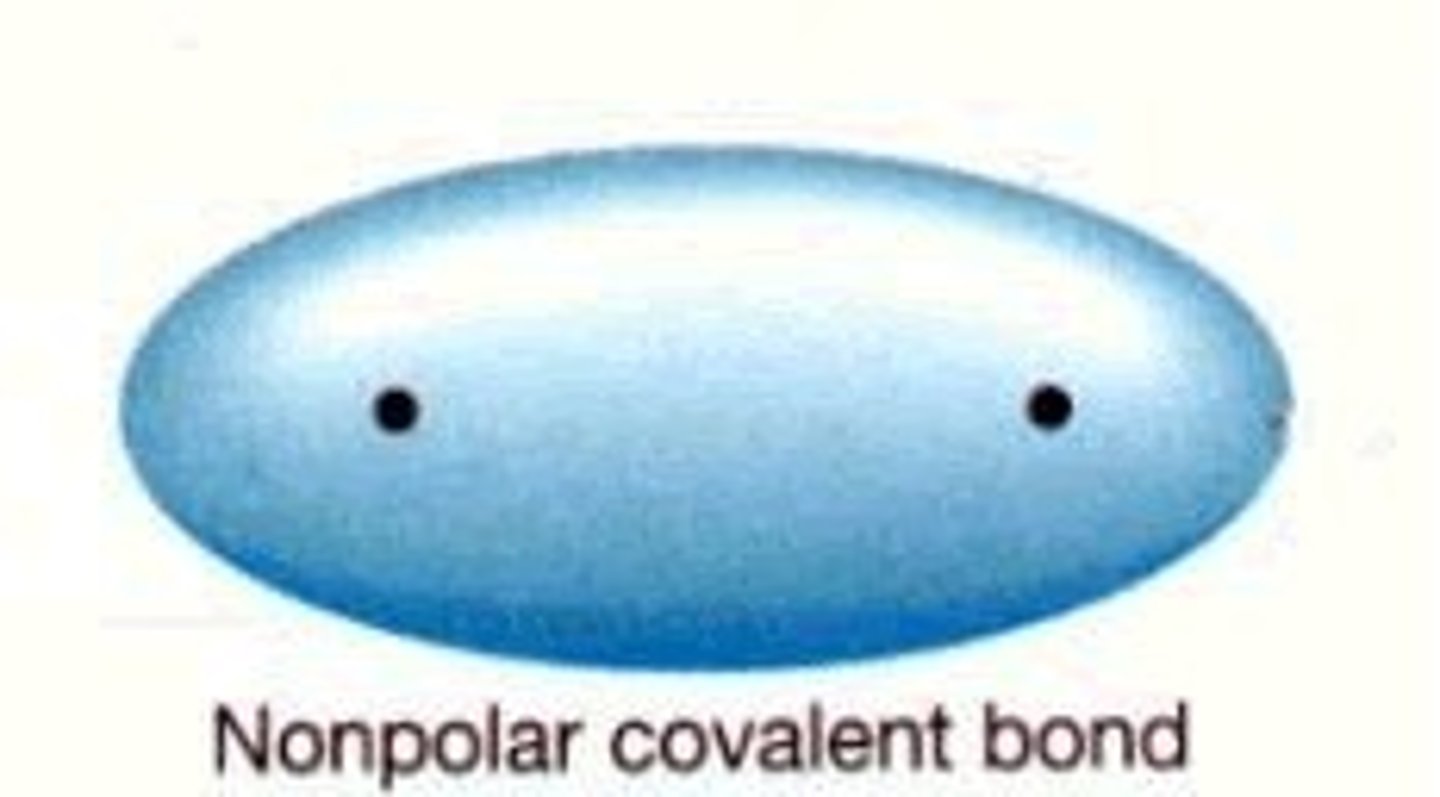
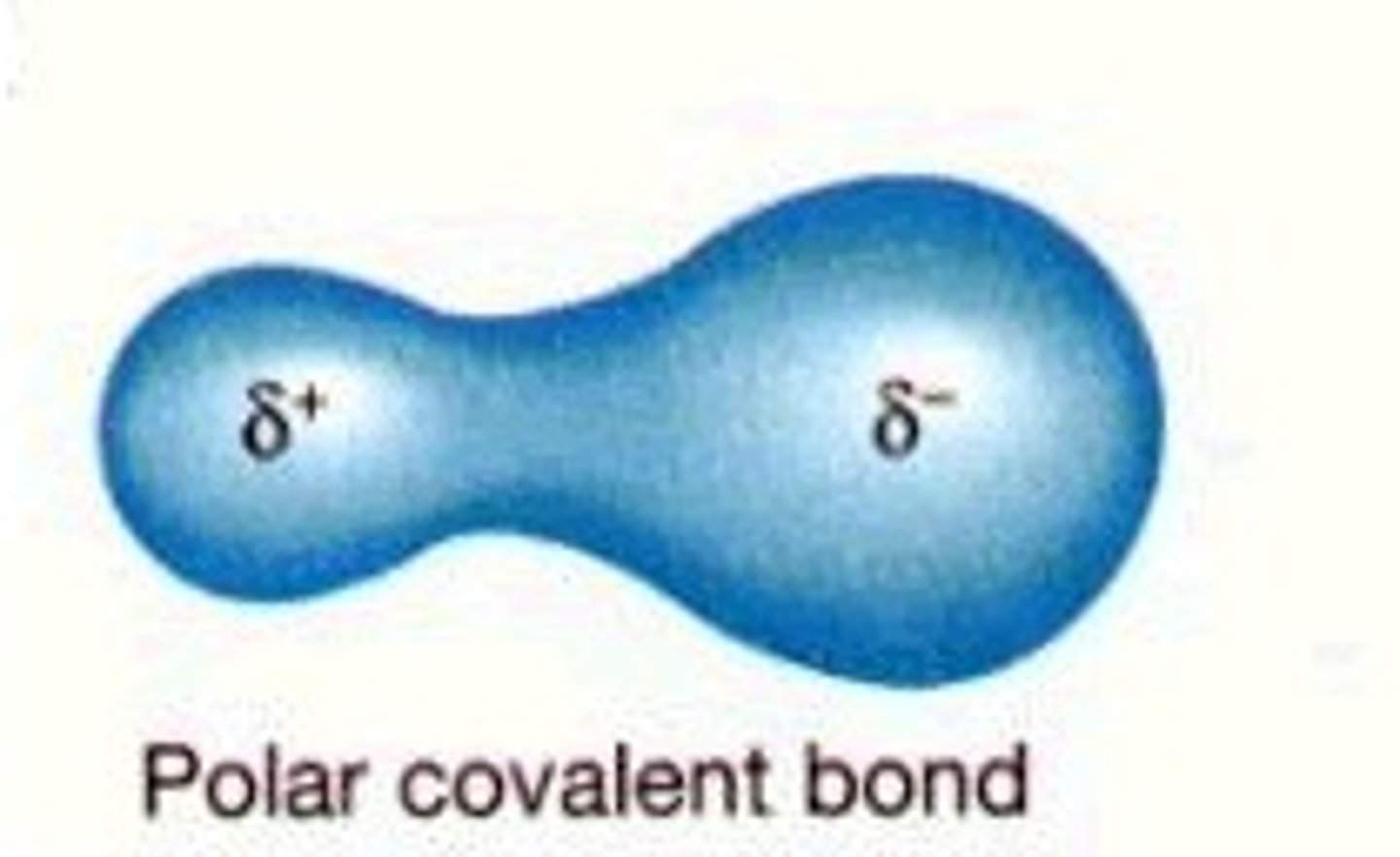
polarity of a covalent bond
Polarity mean charge, if there is a charge associated with e bond we say its polar
non-polar covalent
Polar covalent
Spends more time on side of the orbital
Soluble
Dissolve in a substance
Insoluble
Won't dissolve in a substance
Solute
Is the substance that dissolves
Solvent
What solutes dissolve in
Solution
Mixture of solvent and solute
Solubility
How well it dissolves
Intermoleuclar forces and solubility
Van der waals = Non-polar molecule (Water is polar Van der waals are weak and non polar, they do not attract
Dipole-Dipole and Hydrogen bonds = polar molecule
Both molecules are polar so there forces are attracted.q
Shapes of molecules
Electron pairs will always mutually repel each other as far away as possible
Linear, 180° - 2 pairs of electrons
e.g BeCl₂
Trigonal Planar, 120⁰ - 3 pairs of electrons
e.g BCl₃
Tetrahedral, 109.5° - 4 pairs of electrons
e.g CH₄
Trigonal Bipyramid, 90° and 120⁰ - 5 pairs of electrons
e.g PCl₅
Octahedral, 90⁰ - 6 pairs of electrons
e.g SCl₆
How to draw
1. Draw dot and cross diagram
2. Add on lone pairs and bond pairs
3. Count number of bonds to work out shape