Face & Neck Injuries
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Anterior to the ear (temporal region)
Where can you palpate the superficial temporal artery?
foramen magnum
Large opening at the base of the skull where the brain connects to the spinal cord
Nasal bone
2 maxillae (upper jaw bones)
2 zygomas (cheek bones)
Mandible (jaw bone)
Major bones of the face
pinna
The external visible part of the ear
tragus
Small, rounded, fleshy bulge anterior to the ear canal
Tragus
The superficial temporal artery can be palpated anterior to the ________.
Mastoid process
Prominent bony mass at the bass of the skull
Cricoid cartilage
Firm ridge of cartilage (only complete circular cartilage structure of the trachea) below the thyroid cartilage
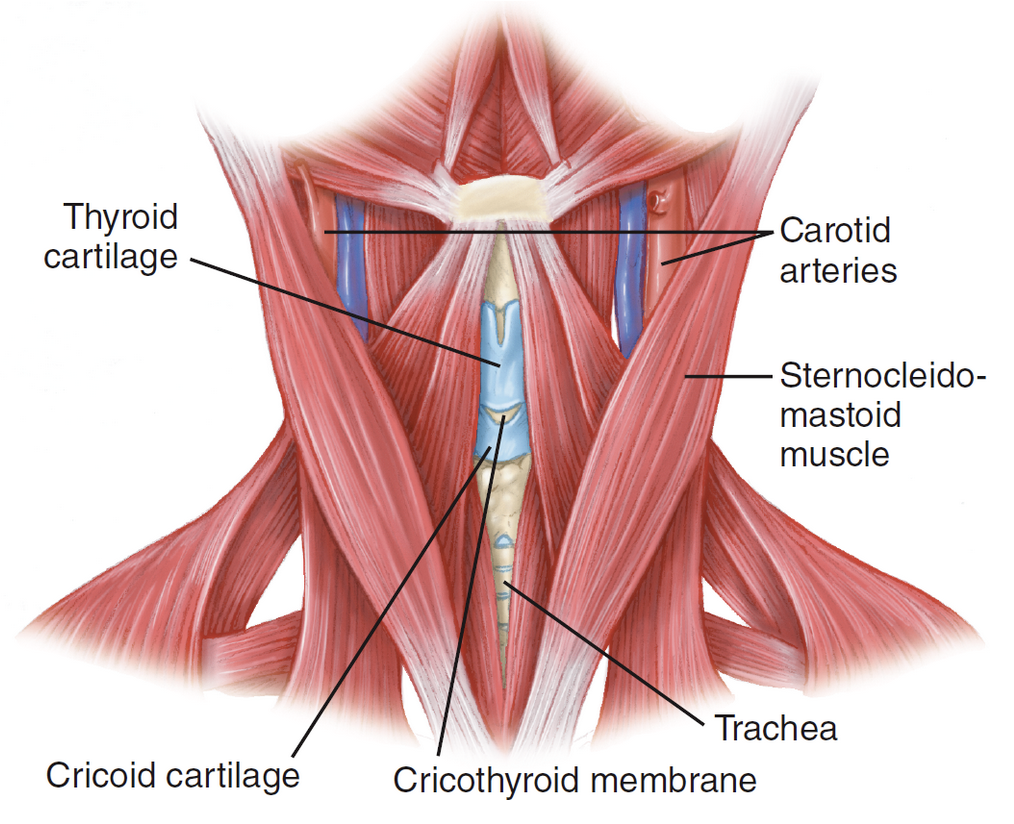
Cricothyroid membrane
Thin sheet of fascia connecting the thyroid and cricoid cartilages in the larynx
Trachea
Connects the oropharynx and the larynx. Main air passages of the lungs (bronchi).
C7
Most prominent spine when the head is flexed
thyroid gland
On either side of the lower larynx and upper trachea
eyeball
Globe
vitreous humor
Clear, jellylike fluid near the back of the eye
aqueous humor
In front of the lens of the eye, watery
conjunctiva
Delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covers the exposed surface of the eye
lacrimal glands
Tear glands, produce fluids to keep the eye moist.
Moves fluid from the lacrimal glands over the surface of the eye, cleans it. Tears drain on the inner side of the eye - through 2 lacrimal ducts → into the nasal cavity.
Describe how fluid moves in the eye during blinking
Sclera
Tough, fibrous, white portion of the eye that protects the more delicate inner structures.
Cornea
Front of the eye, clear transparent membrane that allows light to enter.
Iris
Pigmented - eye color. Muscle behind the cornea that dilates/constricts the pupil
Pupil
Circular opening in the middle of the iris that admits light to the back of the eye
Anisocoria
Pupils that are not equal
Lens
Behind the iris. Focuses images on the light-sensitive area at the back of the globe (retina).
Retina
Nerve endings that respond to light by transmitting nerve impulses through the optic nerve to the brain.
choroid
Layer of blood vessels that nourishes the retina at the back of the globe
Retinal detachment
Separation of the retina from the choroid and sclera at the back of the eye - nerve endings are no longer nourished and blindness ensues
Misaligned/missing teeth, numb chin, can’t open the mouth
Mandibular fx s/sx
Facial swelling, unstable facial bones, misaligned teeth
Maxillary fx s/sx
Risk of pushing the device into the cranial vault and brain tissue
Why is an NPA contraindicated for facial or head trauma?