psychopharmacology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
psychopharmacology
study of the effects of drugs on the nervous system and behavior
drug effects
changes in physiology and behavior following the ingestion of a drug; analgesia, euphoria, etc.
sites of action
are the biological sites at which drug molecules bind to or interact with cells in order to alter their physiological processes
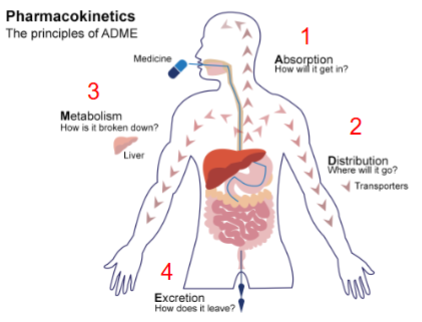
four principles of pharmacokinetics
absorption - how will it get in; distribution - where will it go (transporters); metabolism - how is it broken down (liver); excretion - how does it leave
blood brain barrier
prevents most water-soluble molecules from entering the brain
lipid soluble
molecules are most likely to reach the brain
dose - response curves
are graphs that show how effective a drug is depending on how much is administered
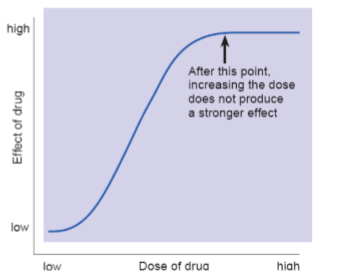
margin of safety
difference between the desired
therapeutic index
the ratio between the ED-50 and LD-50
affinity
level of attraction between drug and binding site
narcan
opioid overdose drug, extremely competitive
tolerance
When repeated administration of the drug causes a decrease in the effectiveness of that drug
sensitization
When repeated administration of the drug causes an increase in the effectiveness of the drug
allostatic load
created by repeated use then
causes withdrawal because of the compensatory
physiological changes caused by the drug
physical dependence
when the allostatic load has become strong enough to produce physical symptoms in the absence of the drug
compensatory changes
1. Decrease or increase in the effectiveness of receptor binding
2. Increase or decrease in the number of receptors available for binding
3. Ion channels coupled to receptors become less effective
4. Second messenger systems become less effective
placebo
inactive substances that contain no active drug molecules
placebo effect
inactive substances that contain no active drug molecules
vesicular transporters
neurotransmitters that are packaged into vesicles by proteins
direct antagonist
drug binds directly to receptor to activate it
noncompetitive binding
occurs when a drug molecule binds to one of these secondary sites
agonist
drugs that prevent increase amount of neurotransmitter at the synapse by blocking either of these causes changes in cellular activity
neurotransmitter
a chemical used for neuron to neuron communication
neuromodulator
chemicals that effect the neurotransmission of a whole group of different neurons in order to effect how they receive communication
gaba
inhibitory transmitter that is ubiquitous in the central nervous system
glutamic acid decarboxylase
synthesized as part of the degradation of glutamate
nigrostriatal
dopamine system projects from the substantia nigra to the basal ganglia
mesolimbic
dopamine system projects from the VTA to the limbic system (including nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hippocampus
mesocortical
dopamine system projects from the VTA to limbic cortex (prefrontal)
histimine system
roles in wakefulness; antihistamines cause drowsiness (newer ones do not break blood brain barrier); produced from histidine by the enzyme histidine decarboxylase
neuropeptides
• Consist of two or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds (large)
• Produced from Large precursor molecules by enzymes
• Released from all parts of the terminal
• Co-released with neurotransmitter
• No Reuptake mechanism
positive effect of endocannabinoids
• Analgesia
• Sedation
• Reduced nausea
• Decreased ocular pressure
negative effects of endocannabinoids
• Impairs concentration
• Affects memory
• Alters sensory perception and time perception