4.3 Organization of the Nervous System Diagram | Quizlet
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Supraspinal
The type of information processing that requires input from the brain and brainstem.
TERM
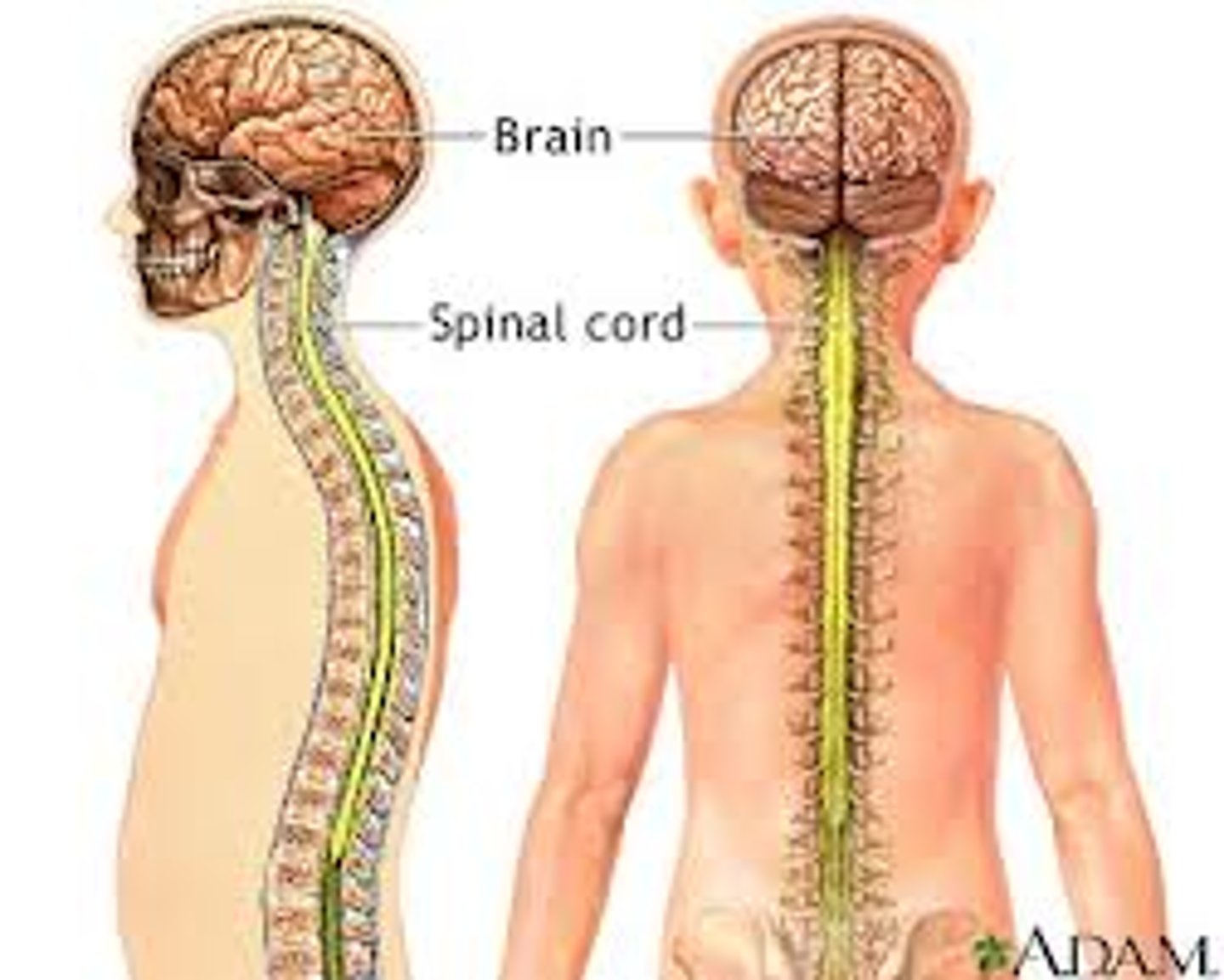
Central Nervous System
DEFINITION
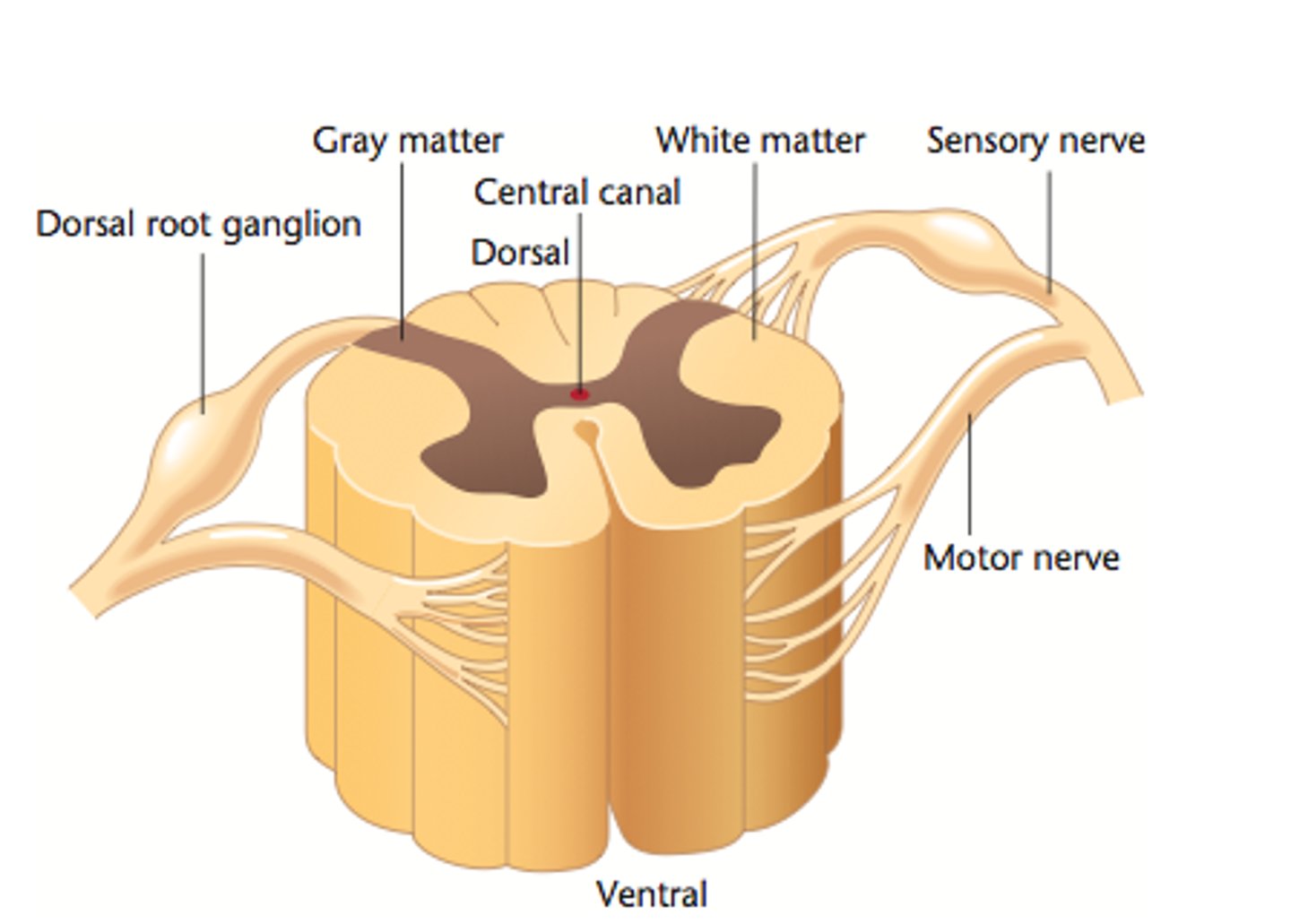
Brain and spinal cord. Consists of white and gray matter. Also includes the olfactory and optic nerves.
White Matter
Consists of axons encased in myelin sheaths. Deeper than gray matter in the brain, more shallow in the spinal cord.
Gray Matter
Consists of unmyelinated cell bodies and dendrites. Shallower than white matter in the brain, deeper in the spinal cord.
TERM
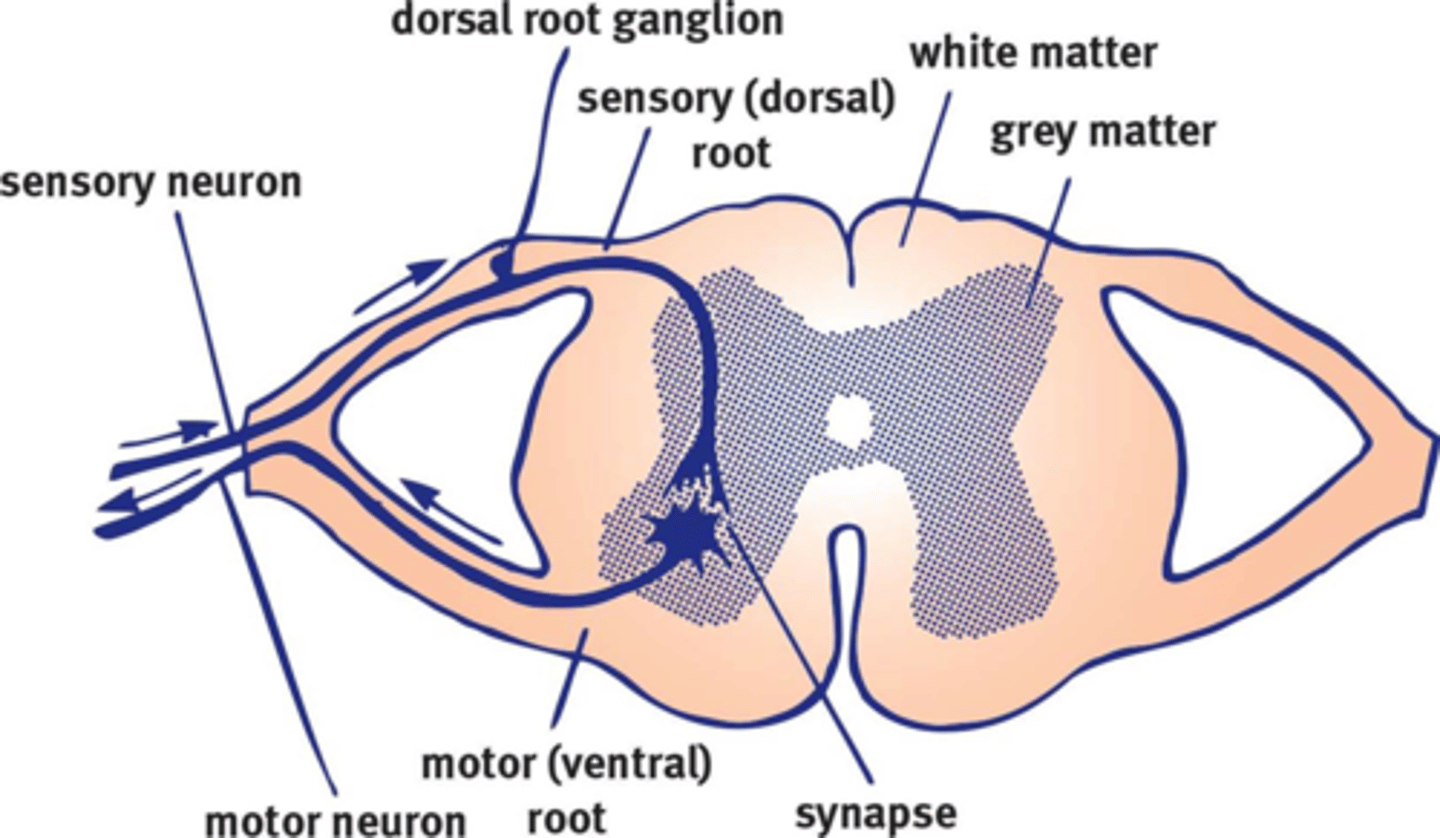
Spinal Cord
DEFINITION
Mnemonic:
SaD MoVie - Sensory roots are the Dorsal roots; Motor roots are the Ventral roots.
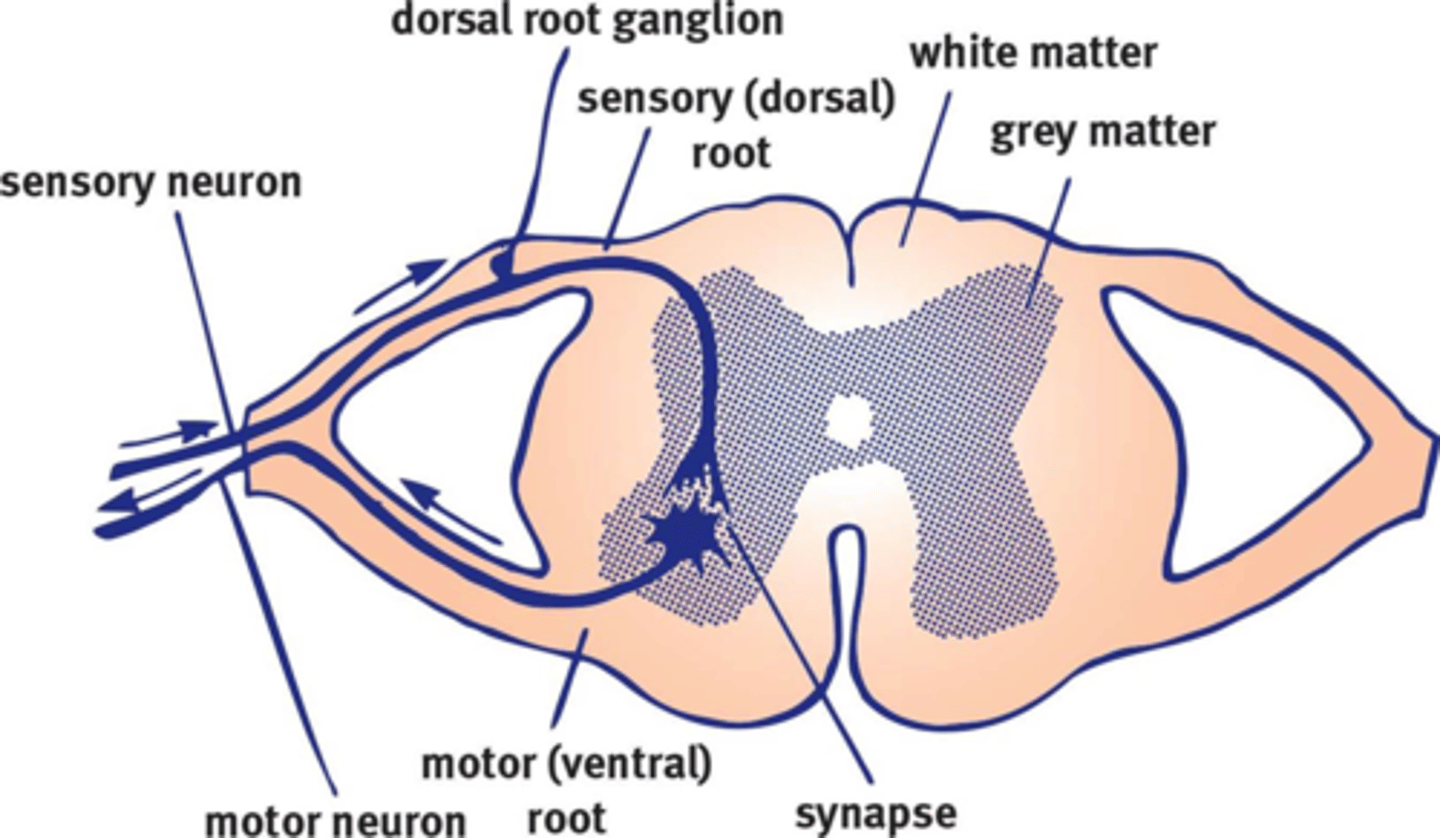
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral
Four divisions of the spinal cord.
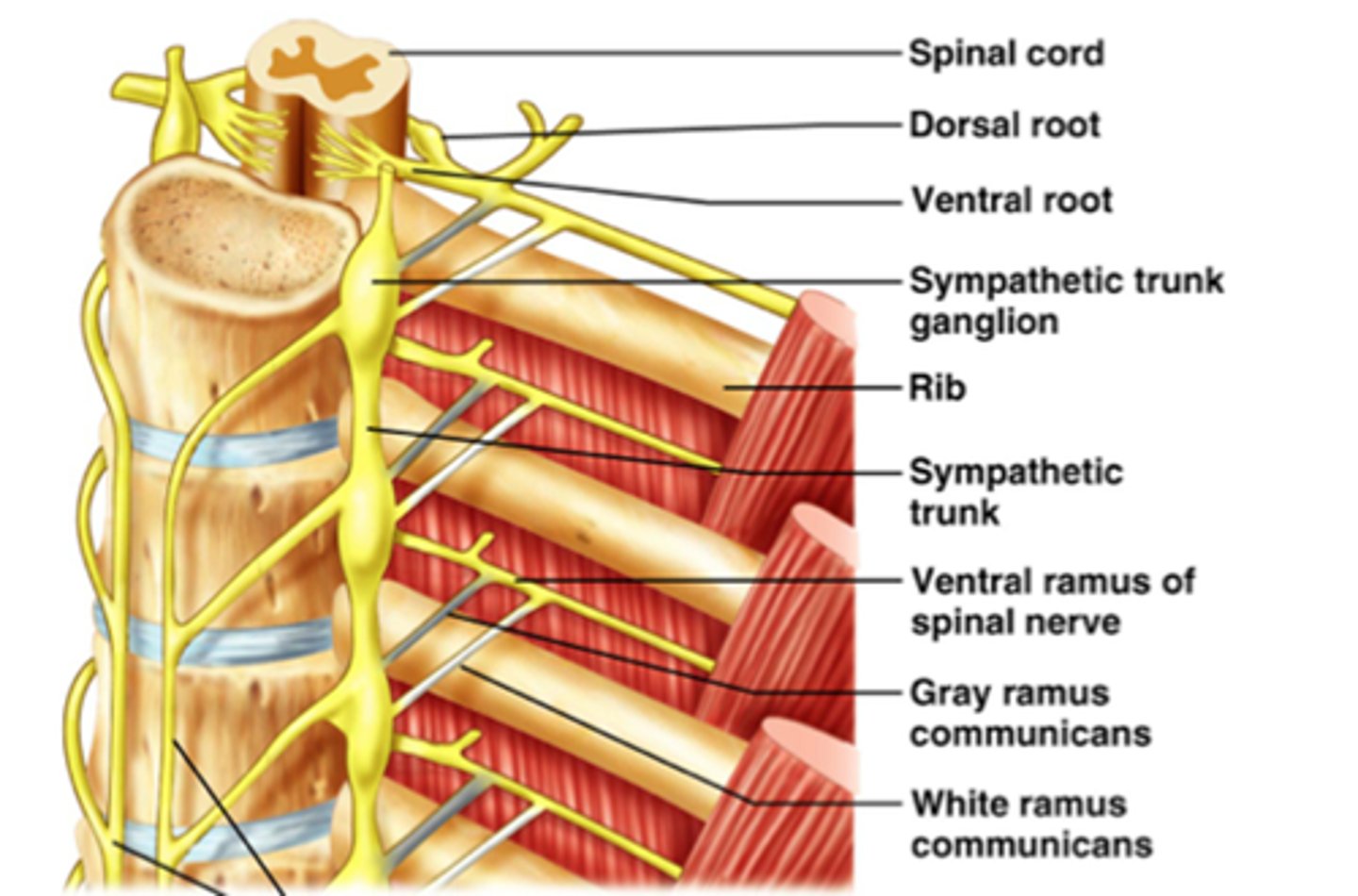
Dorsal Root Ganglia
Arising from embryonic neural crest cells, they contain the cell bodies of the sensory neurons. They are parallel to the cord, but unlike sympathetic ganglia, they are not chained.
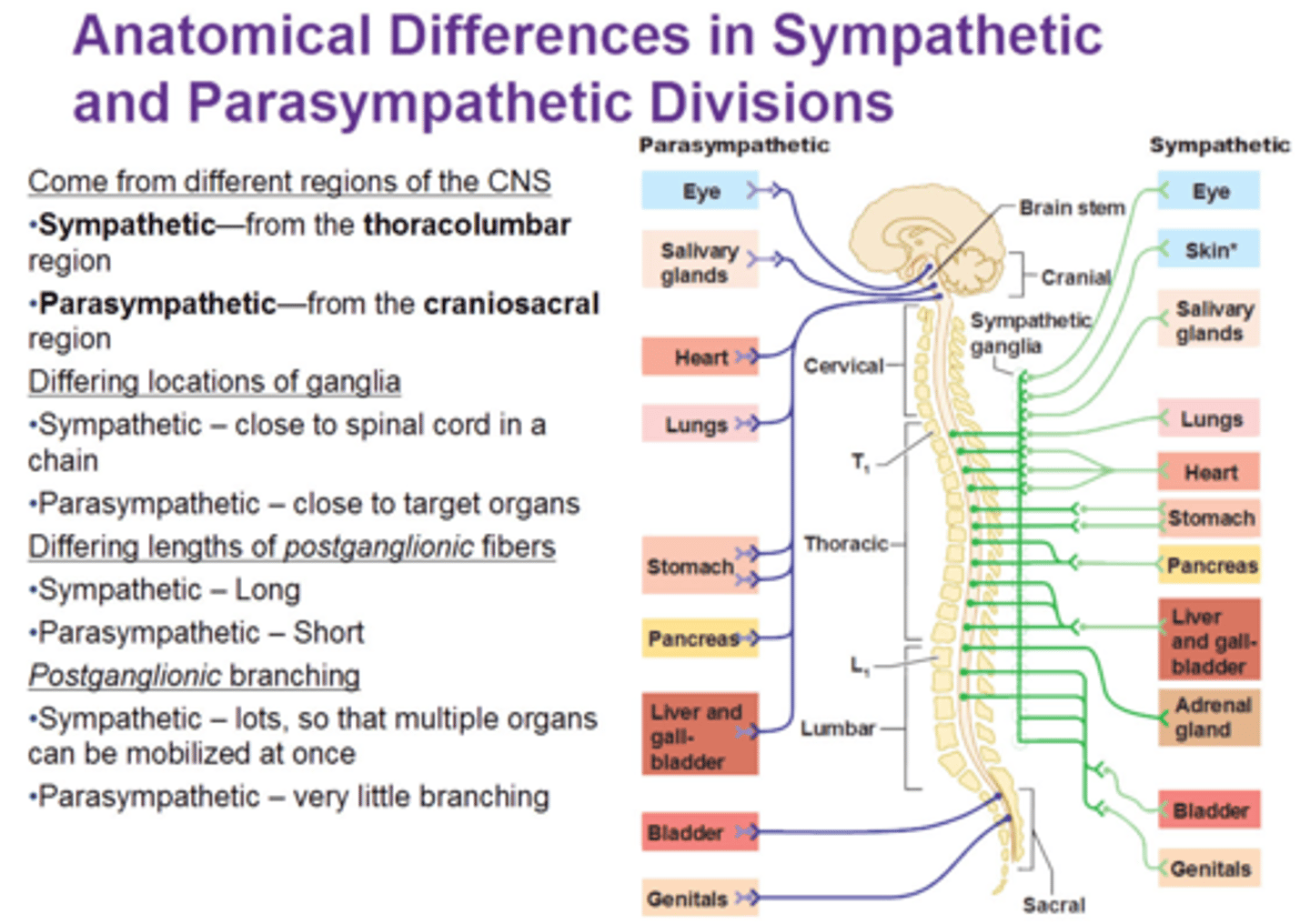
Anatomical Differences Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Ganglia
Sympathetic ganglia come from the thoracolumbar region, parasympathetic ganglia are synapsed by neurons originating in the craniosacral regions.
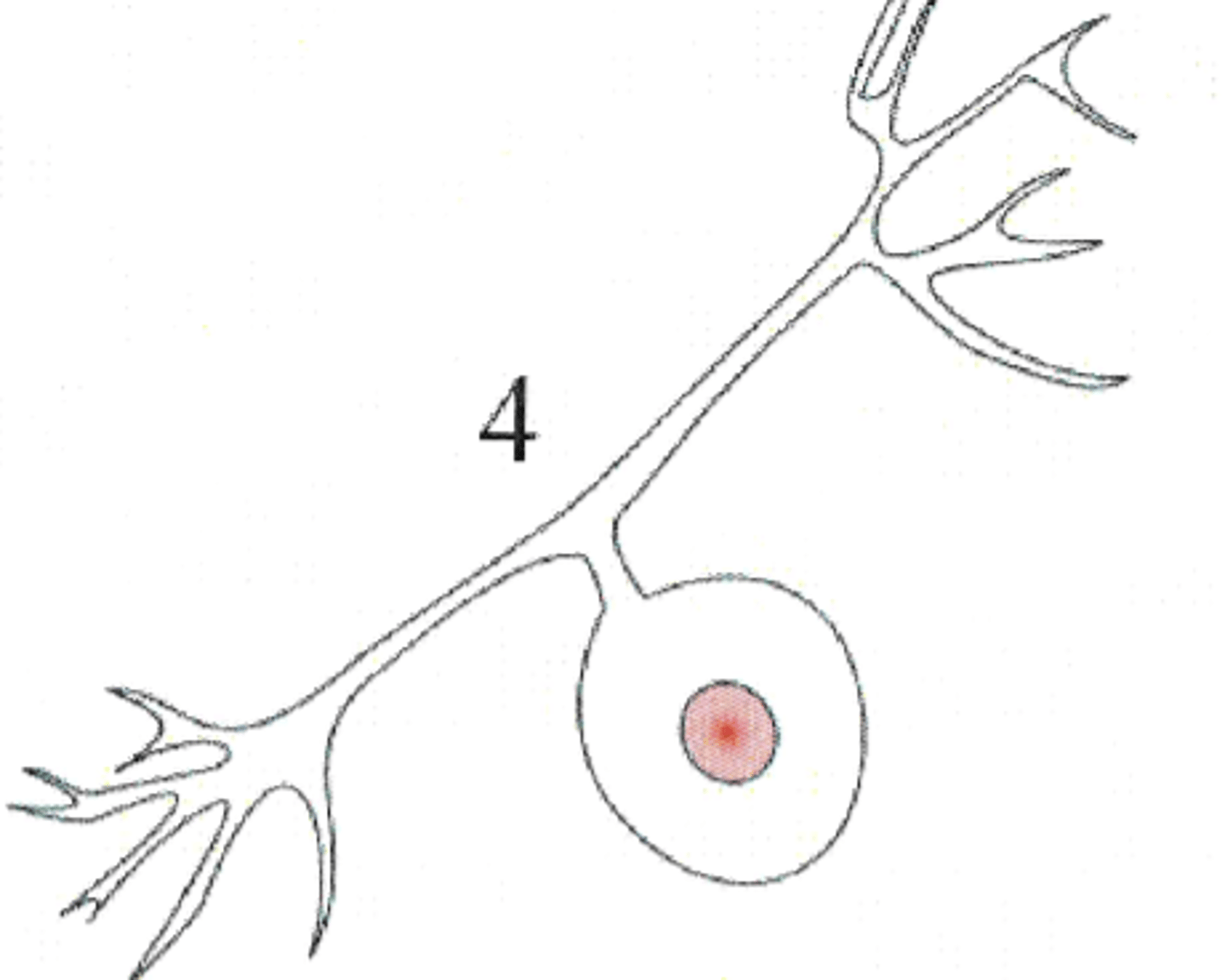
Pseudobipolar Neuron
Found in dorsal root ganglia, i.e. sensory. The offset cell bodies comprise much of the mass of dorsal root ganglia.
First-Order Neurons
Conduct impulses from somatic receptors into the brain stem or spinal cord.
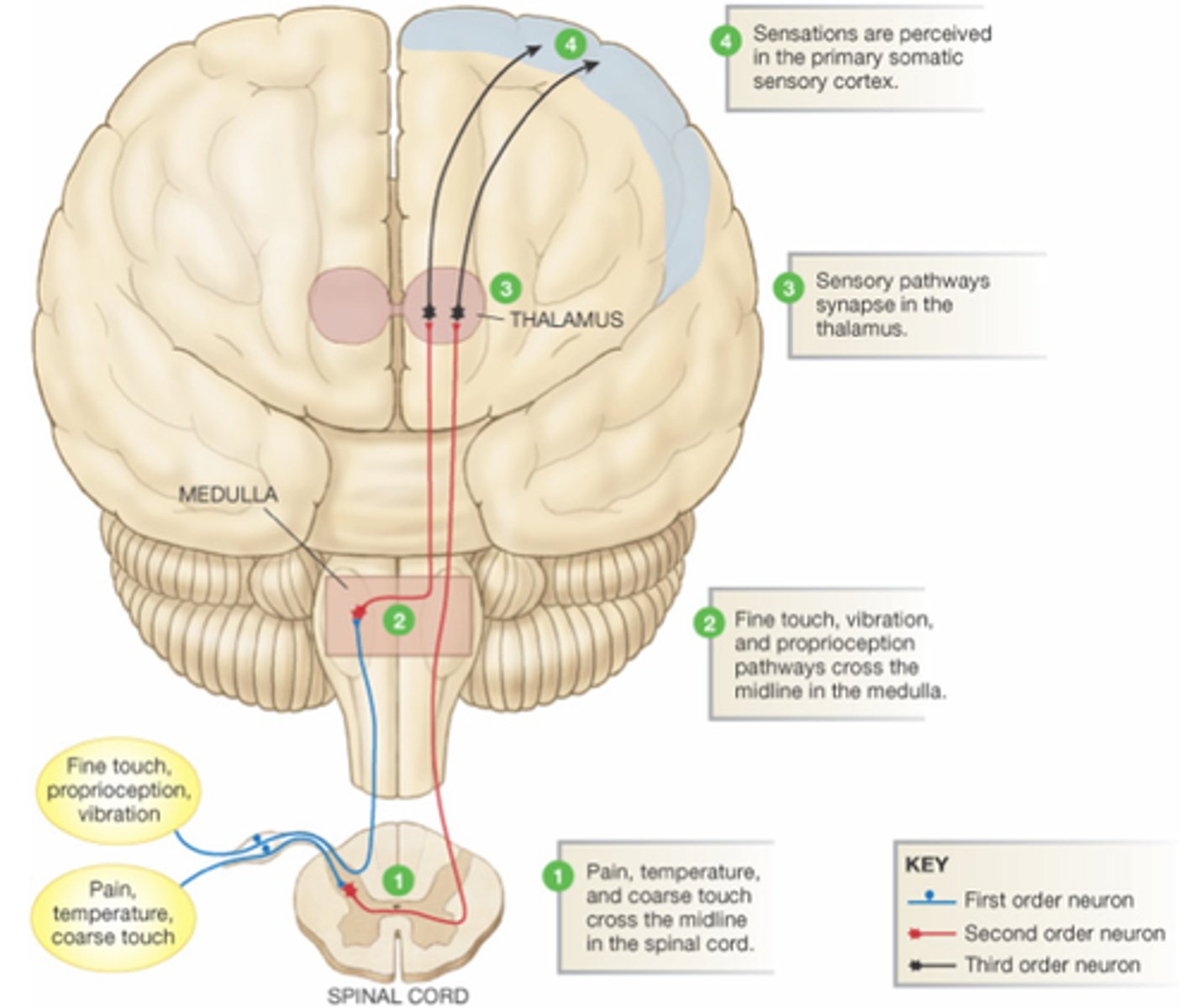
Second-Order Neurons
Transmit impulses from the brain stem and spinal cord to the thalamus.
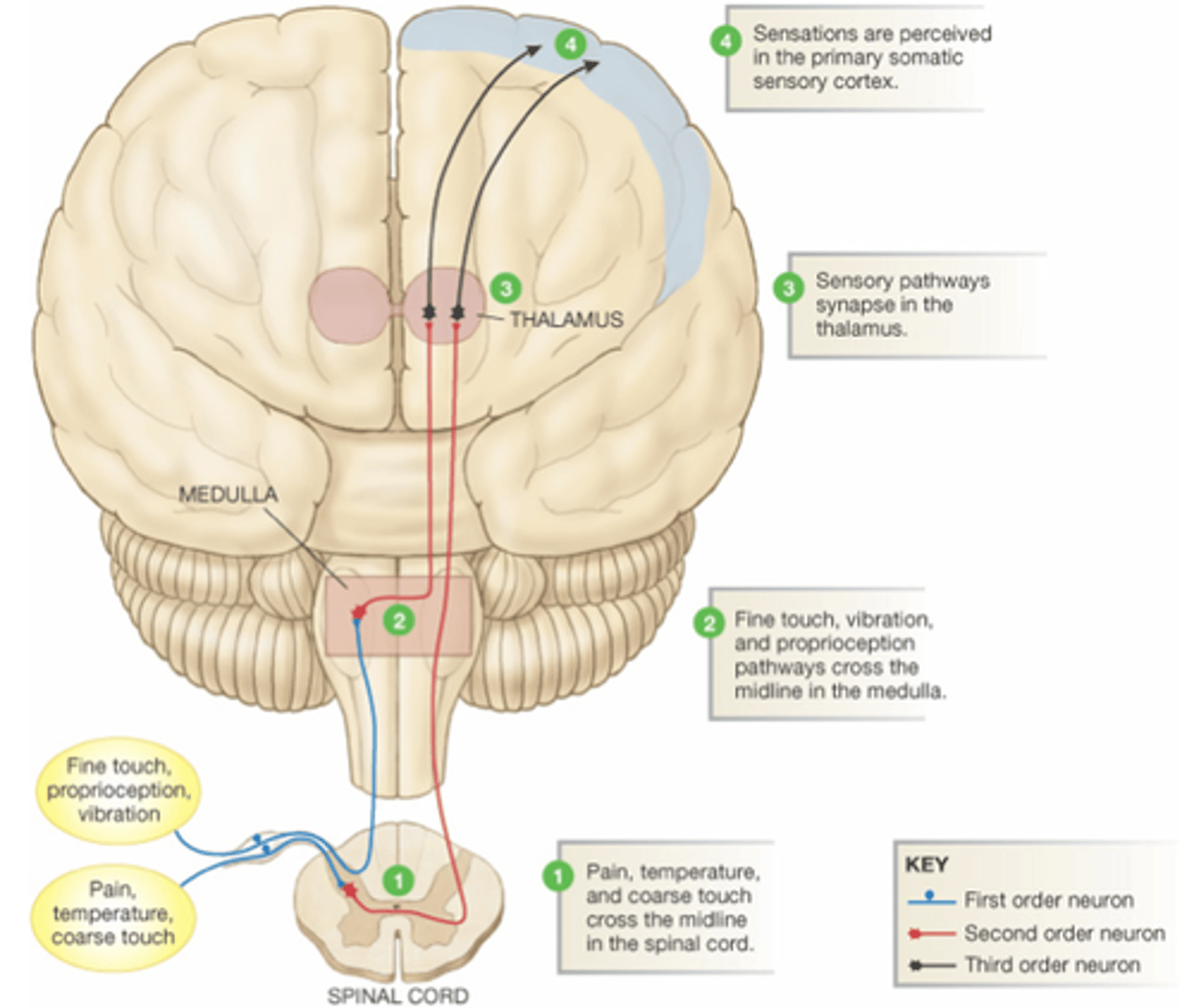
Third-Order Neurons
Conduct impulses from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex on the same side.
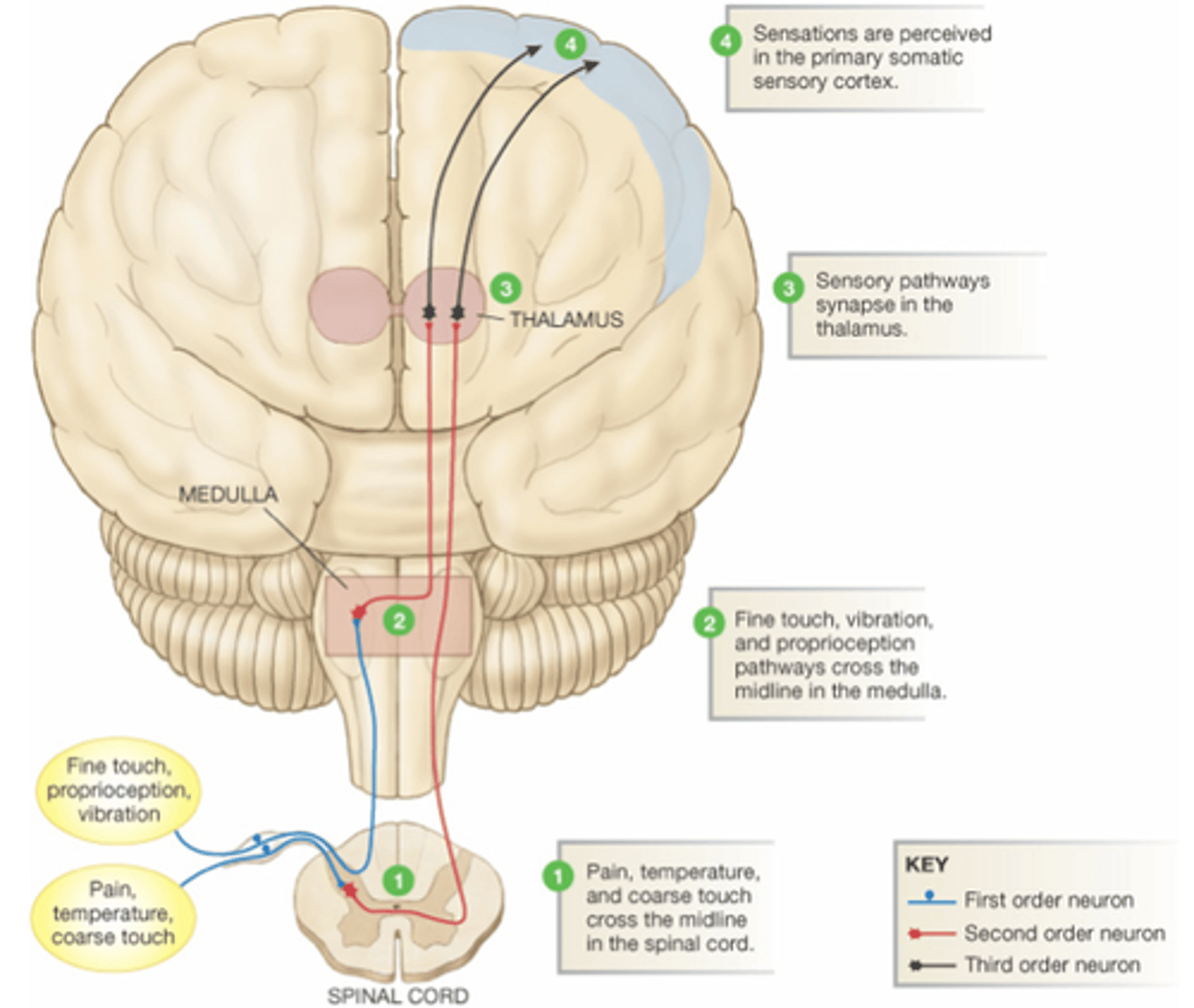
Ventral Root
Contains the axons of motor neurons.
TERM
Peripheral Nervous System
DEFINITION
Includes 10 pairs of cranial nerves, MINUS the olfactory and optic. 31 pairs of spinal nerves, and everything else except the brain and spinal cord.
TERM
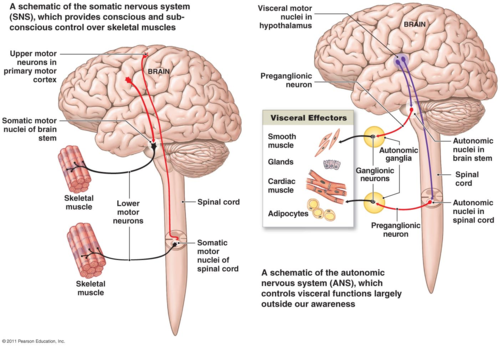
Autonomic Nervous System
DEFINITION
Subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic. Regulates heartbeat, respiration, digestion, glandular secretions, and body temperature (piloerection).
TERM
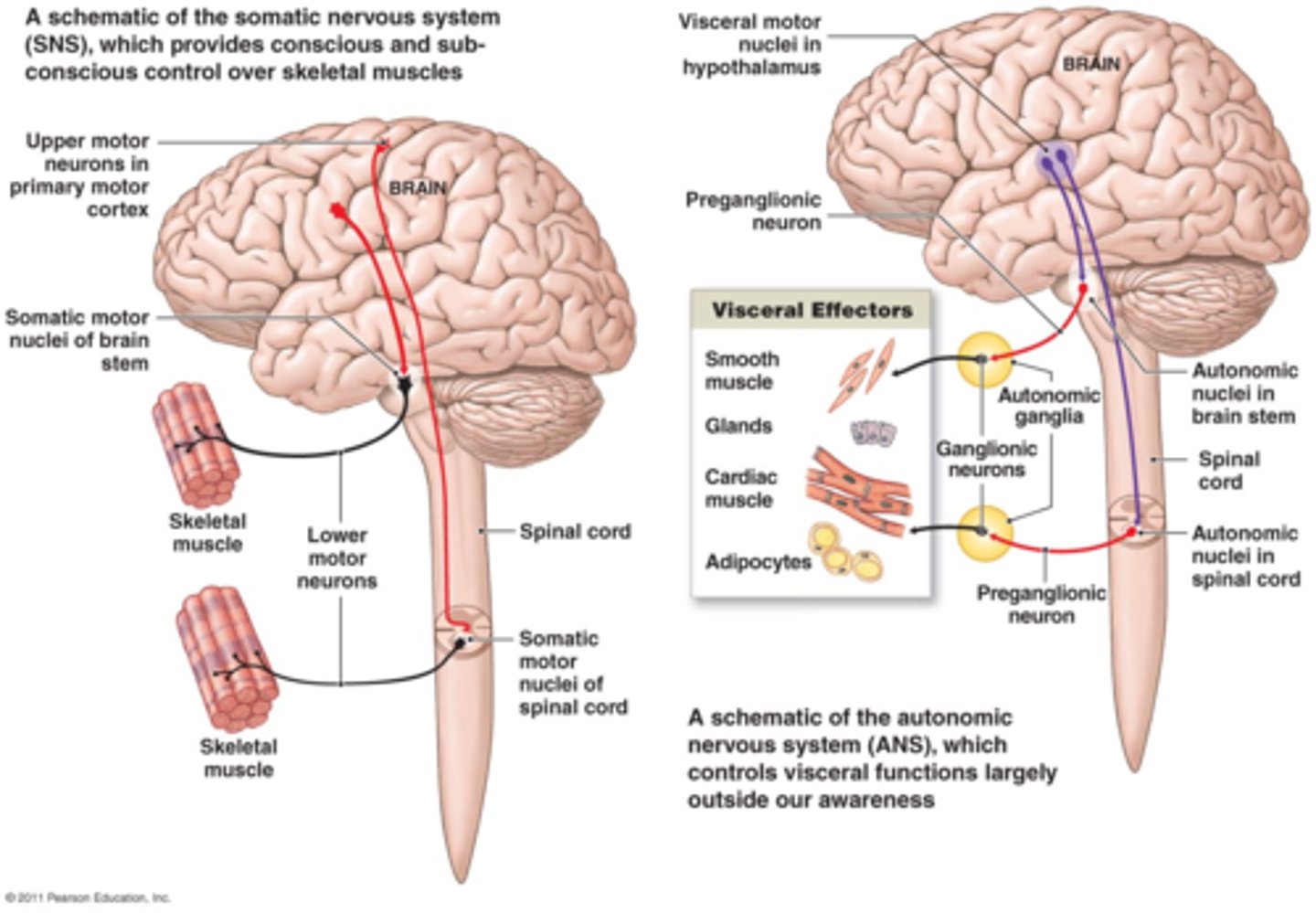
Somatic Nervous System
DEFINITION
Sensory and motor neurons distributed throughout the skin, muscles, and joints.
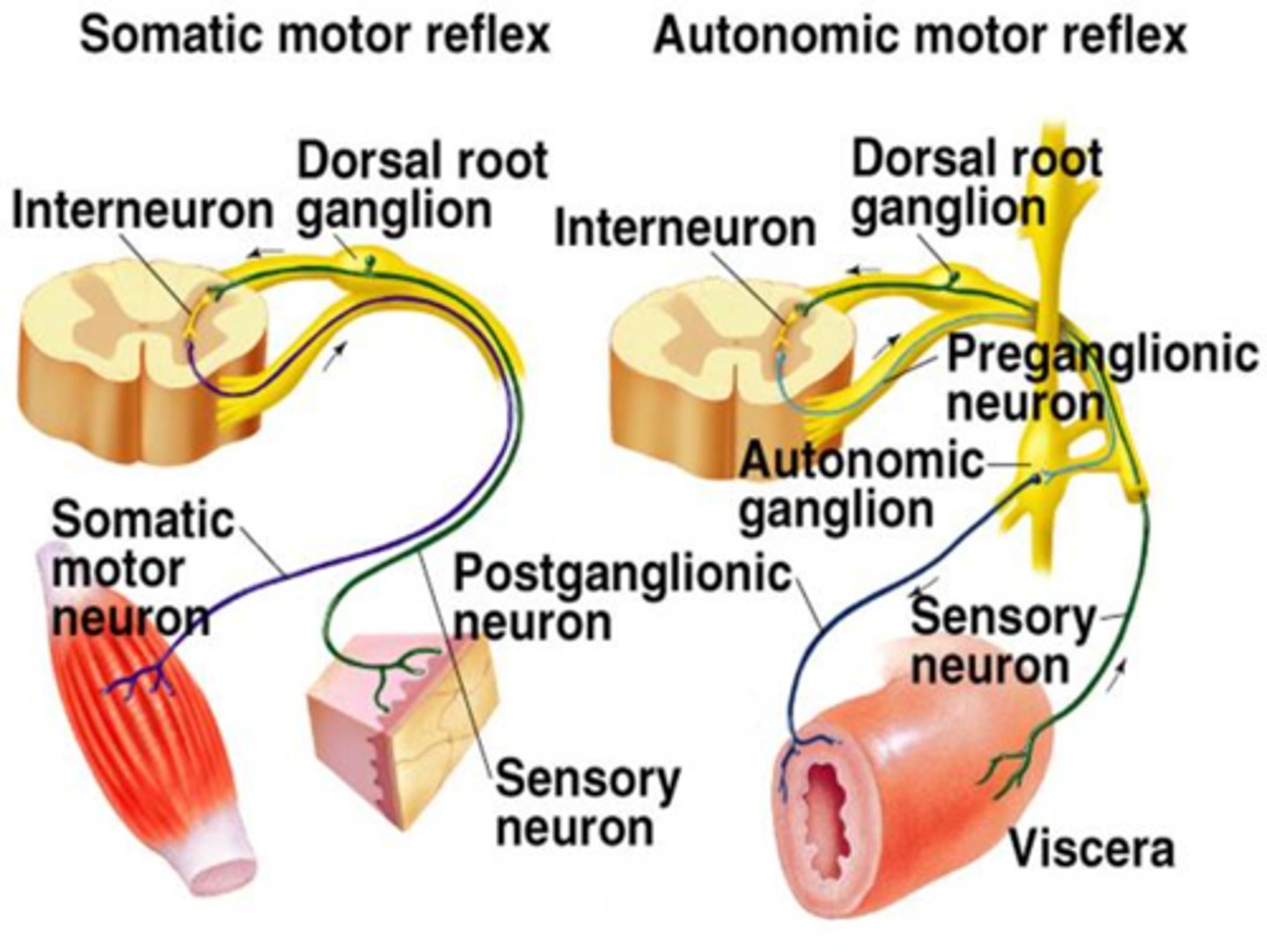
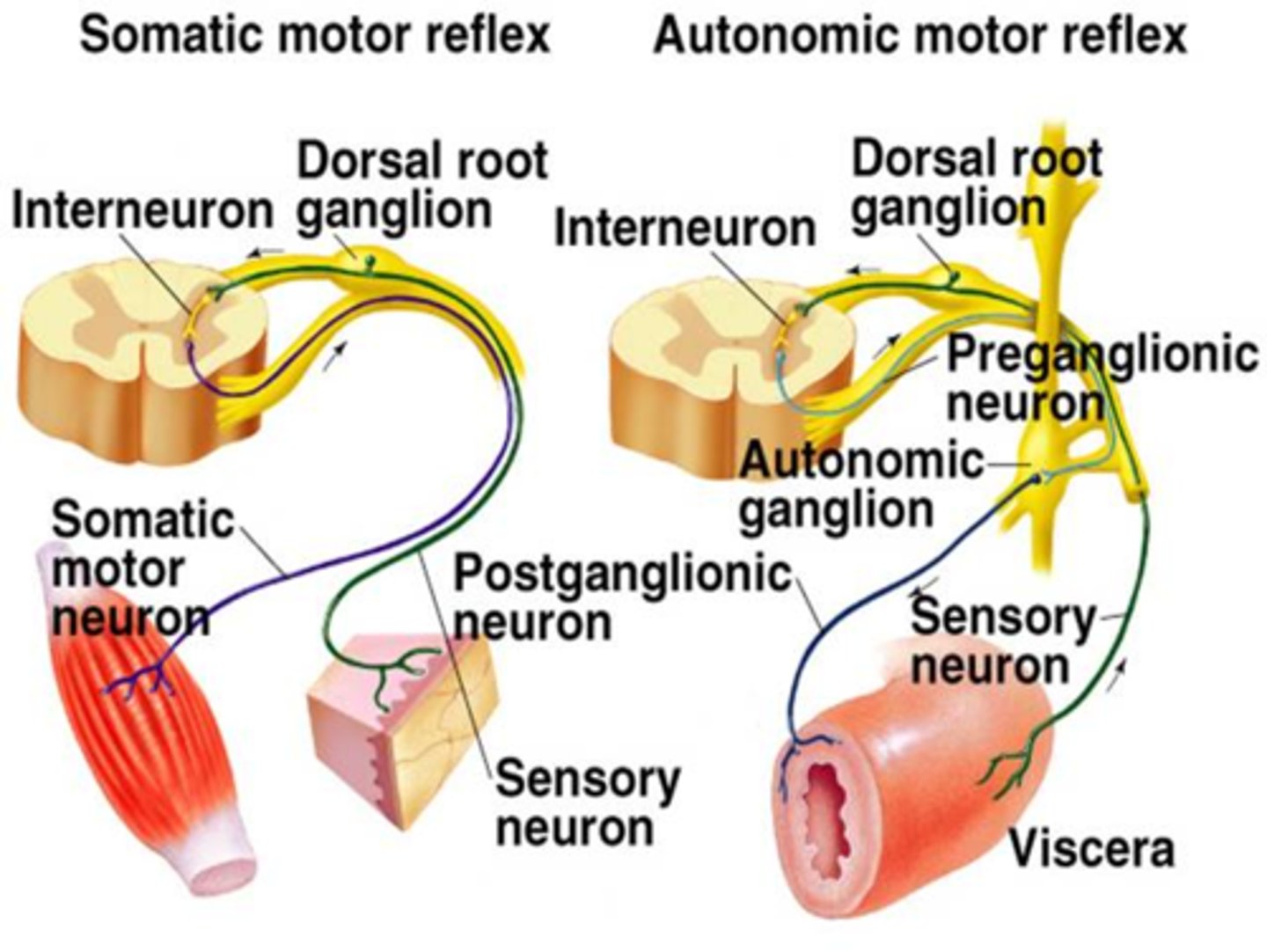
Somatic Versus Autonomic Nervous Systems
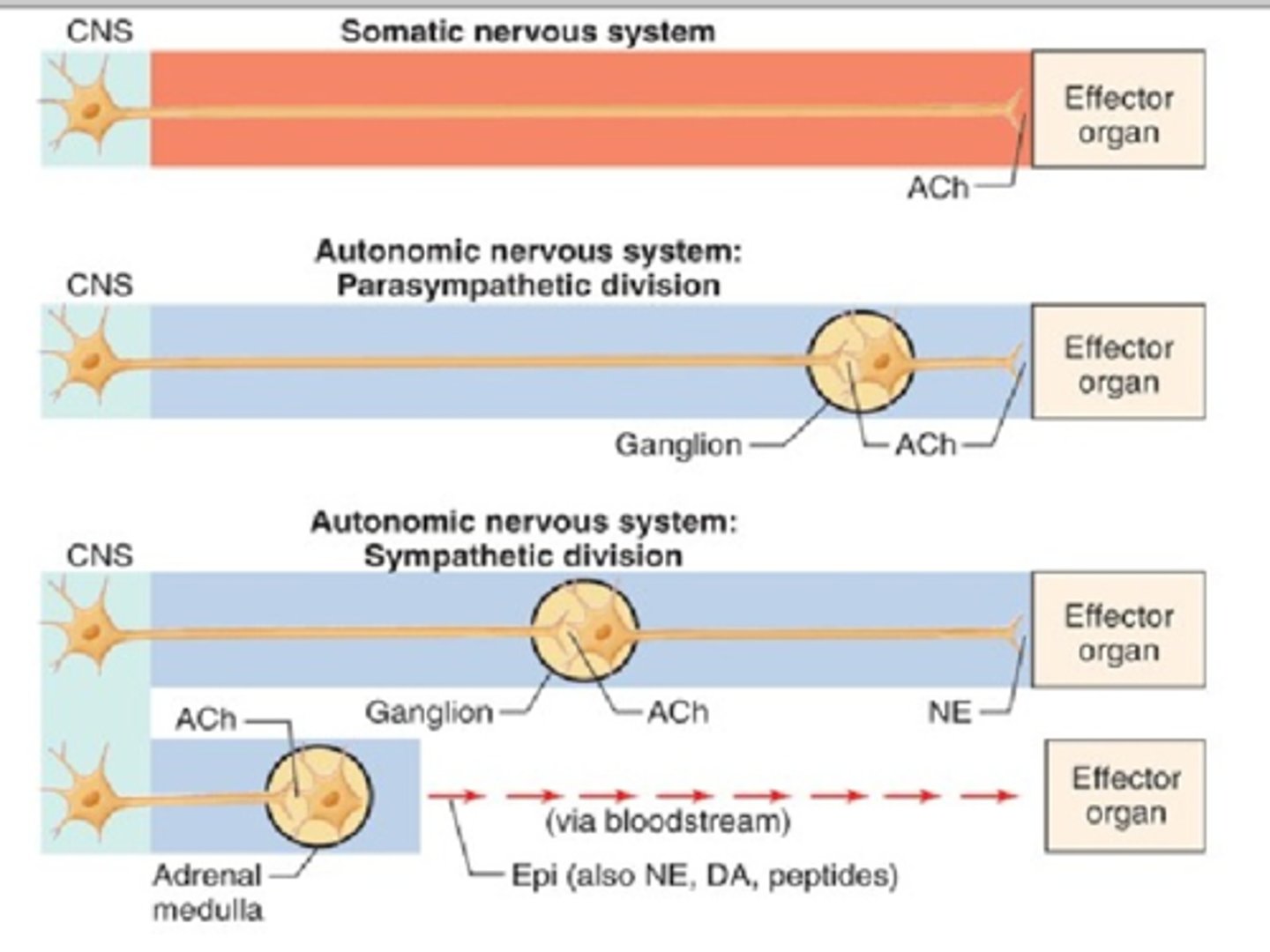
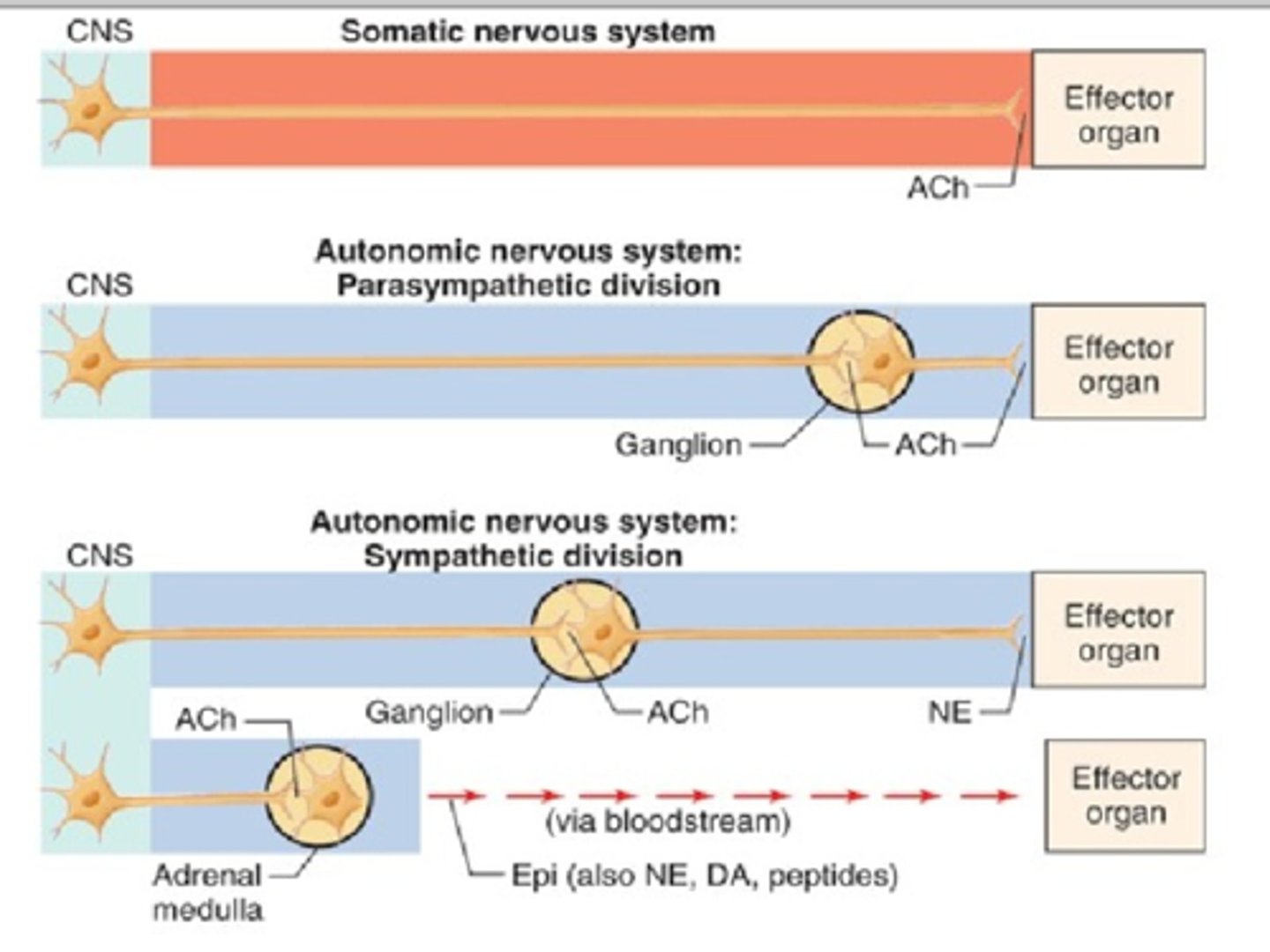
Somatic ganglia lie in the CNS. The autonomic nervous system also has peripheral ganglia. The extra ganglia, therefore, require preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
Preganglionic and Postganglionic Neurons of the Autonomic Nervous System
The peripheral component of the autonomic nervous system contains two neurons in series. This is the primary difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
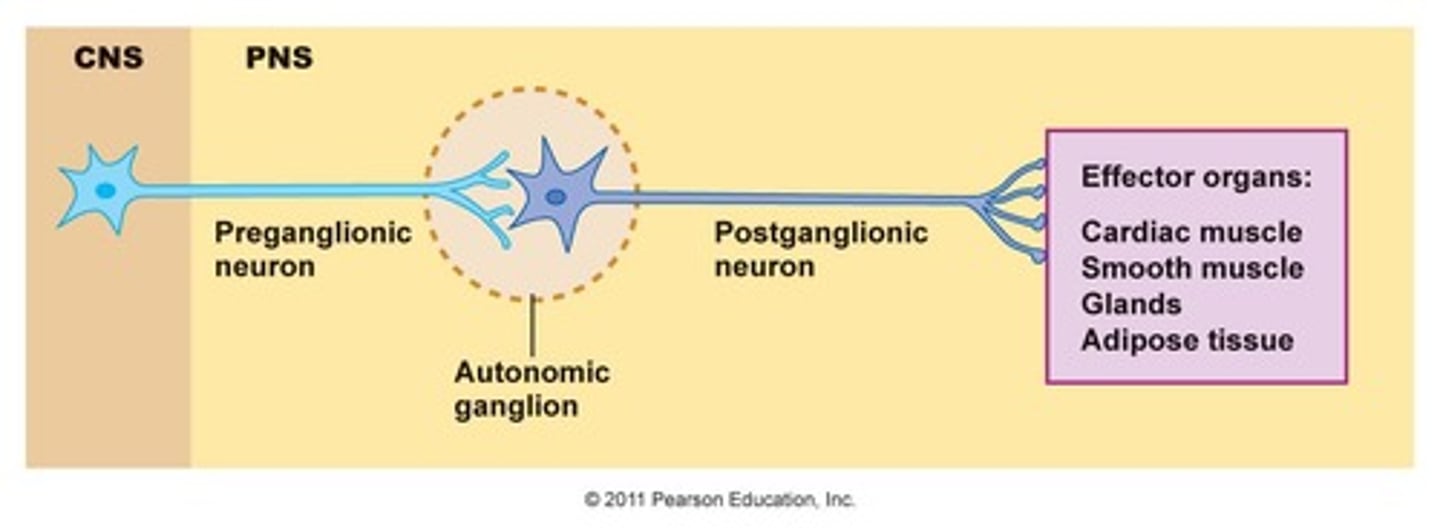
Postganglionic Neuron
In the autonomic division of the PNS, a neuron that has its cell body located in an autonomic ganglion, where a preganglionic neuron synapses with it, and whose axon synapses with the target tissue.
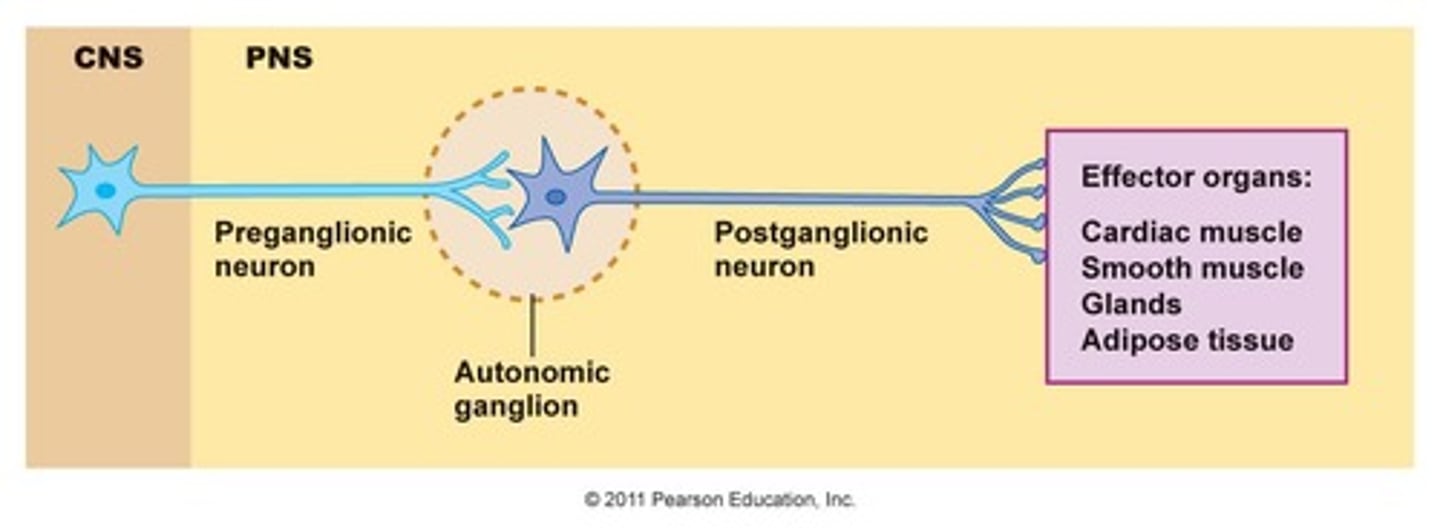
Preganglionic Neuron
In the autonomic division of the PNS, the cell bodies lie in the CNS, and the axons travel to a peripheral autonomic ganglion. Here, it synapses on the cell body of the postganglionic neuron, which then affects the target tissue.
TERM
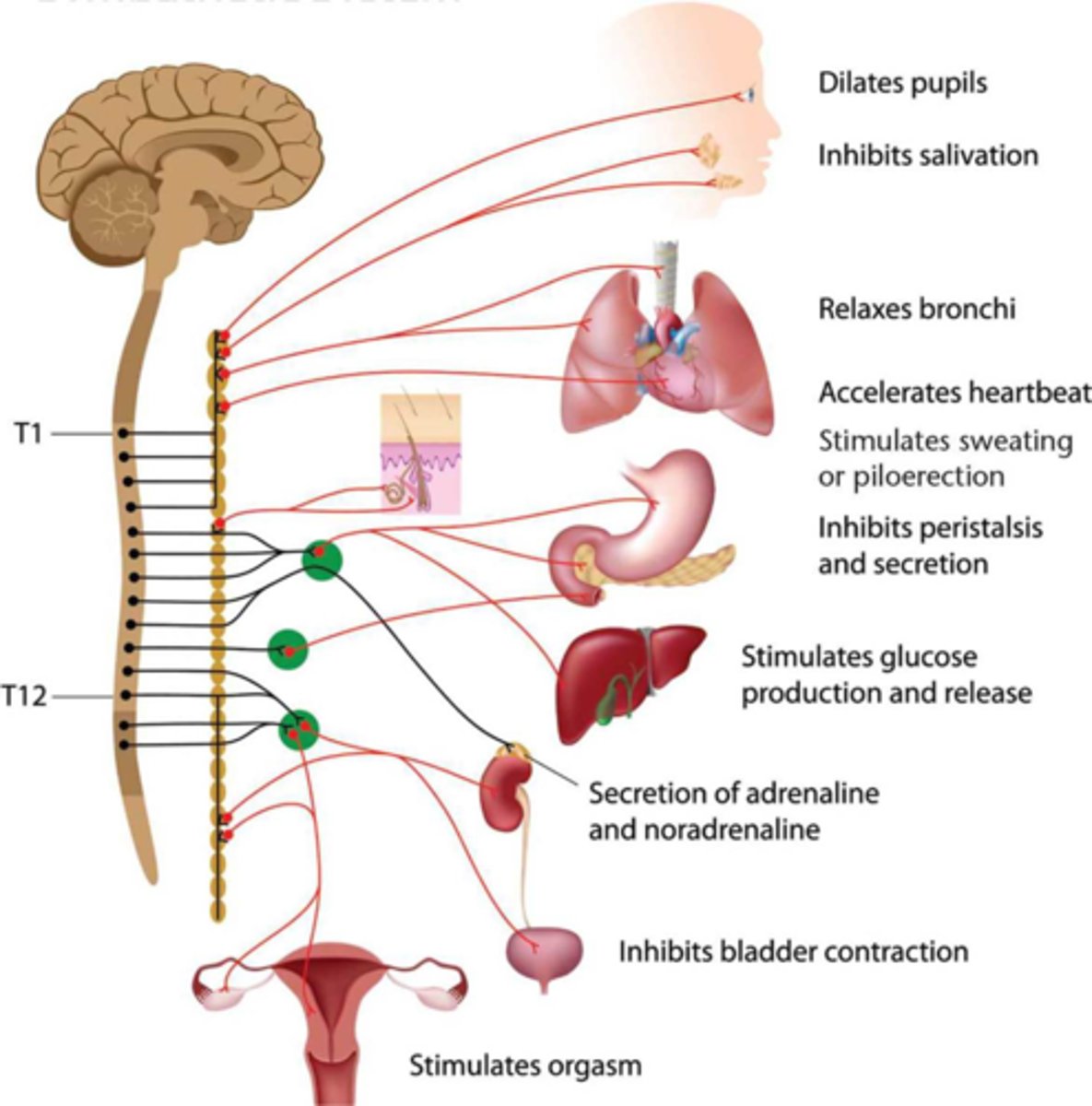
Sympathetic Nervous System
DEFINITION
Activated by stress. When activated, it increases heart rate, redistributes blood to locomotive muscles, increases blood glucose, relaxes the bronchi, decreases digestion and peristalsis, dilates eyes to maximize light intake, releases epinephrine.
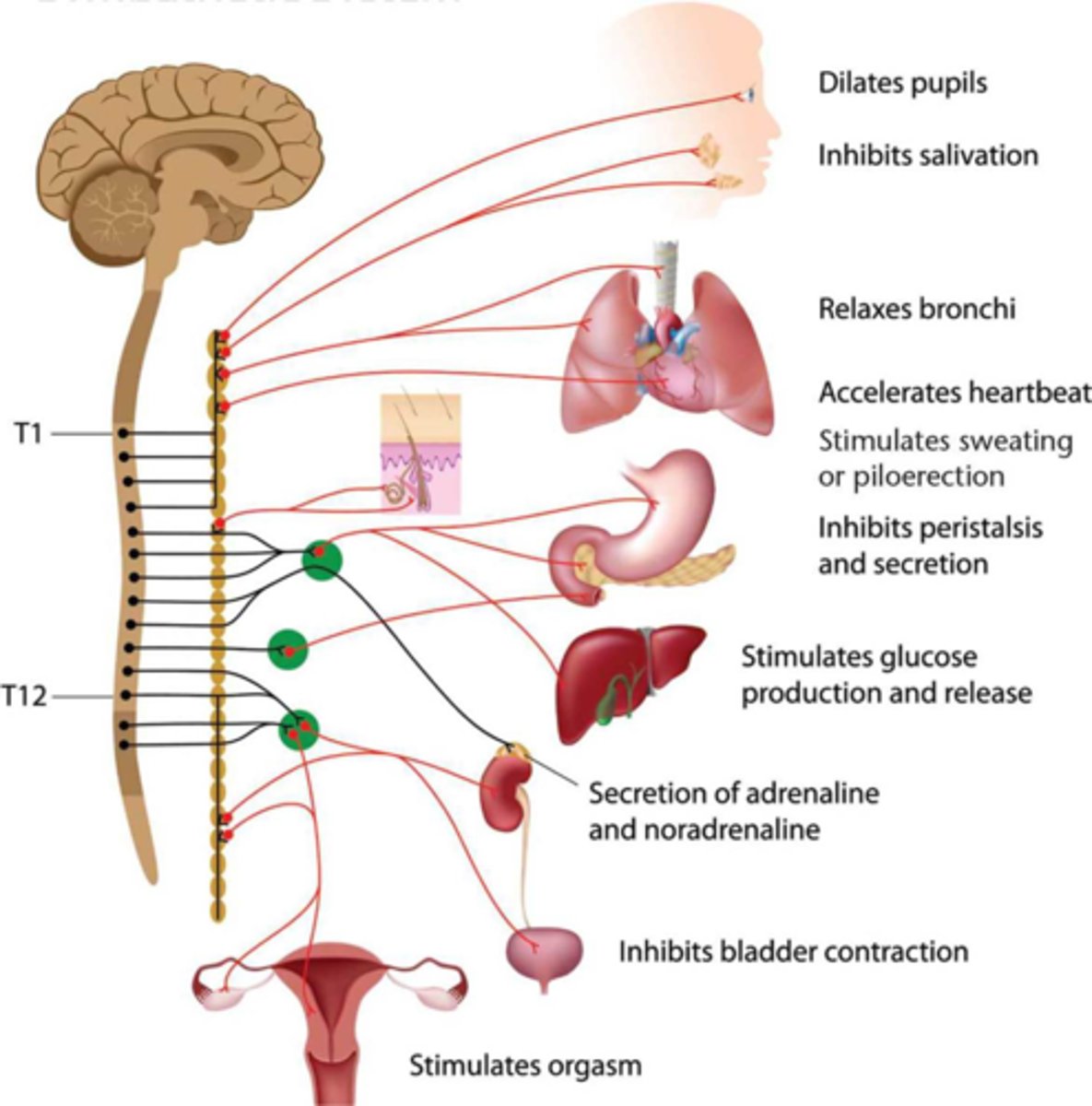
Sympathetic Ganglia
Recognizable by their distinctive chain-like appearance parallel to the spinal cord. A lot of branching, which allows the control of multiple organs through fewer signals.
Preganglionic Neurons of the Sympathetic Nervous System
Release acetylcholine.
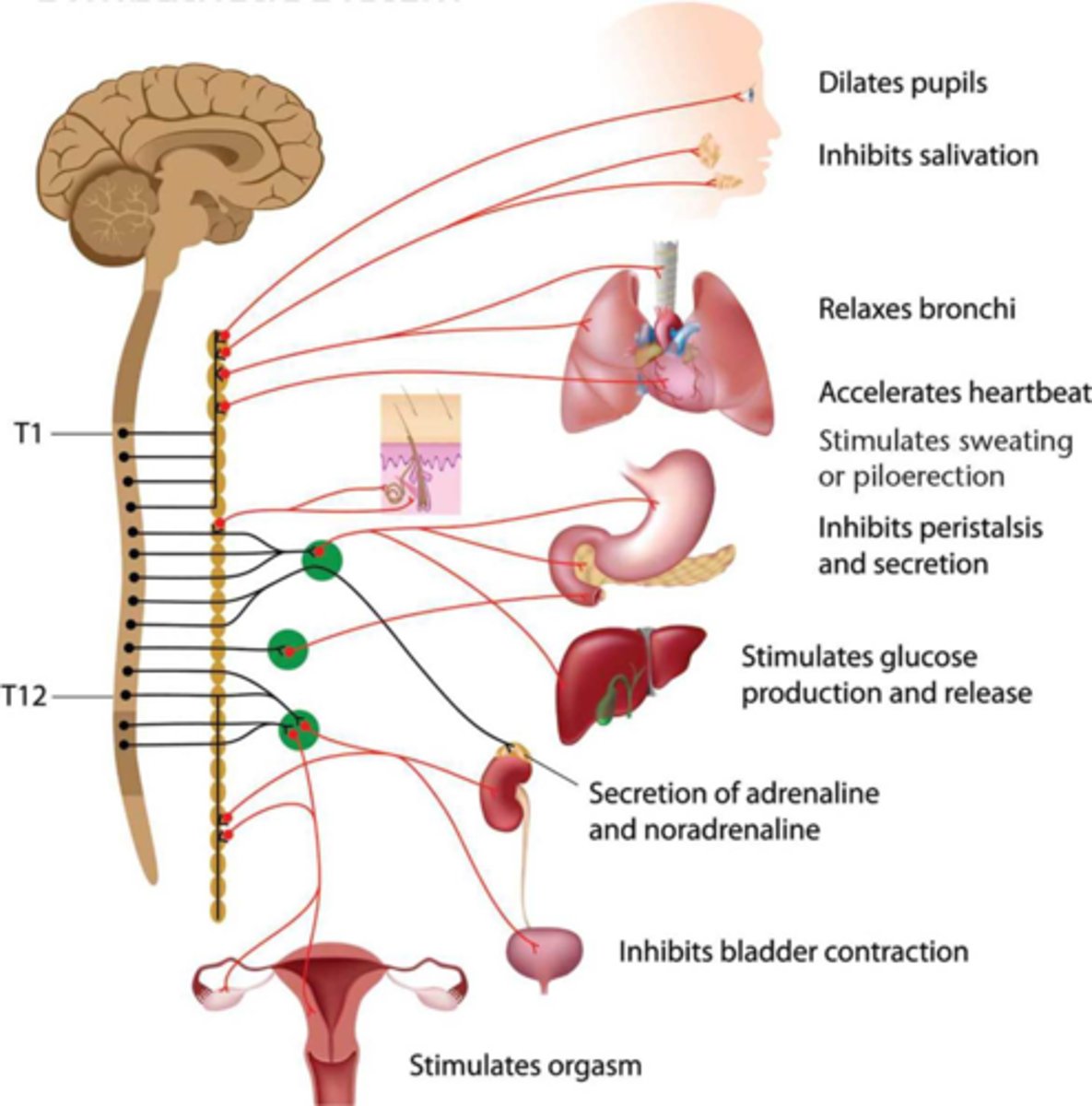
Postganglionic Neurons of the Sympathetic Nervous System
Release norepinephrine.
TERM
Parasympathetic Nervous System
DEFINITION
Conserves energy. Associated with resting and sleeping states and acts to reduce heart rate and constrict the bronchi.
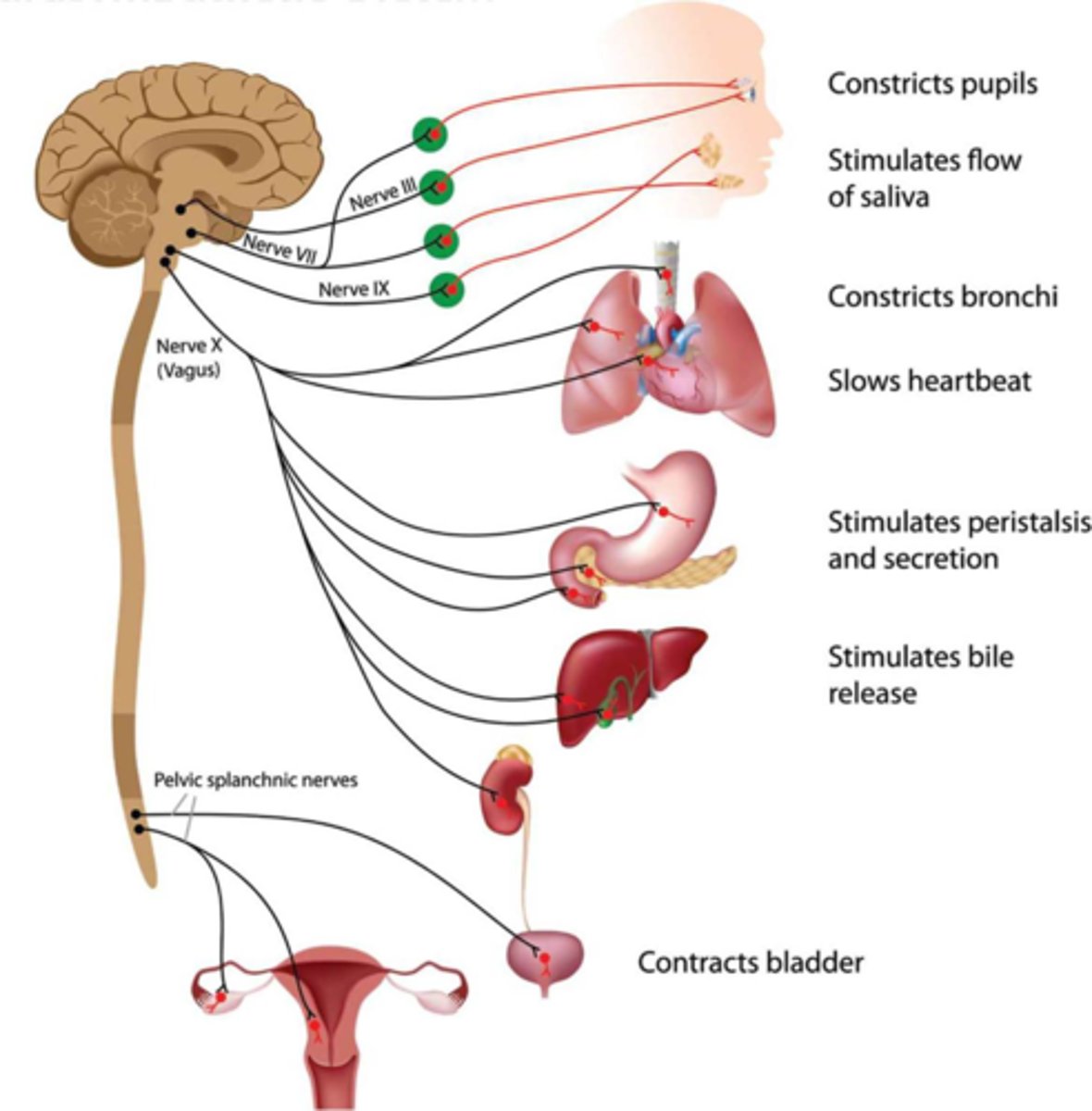
Parasympathetic Ganglia
Located near the organs they control, not near the spinal cord. Not a lot of branching.
Acetylcholine
The primary neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic responses, it is released by both preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
Vagus Nerve
Cranial nerve 10, is responsible for much of the parasympathetic innervation of the thoracic and abdominal cavity.
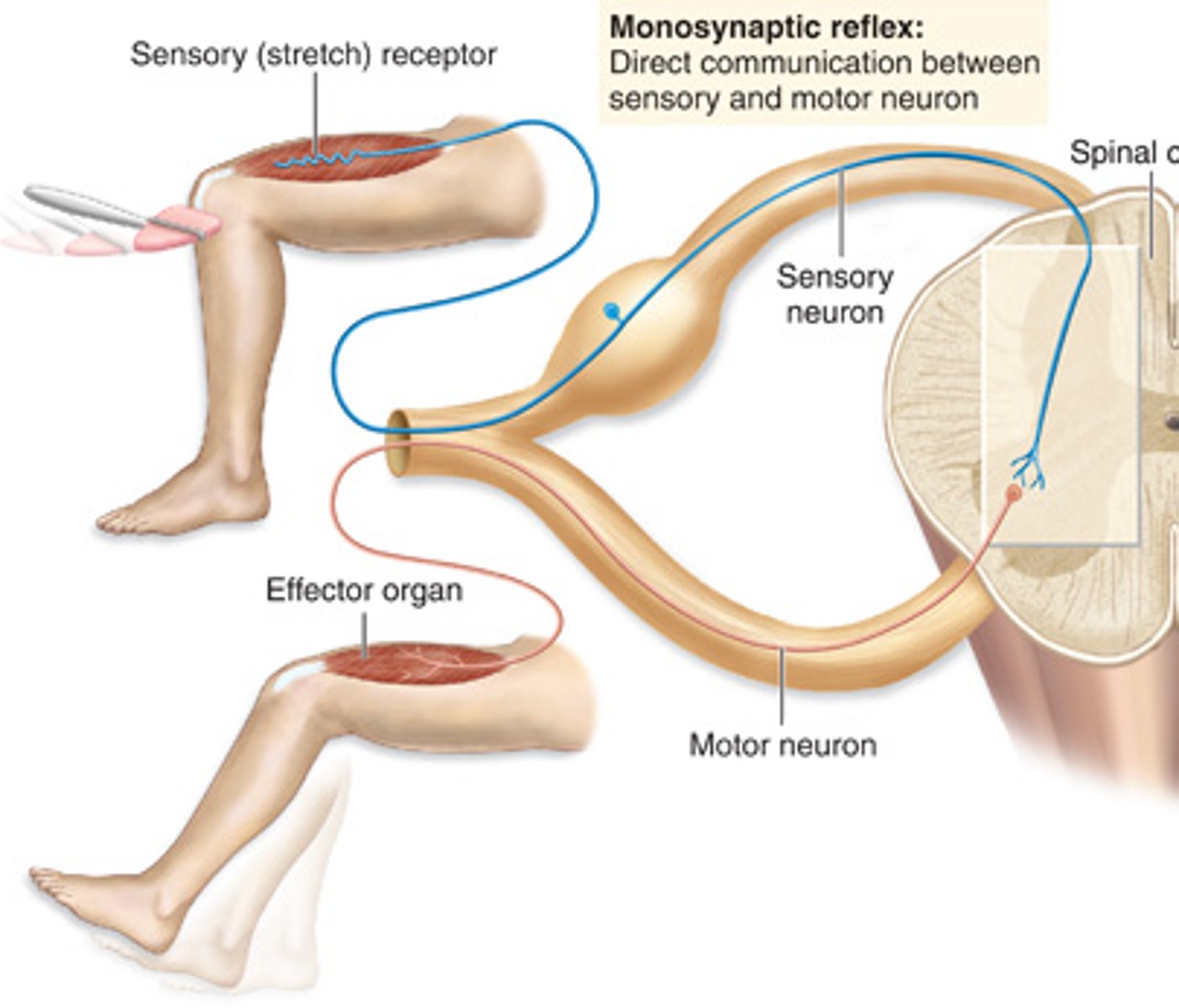
Monosynaptic Reflex Arc
There is a single synapse between the sensory neuron that receives the stimulus and the motor neuron that responds to it. An example is the knee-jerk reflex. No interneurons involved.
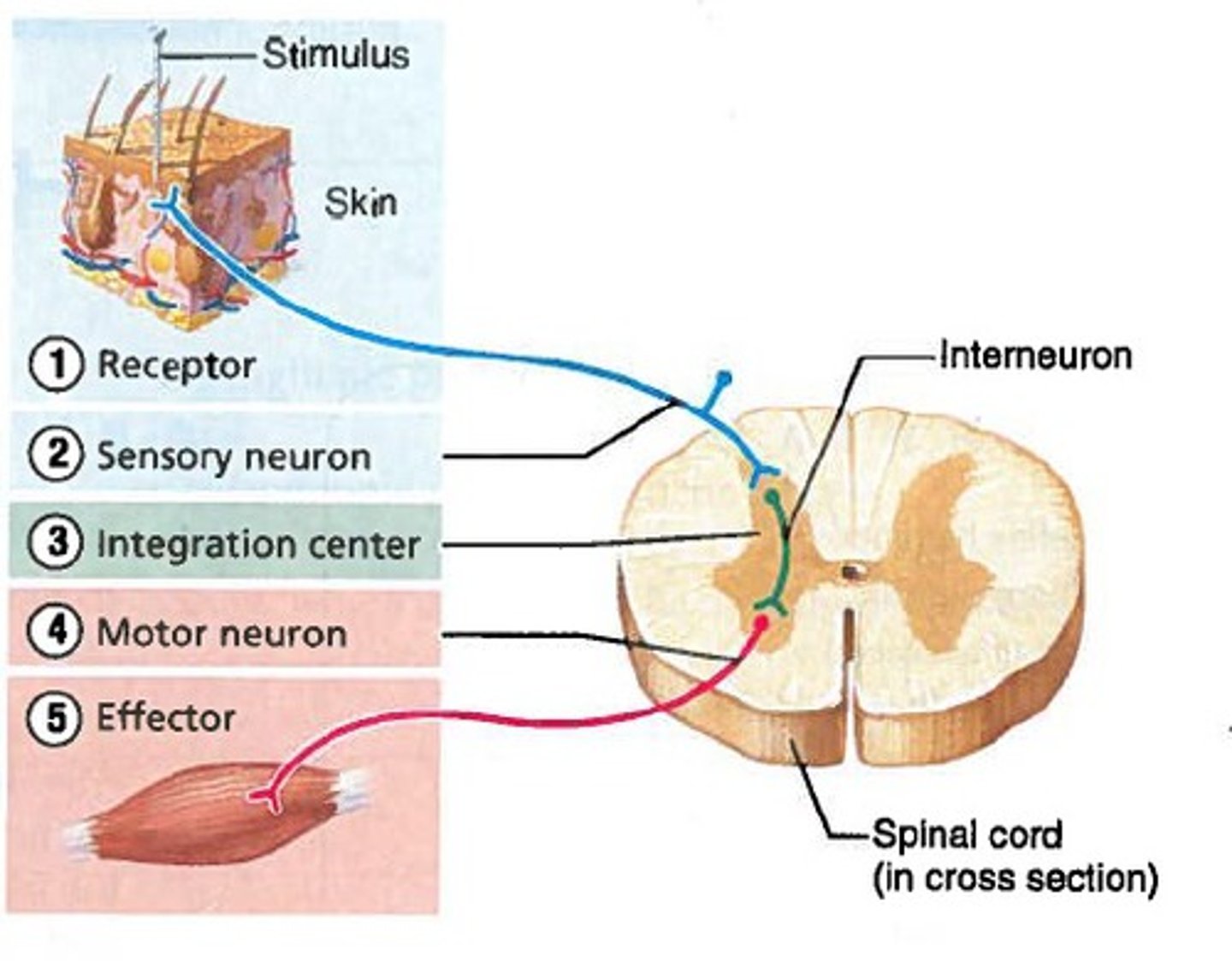
Polysynaptic Reflex Arc
There is at least one interneuron between the sensory and motor neurons.
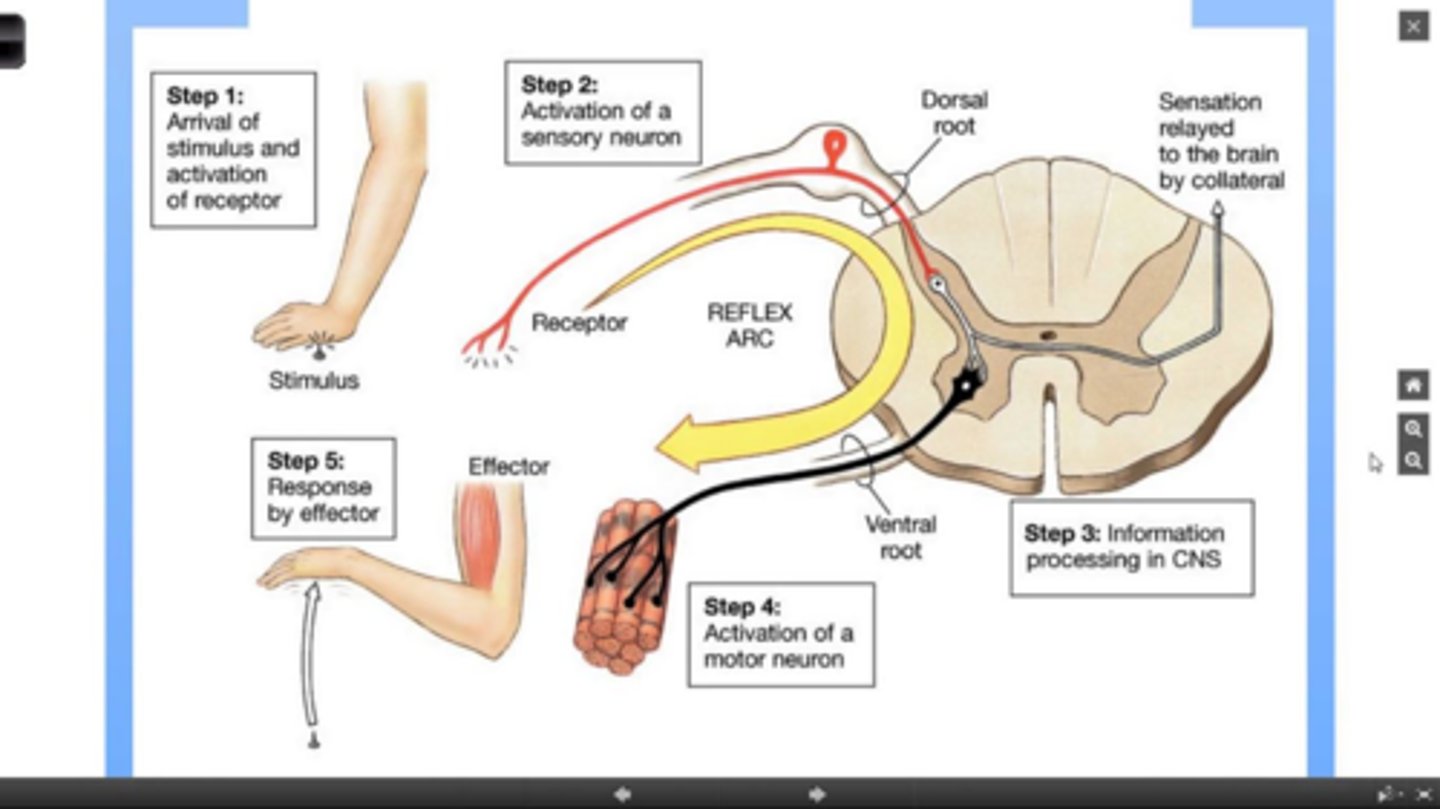
Withdrawal Reflex
Response to stepping on something sharp, the response is through a polysynaptic reflex arc.
Somatic and Autonomic Motor Reflexes