Pulse Wave Operations, Intensity, Attenuation
1/170
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 4, 5, 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
what are the 5 parameters of pulse wave operation
pulse duration, pulse repetition period, pulse repetition frequency, duty factor, and spatial pulse length
short bursts, or pulses of acoustic energy for every picture
pulsed utrasound
talking time is referred to as
on-time or transmit time
listening time is referred to as
off time
Waves that pulse continuously, no off time
continuous waves
2 components of pulsed ultrasound
on time and off time
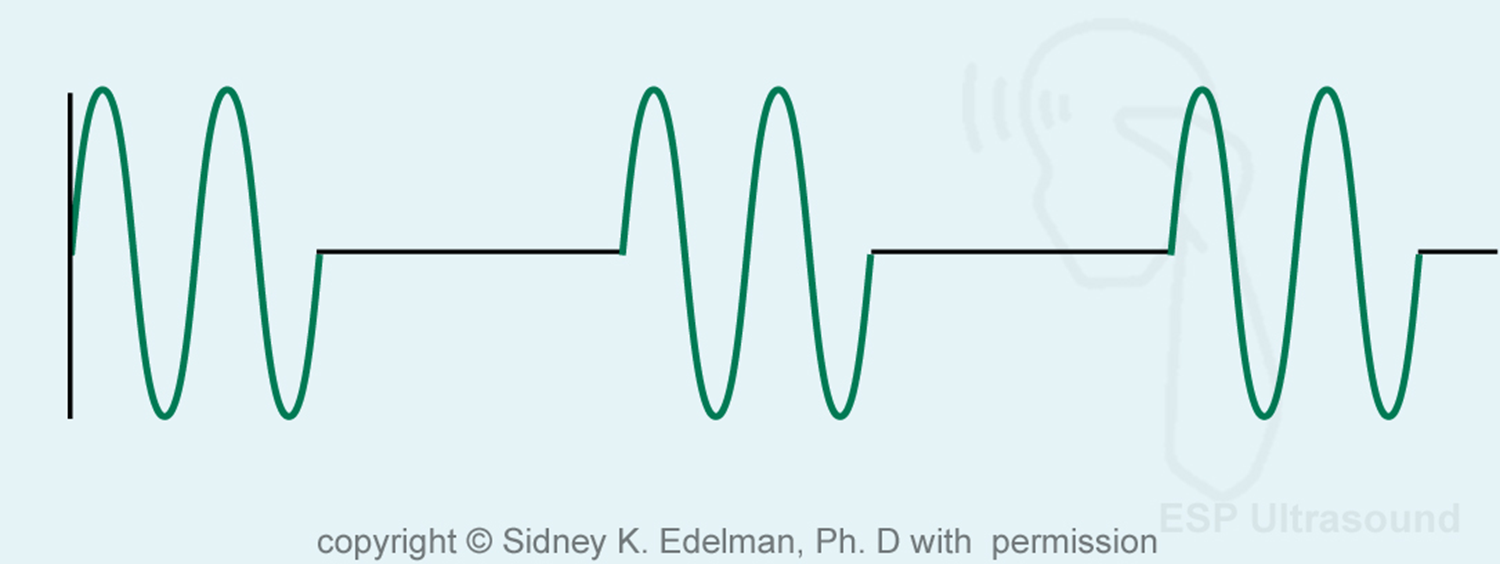
the flat black line refers to
listening (off) time
Actual time from the start of a pulse to the end of that pulse
pulse duration
pulse duration is ____ time
on
is pulse duration adjustable
no
what is the typical unit for pulse duration
microseconds
pulse duration is determined by
sound source
is pulse duration fixed or able to be changed
fixed
#cycles/frequency (MHz)=
pulse duration
is equal to the number of cycles in each pulse, multiplied by the period of each cycle
pulse duration
pulse duration is ________ proportional to the number of cycles in a pulse
directly
pulse duration is ________ proportional to the period
directly
pulse duration is ________ proportional to the frequency
inversely
many cycles in a pulse, and cycles with long periods
long duration
few cycles, short periods
short duration
which is better for imaging short or long duration
short duration
why does short duration provide greater accuracy
provides more listening time
the distance that a pulse occupies in space from the start to the end of a pulse
spatial pulse length
units of spatial pulse lengths
millimeters
spatial pulse length is determined by
both sound and medium
is spatial pulse length adjustable
no
= #cycles X wavelength (mm)
SPL
spatial pulse length is ________ proportional to the number of cycles in the pulse
directly
spatial pulse length is ________ proportional to wavelength
directly
spatial pulse length is _________ proportional to frequency
directly
many cycles and a long wavelength make ____ pulse
long
few cycles and short wavelength makes ______ pulse
short
does short or long pulse create more accurate images
short
from the start of one pulse to the start of another
pulse repetiton period
what is the unit for PRP
microseconds
is PRP adjustable
yes
what is PRP determined by
sound (depth)
does the media change the PRP
no
does the frequency change the PRP
no
if you are scanning at a shallow depth is the PRP short or long
short
is you are scanning at a deep depth is the PRP short or long
long
what is increasing when PRP is taken from short to long
the listening time
PRP and depth are _________ related
directly
deep imaging _____ the listening time, and ______ the PRP
increases, increases
how often a pulse is sent
pule repetition frequency
PRF is _______ proportional to depth
inversely
what is the unit for prf
Hz
is prf adjustable
yes
is prf related to frequency
no
if the depth changes from 10cm to 5 cm, how does the prf change
it increases (pulses more frequently)
prf and depth are ______ proportional
inversely
a depth of 2cm has a ____ prf and _____ prp
high, low
prp and prf are _____ related
inversely
the relationship between prp and prf is a _______ relationship
reciprocal
% or fraction of time that the system transmits a pulse
duty factor
what is the typical value for duty factor
0.2-0.5%
what is the duty factor of a continuous wave
1 or 100%
is duty factor adjustable
yes
what changes duty factor
depth
duty factor has a _____ relationship with prf
direct
shallow depth have ______ listening time
less
shallow depth have ___ prp
short
shallow depths have ____ prf
high
shallow depth have ____ duty factor
high
deep depths have ____ listening time
more
deeper depths have ____ prp
long
deeper depth have _____ prf
low
deeper depth have _____ duty factor
low
deeper imaging means you listen _____, pule _____ frequently, and have a ____ duty factor
more, less, lower
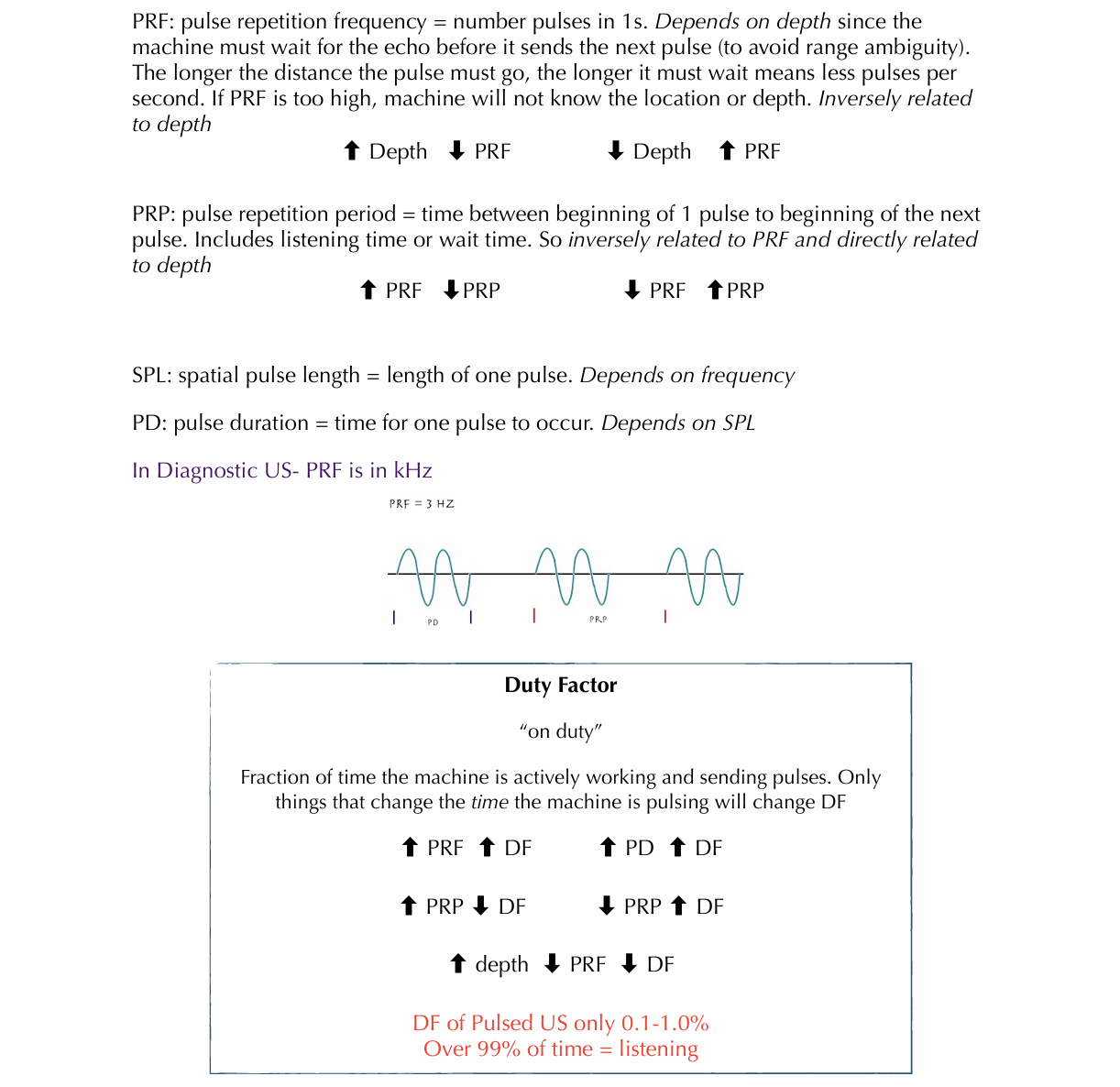
cheat sheet
refers to distance or space
spatial
the maximum value
peak
mathematical middle value
average
refers to all time, transmit and receive
temporal
refers only to transmit time
pulsed
power divided by area
intensity
unit for intensity
watts/cm²
T or F: the strength of a sound beam varies
true
T or F: intensity varies over time
true
beam’s intensity at the location where it is maxiumum
spatial peak intensity (Isp)
average intensity across the beam’s entire cross-sectional area
spatial average intensity (Isa)
spatial peak intensity is _____ ______ than the spatial average intensity
always higher
intensity at the instant in time of its maximum value
temporal peak intensity (Itp)
average intensity during the most intense half cycle
Imax
average intensity during pulse duration
Ipa
intensity during entire pulse repetition period
temporal avergae intensity (Ita)
temporal intensities from largest to smallest
Itp, Imax, Ipa, Ita
measured at location where intensty is max. and at instant in time when the most powerful part of the pulse passes
SPTP
measured at the location where intensity is max. averaged over transmit time
SPPA
measured at location where intensity is max. and averaged over all time
SPTA
measured over the entire cross-sectional area, and overall time
SATA
spatial peak, temporal peak
SPTP
spatial average, temporal peak
SATP
spatial peak, temporal average
SPTA
spatial average, temporal average
SATA
spatial peak, pulse average
SPPA
spatial average, pulse average
SAPA
intensities may be reported in various ways with respect to ____ and _____
time and space
the different measurements of intensities are important in the study of
bioeffects
which is most relevant in terms of bioeffects
SPTA