Physics II Module of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse: Lesson 3: Light Waves (Pro)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Lesson 3: Light Waves
Lesson 3: Light Waves
True or False? Wave Interference is always destructive.
False. Both Constructive Interference and Destructive Interference are examples of Wave Interference.
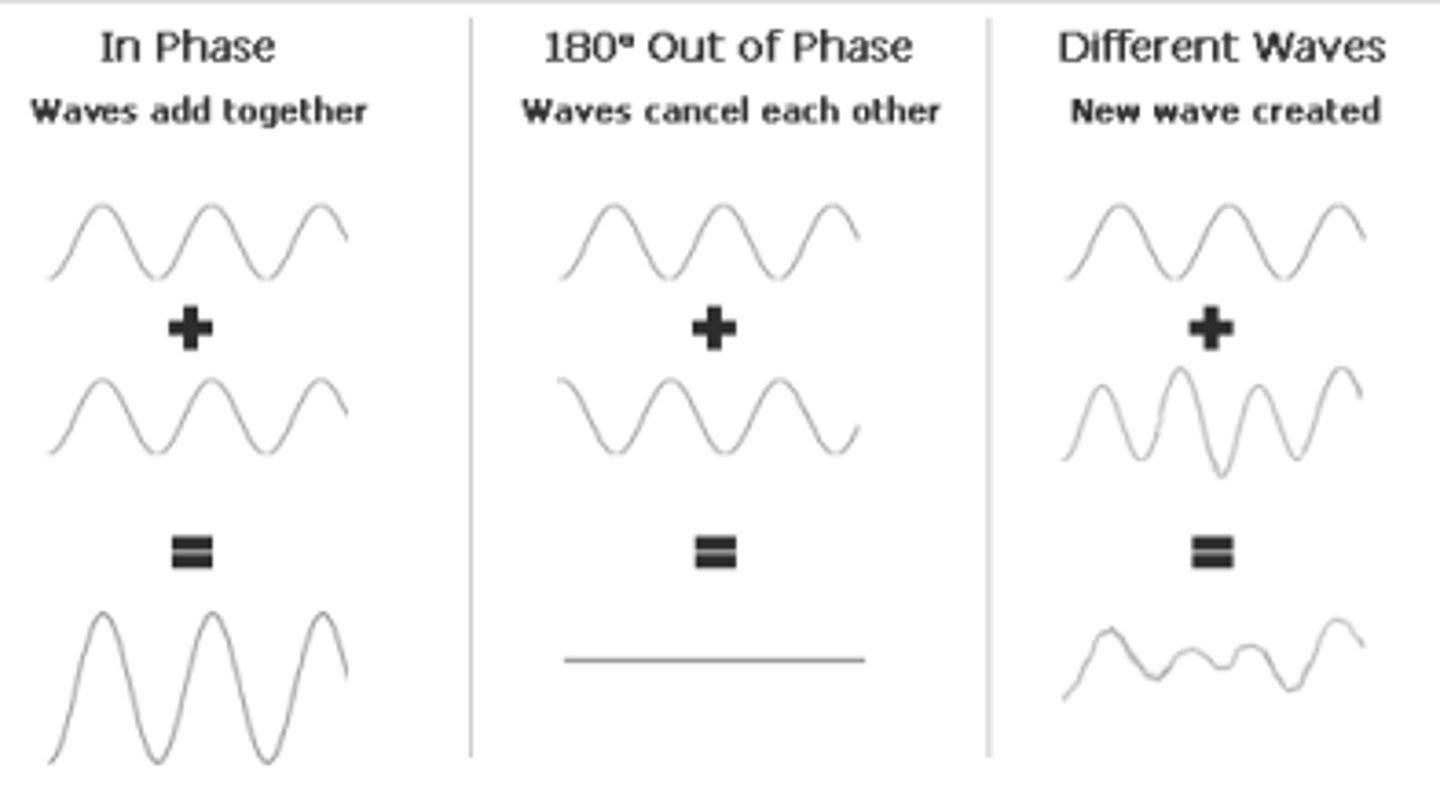
Overlapping waves that are in-phase will result in ____________ Interference. Overlapping waves that are out-of-phase will result in ____________ Interference.
(A) Constructive, Constructive
(B) Constructive, Destructive
(C) Destructive, Destructive
(D) Destructive, Constructive
(B) Constructive, Destructive
Overlapping waves that are in-phase will result in Constructive Interference. Overlapping waves that are out-of-phase will result in Destructive Interference.
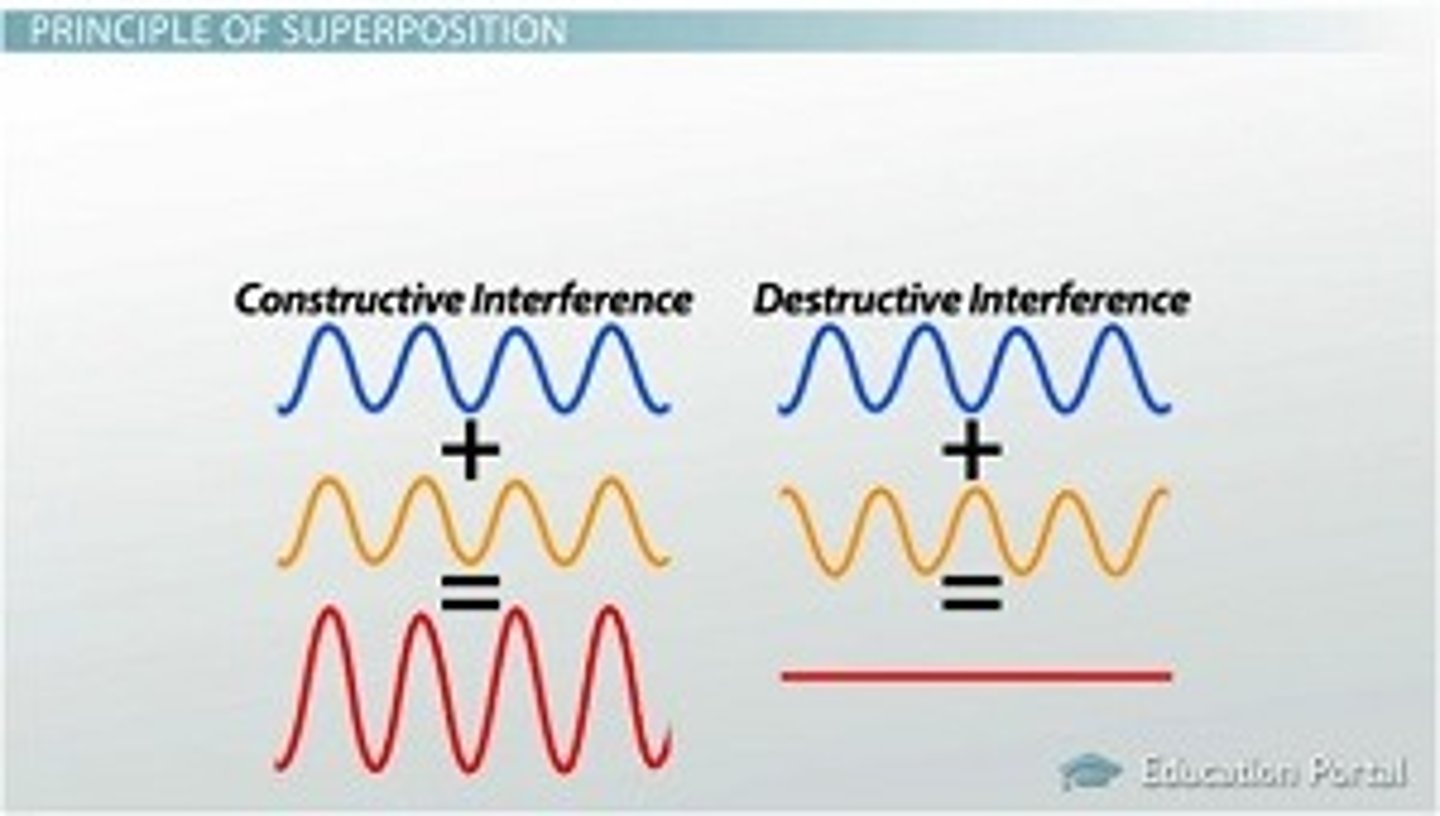
What does it mean for a speaker to be π-phase Shifted? What does it result in in terms of Wave Interference?
For a speaker to be π-phase Shifted, it means that the speaker has been moved by 180 degrees. It results in points of Constructive Interference becoming Destructive Interference and vice versa.
In Young's Double Slit Experiment, you have two slits that are right next to each other. You send a light wave through it, and what pattern will you observe? Why?
You will observe a pattern of light and dark spots due to the fact that light will bend as it comes through a hole, which will result in Wave Interference between the light coming through each slit.
CRB Fill in the blanks: __________________ Interference accounts for the areas with weaker bands of light, whereas ____________ Interference accounts for the brighter bands in the Double Slit experiments.
(A) Constructive, Constructive
(B) Destructive, Destructive
(C) Constructive, Destructive
(D) Destructive, Constructive
(D) Destructive, Constructive
Destructive Interference accounts for the areas with weaker bands of light, whereas Constructive Interference accounts for the brighter bands in the Double Slit experiments.
True or False? The light is the most intense away from the center due to the bending of the light.
False. The light is the most intense in the center due to a greater overlap of waves.
What does ∆x mean in terms of this experiment? What would it mean to say that ∆x = 3λ?
∆x is the difference between the path lengths (distance from slit to where it hits the wall/screen) of the light waves that come through each slit. If ∆x = 3λ, that would mean that the path length for the light from one slit is 3λs longer than the path length for the light from the other slit. In the case of this image, ∆x is equal to r2 - r1 and NOT equal to y.
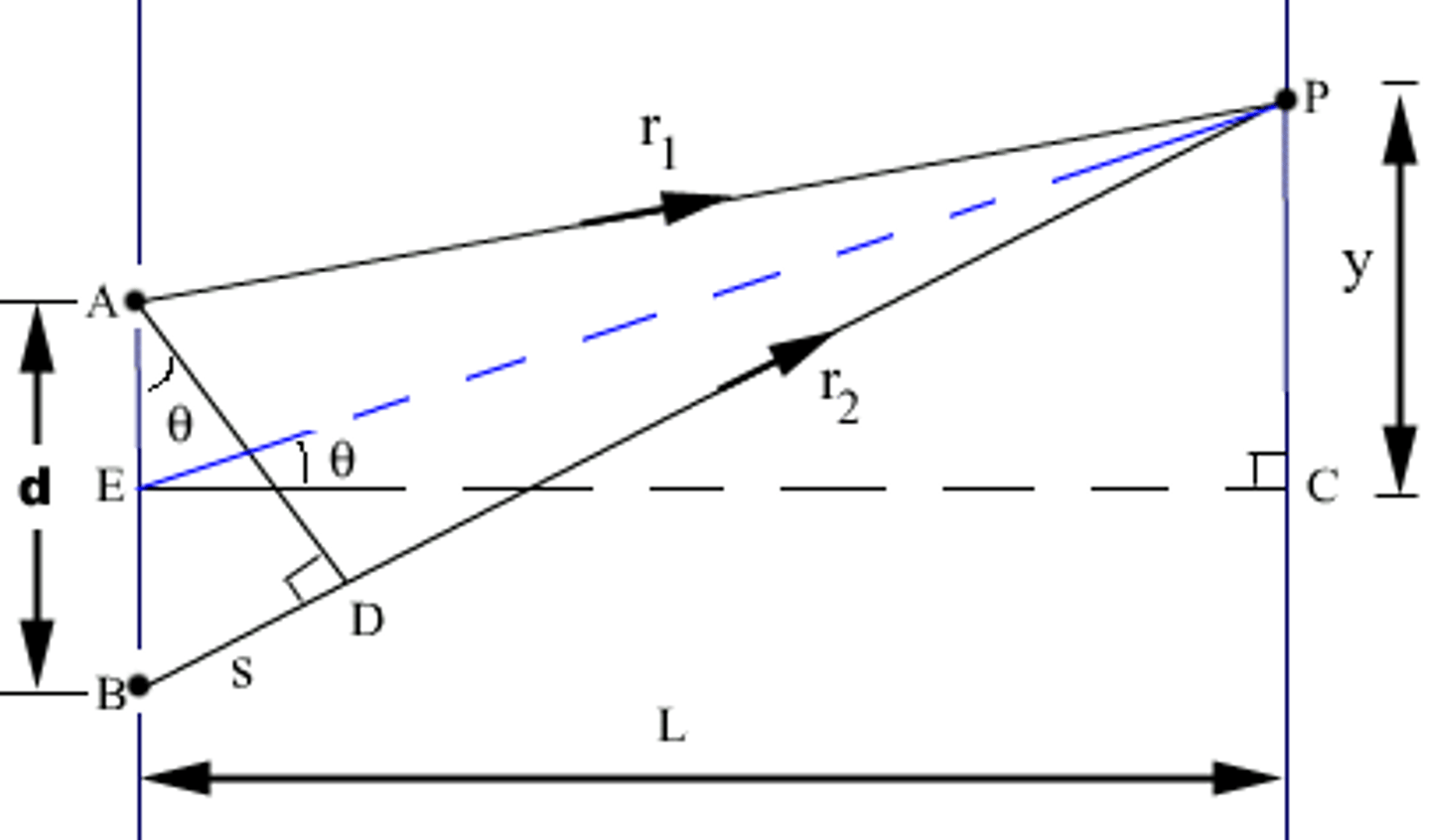
For Young's double slit experiment, when ∆x is equal to whole number λ integers (i.e. 0, λ, 2λ, 3λ, etc.) or half integers (i.e. 1/2λ, 3/2λ, 5/2λ, etc.) will there be Constructive Interference?
For young's double slit experiment, when ∆x is equal to whole number λ integers (i.e. 0, λ, 2λ, 3λ, etc.), there will be Constructive Interference.
What equation relates path length (∆x) and the distance between the slits (d)? Derive this equation.
∆x = dsinθ
∆x = path length
d = distance between the slits
θ = angle between d and perpendicular line
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
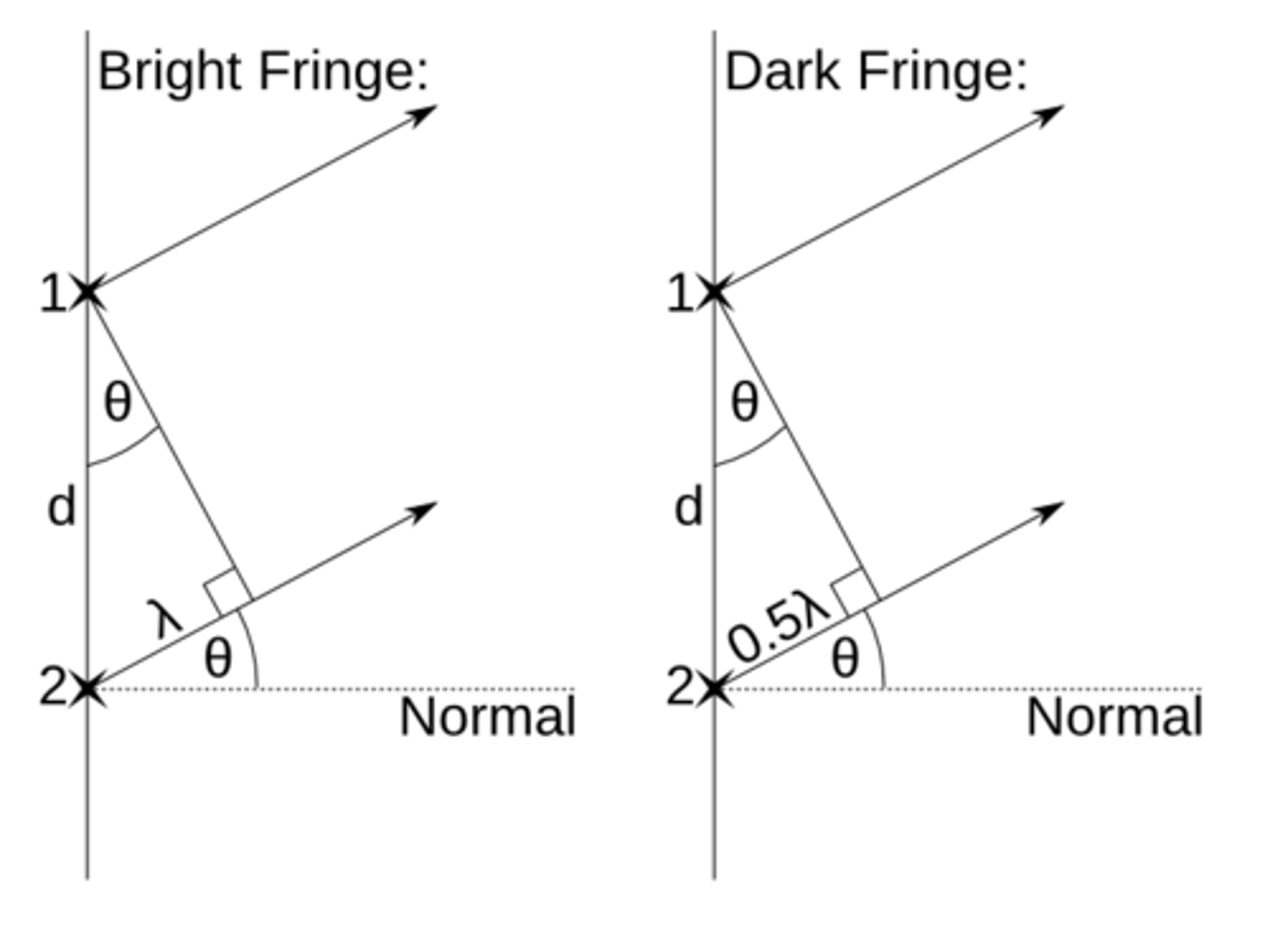
For Young's Double Slit Experiment, what equation will allow you to relate λ to θ (with Constructive Interference)?
mλ = dsinθ
m = the "order" (whole number integers such as 1,2,3...)
λ = wavelength
d = distance between the slits
θ = angle between d and perpindicular line
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
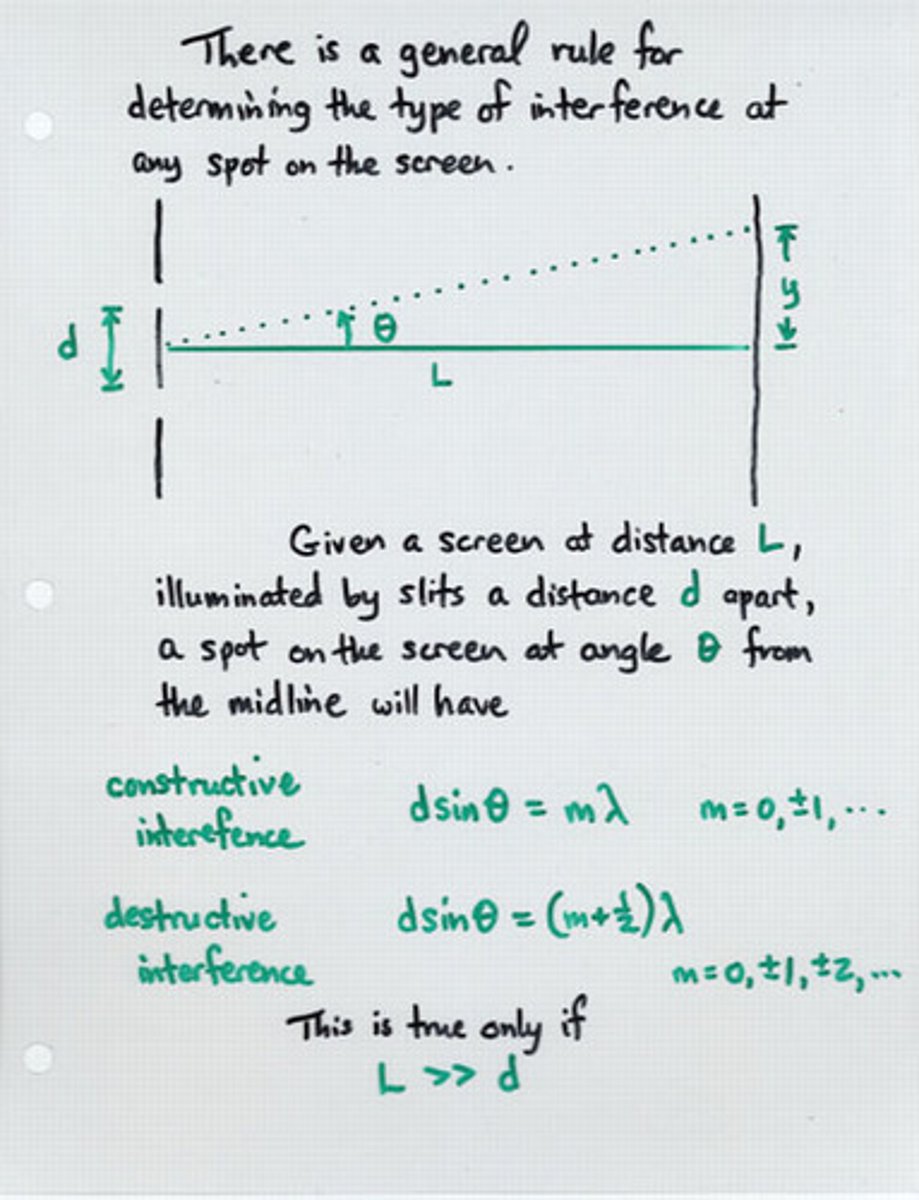
What equation can be used to relate distance between the central bright spot to the next bright spot (∆y) and the distance of the screen from the slits (L)?
tanθ = ∆y/L
θ = angle
∆y = distance between the central bright spot to the next bright spot
L = distance of the screen from the slits
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB A tricky physics professor asked his students to calculate the distance between bright spots if the angle of diffraction at the Slit was 90 degrees. Students couldn't get their calculators to come up with an answer. Why couldn't this be calculated?
Recall that a Slit is a small opening in some barrier. If the light was refracting at 90 degrees, then it would move straight up into the barrier, and would not be able to form a bright spot on the wall outside of the central bright spot!
You are replicating Young's Double Slit Experiment. The slits are 435 nm wide and are 878 nm apart (from the center of one slit to the other). You shine a light with a wavelength of 543 nm through the slits on a screen that sits 2.78 m away from the slits. What will be the distance (in meters) from the central bright spot to the next bright spot on the screen?
(A) 2.19
(B) 3.99
(C) 6.42
(D) 8.56
(A) 2.19
mλ = dsinθ
(1)(543⋅10^-9) = (878⋅10^-9)(sinθ)
(543⋅10^-9)/(878⋅10^-9) = sinθ
approx. .6 (actual: .618) = sinθ
θ = approx. 45° (actual: 38.17°)
tanθ = ∆y/L
tan45° = ∆y/2.78
(approx. 1 (actual: .786))(2.78)
∆y = 2.78 meters (actual: 2.185)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Which of the following is TRUE? As distance between the slits increases, :
I. ∆y decreases
II. λ increases
III. m increases
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III Only
(A) I Only
As distance between the slits increases, ∆y decreases because the θ must decrease according to mλ = dsinθ. λ and m are not affected by a change in d.
CRB True or false? Diffraction refers to the spreading out of light as it passes around obstacles or through small openings, and can be studied in "slit" experiments.
True. Diffraction refers to the spreading out of light as it passes around obstacles or through small openings, and can be studied in "slit" experiments.
What is the advantage of a Diffraction Grating as compared to a Double Slit?
It makes the spots of constructive interference more clearly defined. In fact, they appear as dots.
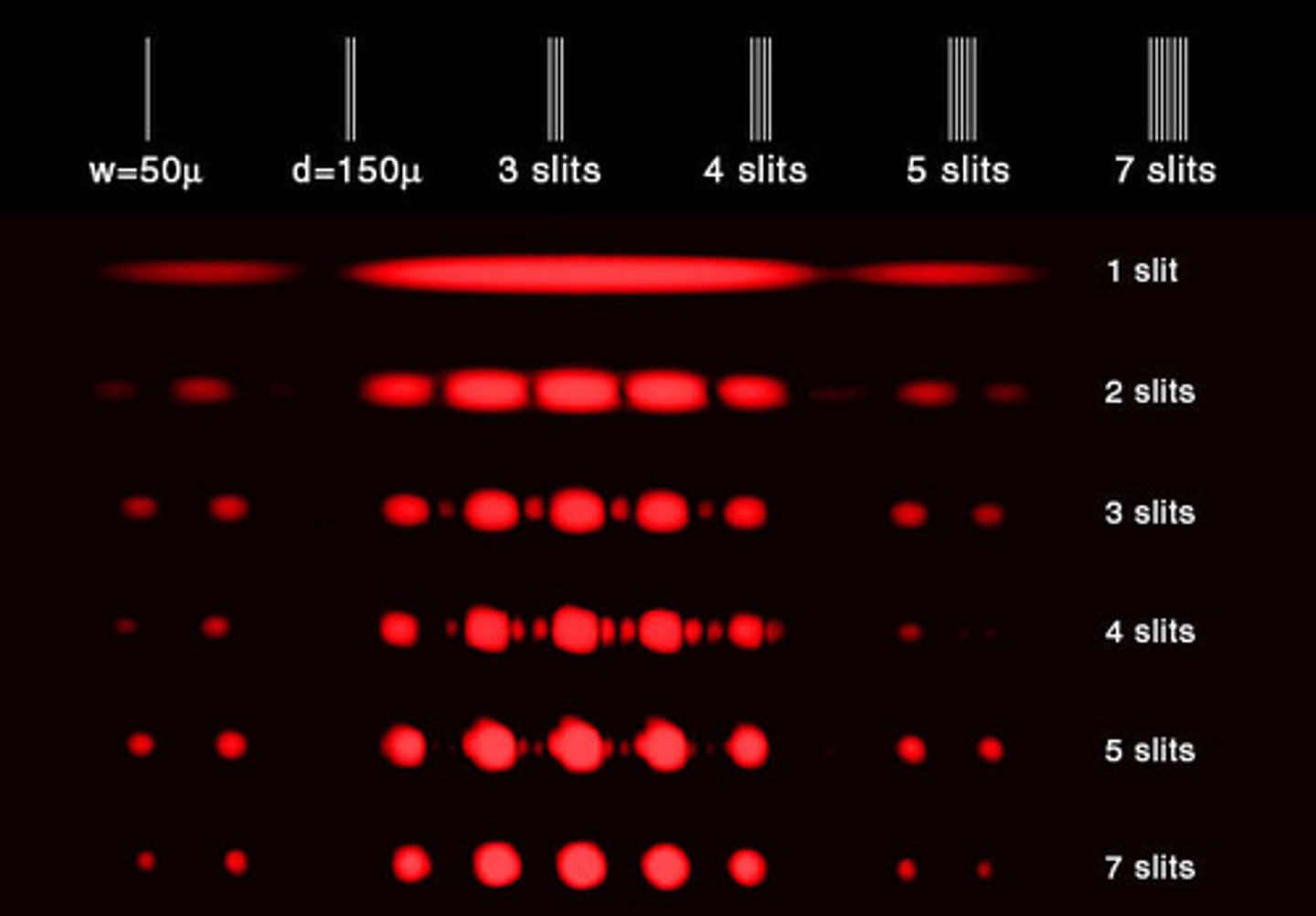
Why is it important to make sure that the distance between all the holes in a Diffraction Grating are an equal distance apart?
It is important because this will allow for perfectly constructive interference between the light from every hole.
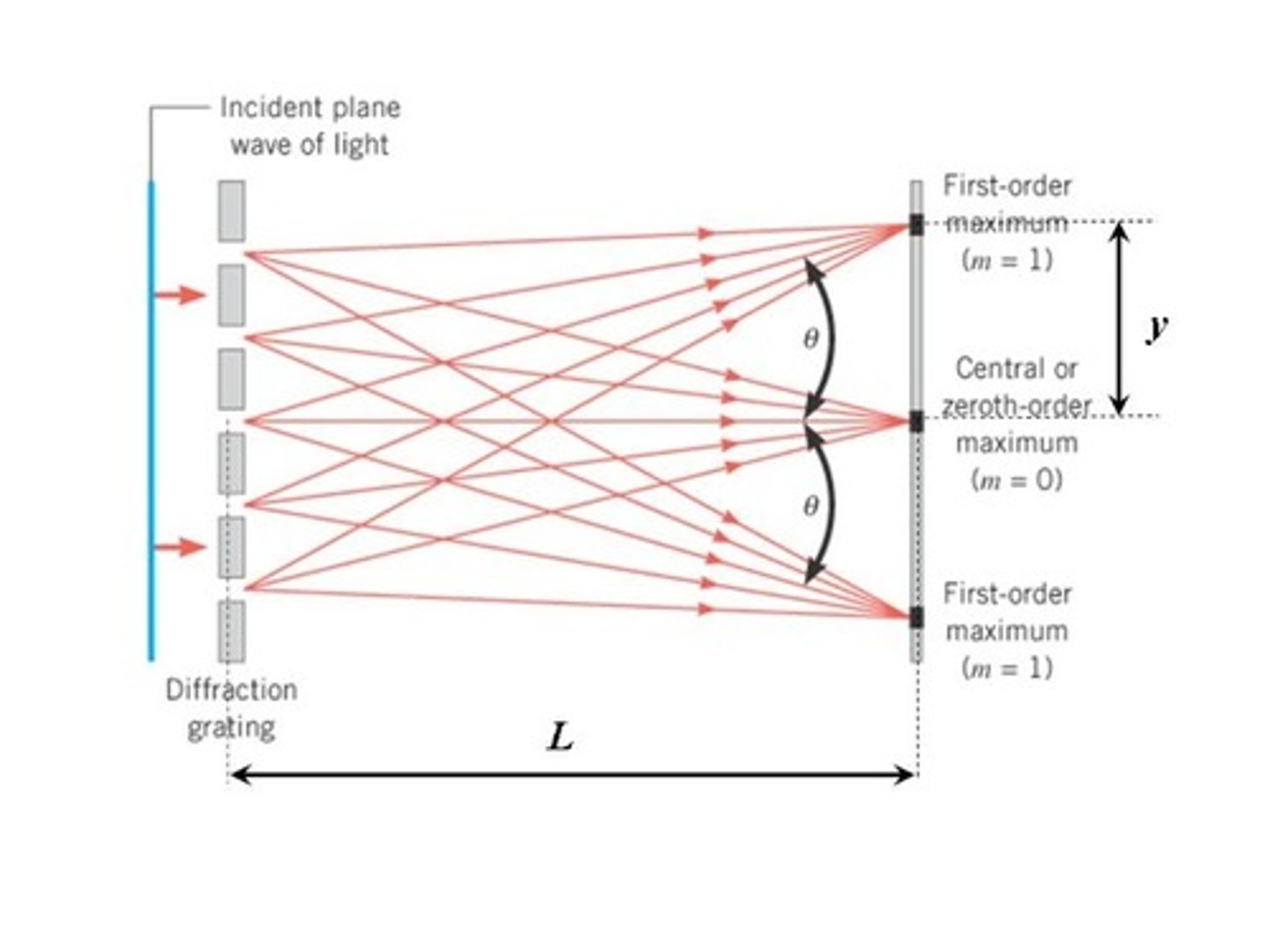
Why do you end up with bright spots with a Diffraction Grating as opposed to a gradation pattern as you get with a Double Slit?
This is due to the fact that the average interference between all the dots results in perfectly destructive interference.
CRB Which of the following materials could act like Diffraction Gratings?
I. Grooves on a CD/DVD
II. Soap Bubbles
III. A puddle with a thin layer of oil on top.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Thin films and very fine grooves can act like diffraction gratings.
What equation relates path length (∆x) and the distance between the holes (d) for a Diffraction Grating?
∆x = dsinθ (same as for the Double Slit!)
∆x = path length
d = distance between the holes
θ = angle between d and perpindicular line
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
For a Diffraction Grating, what equation will allow you to relate λ to θ (with Constructive Interference)?
mλ = dsinθ (same as for Double Slit!)
m = the "order" (whole number integers such as 1,2,3...)
λ = wavelength
d = distance between the holes
θ = angle between d and perpindicular line
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
What principle/law explains why waves spread out/bend as they go through a hole/slit?
(A) Aufbau Principle
(B) Huygen's Principle
(C) Le Chatlier's Principle
(D) Adalgar's Principle
(B) Huygen's Principle
Huygen's Principle explains why waves spread out/bend as they go through a hole/slit.
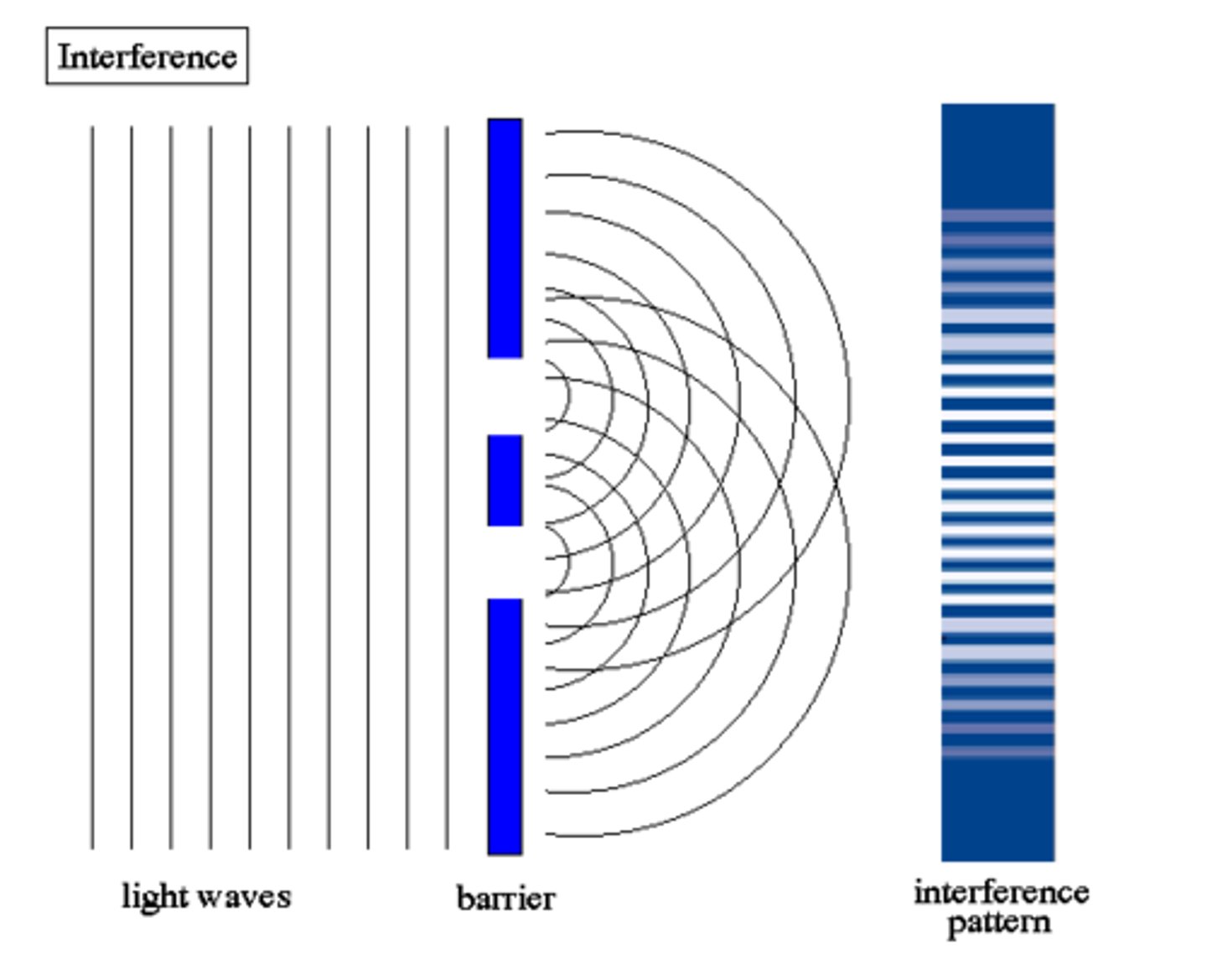
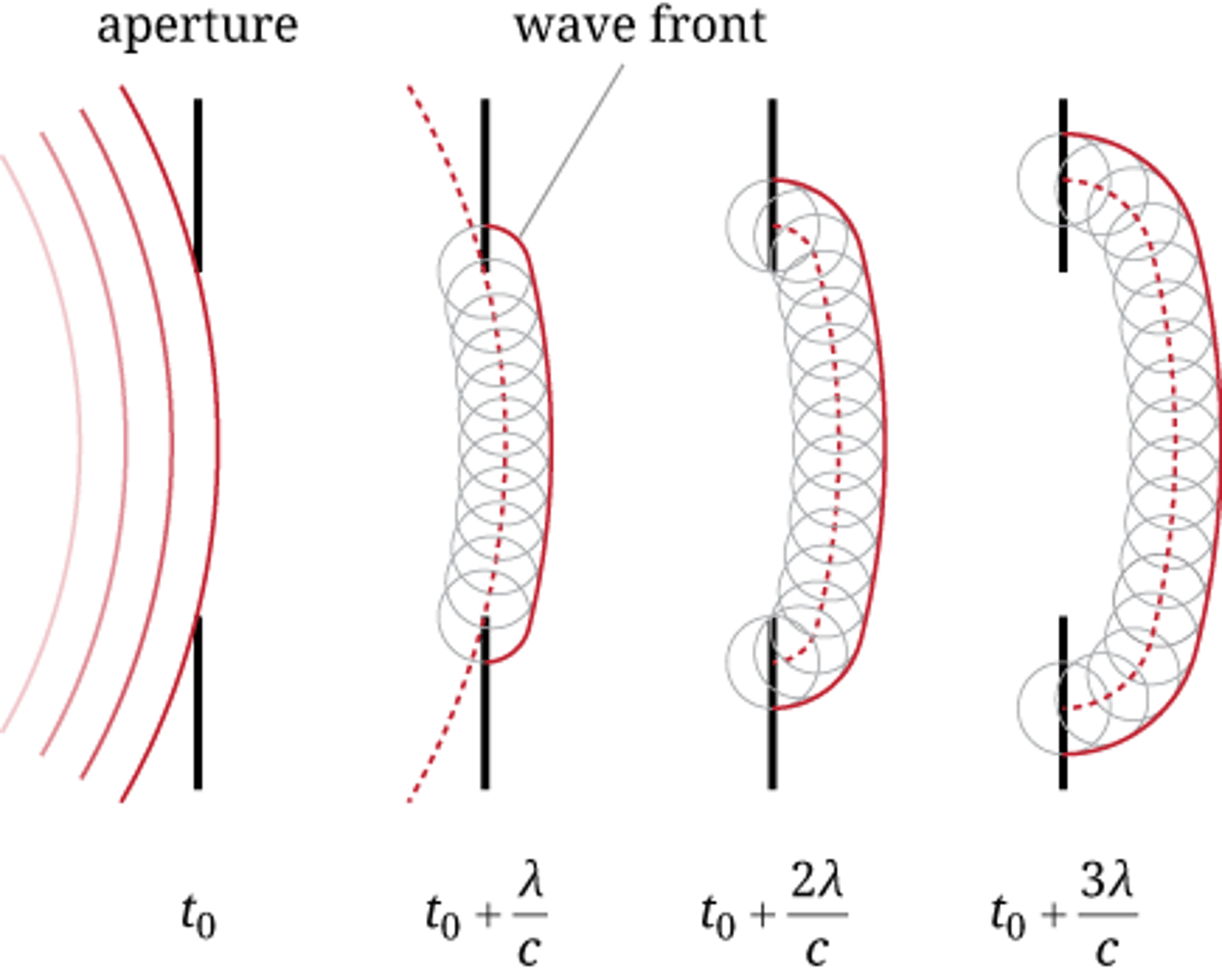
Explain Huygen's Principle.
Huygen's Principle is the idea that each point on wave is a source of another wave.
What pattern is observed on the screen for a Single Slit?
Really big bright spot in the middle followed by spots that are much less bright.
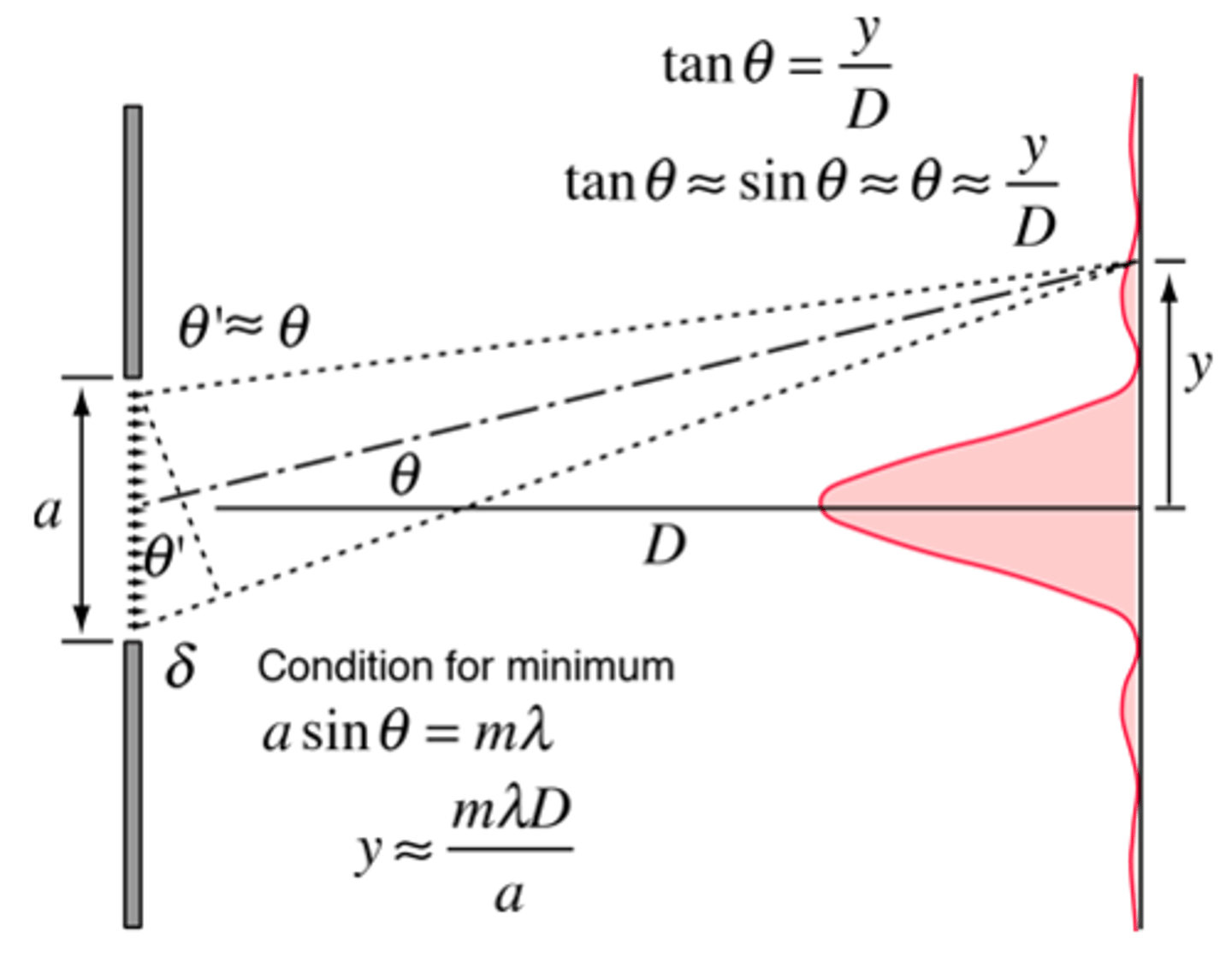
For a Single Slit, what equation will allow you to relate λ to θ (with Constructive Interference)?
TRICK QUESTION! There is no such equation for a Single Slit!
CRB True or false? Due to Huygens' principle, we can consider each discrete space inside the slit as emitting its own waves; because of this, even light in a single slit experiment can experience constructive or destructive interference.
True. Due to Huygens' principle, we can consider each discrete space inside the slit as emitting its own waves; because of this, even light in a single slit experiment can experience constructive or destructive interference.
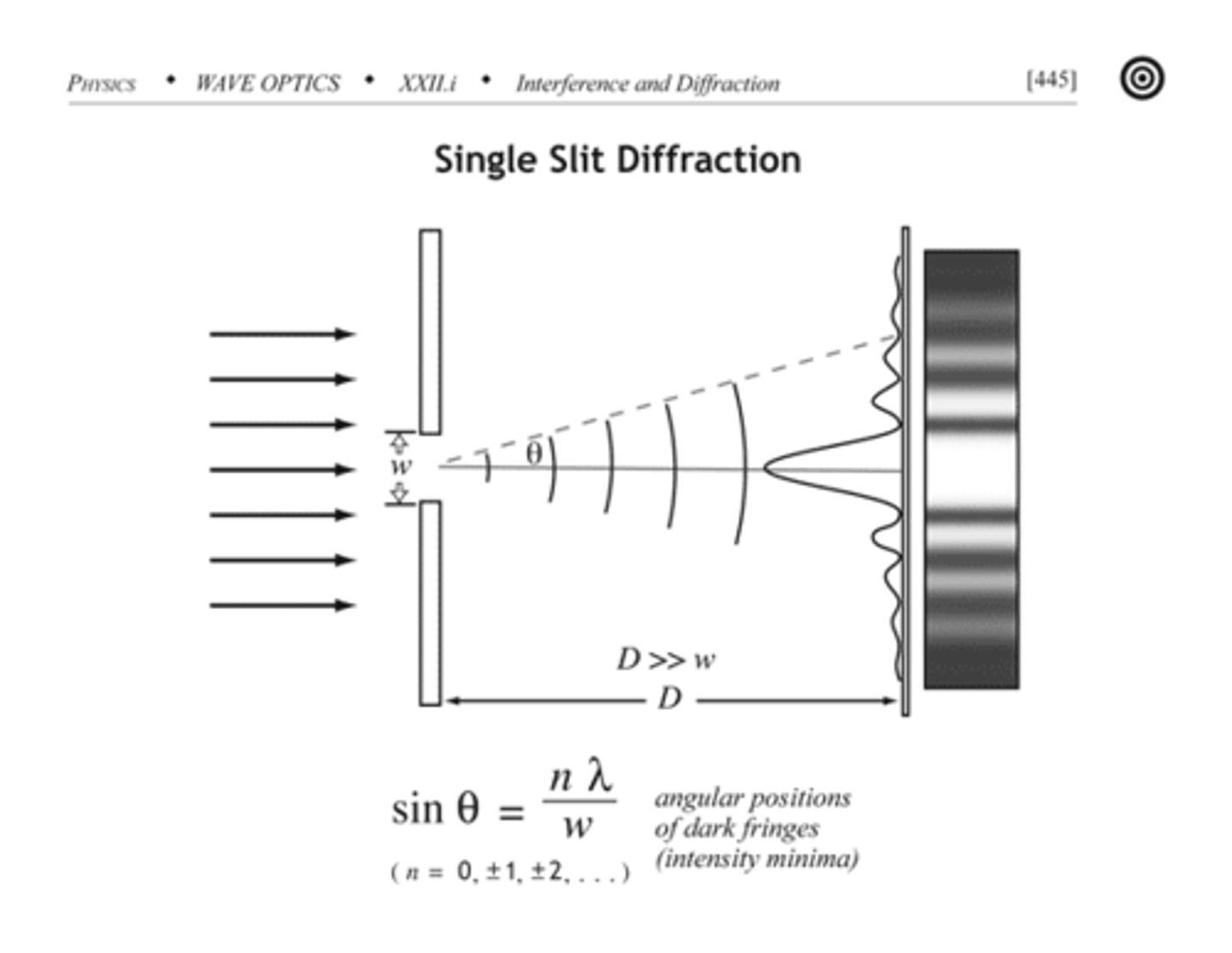
For a Single Slit, what equation will allow you to relate λ to θ (with Destructive Interference)?
mλ = wsinθ
m = the "order" (whole number integers such as 1,2,3...)
λ = wavelength
w = width of the slit
θ = angle between d and perpindicular line
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Why do you end up with Destructive Interference at these certain points?
This is due to how each of the points lower than the previous two points considered and so on and so forth result in Destructive Interference according to the relationship wsinθ = λ.
Why can't you use this equation for Constructive Interference: mλ = (1/2)wsinθ?
This is because you have to consider that the average of all the light rays, including some Destructive Interference among the infinite light rays. In spite of this, the net interference is still constructive.
CRB Recall the Electromagnetic Spectrum and the order of the colors of visible light. Which light would have the highest (sinθ), if keeping the width between slits constant?
(A) Green
(B) Blue
(C) Yellow
(D) Red
(D) Red
Recall the equation mλ = wsinθ. Red is the color with the largest wavelength, and having the largest wavelength means that the sinθ must also be the largest!
CRB True or false? Light Waves that have higher energies will also have larger diffraction angles (sinθ).
False. Light Waves that have higher energies will also have smaller wavelengths, which mean Smaller diffraction angles (sinθ).