Bones and Bone tissue
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Hematopoiesis
blood cell formation
what is a bone with a complex shape?
Irregular bone
ex skull
What is a “sesame seed” shaped bone?
sesamoid bone
ex) knee cap
What is a bone that is longer than it is wide?
Long bone
What is the part of the skeleton with limbs and limb girdles?
Appendicular skeleton
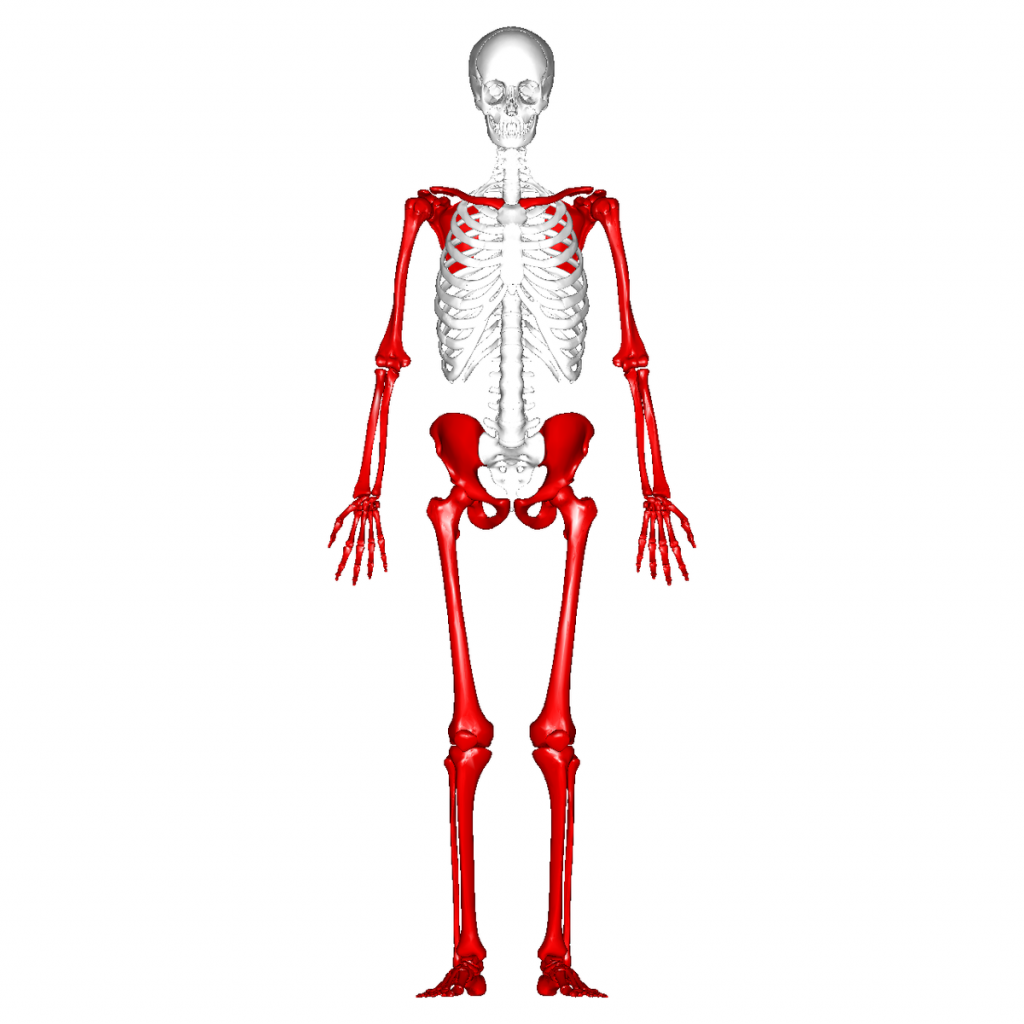
What is the bone that is thin and curved?
ex) ribs
Flat bone
What is a bone with a smaller length and width?
Short bone
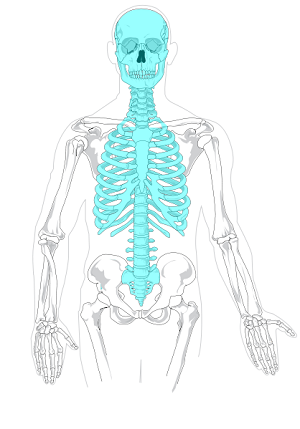
What skeletal system is the skull, vertebral column, and the rib cage defined as?
Axial skeleton
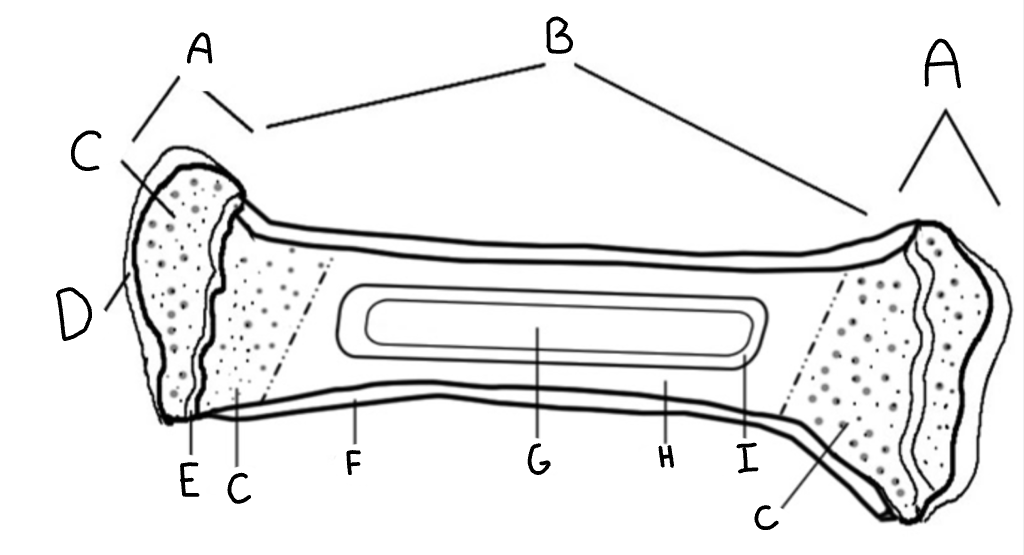
Diaphysis
B- the shaft of a long bone
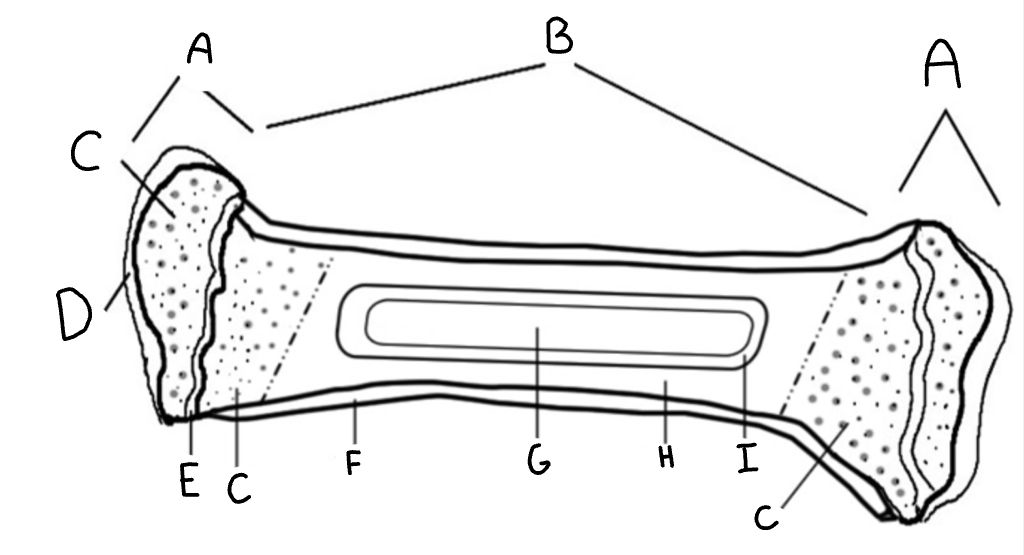
Epiphyseal plate
E- growth plate made of hiline cartlige

Epiphysis
A- Ends of long bone
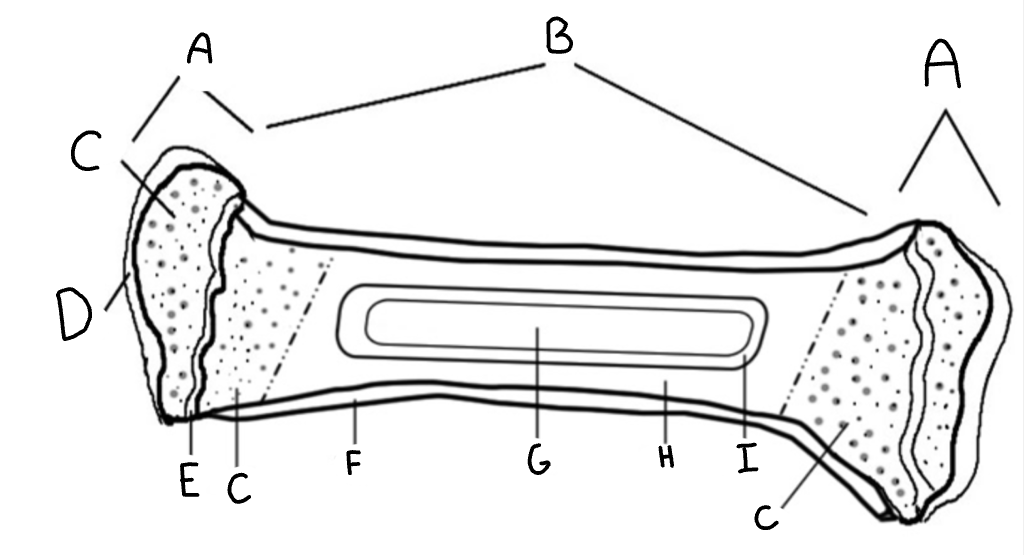
Red marrow
C- produces new blood cells found in spongey bone
Medulary cavity
G- Yellow bone marrow (stores fat)
Articular cartilage
D- prevents bones from rubbing together
Why do most cartilage injuries heal more slowly than bone injuries?
Cartilage does not contain canals and canaliculi to allow direct flow of O2 and nutrients to the living cells.
What are the steps of the endochondral ossification process?
1) the cartilage model of bone is made by chondrocytes
2) periosteum forms
after the periosteum forms around the cartilage model
the collar bone is laid down around the hyaline cartilage model just beneath the periosteum
after the collar bone is laid down around the hyaline cartilage model, just beneath the periosteum
the primary ossification center is created as the diaphysis begins to turn into bone
after the primary ossification center is created as the diaphysis begins to turn into bone
blood vessels from the periosteum invade the primary ossification center, delivering osteoclasts
after the blood vessels from the periosteum invade the primary ossification center, delivering osteoclasts
The osteoclasts remove bone from the bone shaft interior, leaving a marrow cavity
After the osteoclasts remove bone from the bone shaft interior, leaving a marrow cavity
secondary ossification centers appear in each of the epiphyses
After the secondary ossification centers appear in each of the epiphyses
cartilage is left between the primary and secondary ossification centers serves as the growth plate
The last step of the endochondral ossification process is that…
hormones cause the growth plate to ossify and become the epiphyseal line.
Explain the process of intramembranous ossification. How is it different from endochondral ossification?
Bone develops from fibrous membrane, endochondral ossification forms highline cartilage.
What is Wolfs law?
“Use it or lose it"
Closed reduction
Nonsurgical realignment of broken bone ends and splinting of bone
Compression fracture
A fracture in which the bone is crushed; common in vertebral column
Compound (open) fracture
the skin is penetrated
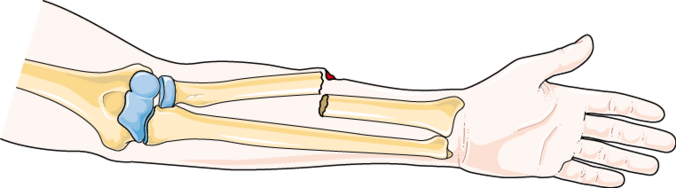
depressed fracture
Broken bone portion is pressed inward

greenstick fracture
Bone breaks incompletely, only one side of the shaft breaks while the other bends.
common in children
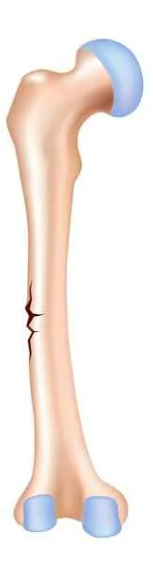
open reduction
Surgical realignment of broken bone ends
simple fracture
Skin is not penitrated
transverse fracture
occurs at an exact 90 degree horizontal angle

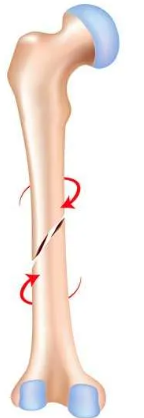
Spiral fracture
a result of twisting forces
atrophy
calcitonin
Brings nutrience IN to the bone
osteoblasts
bone building cells that maintain bone matrix
osteoclasts
Giant, multinucleate cells that break down bone
osteocytes
Mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix
When blood calcium levels bein to drop below homeostatic levels the ______ is released, causing calcium to be released from bones.
parathyroid hormone
What are the important functions of bones?
creation of blood cells
protection for the brain
provision of levers for movement of the limbs
storage of fat
The growth spurt of puberty is triggered by…
high levels of sex hormones
What is the basic structural and functional unit of compact bone:
Osteon
The most common type of cartilage in the skeleton is
hyaline cartilage
True or false: Spongy bone contains osteons.
False
hydroxyapatite
inorganic part of the bone matrix that makes them
What cells dissolve bone and release calcium into the blood?
osteoclasts
Endochondrical ossification
Appositional growth allows a bone to grow in ____.
Width/ thickness