Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
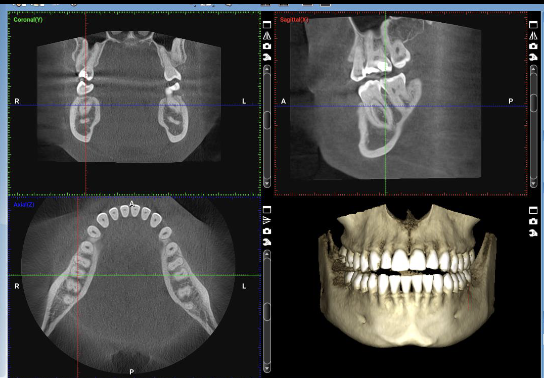
What are CT scans?
Tomographic images in 3D created from many 2D projection images using ionizing radiation
— series of projections
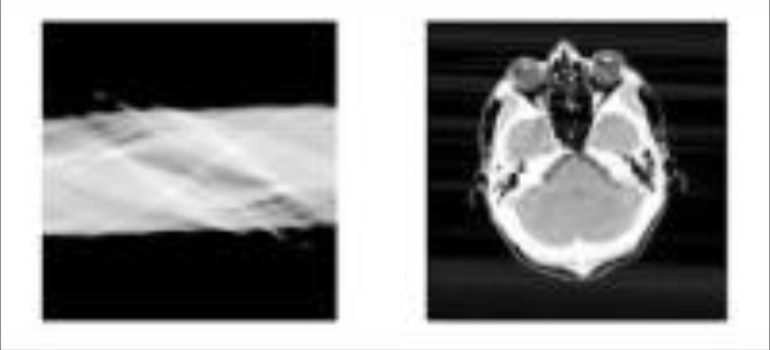
What do CT scans need in order to make an image?
Measurement needs transformation
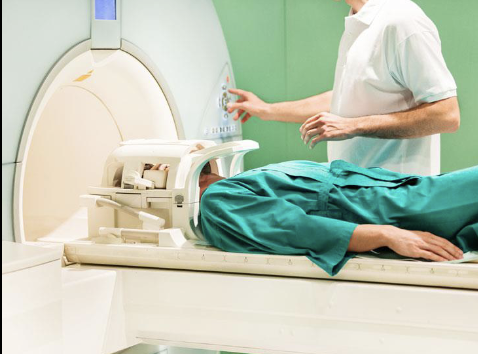
What are MRIs?
Images using three types of magnetic fields created from the transmission of RF from nuclear magnetic moments (of protons)
What is a magnetic field?
A vector field that is direction AND magnitude expressing spatial influence of magnetism
What do magnetic fields describe?
Invisible forces due to
magnets
Electric currents
What are the units of magnetic fields?
1 Tesla = 10,000 Gauss
Examples of magnetic fields
Earth’s magnetic field: ~0.3 G = 30 uT
Clinical MRI “𝐁𝟎” field: 65 mT→7T
Most common clinical MRI 1.5 and 3 T
Name the two types of magnets
Permanent magnet and electromagnet
What is a permanent magnet?
Electron configurations aligned by external field
Ferromagnetic objects can become magnetized
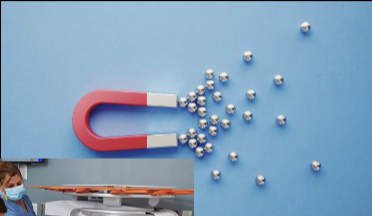
What is an electro-magnet?
Magnetic field from current through a wire (ampere’s law)
MRI fields are mostly made this way
What is the static magnetic field? (B0)
It points along the z-axis, and it is very uniform in the middle. The higher the current you have, the higher the field that goes through this
(Nuclear) magnetic moments and net magnetization
Atoms with an odd number of protons or nucleons (protons + neutrons( have intrinsic magnetic moment
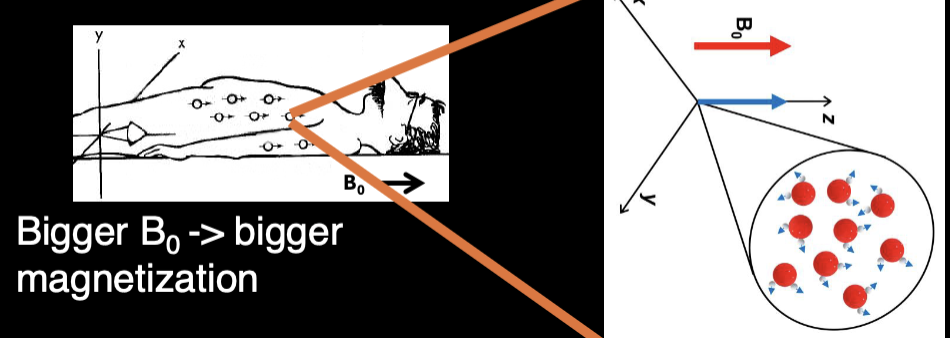
What is you dont have an MRI B0 field?
The nuclei (protons) orient randomly
What do you see when you apply B0 field?
Protons with mag. mom. point slightly towards B0- there is net magnetization
This wants to precess about magnetic fields
Protons/magnetization
In individual spins want to
Precess around B0
The rate depends on the
Nucleus
The net magnetization precesses at the same
Special frequency
What is precession frequency?
Hydrogen nucleus (in water) is most common for MRI