BIOLOGY LAB MIDTERM REVIEW PT. 1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointed forward, and arms hanging at the sides with palms facing forward
Anatomical Position
(above/below)
Superior/inferior
(front/back)
Anterior/posterior
(toward the midline/away from the midline or median plane)
Medial/lateral
(cranial)/(toward the head/toward the tail)
Cephalad/caudal
(belly side/backside)
Ventral/dorsal
(nearer the trunk or attached end/farther from the trunk or point of attachment)
Proximal/distal
(external)/(internal) (toward or at the body surface/away from the body surface)
Superficial/deep
mouth
Oral
boney eye socket
orbital
cheek
buccal
neck
cervical
chest
thoracic
armpit
axillary
arm (upper portion of the upper limb)
brachial
anterior surface of the elbow
antecubital
naval
umbilical
Located below the ribs and above the hips
Abdominal
groin
inguinal
thigh
femoral
genital
pubic
kneecap
patellar
fingers or toes
digital
leg
crural
back of the head
occipital
point of the shoulder
acromial
shoulder blade
scapular
lower back
lumbar
buttocks
gluteal
back of the knee
popliteal
calf
sural
heel of the foot
calcaneal
longitudinal plane that divides the body (or an organ) into anterior and posterior parts
frontal plane/coronal plane
runs longitudinally and divides the body into right and left parts
sagittal plane
runs horizontally, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts
transverse plane
cranial cavity and vertebral cavity
dorsal cavity
contains the brain
cranial cavity
contains spinal cord
vertebral cavity
contains heart (pericardial) and lungs (pleural)
thoracic cavity
contains digestive organs
abdominal cavity
contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
pelvic cavity
contains abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
abdominopelvic cavity
contains thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
ventral cavity
gallbladder, liver
organs found in the right upper quadrant:
stomach, pancreas, spleen
organs found in the left upper quadrant:
organs found in the right lower quadrant:
cecum, appendix
left ureter, left kidney, part of colon
organs found in the left lower quadrant:
right hypochondriac region, epigastric region, left hypochondriac region, right lumbar region, umbilical region, left lumbar region, right iliac (inguinal) region, hypogastric (pubic) region, left iliac (inguinal) region
abdominopelvic regions:
orbital cavity, nasal cavity, oral cavity, middle ear cavity, synovial cavity
other body cavities:
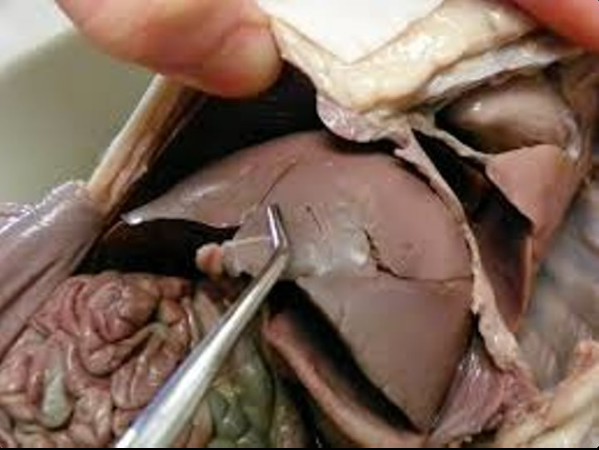
produces bile
liver
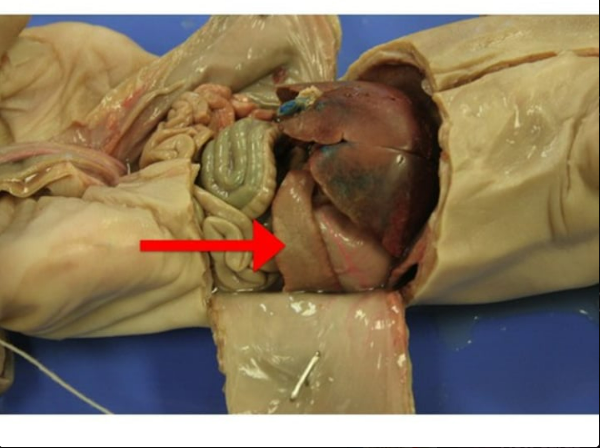
Old red blood cells are recycled, and platelets and white blood cells are stored there
spleen
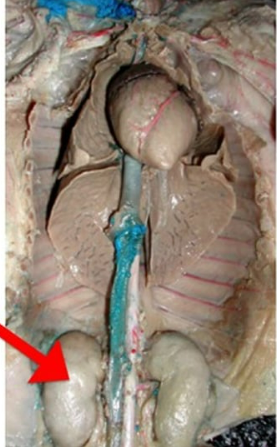
maintain overall fluid balance, regulate and filter minerals from blood, filter waste materials
kidney
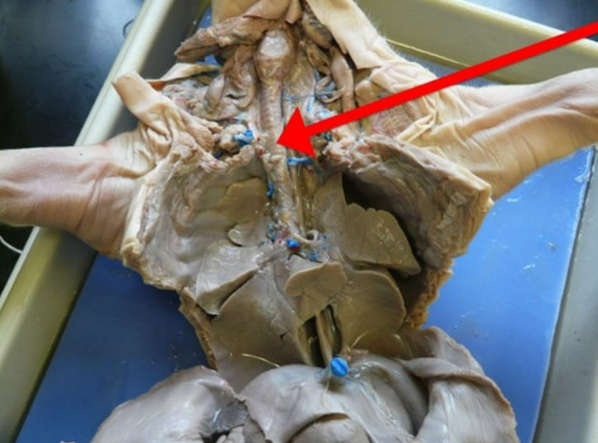
provides air flow to and from the lungs for respiration
trachea
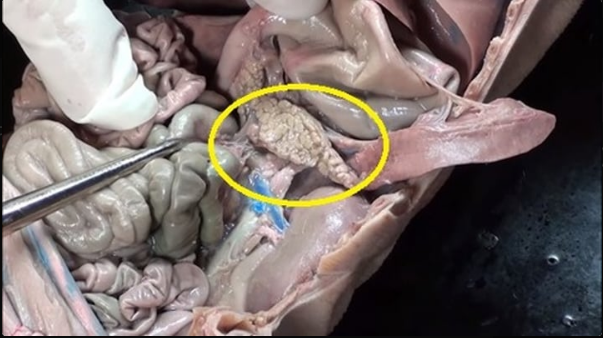
produces insulin, enzymes and hormones that help break down foods
pancreas
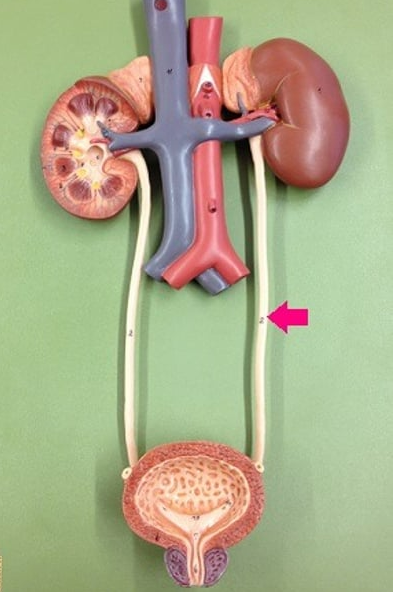
tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
ureter
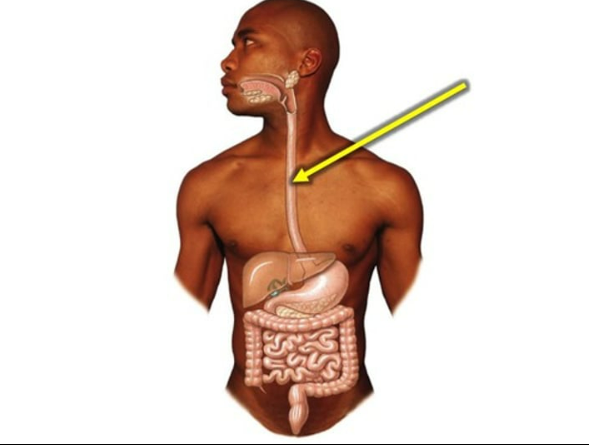
to carry food, liquids, and saliva from the mouth to the stomach
esophagus
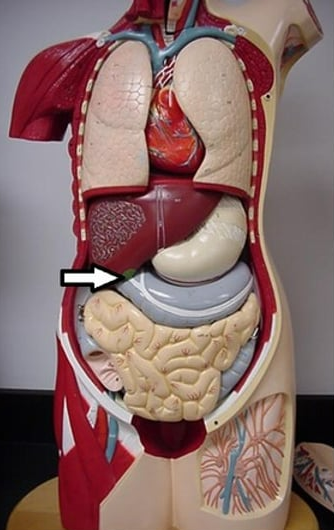
stores and concentrates bile
gallbladder
absorption of nutrients and minerals from food
small intestine
absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and transmit the useless waste material from the body
large intestine
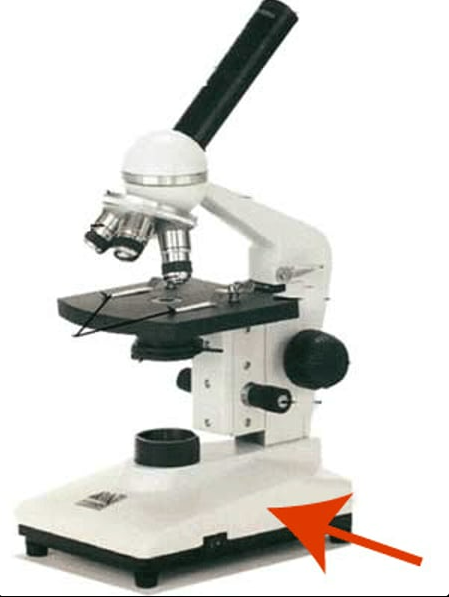

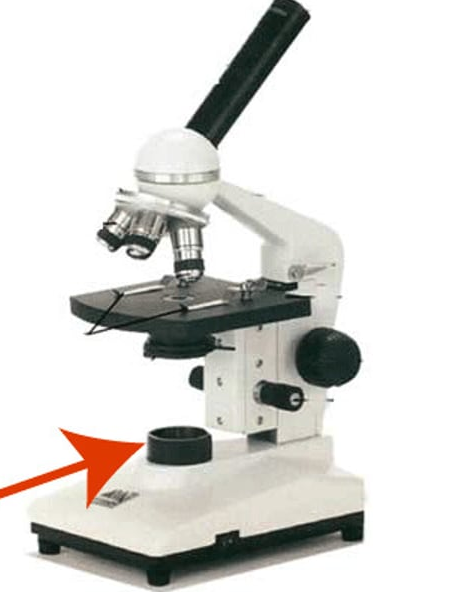
Base
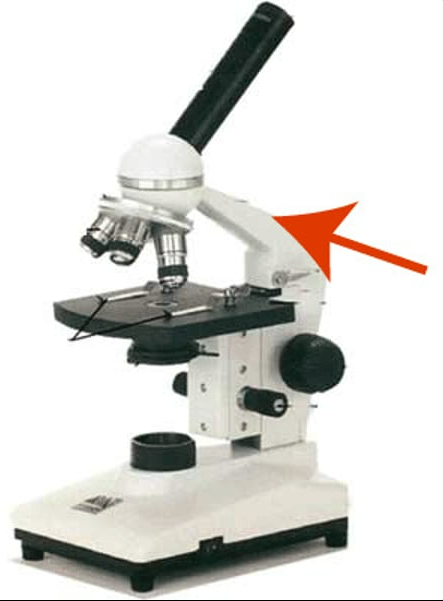
arm
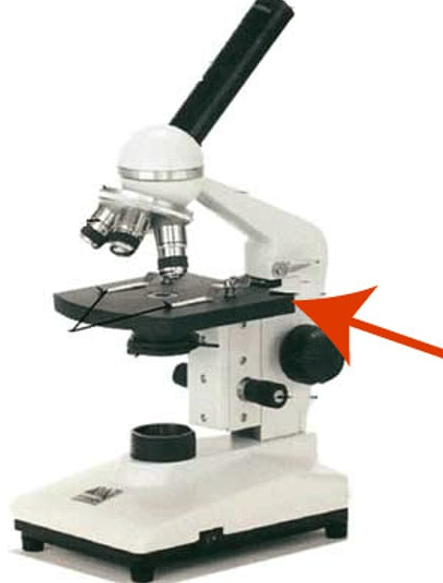
stage
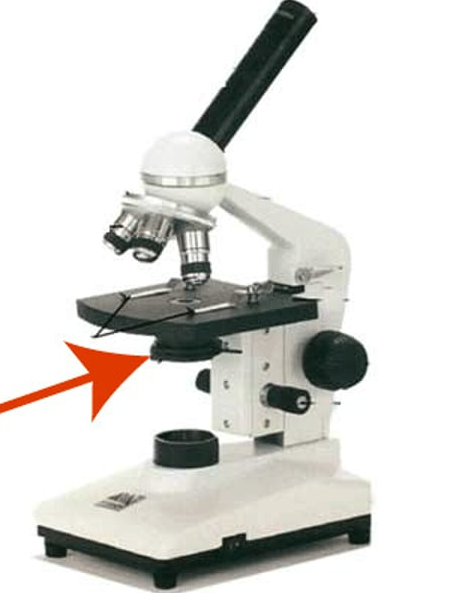
condenser
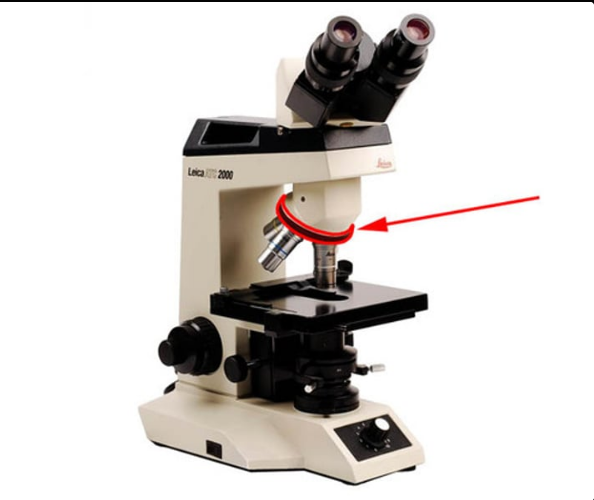
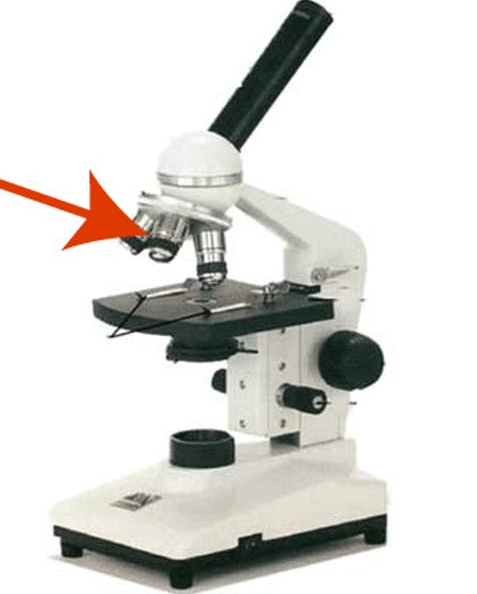
Rotating nosepiece
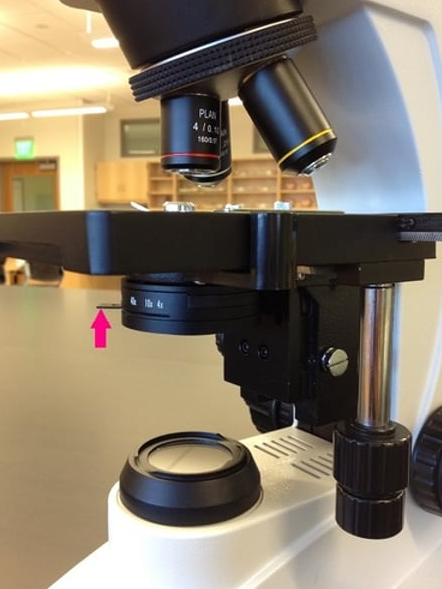

Iris diaphragm lever

Substage light
Ocular lens
Fine adjustment knob

Coarse adjustment knob

Objective lens
10x
Magnification of an ocular lens:
ocular lens x objective lens
total magnification
4x
scanning lenses
10x
low power lenses
40x
high power lenses
the ability to discriminate two close objects as separate
resolution
separates cell contents from the surrounding environment, providing a protective barrier
plasma membrane
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
cytoplasm
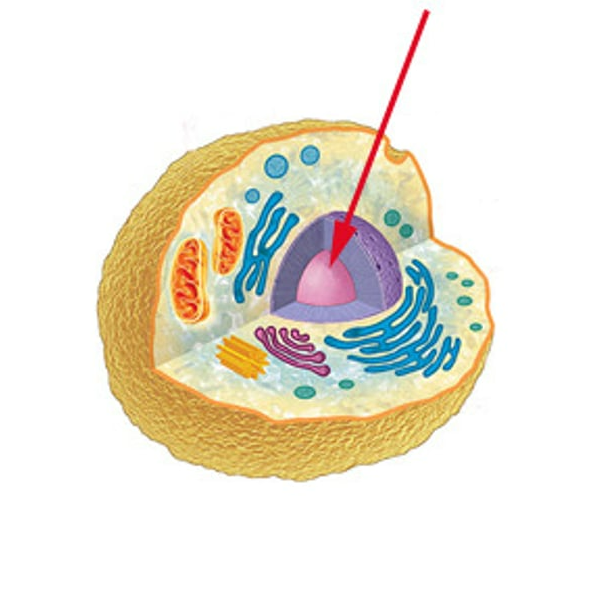
contains DNA, control center of the cell
nucleus
passageway for molecules into and out of the nucleus
nuclear pore
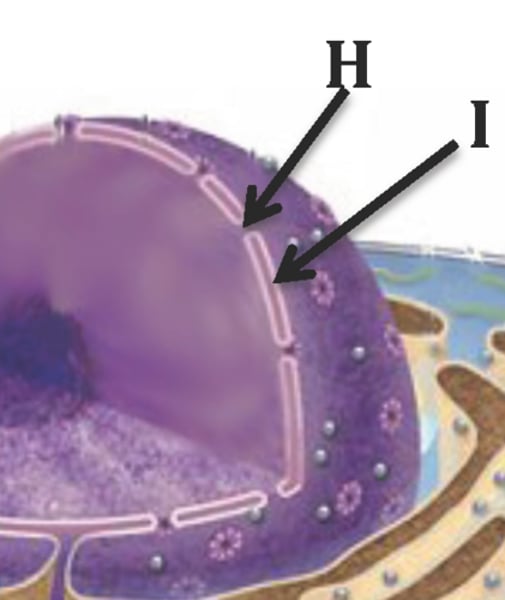
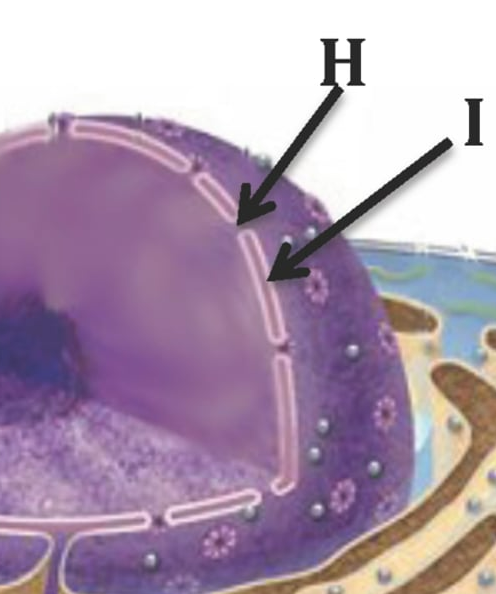
contains dissolved salts, nutrients, and other solutes essential for the cell
nuclear plasma
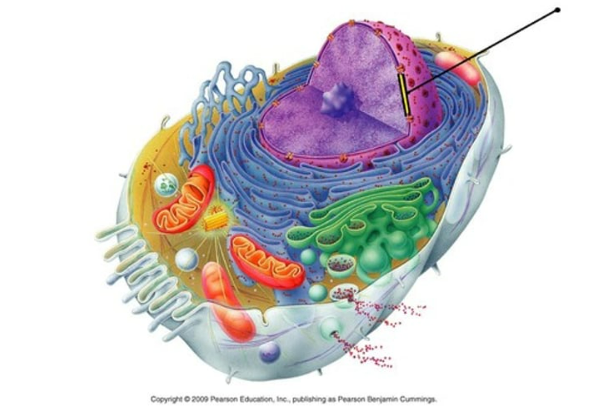
A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
nuclear envelope
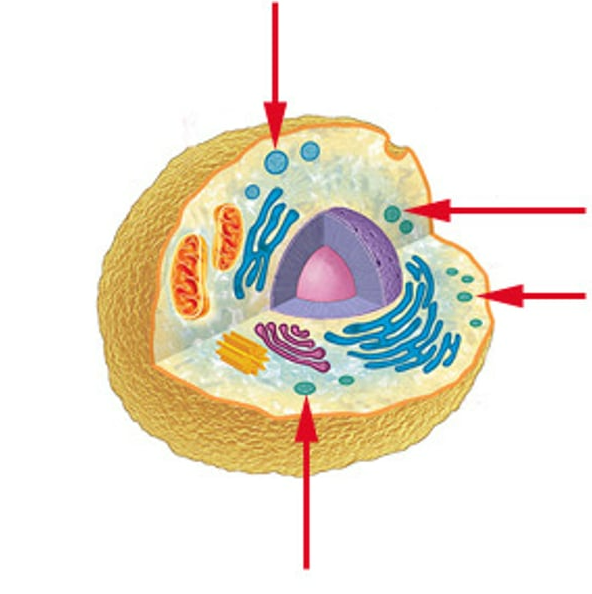
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
vacuole
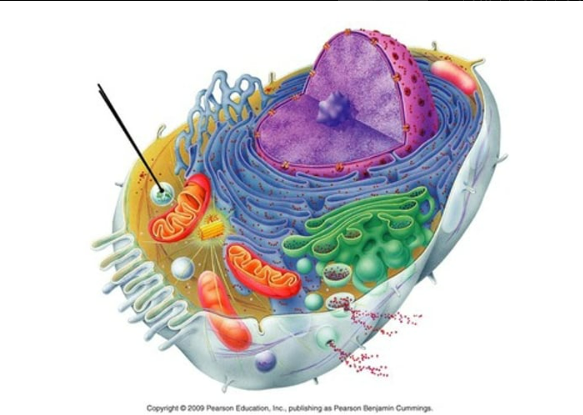
function to digest worn-out cell organelles and foreign substances that enter the cell
lysosome
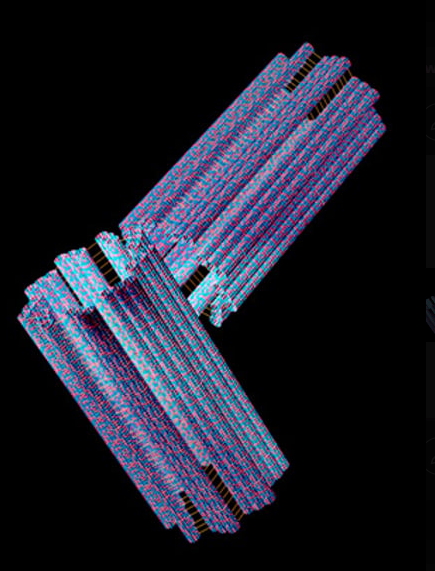
they direct the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division
centrioles
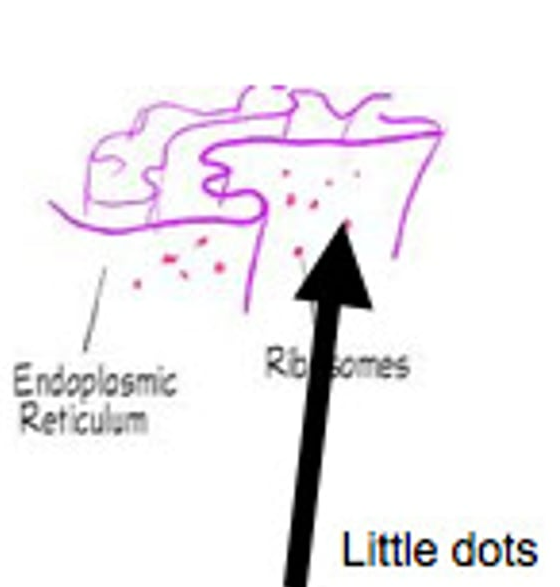
composed of RNA and protein, attached to the rough ER, protein synthesis
ribosomes
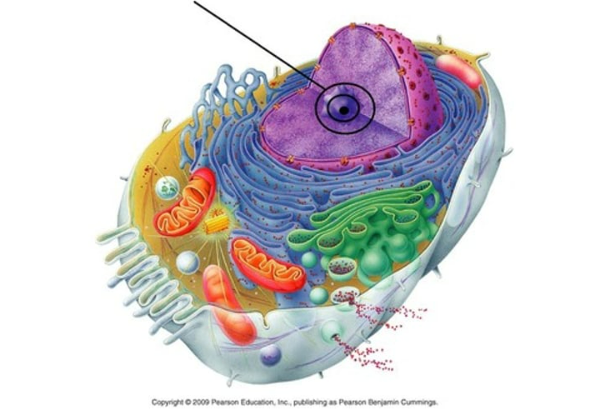
assembly sites for ribosomes
nucleoli
genetic material loosely dispersed throughout the nucleus in a threadlike form
chromatin
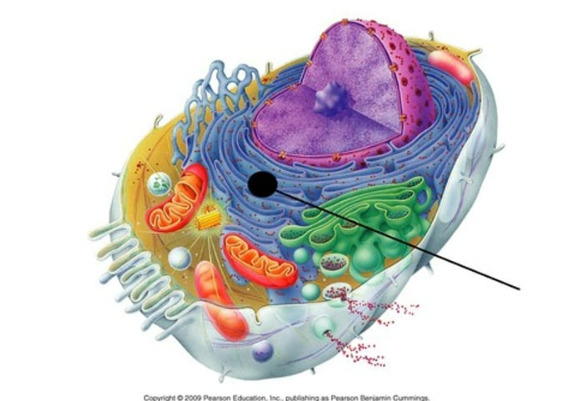
provide an area for storage and transport of the proteins made on the ribosomes to other cell areas
rough endoplasmic reticulum
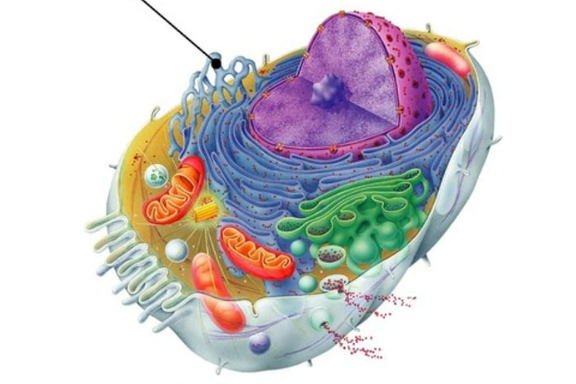
site of steroid and lipid synthesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
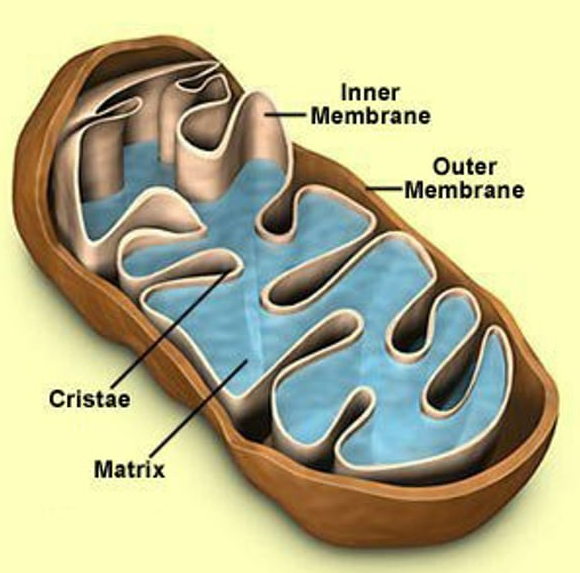
contain enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs to produce cellular energy (ATP), powerhouse of the cell
mitochondria
formed at the plasma membrane to allow the absorption of large molecules
pinocytic vesicle
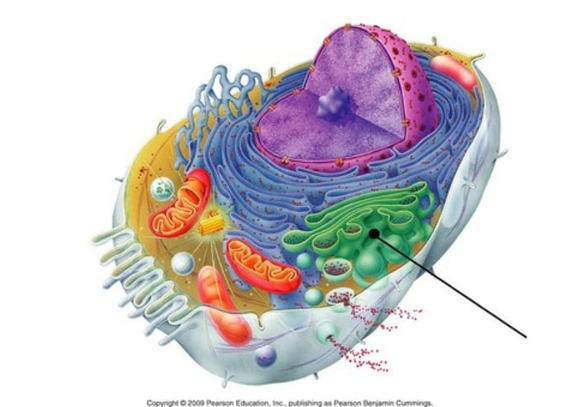
stack of membranes in the cell that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
division of the cytoplasm, begins during late anaphase and continues through and beyond telophase
cytokinesis
G1 (growth, S (DNA synthesis), G2 (final preparations)
interphase
longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus
prophase
phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
metaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
anaphase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
telophase