Pulmonary Two, Ethical and Legal Issues, End of Life Care, EKG Two, & Hemodynamics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What are some nursing interventions to prevent ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP)?
raise the HOB to 30 degrees
do daily sedation vacations
do chlorhexidine oral care q12hr
reposition pt q2hr
fluid conservation
What is autonomy?
the patient has the right to make their own healthcare decisions
What is beneficence?
it is the acting in the patient’s best interest
What is nonmaleficence?
it is to do no harm; avoid actions that could harm the pateint
What is justice?
it is treating the patients fairly and equitably
What is veracity?
it is telling the truth; provide honest communication
What is fidelity?
it is keeping a promise; maintain trust and confidentiality
What is negligence?
it is the failure to act as a reasonably prudent nurse would
What is malpractice?
it is professional negligence resulting in harm
What is battery?
it is touching a patient without consent
What is assault?
it is threatening a patient with harm
What is false imprisonment?
it is restricting a patient’s movement without justification
What is informed consent?
it is when the provider explains risks/benefits; nurse verified understanding from patient
What is the philosophy of care for hospice?
reserved for the terminally ill
appropriate after the decision to withdraw care
home, hospital, inpatient hospice
DNR must be in place to be paid for by insurance or Medicare/Medicaid
Emphasis is on comfort rather than cure
Views dying as a normal human process
What are some nursing interventions for hospice care?
assess changes in mobility, sleep, and weight
educate patient and family on signs of transitioning and active dying
removal of all lines, vent support, and therapies-PRIOR to the referral
assure the family that the patient will not suffer or be abandoned
provide emotional, spiritual care resources: grief counselors, spiritual care providers
facilitate provider visitation and presence of family
promote memory sharing, storytelling, and creation of the lasting legacy
What is palliation?
it is the act or process of relieving a patient’s suffering without curing the disease
What are the requirements when using restraints on a patient?
must have provider orders (need new one every 24 hrs)
check for skin breakdown q2hr
document restraints
make sure you can fit 2 fingers between patient’s skin and restraints
tie restraint to bed frame
What is the rate for sinus bradycardia from the SA Node?
<60bpm
What is the rate for sinus tachycardia from the SA Node?
>100bpm but <150bpm
What is premature atrial contraction?
an early ectopic beat
interrupts regularity
What is atrial flutter?
arises from a single irritable focus in the atria
has flutter waves
What is atrial fibrillation?
arises from multiple ectopic beats in atria
no P waves seen
always irregular
What is premature junctional contraction?
it is an early ectopic beat in the junction that interrupts the regularity
What is supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)?
improper electrical activity above the ventricles
rhythm is regular except it may be hard to distinguish between a P wave and T wave if HR is really high
rate >150-250bpm
What are the treatments for stable supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)?
vagal maneuvers (only done by provider)
adenosine 6mg raid IVP followed by 20mL bolus of NS
if not effective repeat adenosine with 12mg; may repeat 12mg x 2 times
synchronized cardioversion
What is the treatment for unstable supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)?
immediate synchronized cardioversion
SVT
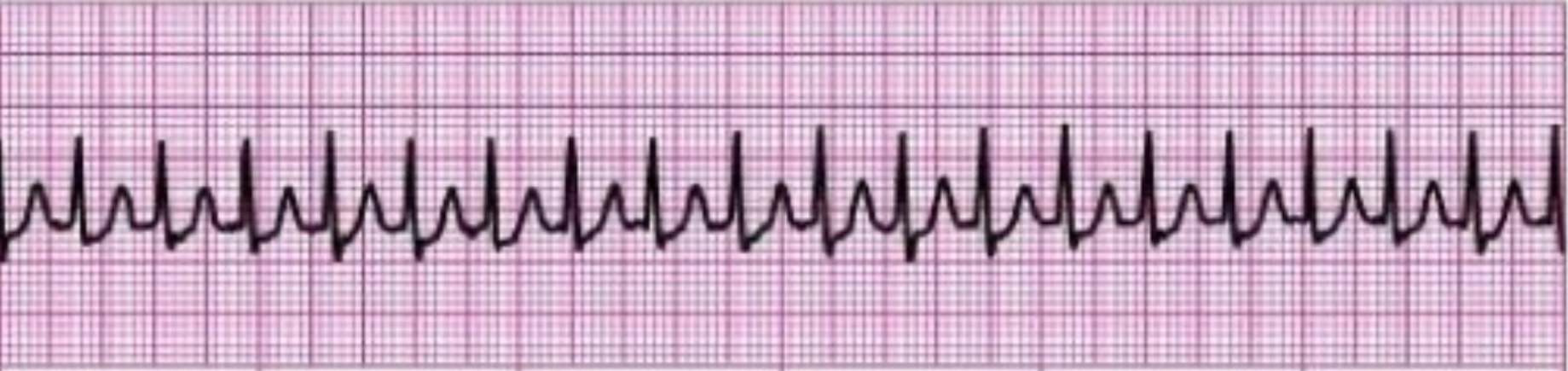
What rhythm does the picture attached depict?
supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
What is premature ventricular contraction?
early ectopic beat in the ventricles that interrupts the regularity
sided by side PVCs are called couplet
What is ventricular tachycardia (VTACH)?
rapid life-threatening dysrhythmia that originates in the ventricles
exists when three or more PVCs occur in immediate succession at a rate higher then 100 bpm
What will we see on the EKG strip if ventricular tachycardia (VTACH) occurs?
QRS wider than 0.10 sec
absent p waves
may present with or without pulse
What are the treatments for stable ventricular tachycardia (VTACH) and torsades?
amiodarone 150mg IVP followed by 300mg IVP
lidocaine 1.1-1.5mg/kg max dose in 3mg/kg
synchronized cardioversion
What is the treatment for unstable ventricular tachycardia (VTACH) and torsades?
immediate synchronized cardioversion
v-tach & torsade
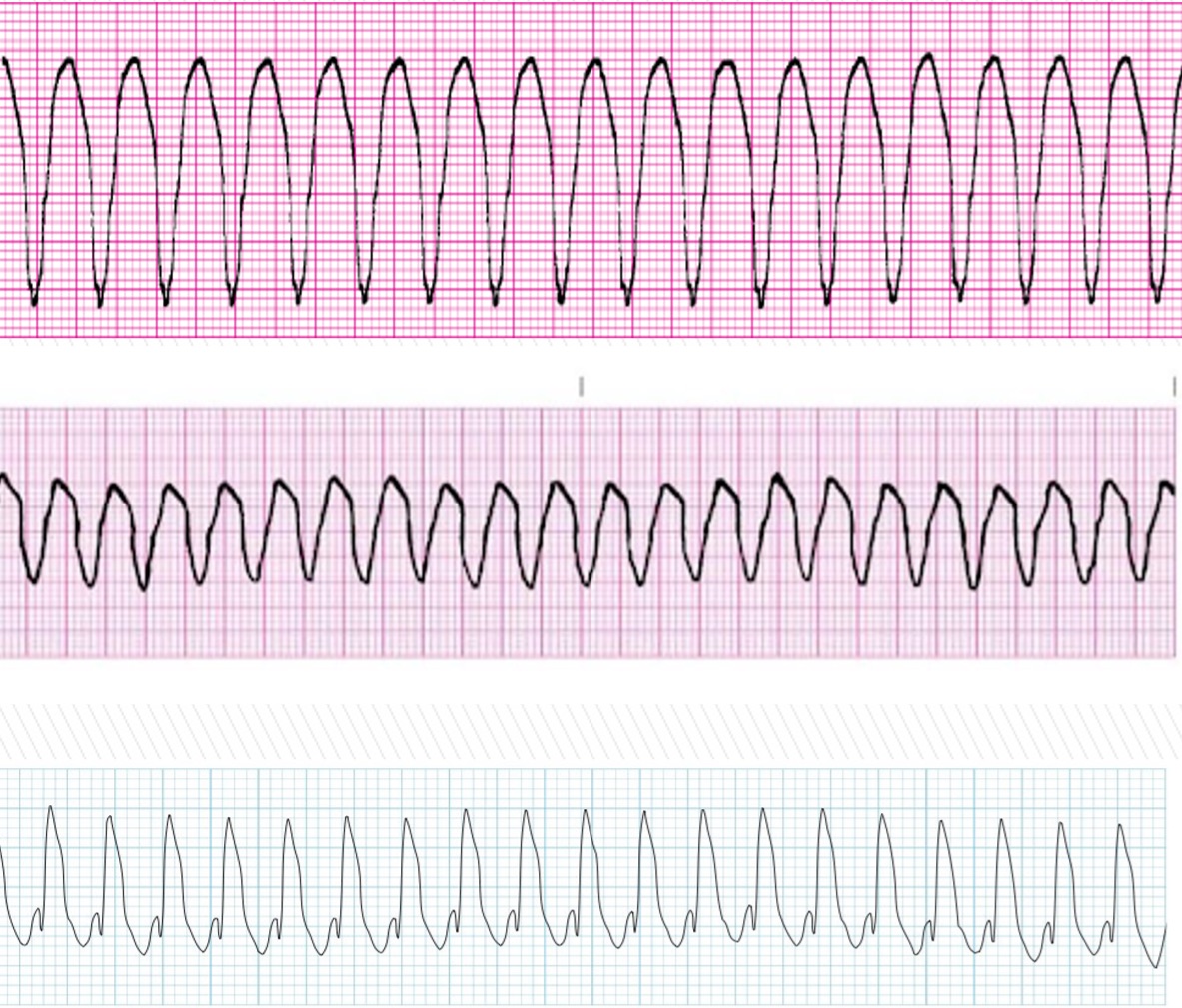
What rhythm does the pictures attached depicts?
ventricular tachycardia (v-tach)
What is the treatment for ventricular tachycardia (VTACH), torsades, and ventricular fibrillation with no pulse?
call for help/ Code Blue
begin CPR until defibrillation is available; defibrillate as soon as possible
on arrival of defibrillator, deliver unsynchronized shocks
epinephrine 1mg IVP q3min; NO MAX DOSE
administer magnesium 1-2gms IV if torsades
What will we see on the EKG strip if torsades occurs?
may be regular or irregular
no P wave or PR interval
QRS is greater than 0.12 sec
gradual alteration in amplitude & direction
may present with or without a pulse
What will you give if torsades is shown on the EKG strip?
administer magnesium 1-2hms IV
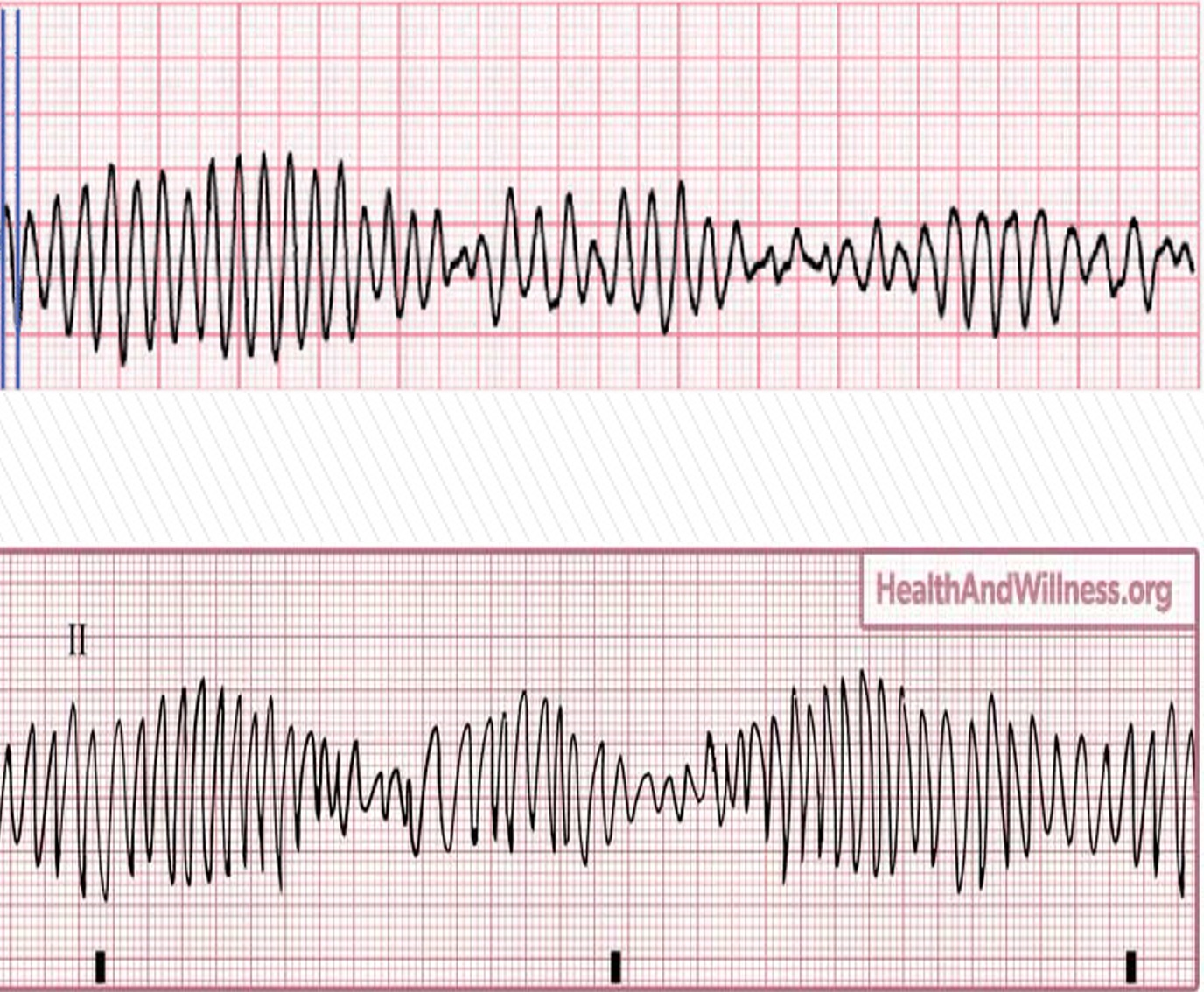
What rhythm is the photo attached depict?
torsades
What will we see on the EKG strip if ventricular fibrillation occurs?
chaotic pattern (meaning a scribbly line)
no discernible P, Q, R, S, or T waves
What is pulseless electrical activity?
it exists when organized electrical activity (other than VT) is present on the cardiac monitor, but the patient is pulseless
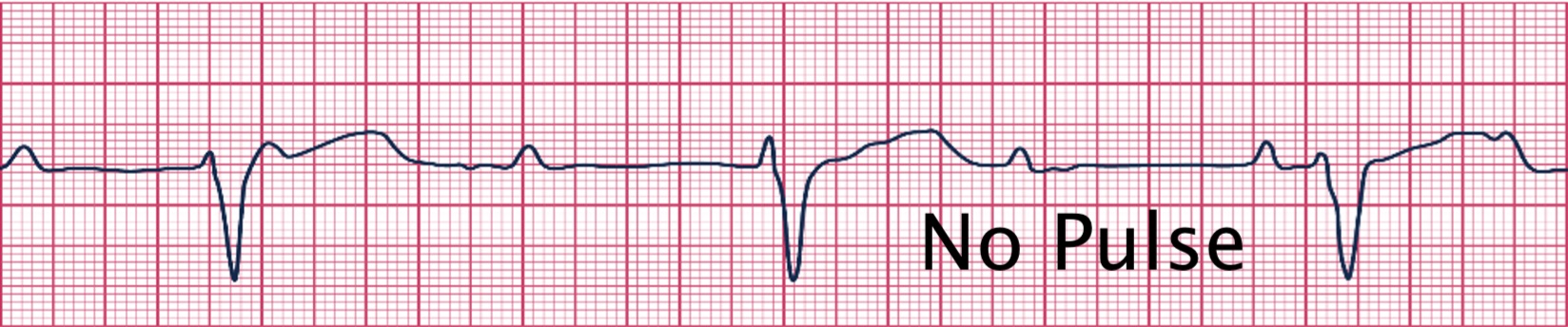
What rhythm does the photo attached depict?
pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
What are the treatments for PEA and asystole?
call for help/ Code Blue
get crash cart/defibrillator (in case pt goes into a rhythm that can be defibrillated the defibrillator is already present)
preform immediate CPR
epinephrine 1mg q3min; NO MAX DOSE
consider possible causes of the rhythm
prepare for endotracheal intubation
NEVER cardiovert or defibrillate PEA or asystole
What is asystole?
total absence of ventricular activity
there is no ventricular rate or rhythm
no pulse
no cardiac output
will see a flat line on EKG
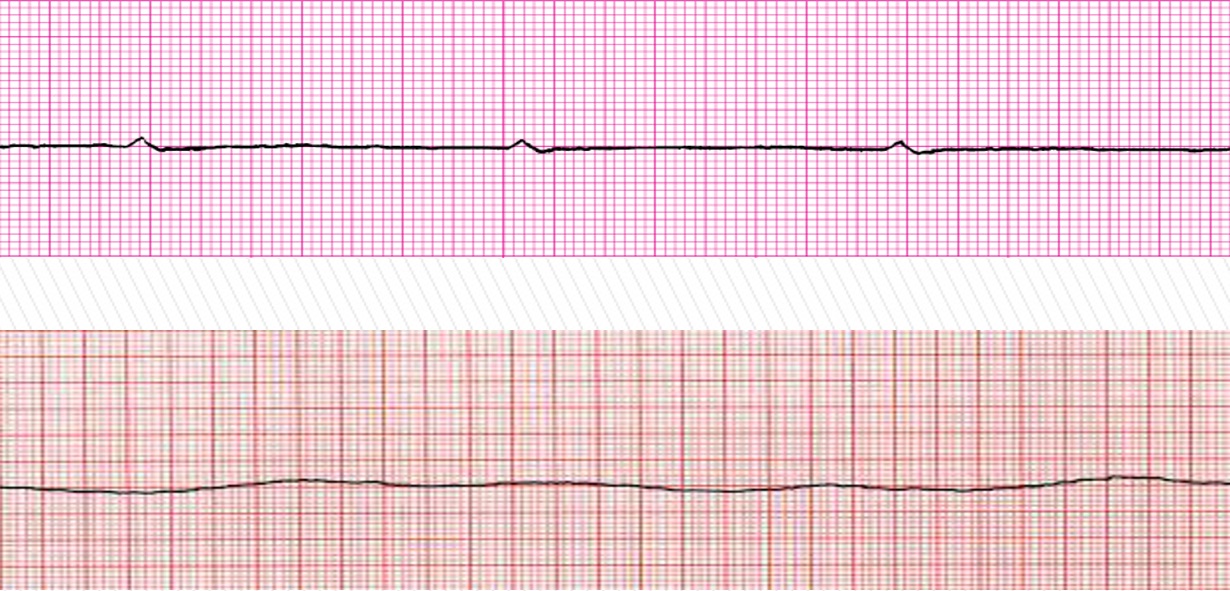
What does the photo attached depict?
asystole
What is an arterial line?
it is a catheter that is inserted into an artery that gives a direct, constant, and more accurate measurement of the blood pressure
can be placed in the radial or femoral arteries
What things can we do with an arterial line?
draw blood
ABG values
blood pressure readings
NEVER give meds through line
What are some patient education points about arterial line care?
we need to protect this line, and if it comes out, a lot of bleeding will happen
What kind of dressing should be used for an arterial line?
clear transparent dressing
- assess circulation and hematoma
- we can use arm boards to keep the arm straight
What three pressures will an arterial line provide?
systolic blood pressure
diastolic blood pressure
mean arterial pressure (70-100 is normal range)
How do you level the transducer on an arterial line??
level the transducer at the phelbostatic axis, 4th intercostal space mid axillary line (leveling at the heart) for a more accurate reading
How do we assess the site of the arterial line?
check the dressing
neurovascular assessment (check perfusion most distal to the site)
-Pulse
-Paralysis
-Parasthesia
-Pain
-Pallor
-Polkliothermia
What are the complications of an arterial line?
bleeding
thrombosis
air embolism
infection
arterial spasm
hematoma
What do we do after removing an arterial line?
we want to hold pressure at the insertion site for at least 5 minutes
What are pulmonary artery catheters?
aka "swan gans" is a specialized catheter placed directly into the pulmonary artery
What does a pulmonary artery catheters (PAC) measure?
CVP (central venous pressure
CO (cardiac output)
PAP (pulmonary artery pressure)
PAWP (pulmonary artery wedge pressure)
SvO2
blood temp
How is pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) performed?
a physician can inflate a balloon on the PAC with 0.8-1.5 mL of air with a special syringe for a MAXIMUM of 15 seconds
this is an indirect measurement of the left side of the heart
What are the nursing interventions after a pulmonary artery catheter is placed?
x ray to confirm placement
monitor EKG rhythm (if line gets pulled out into the RV, PVC can happen)
correct positioning of the pt (anytime we move the pt, we have to re-level the arterial line or PAC to the phelbostaic axis
What nursing interventions should the nurse implement to avoid CLABSI?
daily chlorahexadine baths
changes tubing q 72 to 96 hrs
aseptic treatment of tubing infusion ports (scrub hub)
keep pressure on flush bag 300 mmHg and ensure fluid is in flush bag
monitor waveform
make sure tip is deflated
What medications do we give if a patient has increased preload?
diuretics
venous vasodilators
What do we give to the patient with decreases preload?
vasopressors
fluids
What medications do we give to increase contractility of the heart?
positive inotropes
- digoxin
- dobutamine